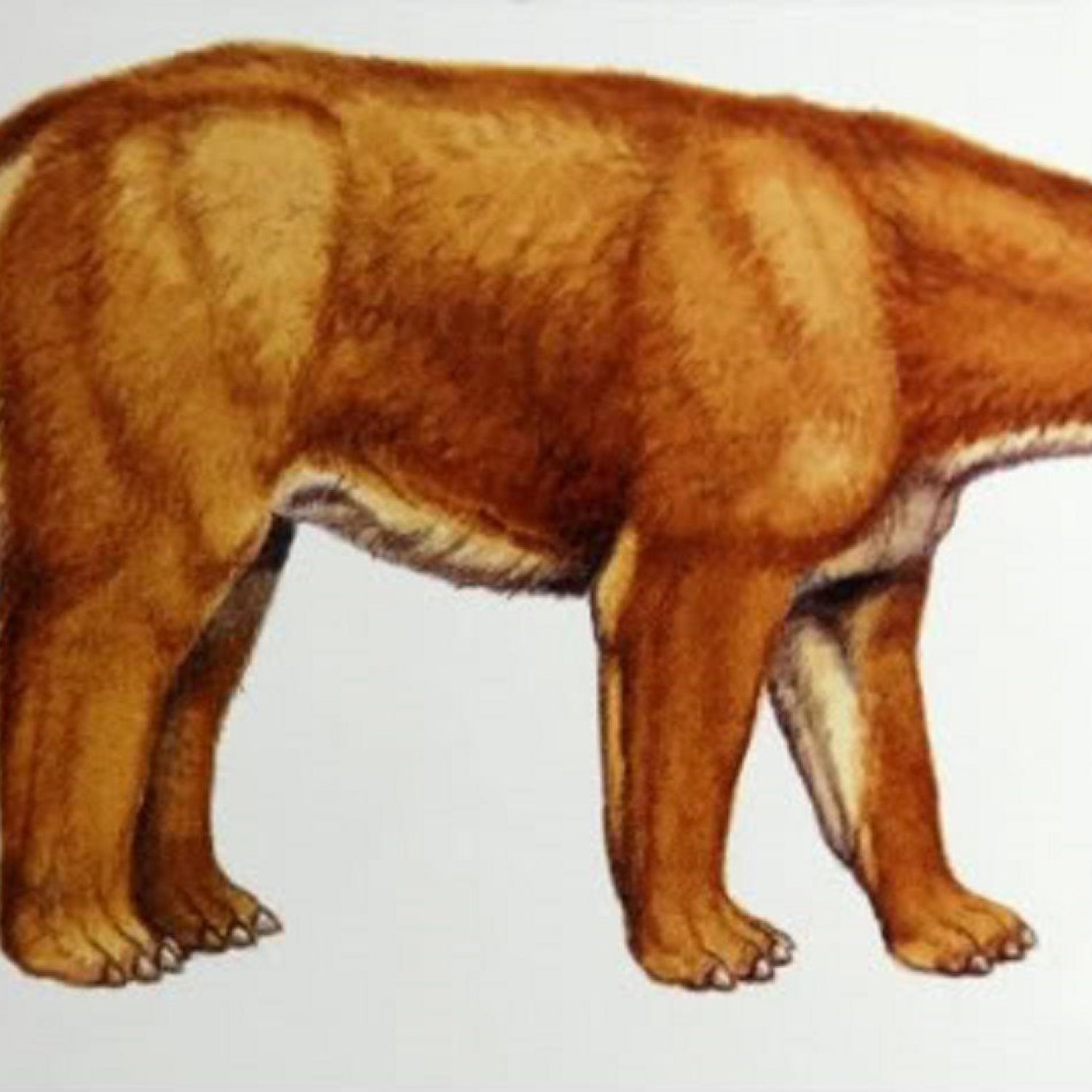
Barylambda
Approximately 2.5 meters (8 feet)
Barylambda, the ancient mammal with a large and stocky body, roamed the Badlands National Park about 40 million years ago. Standing at 2.5 meters tall, this creature belonged to the Barytheriidae family and is believed to have been a distant relative of modern-day rhinos and tapirs. Learn more about this fascinating animal and its surroundings at the park. #Barylambda #BadlandsNationalPark #ancientmammal #prehistoric #naturelovers
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Barylambda
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Terrestrial
Barylambda: The Ancient Giant of North America's Badlands National Park
Deep in the rugged and desolate landscape of Badlands National Park in the United States, there was once an ancient and formidable creature that roamed the earth. This creature was known as Barylambda, a mammal belonging to the order Condylarthra and the only known member of the family Barytheriidae. Despite its extinct status, this majestic animal continues to captivate us with its impressive size, unique features, and mysterious past.The Scientific Discovery of Barylambda
The first recorded discovery of Barylambda was made in 1879 by the renowned paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh Barylambda. Marsh, along with his team, uncovered the remains of a large, unknown mammal in the Badlands of North America. It wasn't until several years later, in 1884, that Marsh named this ancient creature Barylambda, which means "heavy lamb" in Greek. This name was chosen due to the animal's robust and stocky build.Barylambda lived during the early Eocene period, approximately 56 to 49 million years ago. It was a time when the planet was warmer and more humid, and forests covered much of what is now North America. These primeval forests were home to many unique species, including Barylambda.
The Physical Characteristics of Barylambda
Barylambda was a massive animal, measuring approximately 2.5 meters (8 feet) in length. It had a stocky body shape, with short, thick legs that were well-adapted for supporting its weight Black Mamba. Its head was large and elongated, with a broad muzzle and small eyes. Its jaws were filled with powerful teeth, perfect for grinding and chewing the vegetation it consumed.One of the most striking features of Barylambda was its body coloration, which was a deep and rich brown. This coloration acted as camouflage, blending in with the surrounding forests, making it difficult for predators to spot. Its large size also served as a deterrent to potential attackers, as few animals would dare to take on such a formidable opponent.
Habitat and Distribution
Barylambda was a terrestrial animal, meaning it lived and roamed on land. Its preferred habitat was the dense forests that covered North America during the Eocene period. These forests provided an abundant food source for Barylambda, as well as shelter and protection from predators.The geographical distribution of Barylambda was limited to North America, with fossils being found in several states, including Wyoming, Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska. Its fossils have also been discovered in British Columbia, Canada, suggesting that Barylambda may have had a wider range than previously thought.
Feeding Habits of Barylambda
Barylambda was a herbivorous animal, meaning it primarily fed on plants and vegetation. Its diet likely consisted of various fruits, leaves, and nuts, as well as anything else it could find in its forested habitat. Its teeth were perfectly adapted for grinding and chewing tough vegetation, making it an efficient herbivore.Being an herbivore, Barylambda played a vital role in the ecosystem of the early Eocene period. By consuming plants and dispersing seeds through its feces, it helped shape and maintain the forests it lived in. Without Barylambda and other herbivores like it, the ecosystem of this time would have been vastly different.
The Mystery of Barylambda's Extinction
Despite being a dominant and successful species during its time, Barylambda eventually went extinct, and the cause of its extinction remains a mystery. One theory suggests that a change in climate during the late Eocene period may have been the culprit. The planet became cooler and drier, resulting in a decline in the forests that Barylambda depended on for survival.Another theory involves competition with other herbivorous animals, such as tapirs and rhinoceroses, for resources. These larger and more diverse herbivores may have outcompeted Barylambda for food, leading to its eventual extinction.
Barylambda in Modern Culture
Today, Barylambda may be extinct, but its legacy lives on in popular culture. Its impressive size, unique features, and mysterious extinction have left a lasting impression on people's minds, making it a popular subject in books, films, and artworks.In the hit documentary series "Walking with Beasts," Barylambda was featured in one of its episodes, bringing this ancient creature to life with stunning CGI animation. Numerous children's books also feature Barylambda, educating young readers about this remarkable animal and its role in the early Eocene period.
Barylambda: An Enduring Legacy
Despite its extinction, Barylambda continues to fascinate us with its impressive size, unique features, and mysterious past. As we continue to uncover more about this ancient giant, we gain a deeper understanding of our planet's diverse and ever-changing ecosystem. Barylambda may be long gone, but its legacy lives on, reminding us of the importance of preserving and protecting the world's precious and unique species.
Barylambda
Animal Details Barylambda - Scientific Name: Barylambda
- Category: Animals B
- Scientific Name: Barylambda
- Common Name: Barylambda
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Condylarthra
- Family: Barytheriidae
- Habitat: Terrestrial
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Badlands National Park
- Animal Coloration: Brown
- Body Shape: Large and stocky
- Length: Approximately 2.5 meters (8 feet)

Barylambda
- Adult Size: Large
- Average Lifespan: Unknown
- Reproduction: Viviparous
- Reproductive Behavior: Unknown
- Sound or Call: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Unknown
- Social Groups: Unknown
- Behavior: Unknown
- Threats: Extinction
- Conservation Status: Extinct
- Impact on Ecosystem: Unknown
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Long limbs and large teeth
- Interesting Facts: Barylambda is an extinct genus of mammal that lived during the Eocene epoch. It was a large and stocky herbivorous mammal that resembled a rhinoceros with long limbs and large teeth. Barylambda is known from fossils found in North America, particularly in the Badlands National Park in the United States. Despite its size, not much is known about the behavior and biology of Barylambda. It is believed to have lived in a terrestrial habitat and was likely a solitary animal. Barylambda is considered to be extinct and its conservation status is listed as such. The exact reasons for its extinction are unknown, but like many other extinct species, habitat loss and climate change are possible factors. Barylambda had a significant impact on its ecosystem during its existence, but the details of this impact are also unknown. Overall, Barylambda is an intriguing and mysterious species that provides valuable insights into the diversity and evolution of mammals in the past.
- Predator: Unknown
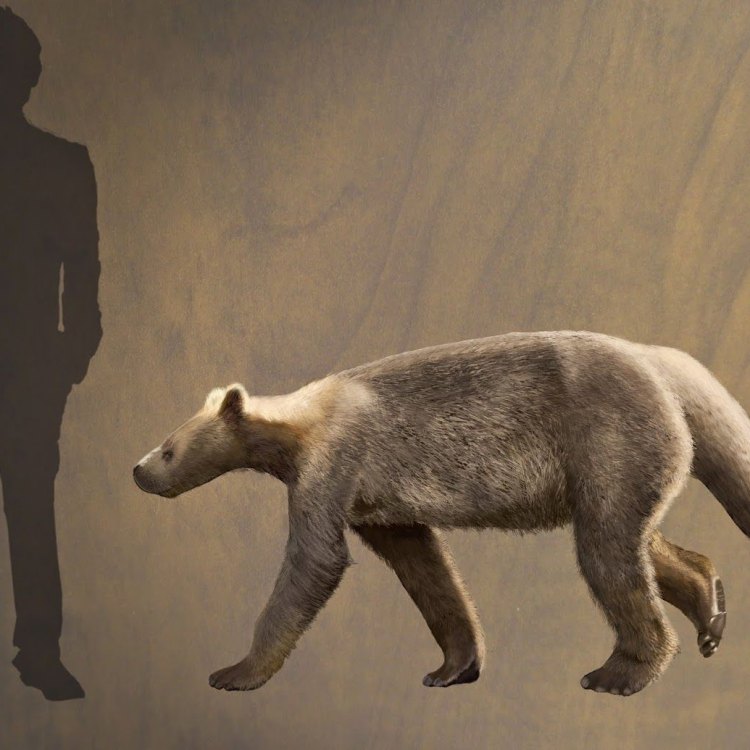

Barylambda
The Mysterious Barylambda: An Extinct Genus of Large Mammals
Imagine a creature that resembled a rhinoceros with long limbs and large teeth, roaming the North American lands during the Eocene epoch. This was the Barylambda, an extinct genus of large mammals that lived millions of years ago. Despite its size, not much is known about this mysterious species. In this article, we will delve into the unique features of Barylambda and uncover the enigmatic nature of this extinct genus PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Barylambda, which means "heavy lamb" in Greek, was first described in 1927 by American paleontologist George Gaylord Simpson. Fossils of Barylambda have been found in North America, particularly in the Badlands National Park in the United States. These fossils have provided researchers with valuable insights into the physical characteristics and distribution of this species.
One of the most distinctive features of Barylambda was its size. It was a large and stocky mammal that could grow up to three meters in length and weighed around 900 kilograms. Due to its size, Barylambda was believed to have been an herbivorous animal, feeding on vegetation such as shrubs, leaves, and fruits. Its large teeth were used to grind and crush tough plant materials.
But Barylambda was more than just a large herbivore. It had unique physical features that set it apart from other mammals Barreleye Fish. Barylambda had long limbs which were beneficial for its terrestrial lifestyle, allowing it to move easily on land. This was quite unusual for a large animal at that time, as many other mammals had adapted to an aquatic or semi-aquatic lifestyle. Its long legs gave it the ability to run quickly, making it a formidable creature in its environment.
Apart from its physical features, not much is known about the behavior and biology of Barylambda. It is believed to have lived in a terrestrial habitat and was likely a solitary animal. This hypothesis is supported by the fossils found, as there is no evidence of social groups or herds. The reproductive behavior of Barylambda is also unknown, although it is known to have been viviparous, giving birth to live young.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Barylambda is the lack of knowledge about its sound or call, migration pattern, and social groups. This adds to the mystery surrounding this extinct species, leaving scientists with many questions and few answers. But one thing is certain – Barylambda had a significant impact on its environment during its existence.
Being a large herbivore, Barylambda played a crucial role in the ecosystem. It grazed on vegetation and helped maintain a balance in plant populations. Its teeth also helped disperse seeds, promoting plant growth and diversity. But the details of its impact on the ecosystem remain unknown, leaving researchers to speculate based on the limited information available.
Despite its importance in the ecosystem, Barylambda is listed as extinct on the conservation status scale. The exact reasons for its extinction are still unknown, but like many other extinct species, habitat loss and climate change are possible factors. Barylambda's extinction serves as a reminder of the fragility of our planet's ecosystem and the importance of preserving and protecting all species, no matter how big or small.
As humans, we often have a tendency to focus on the present and the future. But studying extinct species like Barylambda allows us to look back in time and gain a better understanding of the diversity and evolution of mammals in the past. Through fossils and scientific research, we can piece together the puzzles of these enigmatic creatures and learn from their extraordinary characteristics and behaviors.
In conclusion, Barylambda is an intriguing and mysterious species that fascinates scientists and researchers to this day. Its large size, unique physical features, and minimal information make it a fascinating subject of study. While its exact place in the ecosystem and the reasons for its extinction may elude us, Barylambda provides us with valuable insights into the diversity and evolution of mammals in the past. This extinct genus serves as a reminder of the wonders and mysteries of the natural world, and the importance of preserving our planet's biodiversity for future generations.

Barylambda: The Ancient Giant of North America's Badlands National Park
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












