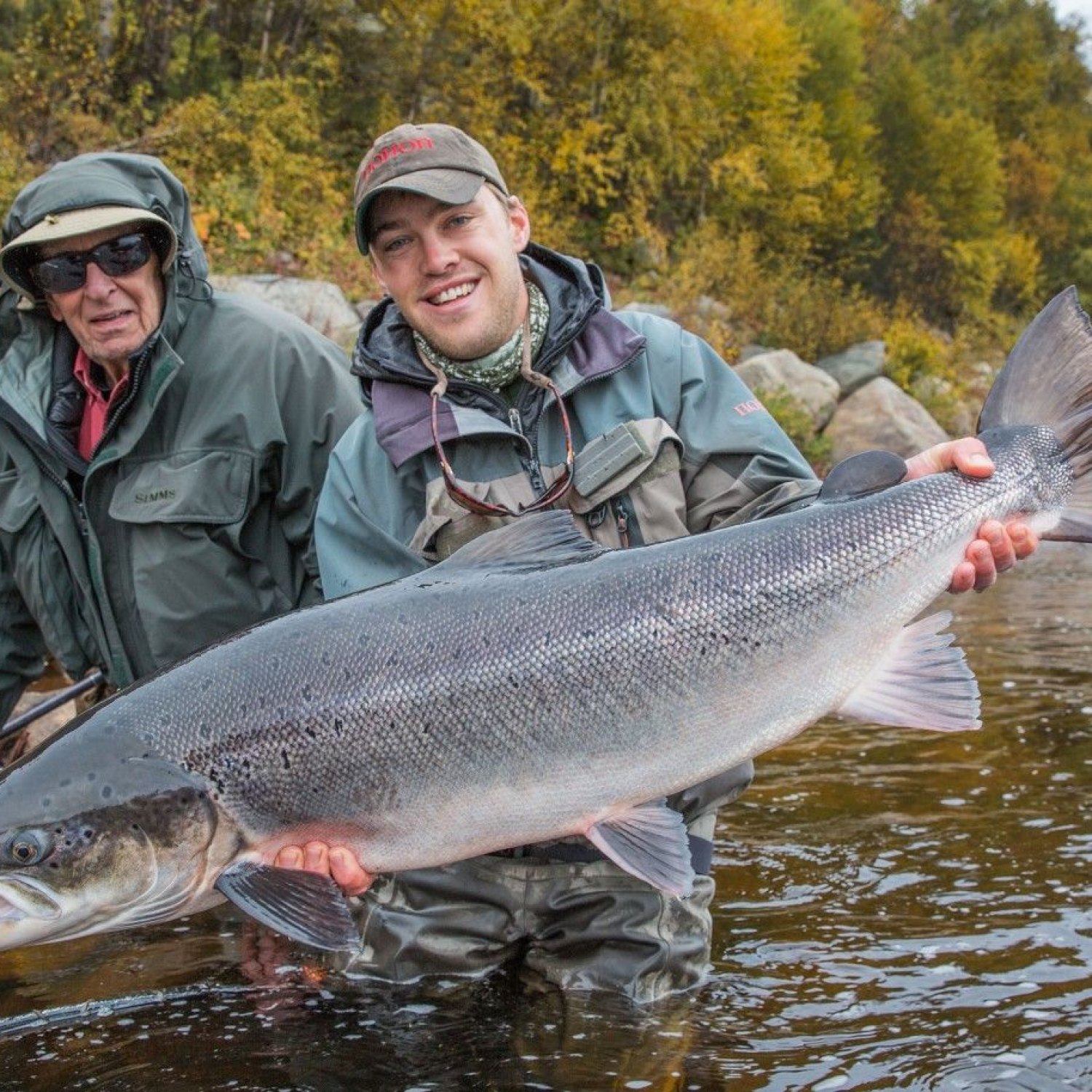
Atlantic Salmon
Adult Atlantic Salmon can reach lengths of up to 4.9 feet (1.5 meters).
Did you know that adult Atlantic Salmon can grow up to 4.9 feet long? These sleek and fast swimming fish can be found in rivers and streams along the eastern coast of North America and in Europe. In the Salmonidae family, their streamlined body shape helps them move effortlessly through the water. #AtlanticSalmon #fishfacts #nature
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Atlantic Salmon
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Atlantic Salmon inhabit freshwater rivers and streams as well as the Atlantic Ocean and its tributaries.
The Mighty Atlantic Salmon: A Magnificent Species of the Northern Atlantic Ocean
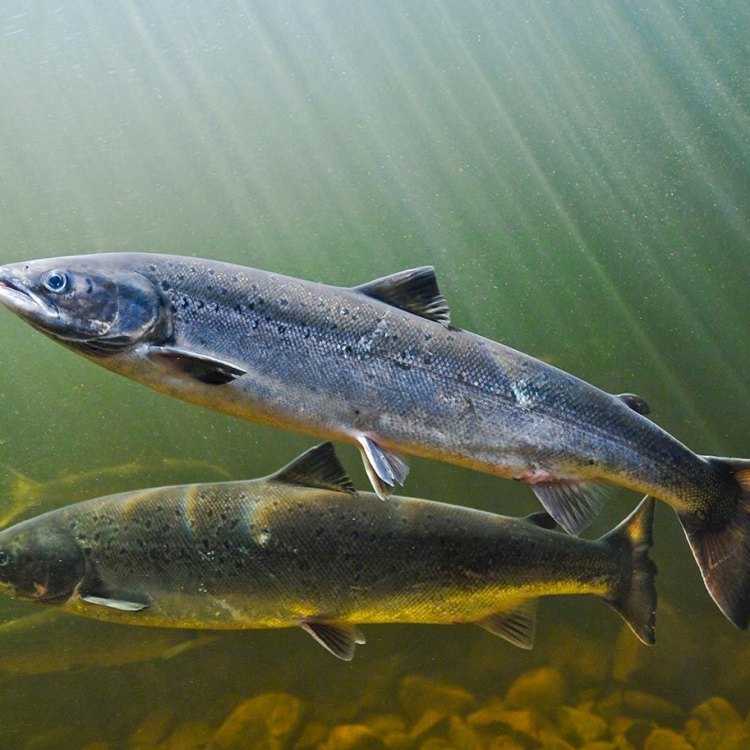
The Atlantic Salmon, scientifically known as Salmo salar, is a remarkable fish species that has captured the hearts and minds of fishermen, conservationists, and nature enthusiasts for centuries. It is a species that is deeply rooted in the history and culture of countries that span the Atlantic Ocean, from North America to Europe. With its stunning appearance, impressive size, and unique life cycle, the Atlantic Salmon is truly a species worth learning about.Native to North America and Europe, the Atlantic Salmon belongs to the animal kingdom, phylum Chordata, and class Actinopterygii Atlantic Salmon. It is a member of the Salmonidae family and can be found in the order Salmoniformes. This fish species has adapted to thrive in different habitats, from freshwater rivers and streams to the vast and open Atlantic Ocean. Its incredible ability to adapt and survive in various environments has allowed it to establish a global presence and become a critically important part of the ecosystem.
Habitat and Distribution
The Atlantic Salmon's habitat is as diverse as its geographical distribution. It is primarily found in the northern Atlantic Ocean, particularly in the North Atlantic and Arctic Ocean. Its widespread distribution also includes various rivers and streams along the eastern coast of North America, as well as several countries in Europe. This species is incredibly adaptable and can thrive in varying water temperatures, from cold, clear rivers to the open and turbulent waters of the ocean.In the past, the Atlantic Salmon was found in abundance in rivers and streams along the eastern coast of North America. However, due to overfishing and habitat destruction, its population has significantly declined Amano Shrimp. As a result, extensive conservation efforts have been put in place to protect and restore this magnificent species to its former glory.
Feeding and Hunting Methods
The Atlantic Salmon is a carnivorous species that primarily feeds on small fish, insects, and crustaceans. Its feeding behavior and hunting techniques vary depending on its location and age. Juvenile salmon feed on smaller prey, such as insects and crustaceans, found in freshwater rivers and streams. As they grow into adults and move towards the ocean, their diet changes to include larger fish, such as herring and capelin.The Atlantic Salmon is a skilled hunter, using its streamlined, elongated body shape to move swiftly through the water. Its powerful tail and fins enable it to control its movements and quickly change direction when chasing prey. This species also has excellent vision and can accurately detect and target its desired prey.
Appearance and Body Structure
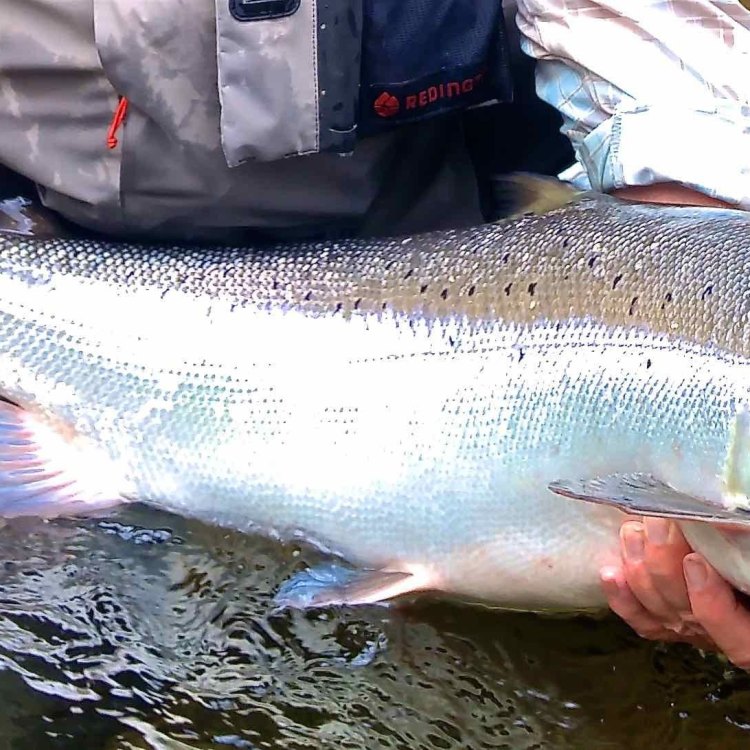
The Atlantic Salmon's appearance and body structure make it a highly distinctive and recognizable species. It has a streamlined, elongated body that is well-suited for a life of swimming through the water. Its body is covered in small, round scales that provide it with protection from predators and also help maintain its buoyancy. Its powerful tail and fins are essential for its survival, allowing it to travel vast distances and navigate varying water conditions.Adult Atlantic Salmon have a silver-blue color on their backs and sides, with a white belly. During breeding season, they undergo a dramatic transformation, developing a reddish coloration on their sides and a greenish coloration on their heads. This stunning color change is critical for attracting a mate, with males becoming more vibrant and colorful than females.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
The Atlantic Salmon has a complex and fascinating life cycle that involves both freshwater and saltwater environments. It begins its life as an egg in a freshwater stream, where it stays for several months until it hatches. Once hatched, the young salmon, called alevins, remain in the stream, feeding on insects and crustaceans until they are ready to migrate towards the ocean.After spending a few years in the ocean, the mature salmon return to the same freshwater stream where they were born to spawn. This journey can be thousands of kilometers long and is considered one of the most challenging feats in the animal kingdom. Once they reach their destination, the female salmon will lay her eggs in a shallow depression in the gravel bed of the stream. The male salmon then fertilizes the eggs, and the female will cover them with gravel to protect them.
After spawning, the salmon will die, and the young fry will hatch and remain in the stream for a year before heading towards the ocean to start the cycle all over again. This life cycle is a crucial part of the salmon's existence, and the migration of these magnificent creatures has been celebrated and studied for centuries.
Importance to Ecosystem and Human Culture
The Atlantic Salmon is a vital and irreplaceable part of the ecosystem. Its migration brings vital nutrients from the ocean to freshwater streams, enriching their surroundings, and providing food for other species. It is also a crucial game fish, prized for its beauty, strength, and delicious taste. The Atlantic Salmon is also deeply ingrained in the cultures of countries along the Atlantic coast, with many traditions and festivities centered around its yearly migration.Unfortunately, the Atlantic Salmon's numbers have been declining over the years due to various human activities, from overfishing to habitat destruction. However, with increased conservation efforts and regulations in place, there is hope that this magnificent species can make a comeback and continue to thrive in its diverse habitats.
Conclusion
The Atlantic Salmon is a species that has captured the imagination and hearts of many people worldwide. Its striking appearance, unique life cycle, and essential role in the ecosystem make it a truly remarkable animal. Despite facing challenges and threats, this species has managed to maintain its presence and adapt to different habitats, showcasing its resilience and strength. As we continue to protect and preserve the Atlantic Salmon, we can ensure that future generations will have the opportunity to witness this incredible species in all its glory.
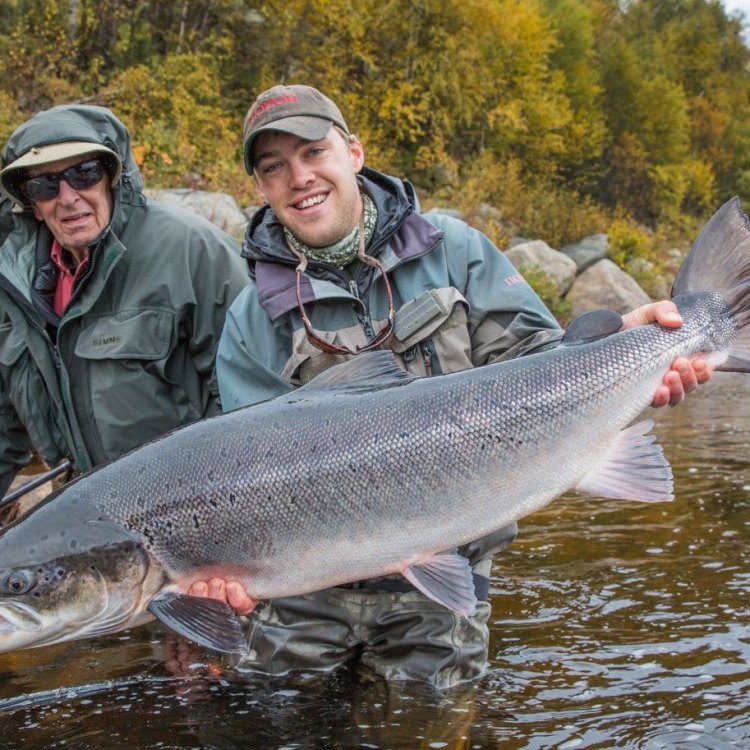

Atlantic Salmon
Animal Details Atlantic Salmon - Scientific Name: Salmo salar
- Category: Animals A
- Scientific Name: Salmo salar
- Common Name: Atlantic Salmon
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Salmoniformes
- Family: Salmonidae
- Habitat: Atlantic Salmon inhabit freshwater rivers and streams as well as the Atlantic Ocean and its tributaries.
- Feeding Method: Atlantic Salmon are carnivorous and primarily feed on small fish, insects, and crustaceans.
- Geographical Distribution: Atlantic Salmon are found in the northern Atlantic Ocean, particularly in the North Atlantic and Arctic Ocean.
- Country of Origin: Atlantic Salmon are native to North America and Europe.
- Location: Atlantic Salmon can be found in rivers and streams along the eastern coast of North America, as well as in various countries in Europe.
- Animal Coloration: Adult Atlantic Salmon have a silver-blue color on their backs and sides, with a white belly. During breeding season, they develop a reddish coloration on their sides and greenish coloration on their heads.
- Body Shape: Atlantic Salmon have a streamlined, elongated body shape that allows them to swim quickly through the water.
- Length: Adult Atlantic Salmon can reach lengths of up to 4.9 feet (1.5 meters).
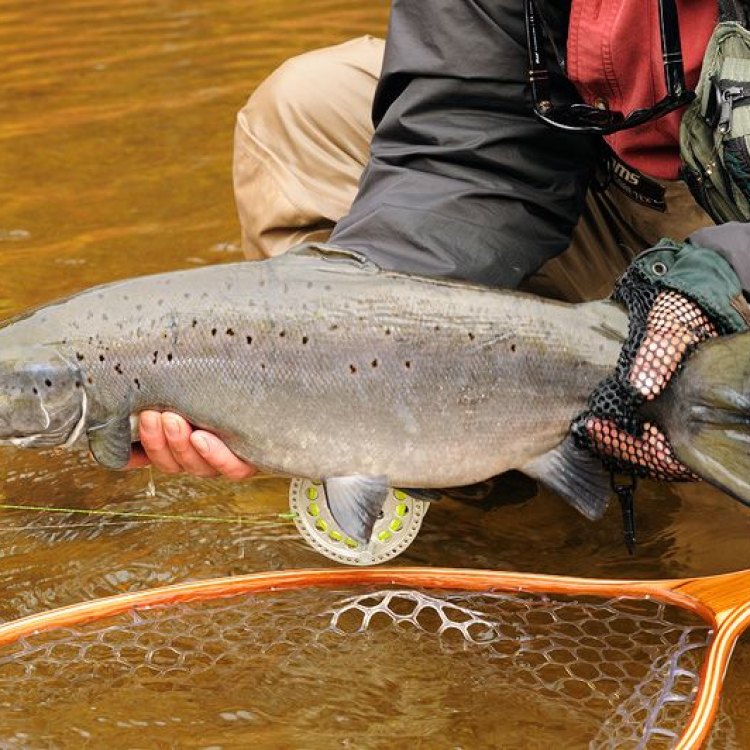

Atlantic Salmon
- Adult Size: Adult Atlantic Salmon typically weigh between 8 to 30 pounds (3.6 to 13.6 kilograms).
- Average Lifespan: Atlantic Salmon can live for up to 12 years.
- Reproduction: Atlantic Salmon are anadromous, which means they migrate from the ocean to freshwater rivers to spawn. Female salmon build nests called redds in the gravel beds of rivers, where they deposit their eggs. Male salmon fertilize the eggs with their milt.
- Reproductive Behavior: Male Atlantic Salmon exhibit aggressive behavior during breeding season, competing with other males for mates. They will often engage in physical fights to establish dominance.
- Sound or Call: Atlantic Salmon do not produce distinct sounds or calls.
- Migration Pattern: Atlantic Salmon have complex migration patterns. They migrate from their ocean feeding grounds to freshwater rivers and streams to spawn. After spawning, the juvenile salmon migrate back to the ocean to grow and mature.
- Social Groups: Atlantic Salmon are primarily solitary animals, but they may form small groups during spawning season.
- Behavior: Atlantic Salmon are highly migratory and can travel long distances in search of food or suitable spawning grounds. They are also known for their jumping ability, as they can leap out of the water to overcome obstacles.
- Threats: The Atlantic Salmon population has declined due to various factors including overfishing, habitat loss, pollution, and the construction of dams that block their migratory routes.
- Conservation Status: The Atlantic Salmon is listed as a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, certain populations of Atlantic Salmon are considered endangered or threatened in specific regions.
- Impact on Ecosystem: Atlantic Salmon play an important role in the ecosystem as a key predator in both freshwater and marine environments. They also contribute nutrients to their freshwater habitats through their carcasses after spawning.
- Human Use: Atlantic Salmon are highly valued as a commercial and recreational fish species. They are commonly consumed as food and are also prized by anglers for sport fishing.
- Distinctive Features: Some distinctive features of Atlantic Salmon include their silver-blue coloration, elongated body shape, and their jumping ability.
- Interesting Facts: 1. Atlantic Salmon are capable of navigating back to the same river or stream where they were born to spawn. 2. They have a strong sense of smell, which helps them navigate and locate their spawning grounds. 3. The largest Atlantic Salmon ever recorded weighed 109 pounds (49.4 kilograms). 4. Atlantic Salmon are able to tolerate both saltwater and freshwater environments.
- Predator: Predators of Atlantic Salmon include larger fish species such as sharks, seals, and other predatory fish.

Salmo salar
The Incredible World of Atlantic Salmon: Migratory Marvels with a Struggle for Survival
When one thinks of salmon, images of vibrant red fleshed fish swimming upstream in a river might come to mind. However, there is a species of salmon that is much more diverse and fascinating than that – the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Atlantic Salmon have a distinct lifecycle that takes them through the vastness of the ocean to the quiet depths of rivers. They are surrounded by unique behaviors, abilities, and threats that make them a valuable and intriguing species PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Let's dive into the world of Atlantic Salmon and uncover what makes them a one-of-a-kind creature.
Size & Lifespan
The Atlantic Salmon is a medium-sized fish, with an average adult weight of 8 to 30 pounds (3.6 to 13.6 kilograms). Despite their size, they hold the record for being one of the world's strongest fish, able to swim up to 300 miles in one go. The largest recorded Atlantic Salmon weighs a whopping 109 pounds (49.4 kilograms)!In terms of lifespan, Atlantic Salmon can live up to 12 years. However, the majority of their life is spent in the ocean and only a small portion in rivers during their spawning season.
Reproduction & Behavior
Atlantic Salmon are anadromous, which means they begin their life in freshwater rivers and eventually migrate to the ocean Amphicoelias Fragillimus. When they reach adulthood, they return to their natal rivers to spawn. Female salmon build nests called redds in the gravel beds of rivers, where they lay their eggs. The male salmon then fertilize the eggs with their milt.During the breeding season, male Atlantic Salmon exhibit aggressive behavior, competing with other males for mates. They may even engage in physical fights to establish dominance and secure a mate.
Interestingly, Atlantic Salmon do not produce any distinct sounds or calls, relying instead on their other senses for communication and navigation.
Migration Pattern & Social Groups
Atlantic Salmon have complex migration patterns. After spending their juvenile years in freshwater, they migrate to the ocean for food and growth. Then, they return to their natal rivers to spawn. This journey can range from a few hundred miles to over one thousand miles. What's even more impressive is that they are able to navigate back to the very same river or stream where they were born.While Atlantic Salmon are primarily solitary animals, they may form small groups during their spawning season. However, once the spawning is over, they return to their solitary habits.
Behavior & Threats
The behavior of Atlantic Salmon is highly migratory, as they travel long distances in search of food or suitable spawning grounds. Their strong jumping ability allows them to leap out of the water to overcome obstacles such as waterfalls or dams.Unfortunately, the Atlantic Salmon population has been declining due to various threats. Overfishing, habitat loss, pollution, and the construction of dams that block their migratory routes have all contributed to their decline. In some regions, certain populations of Atlantic Salmon are considered endangered or threatened.
Conservation Status & Impact on Ecosystem
Despite the multiple threats, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists the Atlantic Salmon as a species of least concern. However, it is important to note that conservation efforts are still necessary to protect the different populations of this species.Atlantic Salmon play a crucial role in the ecosystem as a key predator in both freshwater and marine environments. They also contribute nutrients to their freshwater habitats through their carcasses after spawning.
Human Use & Distinctive Features
Aside from their ecological importance, Atlantic Salmon also have significant value to humans. They are highly prized as a commercial and recreational fish species. This species is commonly consumed as food and is also a prized catch for anglers.Some distinctive features that make Atlantic Salmon stand out include their silver-blue coloration, elongated body shape, and their impressive jumping ability. They are also able to tolerate both saltwater and freshwater environments, making them highly adaptable to different habitats.
Interesting Facts
As if Atlantic Salmon weren't already fascinating enough, here are some additional interesting facts about this species:1. They have a strong sense of smell, which helps them navigate and locate their spawning grounds.
2. The largest Atlantic Salmon ever recorded weighed 109 pounds (49.4 kilograms).
3. Atlantic Salmon are able to tolerate both saltwater and freshwater environments.
4. They are capable of navigating back to the same river or stream where they were born to spawn.
Predators
While Atlantic Salmon may seem like powerful and resilient creatures, they do have predators in the wild. Larger fish species such as sharks, seals, and other predatory fish are known to prey on Atlantic Salmon.In Conclusion
The world of Atlantic Salmon is a complex and intriguing one. Their unique lifecycle, behaviors, and abilities make them a valuable and impressive species. However, they are also faced with numerous threats that have led to a decline in their population. It is crucial that we continue to conserve and protect this species for future generations to come. Atlantic Salmon truly are migratory marvels with a struggle for survival.

The Mighty Atlantic Salmon: A Magnificent Species of the Northern Atlantic Ocean
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.