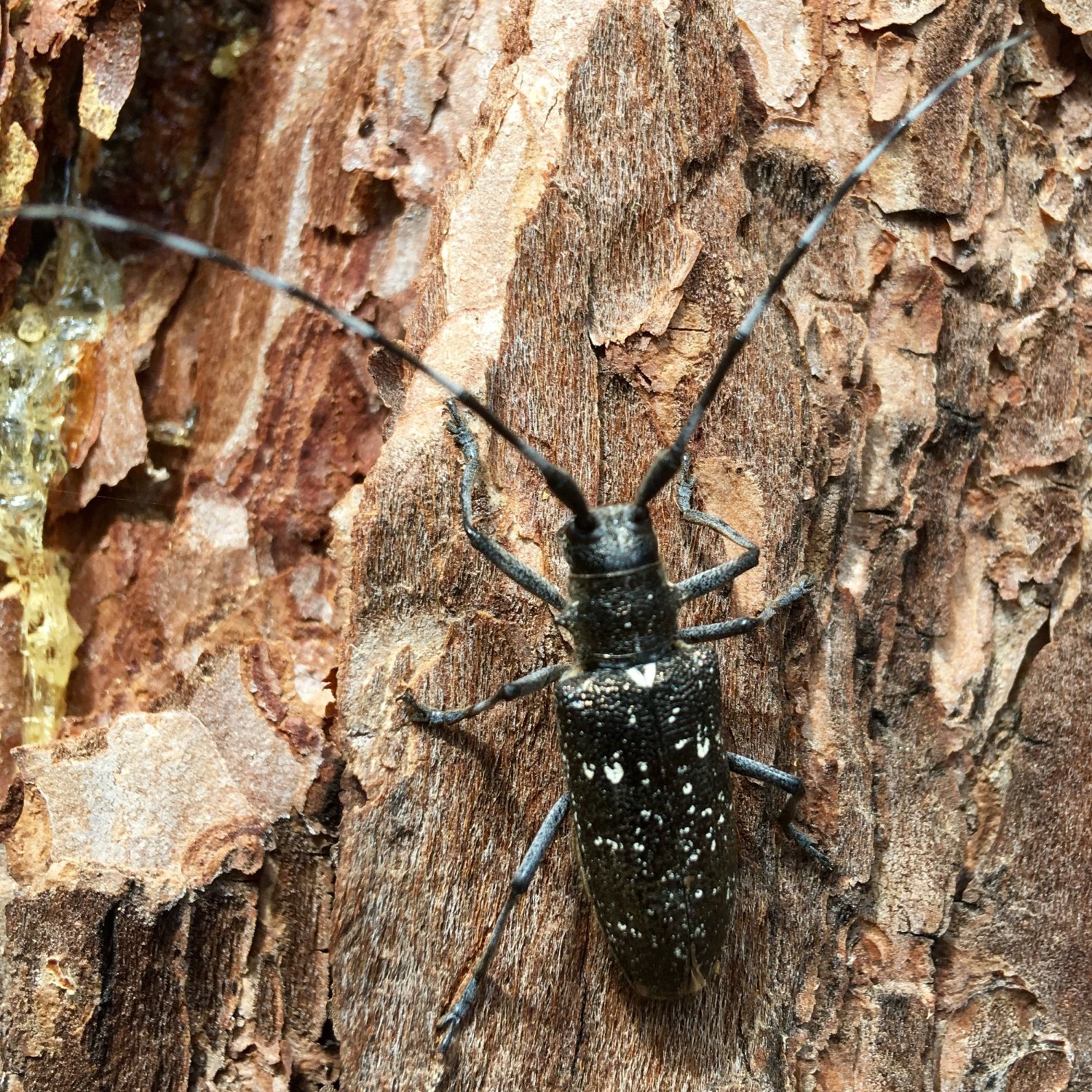
Asian Longhorn Beetle
About 1 to 1.5 inches
The Asian Longhorn Beetle is a striking insect found in North America and Europe. With a cylindrical body shape and growing up to 1.5 inches in length, it belongs to the Cerambycidae family. Keep an eye out for these beautiful creatures on your next nature walk! #AsianLonghornBeetle #Naturefacts #Cerambycidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Asian Longhorn Beetle
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Deciduous and broadleaf trees
The Fascinating World of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
Nature is full of wonders, and it never ceases to surprise us with its diversity. From the majestic elephants roaming the African savannas to the tiny insects that crawl on our backyard plants, every creature has a unique story to tell.One such intriguing insect is the Asian Longhorn Beetle. With its distinct appearance and fascinating behavior, this beetle has captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike Asian Longhorn Beetle. In this article, we will delve into the world of this incredible beetle and uncover its secrets.
An Introduction to the Asian Longhorn Beetle
Scientifically known as Anoplophora glabripennis, the Asian Longhorn Beetle belongs to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Arthropoda, class Insecta, and order Coleoptera. Its family is Cerambycidae, which includes other longhorn beetles, and it is commonly referred to as the Asian Longhorn Beetle.The beetle is native to Asia, particularly found in China, and it is believed to have been introduced to other parts of the world through wood packaging materials. It is a wood-boring insect, meaning it feeds on the wood of trees, and its geographical distribution has expanded to North America and Europe.
The Habitat of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
The Asian Longhorn Beetle prefers to reside in deciduous and broadleaf trees, with a preference for maples, elms, and willows. These trees provide the perfect feeding and breeding ground for this beetle, making it a natural habitat for them.Moreover, the beetle is also known to infest urban trees, such as street trees, park trees, and backyard trees, making it a potential threat to the landscaping and forestry industry.
Feeding Method of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
As mentioned earlier, the Asian Longhorn Beetle is a wood-boring insect that feeds on the wood of trees Alaskan Shepherd. It has strong jaws that can chew through the bark, creating oval-shaped wounds that expose the inner wood. From there, the beetle burrows through the wood, creating tunnels or galleries.These galleries serve as the beetle's feeding and breeding grounds. The larvae, or young beetles, feed on the inner tissue of the tree, while the adults feed on the bark and leaves. This feeding method can cause severe damage to the trees, resulting in tree mortality if left unchecked.
Geographical Distribution and Country of Origin
The country of origin for the Asian Longhorn Beetle is China, where it is believed to have evolved and adapted to feed on specific tree species. However, due to the global trade of wood products, it has been introduced to other parts of the world, particularly North America and Europe.In these regions, the beetle has become an invasive species with destructive feeding habits, posing a threat to the local tree populations.
The Physical Characteristics of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
The most striking feature of the Asian Longhorn Beetle is its coloration. It has a shiny jet-black body with white spots on its wing covers, giving it a distinct appearance. This coloration serves as a warning to predators, as it contains toxins that can be harmful if consumed.The beetle has a cylindrical body shape, measuring about 1 to 1.5 inches in length. Its antennae are long and thin, with black and white stripes, giving it the name "longhorn." The larvae have a creamy white color with dark brown heads and can grow up to 2 inches in length.
The Life Cycle of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
Like most insects, the Asian Longhorn Beetle has a four-stage life cycle: egg, larvae, pupa, and adult. The adult beetles emerge in early summer, with females laying eggs on the bark of trees. The eggs then hatch, and the larvae bore into the tree, where they spend the next 1 to 2 years feeding and growing.Once they have completed their development, the larvae pupate within the tree, transforming into an adult beetle. The adult beetle then emerges from the tree, leaving a distinctive D-shaped exit hole. The entire life cycle can take up to 3 years to complete.
The Impacts of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
While the Asian Longhorn Beetle may seem like an innocent creature, its introduction to non-native areas has caused significant ecological and economic impacts.First and foremost, the beetle poses a threat to the trees in its habitat. Its wood-boring behavior can cause significant damage to the trees, eventually leading to their death. This not only affects the aesthetic value of the trees but also the ecosystem they support.
Moreover, the control and eradication efforts of this invasive species can be expensive and time-consuming. In the United States alone, millions of dollars have been spent to monitor, contain, and ultimately eradicate the beetle from infested areas.
The Fight Against the Asian Longhorn Beetle
To combat the spread and destruction caused by the Asian Longhorn Beetle, various measures are being taken. One of the most crucial steps is to prevent its introduction into non-native areas. This involves strict regulations on the import and export of wood products and quarantine measures for potentially infested areas.Additionally, efforts are being made to monitor and detect the presence of the beetle in susceptible areas. This is done through visual surveys, tree banding techniques, and the use of pheromone traps. Once detected, immediate actions are taken to contain and eradicate the beetle from the area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Asian Longhorn Beetle may seem like just another insect, but its impact on the environment and economy cannot be ignored. This intriguing beetle has a unique story and behavior that both fascinates and poses a threat to our ecosystems.It is our responsibility to protect and preserve our planet's biodiversity, and understanding and raising awareness about invasive species like the Asian Longhorn Beetle is crucial in achieving this. So the next time you spot a black beetle with white spots on your favorite tree, remember the story of the Asian Longhorn Beetle and its journey from China to the rest of the world.
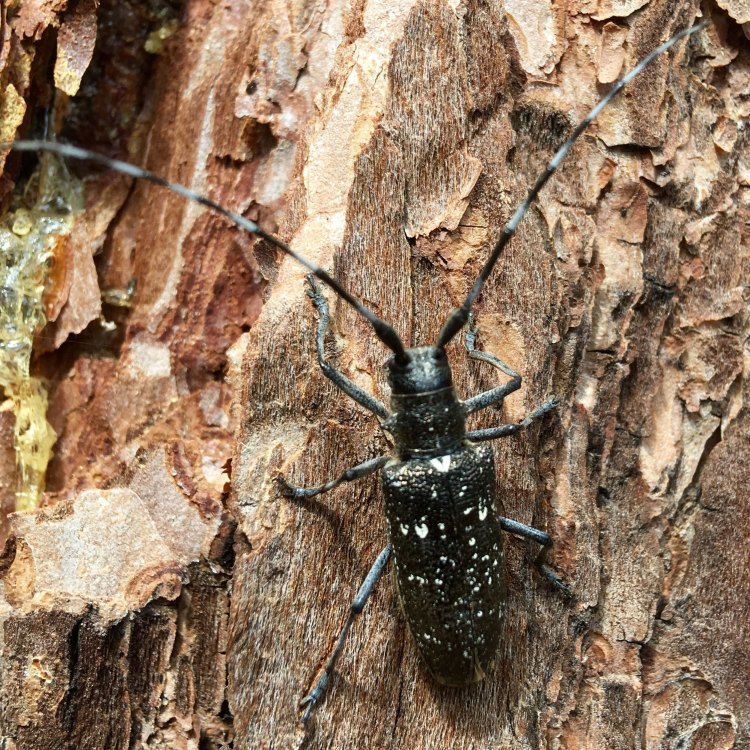

Asian Longhorn Beetle
Animal Details Asian Longhorn Beetle - Scientific Name: Anoplophora glabripennis
- Category: Animals A
- Scientific Name: Anoplophora glabripennis
- Common Name: Asian Longhorn Beetle
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Family: Cerambycidae
- Habitat: Deciduous and broadleaf trees
- Feeding Method: Wood-boring
- Geographical Distribution: Asia
- Country of Origin: China
- Location: North America, Europe
- Animal Coloration: Black with white spots
- Body Shape: Cylindrical
- Length: About 1 to 1.5 inches
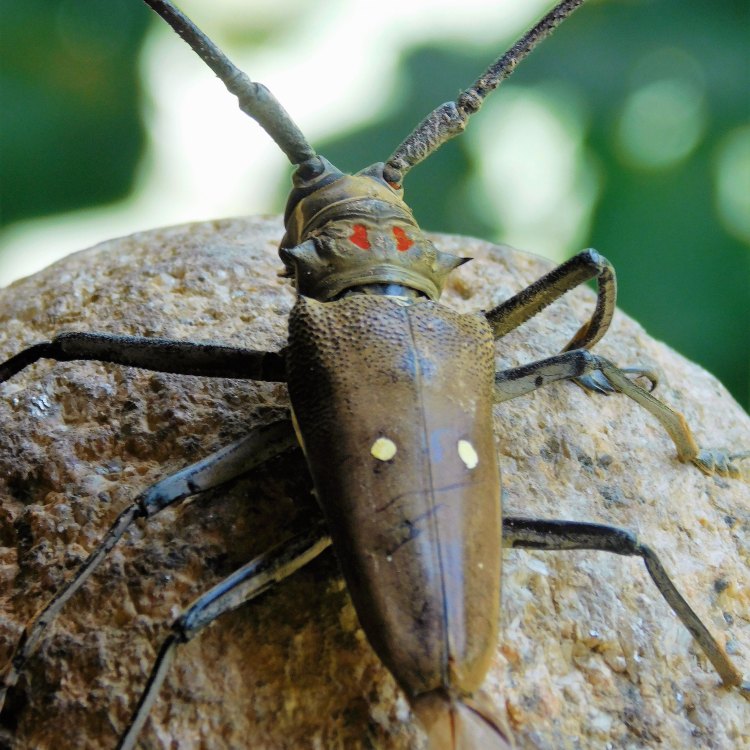

Asian Longhorn Beetle
- Adult Size: Medium-sized beetle
- Average Lifespan: 1 to 3 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs on trees
- Sound or Call: No specific sound or call
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Active during the day
- Threats: Destruction of trees
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Can cause significant damage to forest ecosystems
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Long antennae and pronounced mandibles
- Interesting Facts: Asian Longhorn Beetles are considered invasive species in many countries
- Predator: Predators include birds and small mammals
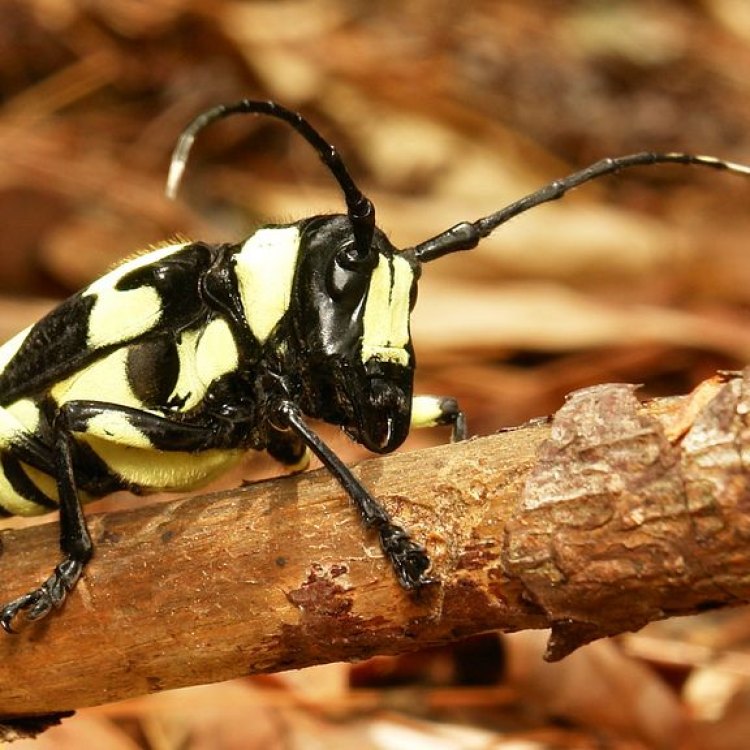

Anoplophora glabripennis
The Invasive Monster: Exploring the Intriguing World of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
The Asian Longhorn Beetle, with its striking appearance, is a medium-sized beetle that has captivated the attention of many. While its distinctive features, including long antennae and pronounced mandibles, make it stand out among its peers, this insect has also gained notoriety as an invasive species. With an average lifespan of 1 to 3 years, these creatures may seem harmless, but their impact on the ecosystem can be devastating.In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of the Asian Longhorn Beetle, exploring its behavior, threats, and other interesting facts that make it a unique and fascinating insect PeaceOfAnimals.Com.
Origin and Distribution
The Asian Longhorn Beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis) is a species of beetle native to China and Korea. It is believed that these insects were first introduced to the United States through wooden packaging materials that were imported from Asia. They were first discovered in the late 1990s in Brooklyn, New York, and have since spread to other parts of the United States and Canada.
Currently, it is found in 47 states in the US and three provinces in Canada, while also being present in several European countries including Austria, France, Italy, and the United Kingdom. In Asia, it has been reported in Japan, South Korea, and China.
Appearance and Behavior
The Asian Longhorn Beetle has a distinctive appearance that sets it apart from other beetles. They have a shiny black body, with white spots on their wings and a hint of blue coloring on their back. Their most distinguishing feature is their long antennae, measuring up to twice the length of their bodies.
As adults, these beetles have an average size of 1-1 Allosaurus.5 inches, making them medium-sized compared to other beetle species. They are active during the day and are often seen flying around or crawling on trees.
Reproduction and Mating Behavior
The Asian Longhorn Beetle is a sexual species, with males and females mating to reproduce. Mating typically occurs on trees, with the female laying eggs on the bark of the host tree. A female beetle can lay up to 200 eggs at a time.
After the eggs hatch, the larvae bore into the tree, making it their home for the next 1-2 years. As they grow and feed on the wood of the tree, they create tunnels and galleries, effectively damaging and weakening the tree. Once they reach maturity, the larvae emerge as adult beetles, creating exit holes in the tree's bark.
Threats and Impact on Ecosystem
While Asian Longhorn Beetles may seem harmless, they pose a significant threat to the environment. They are known to be destructive to a wide variety of hardwood trees, such as maples, willows, and poplars. These beetles feed on the inner wood of the trees, creating extensive damage and even killing the host tree.
The damage caused by Asian Longhorn Beetles not only affects individual trees but also has a significant impact on forest ecosystems. These insects can quickly spread, infesting large areas of forest, and causing a decline or even extinction of certain tree species. This, in turn, affects other organisms that depend on these trees for food and shelter, creating a ripple effect on the entire ecosystem.
Control and Management
To prevent the spread and damage caused by the Asian Longhorn Beetle, extensive measures have been taken to control and manage their population. In the affected areas, infested trees are cut down and destroyed, along with any nearby trees that may be at risk. Chemical treatments have also been used, though they are not considered to be entirely effective.
In some areas, the introduction of natural predators, such as woodpeckers and parasitic wasps, has been attempted as a form of biological control. However, due to the potential harm these predators may cause to other beneficial insects, this method is not widely accepted.
Human Use and Conservation Status
The Asian Longhorn Beetle has no known economic importance for humans. In fact, they are considered to be a major pest, causing significant damage to forests and urban landscapes. As such, there is no known use of these beetles in any human activity.
Despite their destructive nature and impact on the ecosystem, the conservation status of the Asian Longhorn Beetle is not evaluated. This may be because it is an introduced and invasive species, and its populations are still being monitored.
Interesting Facts
Apart from their invasive nature and destructive behavior, Asian Longhorn Beetles have a few other interesting facts that make them stand out.
Firstly, these beetles are known to be adept at hiding and are challenging to spot in the wild. Their dark color helps them blend in with the bark of trees, making it difficult for predators to see them.
Secondly, while these beetles do not have a sound or call of their own, they are known to cause some noise. As they chew through the wood of trees, the sound can sometimes be heard by humans nearby.
Finally, Asian Longhorn Beetles are not the only species of longhorn beetles. In fact, there are over 20,000 species of longhorn beetles worldwide, with varying sizes, colors, and behaviors.
Predators
As with any species, the Asian Longhorn Beetle has its fair share of predators. Their natural predators include birds and small mammals, such as woodpeckers and squirrels. These predators feed on the larvae and adults of the beetles, helping to keep their populations in check.
However, human activities such as deforestation and the trade of wood products have created a perfect habitat for these beetles to thrive, reducing the impact of their predators and allowing them to spread and cause damage.
Conclusion
The Asian Longhorn Beetle may seem like a small and insignificant insect, but its impact on the environment is significant. With its ability to infest and damage a wide variety of trees and its invasive nature, it has the potential to cause significant harm to forest ecosystems.
Efforts are being made to control and manage their populations, but the best way to prevent their spread is through increased awareness and prevention methods. As individuals, we can play our part by being mindful of the wood products we use and disposing of them properly to prevent the introduction of invasive species like the Asian Longhorn Beetle. Only through collective action, can we protect our natural habitats and preserve the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
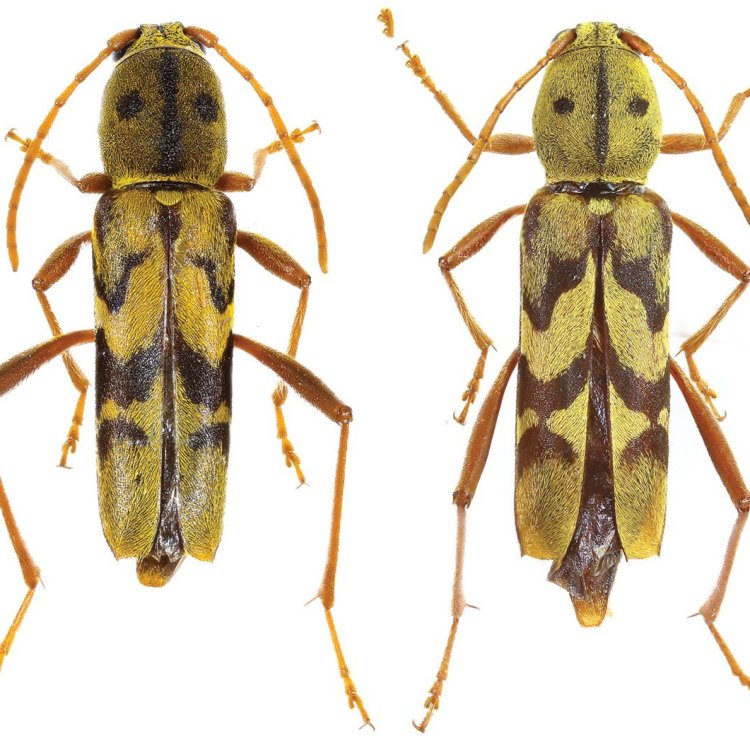

The Fascinating World of the Asian Longhorn Beetle
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.