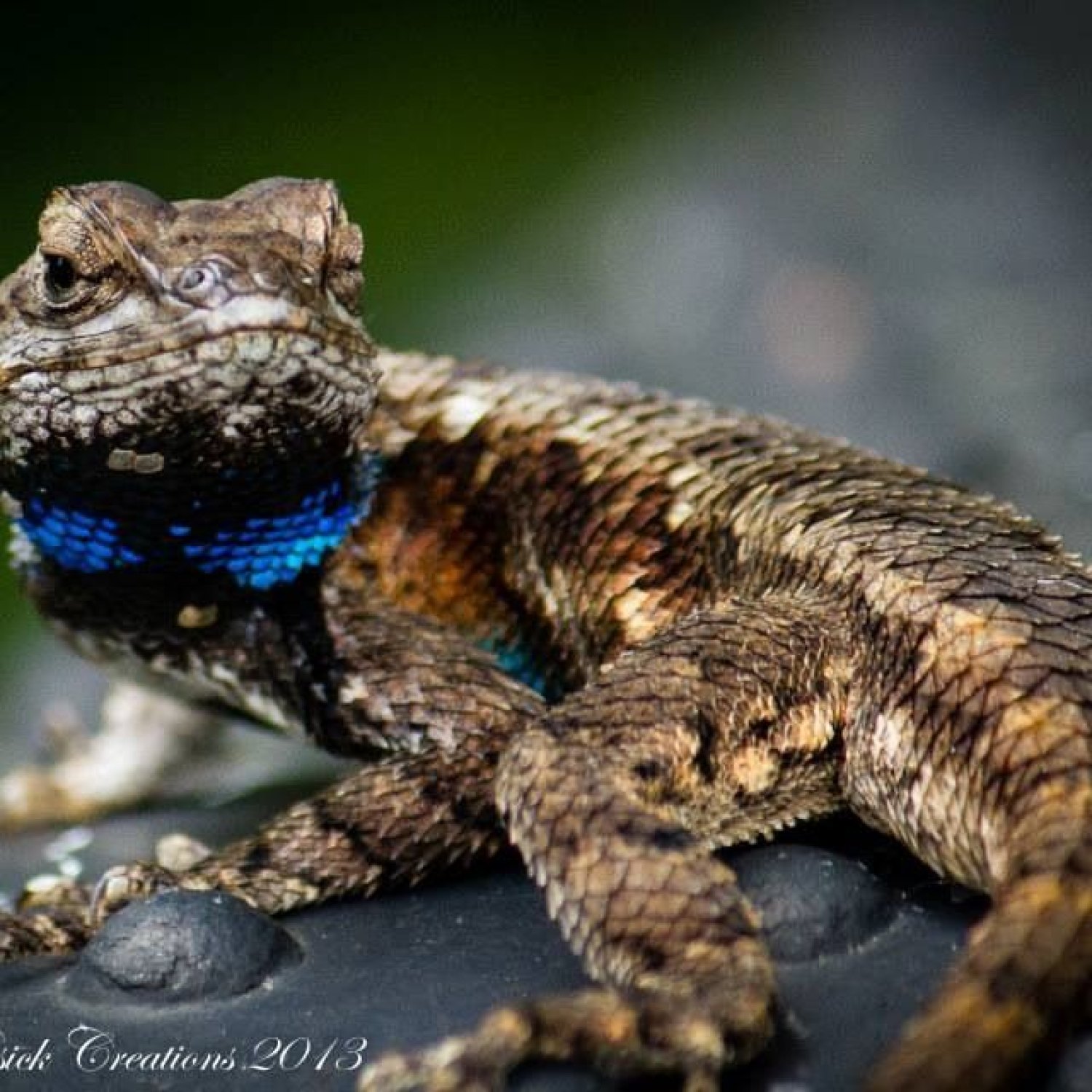
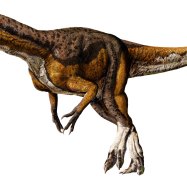
Blue Belly Lizard
5.1 to 8.7 inches
The stunning Blue Belly Lizard, found in California, Oregon, Washington, and Nevada, is a slender creature with long legs and tails. Belonging to the Phrynosomatidae family, these B-Category animals can grow up to 8.7 inches in length. With their vibrant blue stomachs, these lizards are a must-see for animal lovers. #BlueBellyLizard #AnimalsB #California #Oregon #Washington #Nevada
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Blue Belly Lizard
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Deserts, woodlands, grasslands, and rocky areas
The Fascinating Blue Belly Lizard: A Master of Adaptability in the Western United States
In the world of reptiles, the Blue Belly Lizard stands out with its vibrant blue belly and throat, making it a captivating sight in the desert, woodlands, and grasslands of the western United States. Officially known as Sceloporus occidentalis, this unique species of lizard has a lot more to offer than just its striking coloration. From its diverse habitat to its specialized diet, let's dive deep into the world of the Blue Belly Lizard and discover what makes it such a remarkable creature.A Creature of Many Names
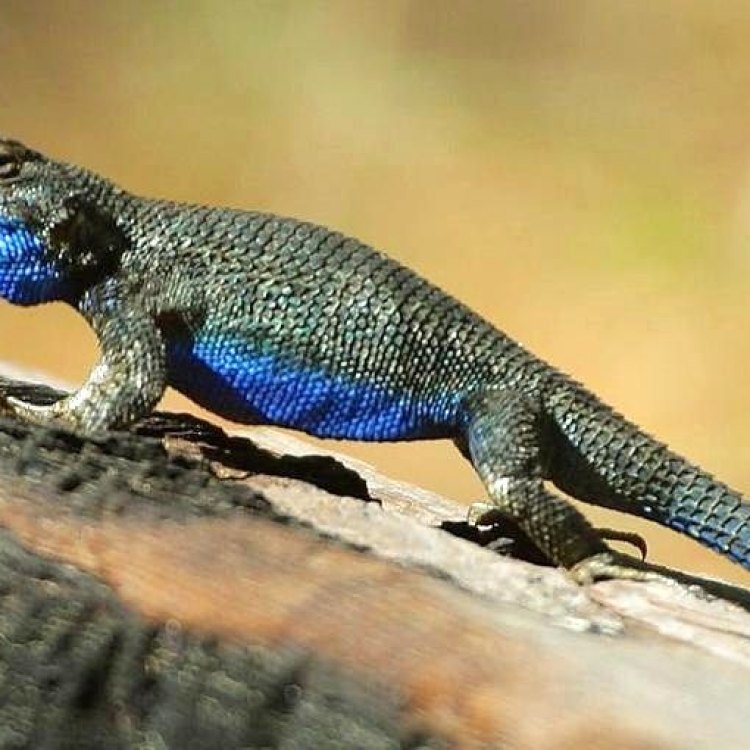
Also commonly referred to as the Western Fence Lizard or the Swift Lizard, the Blue Belly Lizard is easily identified by its bright blue coloration on its belly and throat Blue Belly Lizard. This feature has given it various creative names, such as "Blue-bellied Swift", "Blue-throated Fence Lizard", and even "Blue Belly", which is now commonly used as its common name.Classification and Distribution
Belonging to the Kingdom Animalia and the Phylum Chordata, the Blue Belly Lizard is classified as a reptile in the Class Reptilia and Order Squamata. It is part of the Phrynosomatidae family, which includes many other species of lizards found in North America.As the name suggests, the Blue Belly Lizard is primarily found in the western United States, with a specific distribution in California, Oregon, Washington, and Nevada. It is a common sight in these states, often seen basking in the sun or scurrying through rocky areas and shrubs.
A Versatile Habitat
The Blue Belly Lizard's ability to thrive in diverse habitats is one of its most exceptional features. This species of lizard is known to inhabit a wide range of environments, including deserts, woodlands, grasslands, and rocky areas. They are also adept at surviving in various altitudes, ranging from sea level to elevations over 8,000 feet.Such adaptability allows the Blue Belly Lizard to remain in suitable habitats even as its environment changes with the seasons Bigfin Reef Squid. During the summer, they can be found in more open areas, while during the cooler months, they retreat to wooded areas to hibernate.
Specialized Diet of a Carnivore
As a carnivorous species, the Blue Belly Lizard feeds mainly on insects and other small invertebrates such as spiders, snails, and crickets. They use their sharp claws and long, slender tongues to catch their prey and are known to be skilled hunters when it comes to catching fast-moving insects.Interestingly, the Blue Belly Lizard is known to have a highly specialized diet. They have a particular liking for Argentine ants, an invasive species, which has become a primary food source for lizards living in urban and suburban areas.
A Stunning Coloration and Body Shape
One of the most striking features of the Blue Belly Lizard is, of course, its unique blue coloration on its belly and throat. This blue coloration is more prominent in males, who also have a more intense orange-rust color on their sides and head.Apart from its coloration, the Blue Belly Lizard has a slender body with long legs and tails, making it an excellent climber and runner. They use their long tails to maintain balance while leaping from rock to rock, and their long legs allow them to move with swift and fluid movements.
A Surprisingly Short Length
Despite its slender body and long tail, the Blue Belly Lizard is not a very large lizard. The average length for this species ranges from 5.1 to 8.7 inches, with males being slightly larger than females. However, what they lack in size, they make up for in speed and agility, making them difficult prey for predators such as snakes and birds.A Protected Species
With its widespread distribution and adaptability, it may come as a surprise that the Blue Belly Lizard is actually a protected species. In California, it is illegal to capture, kill, or harm these lizards without a permit. This is due to their vital role in the ecosystem, where they help control the population of insects and act as a food source for larger predators.Tips for Spotting the Elusive Blue Belly Lizard
Due to their small size and quick movements, spotting a Blue Belly Lizard in the wild can be quite a challenging task. However, here are a few tips that can help you catch a glimpse of this elusive creature:- Visit rocky areas: As agile climbers, the Blue Belly Lizard loves basking on rocks and using them as lookout points, making them easier to spot.
- Look out for their unique coloration: The bright blue belly and throat make it easy to identify this lizard from other species found in the same habitat.
- Visit during the right time: Blue Belly Lizards are most active during the day and prefer basking in the sun. So, make sure to plan your viewing trip in the morning or late afternoon.
In Conclusion
The Blue Belly Lizard is a gem of the western United States, with its stunning coloration, impressive adaptability, and vital role in the ecosystem. Despite its small size, it has managed to carve a place for itself in the vast and often harsh landscapes of the western United States. So, the next time you spot this little creature, take a moment to appreciate its unique features and remember how it has mastered the art of survival in its natural habitat.
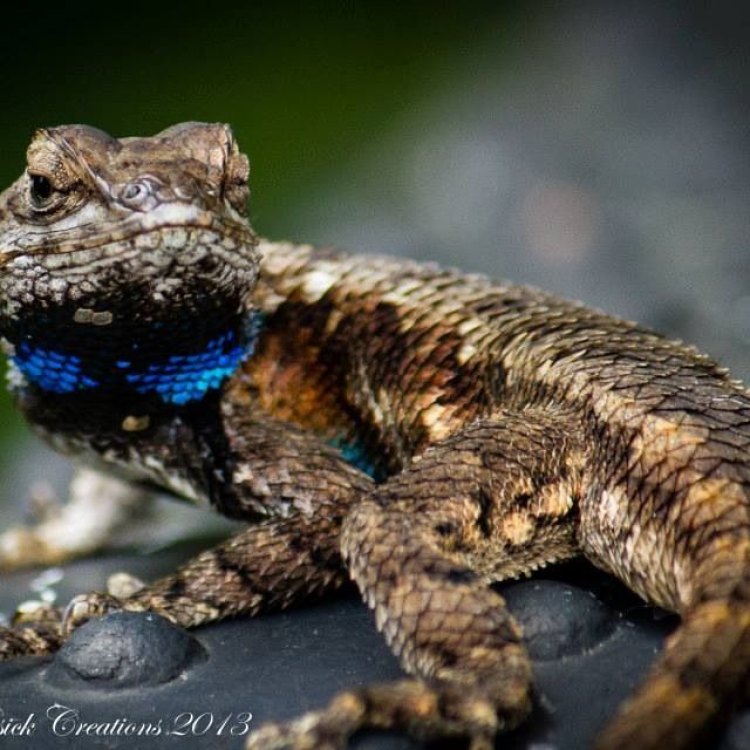

Blue Belly Lizard
Animal Details Blue Belly Lizard - Scientific Name: Sceloporus occidentalis
- Category: Animals B
- Scientific Name: Sceloporus occidentalis
- Common Name: Blue Belly Lizard
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Family: Phrynosomatidae
- Habitat: Deserts, woodlands, grasslands, and rocky areas
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Western United States
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: California, Oregon, Washington, Nevada
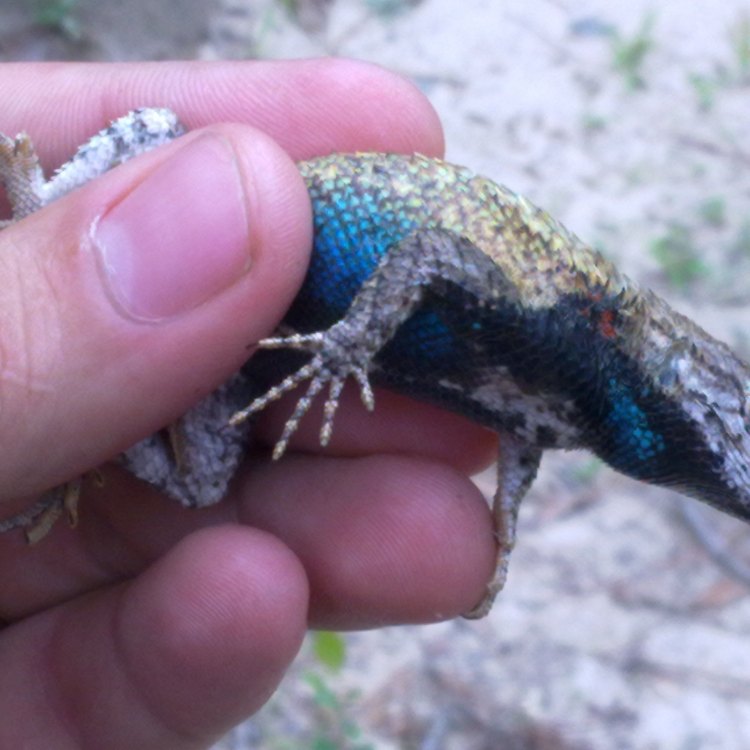
- Animal Coloration: Blue belly and throat, tan body with dark spots
- Body Shape: Slender body with long legs and tails
- Length: 5.1 to 8.7 inches
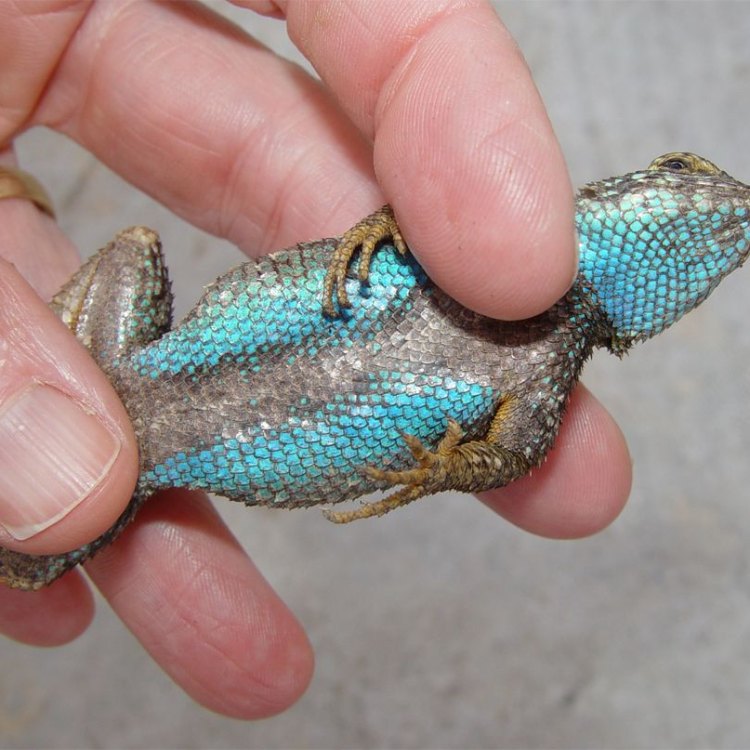

Blue Belly Lizard
- Adult Size: Small to medium-sized lizard
- Average Lifespan: Up to 5 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs in spring and females lay eggs in early summer
- Sound or Call: Males produce a series of rapid movements and head bobbing
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Diurnal and basking reptile
- Threats: Habitat loss, predation by birds, snakes, and mammals
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Predator control
- Human Use: Popular in the pet trade
- Distinctive Features: Bright blue coloration on the belly and throat
- Interesting Facts: Blue Belly Lizards can lose their tail as a defense mechanism
- Predator: Birds, snakes, and mammals

Sceloporus occidentalis
The Unique and Vibrant Blue Belly Lizard: A Small but Mighty Reptile
The world is home to an incredibly diverse and fascinating array of animals, each with their own unique traits and characteristics. Some are well-known and easily recognizable, while others may be less familiar to the average person. In this article, we will dive into the world of the Blue Belly Lizard, a small but mighty reptile that stands out with its striking blue coloration and intriguing behaviors.The Blue Belly Lizard, also known as the Eastern Fence Lizard or Sceloporus undulatus, is a species of small to medium-sized lizard found throughout the eastern United States and parts of Mexico PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They are a member of the Phrynosomatidae family, commonly referred to as spiny lizards, which includes over 200 species.
Size and Appearance
The Blue Belly Lizard typically measures around 4-7 inches in length, making it one of the smaller species of lizard. They have flattened bodies and a triangular shaped head with a pointed snout. Their body is covered in small, rough scales, and their coloration can vary from brown, gray, or green on their back to a vibrant blue on their belly and throat. This distinctive blue color is what gives them their common name, and it is especially vivid in males during the breeding season.Lifespan and Reproduction
On average, the Blue Belly Lizard has a lifespan of up to 5 years in the wild, with some individuals living slightly longer in captivity. They are a sexually reproducing species, meaning they require both a male and female to reproduce. Mating typically occurs in the spring, with males performing elaborate courtship displays to attract females. During this display, males will produce a series of rapid movements and head bobbing, accompanied by vocalizations Bottlenose Dolphin.Once mating is successful, females will lay a clutch of 2-12 eggs in early summer, typically in a sandy or gravelly area. The eggs are left to incubate for 6-8 weeks, and the offspring are fully independent upon hatching.
Behavior and Social Groups
Blue Belly Lizards are diurnal, meaning they are active during the day, and they are primarily solitary animals. You may come across them basking in the sun on rocks or logs, as they are ectothermic and need external heat sources to regulate their body temperature. They are also agile climbers and can often be found perched on low branches or fences.One interesting behavior observed in Blue Belly Lizards is their ability to lose their tail as a defense mechanism, known as autotomy. When threatened, the lizard's tail will detach from its body and continue to wiggle, distracting and confusing the predator while the lizard makes its escape. The tail will often grow back over time, although the regenerated tail may look different from the original.
Threats to Survival
Despite their impressive defense mechanisms, Blue Belly Lizards face several threats in their natural habitat. Habitat loss is one of the biggest threats, as human development and agricultural practices encroach on their habitat. They are also preyed upon by a variety of animals, including birds, snakes, and mammals, with juveniles being particularly vulnerable.Conservation Status and Impact on the Ecosystem
The Blue Belly Lizard is listed as Least Concern on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, meaning they are not currently facing a high risk of extinction. However, ongoing efforts are being made to protect and conserve their habitat, especially in areas where their populations have declined.One significant impact that the Blue Belly Lizard has on the ecosystem is its role in predator control. As an abundant prey species, they help to maintain a balance in predator populations, ensuring that other animals do not become too numerous and disrupt the delicate ecosystem.
Human Interaction and Use
The Blue Belly Lizard is a popular species in the pet trade, especially among reptile enthusiasts. However, it is essential to ensure that individuals are sourced ethically and not taken from the wild. Most Blue Belly Lizards sold as pets are captive-bred, and responsible pet owners should ensure they have the proper knowledge and resources to care for these unique creatures.In Conclusion
The Blue Belly Lizard may be small in size, but it certainly packs a punch with its vibrant coloration and fascinating behaviors. As we continue to learn more about this species, it is crucial to protect their habitat and ensure their survival for future generations to enjoy. So the next time you are out in nature, keep an eye out for these remarkable reptiles, and take a moment to appreciate their beauty and importance in our world.

The Fascinating Blue Belly Lizard: A Master of Adaptability in the Western United States
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.