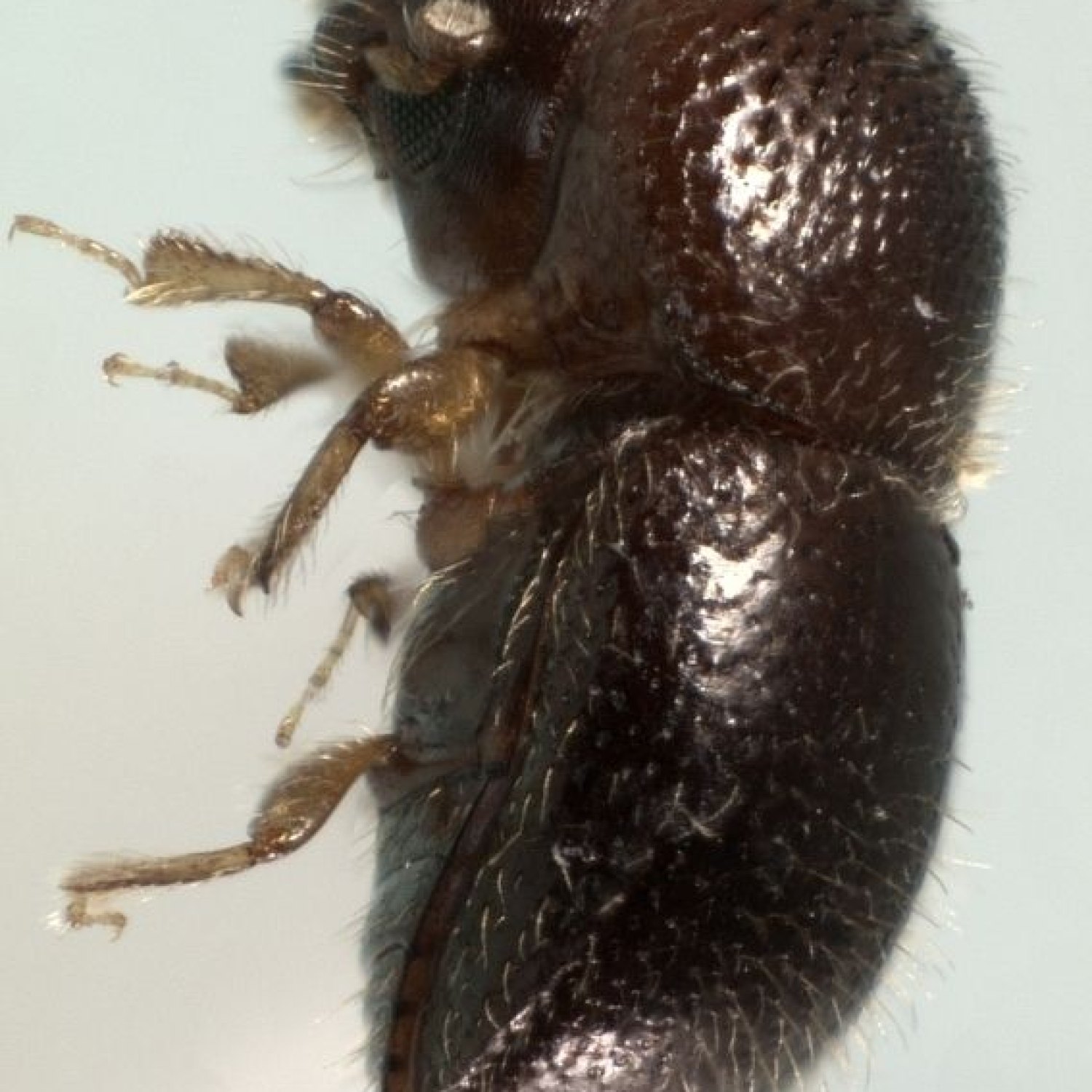

Ambrosia Beetle
1.5-3.5 mm
The Ambrosia Beetle, measuring 1.5-3.5 mm in length, can be found all over the world. Belonging to the Curculionidae family, this tiny yet destructive insect has a cylindrical body shape. It is known for its ability to bore into trees, causing damage to plants and trees worldwide. Protect your garden from these pests by keeping your trees healthy and free of dead wood. #AmbrosiaBeetle #InsectFacts #GardenPests
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Ambrosia Beetle
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Deciduous forests, orchards, gardens
The Tiny Ambrosia Beetle: A Hidden Forest Resident
Hidden within the depths of leafy deciduous forests or hidden in the orchards and gardens we enjoy lie a tiny, but fascinating creature: the Ambrosia Beetle. This inconspicuous insect may seem unassuming at first glance, but it holds a crucial role in the ecosystem. From mysterious origins and worldwide distribution to unique feeding habits and symbiotic relationships, the Ambrosia Beetle is a remarkable creature that deserves to be in the spotlight.A Closer Look at the Ambrosia Beetle
The Ambrosia Beetle, also known by its scientific name Xyleborinus saxesenii, is a member of the larger family Curculionidae, also known as weevils Ambrosia Beetle. In terms of size, they are relatively small, measuring only 1.5-3.5 mm in length. Their cylindrical body shape is typically a reddish-brown to black color, making them blend seamlessly into their surroundings.This tiny insect can be found in deciduous forests, orchards, and gardens, making its presence known in various parts of the world. From North America to Europe and Asia, the Ambrosia Beetle has a wide geographical distribution, showing just how adaptable and resilient it is.
A Unique Feeding Method
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Ambrosia Beetle is its feeding method. Unlike other insects, the Ambrosia Beetle does not feed on plants or leaves. Instead, it bores into trees, creating intricate tunnels, and feeding on fungi Amethystine Python.But here's where it gets interesting – this beetle is not capable of breaking down the cellulose found in wood, making it unable to digest the wood itself. So how does it survive? The answer lies in the symbiotic relationship it has with fungi.
A Symbiotic Relationship
The Ambrosia Beetle has a unique and intricate symbiotic relationship with fungi. As it bores into trees, it introduces fungi into the tree's wood. This fungi feed on the tree's starches and sugars, breaking them down into simpler carbohydrates that the beetle can then feed on.What's even more fascinating is that the fungi need the beetle to create tunnels within the tree, allowing air and water to penetrate the tree's inner layers. In return, the beetle relies on the fungi for its food source.
This interdependent relationship between the Ambrosia Beetle and fungi highlights just how delicate and essential balance is within the ecosystem. If one element is removed, it can have a significant impact on the others.
Hidden Origins
Despite the Ambrosia Beetle's worldwide distribution, its country of origin is still unknown, making it a mysterious creature. Its secretive habits and love for hidden habitats, such as the insides of trees, make it challenging to study.But researchers believe that this beetle may have existed for millions of years, evolving with the trees it inhabits. It is also believed that it may have originated from Asia and spread to other parts of the world over time.
A Common Forest Pest
While the Ambrosia Beetle may seem like a harmless creature, it has gained notoriety in recent years as a common forest pest. Invasive species of Ambrosia Beetles have caused significant damage to forests and crops, leading to economic losses for farmers and foresters.One notable example is the Asian Ambrosia Beetle, which has been invading various parts of the world, including the United States. This beetle bores into many different tree species, causing significant damage and even death to the trees.
The Importance of Natural Language Processing
As we continue to learn more about the world around us, we must also strive to protect and preserve it. And this is where natural language processing (NLP) comes into the picture.NLP uses advanced algorithms to extract information and insights from natural language text. By applying NLP techniques, we can understand the intricate relationships and dependencies within ecosystems better. This knowledge can help us identify potential threats and take necessary actions before they become a widespread problem.
The Future of Ambrosia Beetles
As we continue to study and observe the Ambrosia Beetle, we will gain a better understanding of its role in the ecosystem and its impact on the environment. Scientists are also exploring ways to control invasive species of Ambrosia Beetles to protect forests and crops.Through research and advanced technologies like NLP, we can ensure that this tiny yet essential insect continues to thrive and contribute to the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
In Conclusion
The Ambrosia Beetle may seem like a tiny, insignificant creature, but it holds a crucial role in our environment. From its mysterious origins and unique feeding habits to its worldwide distribution and symbiotic relationships, this beetle is truly an exceptional creature worth learning about.As we continue to develop and advance as a society, it is vital that we also prioritize the preservation and protection of our natural world. Thanks to technologies like NLP and ongoing research, we can better understand and appreciate the Ambrosia Beetle and all the other hidden residents of our forests.
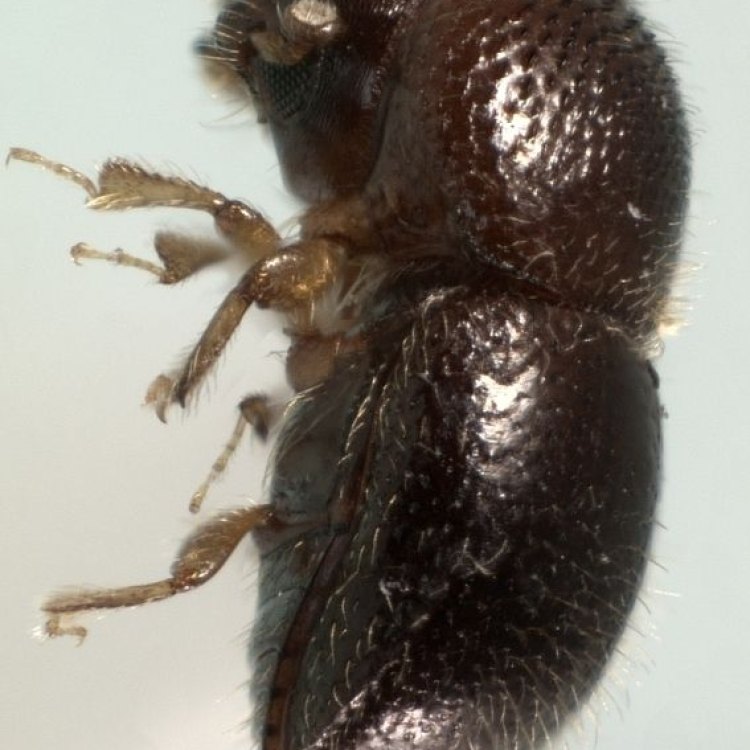

Ambrosia Beetle
Animal Details Ambrosia Beetle - Scientific Name: Xyleborinus saxesenii
- Category: Animals A
- Scientific Name: Xyleborinus saxesenii
- Common Name: Ambrosia Beetle
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Family: Curculionidae
- Habitat: Deciduous forests, orchards, gardens
- Feeding Method: Boring into trees and feeding on symbiotic fungi
- Geographical Distribution: North America, Europe, Asia
- Country of Origin: Unknown
- Location: Worldwide
- Animal Coloration: Reddish-brown to black
- Body Shape: Cylindrical
- Length: 1.5-3.5 mm
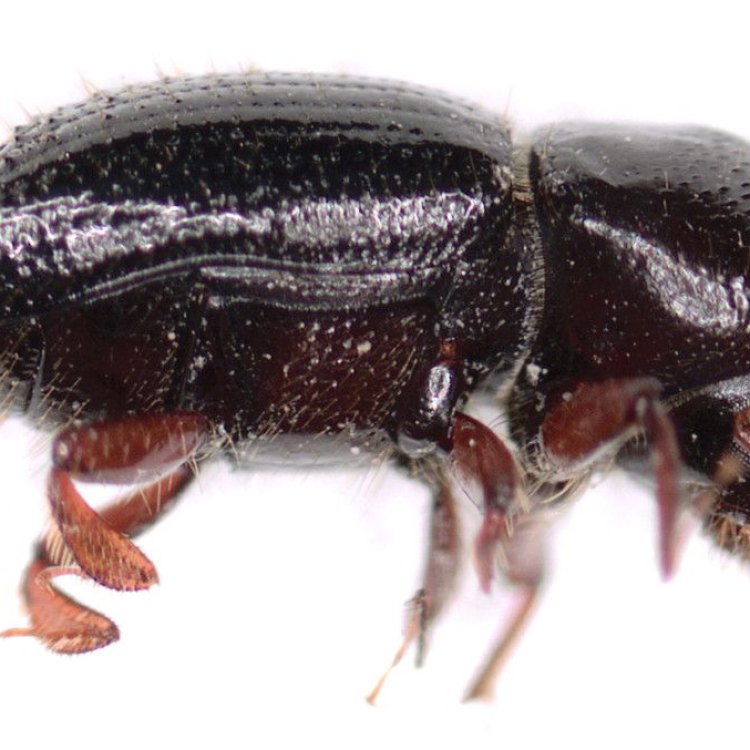

Ambrosia Beetle
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 1-2 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Females attract males by emitting pheromones and then lay eggs
- Sound or Call: No sound or call
- Migration Pattern: No migration pattern
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Burrowing and boring into trees to create tunnels for the cultivation and growth of fungal gardens
- Threats: Can cause damage to trees by introducing pathogenic fungi
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Can contribute to forest decline and tree mortality
- Human Use: Not used by humans
- Distinctive Features: Small size, cylindrical body shape, boring behavior
- Interesting Facts: Ambrosia beetles are named after the ambrosia fungi they cultivate in their tunnels
- Predator: Various species of birds and other insects
Xyleborinus saxesenii
The Fascinating World of Ambrosia Beetles: Nature's Tiny Gardeners
When most people think of beetles, they often imagine large and colorful insects that scuttle across the ground. However, there are also countless species of small beetles, each with their unique characteristics and behaviors. One such species that is often overlooked but has a significant impact on the ecosystem is the Ambrosia beetle.The Ambrosia beetle, also known as the ambrosia bark beetle, is a tiny beetle with a cylindrical body shape PeaceOfAnimals.Com. These small insects measure only a few millimeters in length, making them easy to overlook. However, despite their diminutive size, they play a critical role in the health of forests and trees.
In this article, we'll dive into the fascinating world of Ambrosia beetles, learning about their unique features, behaviors, and impact on the environment.
Visual Appearance and Average Lifespan
As mentioned, Ambrosia beetles are small insects, with an average adult size ranging from 2 to 4 millimeters in length. They have a cylindrical body shape, with a hardened exoskeleton that comes in varying shades of brown. Some species also have distinct markings or patterns on their exoskeleton, making them easily recognizable.The average lifespan of an Ambrosia beetle is 1 to 2 years, with most individuals reaching maturity within a year. However, their lifespan can vary depending on environmental conditions and availability of resources.
Reproductive Behavior
Ambrosia beetles reproduce sexually, with males and females coming together to mate and produce offspring Apple Head Chihuahua. What is interesting about their reproductive behavior is how females attract males. Females emit pheromones, which are chemical compounds that act as signals to attract males for mating.After mating, female Ambrosia beetles then move on to create a home for their offspring – inside trees. This leads us to their most intriguing behavior – burrowing and boring into trees.
Cultivating Fungal Gardens
Ambrosia beetles are considered "farmers" in the insect world as they cultivate and tend to fungal gardens inside trees. Their burrowing and boring behavior serves a crucial purpose – create a suitable environment for the growth of fungi.Once inside a tree, female beetles dig tunnels and then introduce their fungi of choice. The beetles carry the fungus in specialized sacs on their bodies, which they transfer to the tunnel walls and floor. As the fungus grows, it creates a food source for the Ambrosia beetles and their larvae.
This symbiotic relationship between the beetles and fungi is what gives the Ambrosia beetle its name. In Greek mythology, ambrosia is the food of the gods, and these beetles cultivate their own version of it inside trees.
No Sound or Call
One unique aspect of Ambrosia beetles is that they do not have any sound or call, unlike other insects such as crickets or cicadas. This can make it challenging for researchers and scientists to study their behavior, as they primarily rely on visual observation and field experiments.Migration Pattern and Social Groups
Unlike many other species of beetles, Ambrosia beetles do not have a migration pattern. Once they find a suitable tree to colonize, they remain there for the duration of their lives. This also means that they do not form or belong to any social groups. They are solitary insects, preferring to live and work alone in their fungal gardens.Threats to Trees and Forests
While Ambrosia beetles may seem harmless, their burrowing and fungal cultivation behavior can actually cause significant damage to trees. As they tunnel into trees, they introduce pathogenic fungi, which can weaken and even kill the trees. This can then have a cascading effect on the surrounding forest, leading to forest decline and tree mortality.Conservation Status
As of now, the conservation status of Ambrosia beetles has not been evaluated. This is because there are thousands of species of Ambrosia beetles worldwide, and studying and assessing their conservation needs is a massive undertaking. However, given their impact on forest health, it is essential to continue monitoring their populations and ensuring their habitats remain intact.Impact on the Ecosystem
As mentioned earlier, the burrowing and fungal cultivation behavior of Ambrosia beetles can cause damage to trees, leading to forest decline and tree mortality. This, in turn, can affect the ecosystem in various ways.First, trees play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance in the ecosystem. They provide shelter and food for countless other organisms, and their removal or decline can cause significant disruptions. Additionally, the fungi cultivated by Ambrosia beetles also play a vital role in the decomposition process, which is crucial for nutrient cycling in the forest.
When Ambrosia beetles cause damage to trees and the trees die, it can also lead to changes in the structure of the forest. This can create new habitats for certain species while displacing others, ultimately altering the entire ecosystem's dynamics.
Human Use
Unlike other insects, Ambrosia beetles are not used by humans in any way. They do not have any commercial value, nor do humans typically interact with them in any significant way. However, their importance in maintaining a balanced ecosystem means that their presence should not be taken for granted.Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts
The most distinctive features of Ambrosia beetles are their small size, cylindrical body shape, and their intriguing burrowing behavior. These characteristics make them stand out among other beetles and contribute to their vital role in the ecosystem.One interesting fact about Ambrosia beetles is that they are named after the ambrosia fungi they cultivate. This unique relationship between the beetles and the fungus is what gives them their name and makes them stand out in the insect world.
Natural Predators
Like any other species, Ambrosia beetles also have natural predators. Various species of birds, such as woodpeckers, and other insects, such as parasitic wasps, feed on Ambrosia beetles and their larvae. These predators play a crucial role in keeping the beetle population in check, ensuring that they do not cause significant damage to trees and forests.In Conclusion
The world of Ambrosia beetles is a tiny but critical part of the ecosystem. These small insects, with their unique features and behaviors, play a significant role in maintaining the health and balance of forests and trees. From their cultivation of fungal gardens to their natural predators, every aspect of the Ambrosia beetle's life has a purpose.As with all species, it is essential to understand and appreciate the role of Ambrosia beetles in the ecosystem. Their presence may be small, but their impact is significant, reminding us of the intricate connections between all living beings in nature. So the next time you see a tiny beetle burrowing into a tree, you'll know that it's not just a mere insect, but a tiny gardener playing a crucial role in nature's delicate web of life.
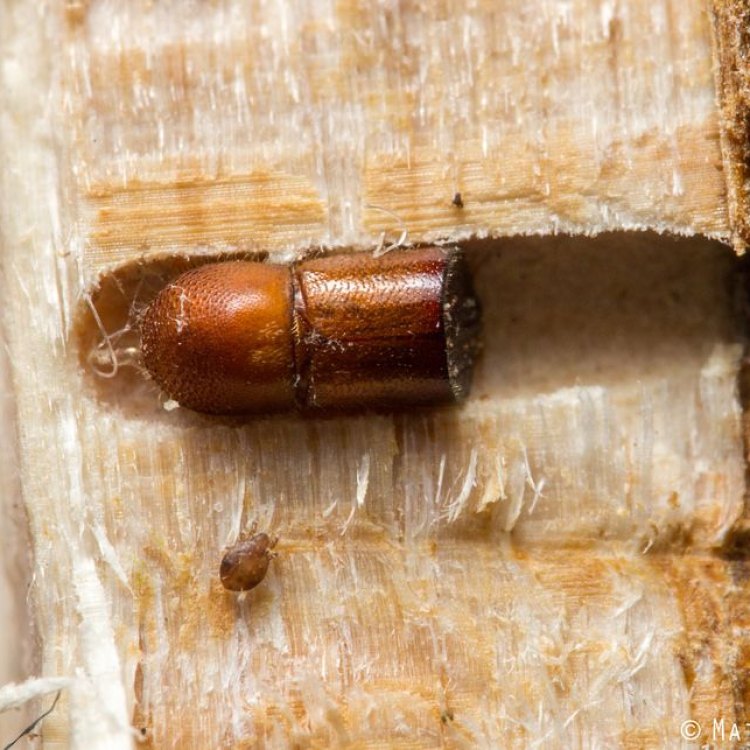

The Tiny Ambrosia Beetle: A Hidden Forest Resident
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












