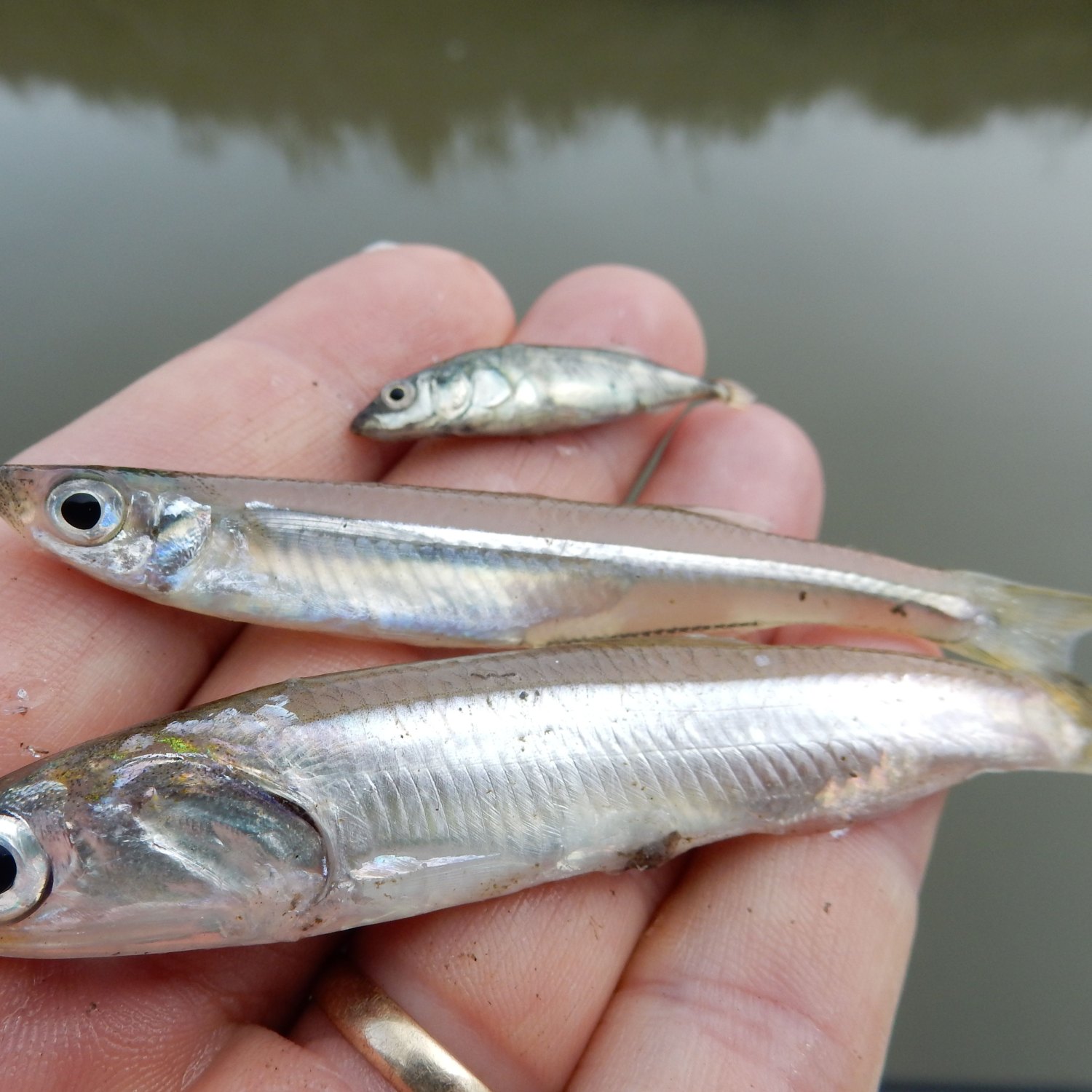
Anchovies
2 to 20 centimeters
Anchovies are small, streamlined fish found in coastal areas and open oceans. Ranging from 2 to 20 centimeters in length, these ocean dwellers belong to the Engraulidae family. These tiny and tasty creatures play a crucial role in the marine food chain, making them important for both humans and other animals. #Anchovies #OceanLife #MarineFoodChain
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Anchovies
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Marine
A Tale of the Mighty Anchovies: A Small Fish with a Big Impact
In the vast expanse of the ocean, there is a small but mighty creature that roams the waters, often unnoticed by humans. These tiny creatures, known as anchovies, may seem insignificant at first glance, but they play a crucial role in the marine ecosystem and have a fascinating story to tell.Anchovies belong to the scientific family Engraulidae, with the scientific name Engraulidae. They are commonly referred to as anchovies and are found worldwide in temperate and tropical waters Anchovies. These small fish can be spotted in coastal areas and even in open ocean waters, making them a widely distributed species.
A Fish Family Tree: Classification of Anchovies
Anchovies fall under the Animalia Kingdom, characterized by multi-cellular, eukaryotic organisms. They belong to the Chordata Phylum, which includes animals with a backbone. Within this phylum, anchovies belong to the Actinopterygii Class, which encompasses all ray-finned fish.These tiny fish are part of the Clupeiformes Order, which includes herring, sardines, and shad. Within the Clupeiformes order, anchovies are classified under the Engraulidae Family, along with other small fish such as the European sprat and Californian anchovy.
A Habitat Fit for Anchovies
Anchovies are well adapted to living in the marine environment, making their home in the vast and ever-changing ocean. They can be found in both coastal areas and open ocean waters, with some specific species being more specific in their habitat preferences.As filter feeders, they thrive in areas with high concentrations of plankton, their preferred food source American Dog Tick. Their streamlined and elongated body shape makes it easier for them to navigate through the water and catch their food efficiently.
A Filter-Feeding Strategy
One of the unique features of anchovies is their feeding method. These small fish are filter feeders, which means they feed on small planktonic animals and plants by filtering them from the water. With their gill rakers and pharyngeal teeth, anchovies strain their food from the water as they swim.This feeding method has allowed anchovies to thrive in the ocean, with an abundant food supply. It also plays a vital role in the marine food chain, as anchovies are a valuable food source for a variety of predators, including larger fish, seabirds, and marine mammals.
A Splash of Silver in the Ocean
One of the remarkable qualities of anchovies is their shimmering silver coloration. This is not only an aesthetic feature but also serves a functional purpose. The silver color of anchovies acts as camouflage, making them less visible to predators and allowing them to blend in with the ocean waters.This coloration also plays a role in navigation and communication among anchovy schools, as they can quickly identify members of their own species through their distinctive silver color.
A Range of Sizes: From 2 to 20 Centimeters
Anchovies may be tiny fish, but they come in a variety of sizes. Ranging from 2 to 20 centimeters, anchovies can be both one of the smallest and largest fish in their family. Their size is not only determined by their species but also by the environment they live in and the availability of food.This range of sizes allows anchovies to adapt to different habitats and thrive in a variety of ocean environments, as they can find a niche that suits their size.
A Global Citizen: Worldwide Distribution of Anchovies
Anchovies have spread their fins and established a presence in all oceans worldwide, with the exception of Antarctica. They can be found in temperate and tropical waters, inhabiting the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans.Their ability to adapt to different environments and their wide distribution has made anchovies a vital part of the marine ecosystem. They play a critical role in maintaining a healthy balance in the ocean, making them a global citizen in the vast blue expanse.
Anchovies: A Small Fish with a Big Impact
Despite their small size, anchovies have a significant impact on the marine ecosystem. As filter feeders, they play a crucial role in keeping the oceans' delicate balance by consuming large amounts of plankton and becoming prey for a variety of marine animals.Their widespread distribution also makes them an essential source of food for humans, with anchovies being a popular ingredient in many cuisines, particularly in Mediterranean countries.
But perhaps the most crucial role that anchovies play is their contribution to scientific research. As a widely distributed and abundant species, they serve as indicators of the ocean's health and can provide valuable insights into the marine ecosystem.
The Future of Anchovies: A Sustainable Approach
As humans continue to increase their presence and impact on the ocean, it is essential to consider the sustainability of anchovies and other marine life. Overfishing and the decline of plankton populations due to climate change can have devastating effects on anchovy populations and the entire ocean ecosystem.To ensure the future of anchovies, and the oceans as a whole, a sustainable approach to fishing and protecting their environment is necessary. This includes initiatives such as sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution, and combatting climate change. By taking these steps, we can ensure that anchovies continue to thrive and maintain their crucial role in the marine ecosystem.
A Final Note: Small Fish, Big Impact
In conclusion, anchovies may seem like small and insignificant fish in the vastness of the ocean. Still, they have a fascinating story to tell and play an essential role in maintaining a healthy marine ecosystem.From their unique classification to their filter-feeding abilities and global distribution, anchovies are a species to be admired and protected. So next time you see a school of anchovies in the ocean, take a moment to appreciate the small but mighty impact of these tiny fish.
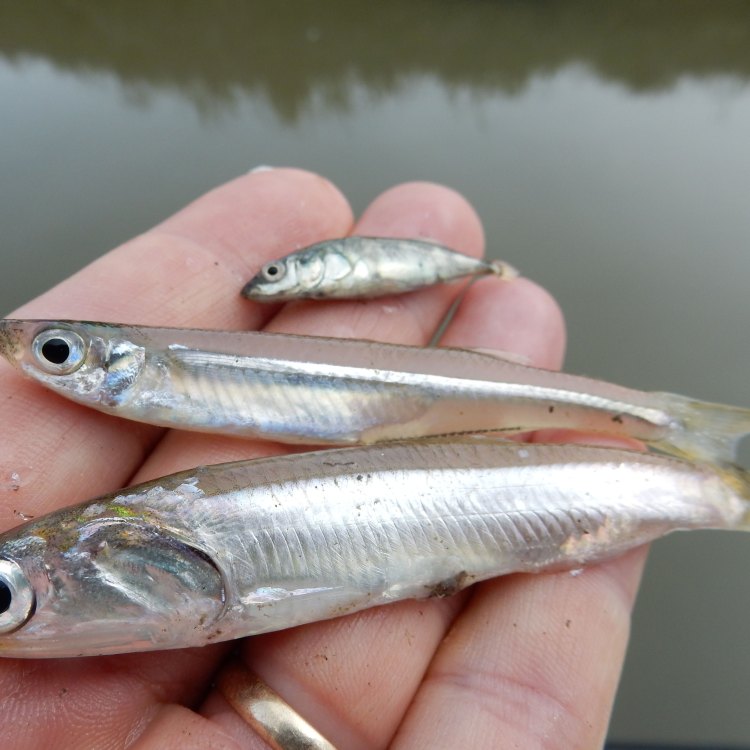

Anchovies
Animal Details Anchovies - Scientific Name: Engraulidae
- Category: Animals A
- Scientific Name: Engraulidae
- Common Name: Anchovies
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Clupeiformes
- Family: Engraulidae
- Habitat: Marine
- Feeding Method: Filter Feeder
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide in temperate and tropical waters
- Country of Origin: N/A
- Location: Coastal areas and open ocean
- Animal Coloration: Silver
- Body Shape: Streamlined and elongated
- Length: 2 to 20 centimeters
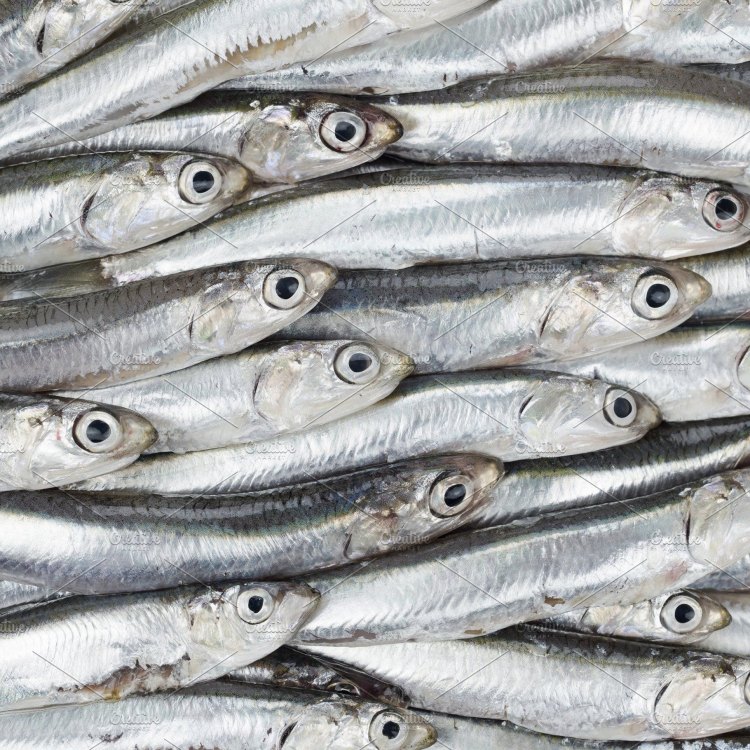

Anchovies
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 1 to 4 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Spawning
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Seasonal
- Social Groups: Schools
- Behavior: Highly social and migratory
- Threats: Overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important prey species
- Human Use: Food source, bait, fish oil
- Distinctive Features: Large eyes, distinct lateral line
- Interesting Facts: Anchovies are known for their strong schooling behavior and are often used as bait in fishing.
- Predator: Larger fish, marine mammals, and seabirds
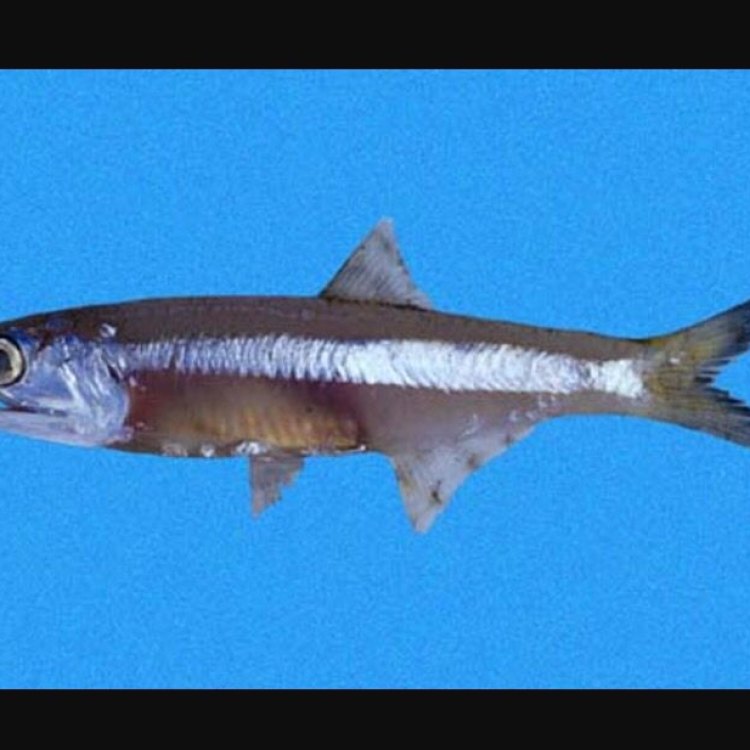

Engraulidae
The Fascinating World of Anchovies: Small but Mighty
When you think of anchovies, you might imagine a small, oily fish often used as a pizza topping or in Caesar salads. However, there is so much more to these tiny creatures than meets the eye. Anchovies are a fascinating species with a unique set of features and behaviors that make them an integral part of our ocean ecosystems. Let's dive into the world of anchovies and discover what makes them such an interesting and important species PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Anchovies, scientifically known as Engraulidae, are a family of small fish found in oceans all over the world. They are closely related to herring and sardines, and like their relatives, are known for their highly social and migratory nature. They typically grow to about 8 inches in length, with some species reaching up to 12 inches. Despite their small size, anchovies play a vital role in our oceans and have a surprisingly complex life cycle.
[One of the most notable features of anchovies is their short lifespan. On average, they live for just 1 to 4 years. This may seem short compared to other fish species, but it actually allows anchovies to adapt quickly to changes in their environment. This shorter lifespan also means that anchovies reproduce at a faster rate, ensuring their population remains stable.]
[Speaking of reproduction, anchovies reproduce sexually through spawning Asian Carp. This means that males and females release sperm and eggs into the water, which then join to form fertilized eggs. These eggs hatch into larvae, which then grow and develop into adult anchovies. This method of reproduction allows for a large number of offspring to be produced, increasing the chances of survival for the species.]
Anchovies are highly social and prefer to live in large schools, sometimes numbering in the thousands. This behavior not only helps them protect themselves from predators but also allows for efficient foraging and migration. These social groups are not limited to just their own species, as anchovies have been known to form mixed schools with other fish species, such as sardines and herring. This communal behavior also makes anchovies an important keystone species in the ocean, as they provide a food source for larger predators.
[Anchovies are highly migratory fish, and their movement patterns are mainly influenced by food availability and water temperature. They tend to follow the ocean's currents, and their migrations are often seasonal. This means that anchovies can be found in different locations throughout the year, making them a crucial part of the marine food chain in various ecosystems.]
Despite their small size, anchovies have some significant distinctive features that set them apart from other fish species. They have large, round eyes, which are an essential adaptation for their deep-sea lifestyle. These eyes help them navigate in low light conditions and spot predators in the water. Another distinctive feature is their lateral line, a row of microscopic sensory organs that run along their sides. This lateral line helps anchovies detect any changes in water pressure or movement, which is crucial for their survival in the ocean.
[An interesting fact about anchovies is their strong schooling behavior, which has earned them the nickname "the wolf pack of the sea." They swim close together in a synchronized pattern, making it challenging for predators to single out one fish. This behavior also helps them conserve energy and increases their chances of finding food.]
Anchovies are an essential part of many ocean ecosystems and play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance. As with many marine species, they face numerous threats to their survival, primarily due to human activities. Overfishing is a significant concern for anchovy populations, as they are heavily targeted for their use as food and bait. This overexploitation can lead to a decline in their population, which can have significant implications for the ocean's health.
[Another significant threat to anchovies is habitat destruction. As humans continue to expand into coastal areas, we destroy the critical habitats where anchovies live and reproduce. This destruction can also lead to a decline in other species that rely on anchovies for survival.]
Pollution is also a severe threat to anchovies, as they are sensitive to changes in water quality. Chemicals and plastics can harm their health and disrupt their behavior, making them more vulnerable to predators. If anchovy populations decline due to these threats, it can have a domino effect on the entire marine ecosystem, as they are an important prey species for larger fish, marine mammals, and seabirds.
[Despite facing these threats, anchovies have not been evaluated for their conservation status by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is because they are still considered a commercially viable and abundant species. However, it is essential to monitor anchovy populations and manage their fishing sustainably to ensure their long-term survival and the health of our oceans.]
Anchovies have been a vital species for humans for centuries. They are an essential food source for many coastal communities, providing valuable nutrients and protein. They are also used as bait for fishing, and their oil is extracted and used in various products, including supplements. However, with the increasing demand for anchovies, it is crucial to manage their harvesting sustainably to prevent overexploitation and ensure their population remains healthy.
[Anchovies also have a significant impact on our ecosystem beyond their value as a food source. As mentioned earlier, they are an essential prey species for larger predators, including commercially valuable fish species. Without anchovies as a food source, these predator populations could decline, leading to a domino effect on the entire food chain. This makes anchovies a vital indicator species for the overall health of our oceans.]
In conclusion, although small in size, anchovies are mighty creatures with a fascinating set of features and behaviors. They are highly social and migratory, making them an integral part of the ocean's ecosystem. However, they face numerous threats, including overfishing, habitat destruction, and pollution. It is up to us as humans to ensure their survival and maintain a healthy balance in our oceans. So next time you see a tin of anchovies or spot them swimming in the ocean, remember the significant role they play in our world.
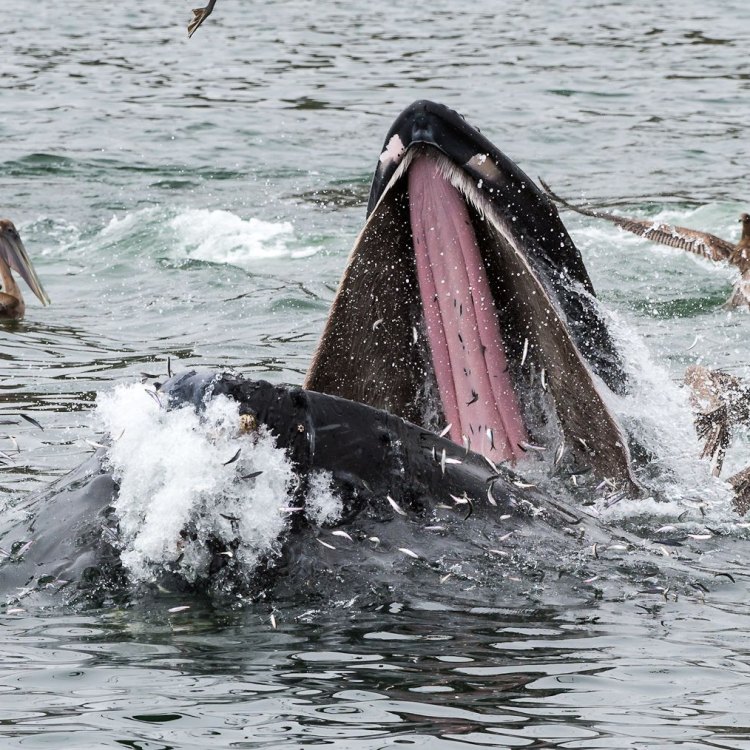

A Tale of the Mighty Anchovies: A Small Fish with a Big Impact
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.