Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
10.5 to 13 cm (4.1 to 5.1 inches)
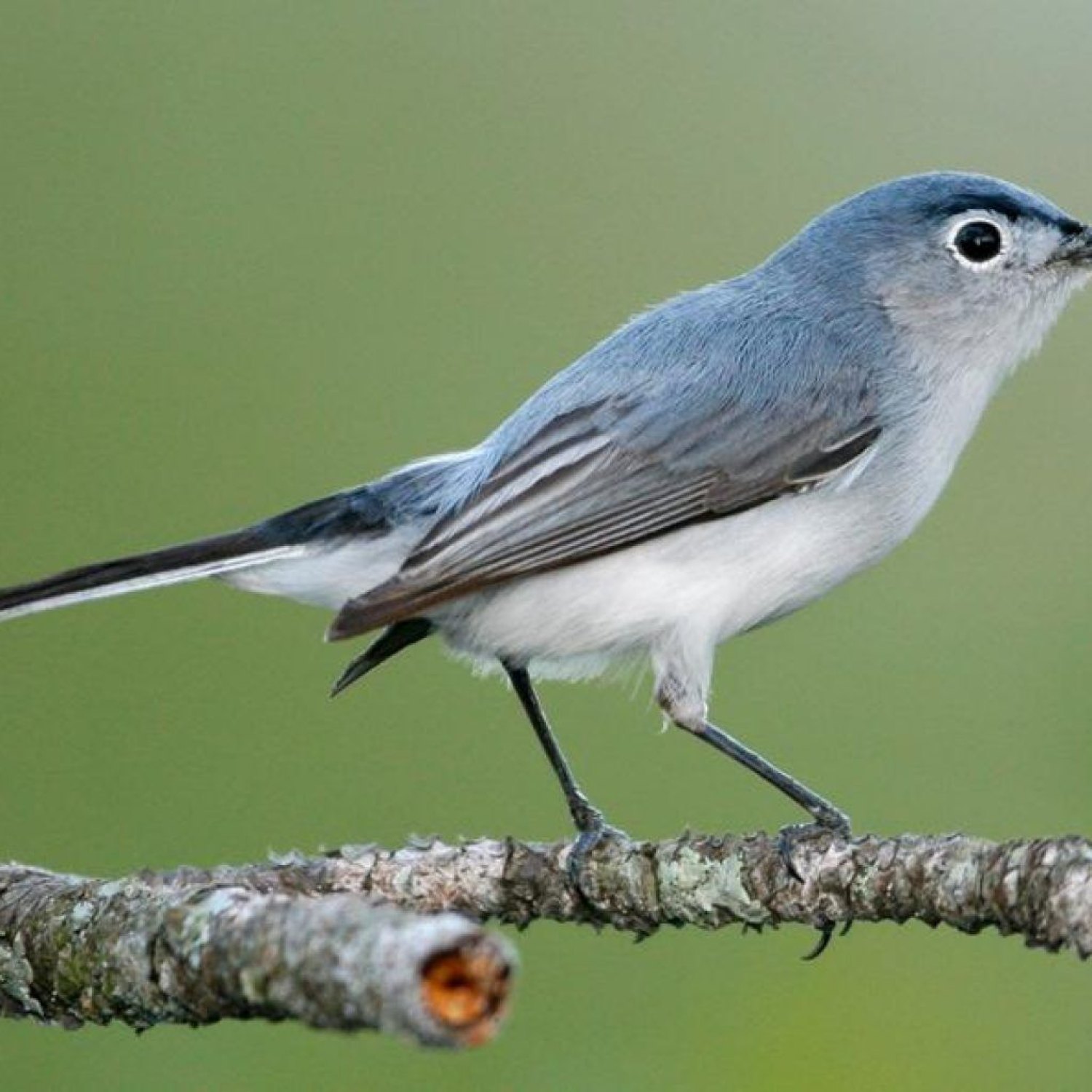
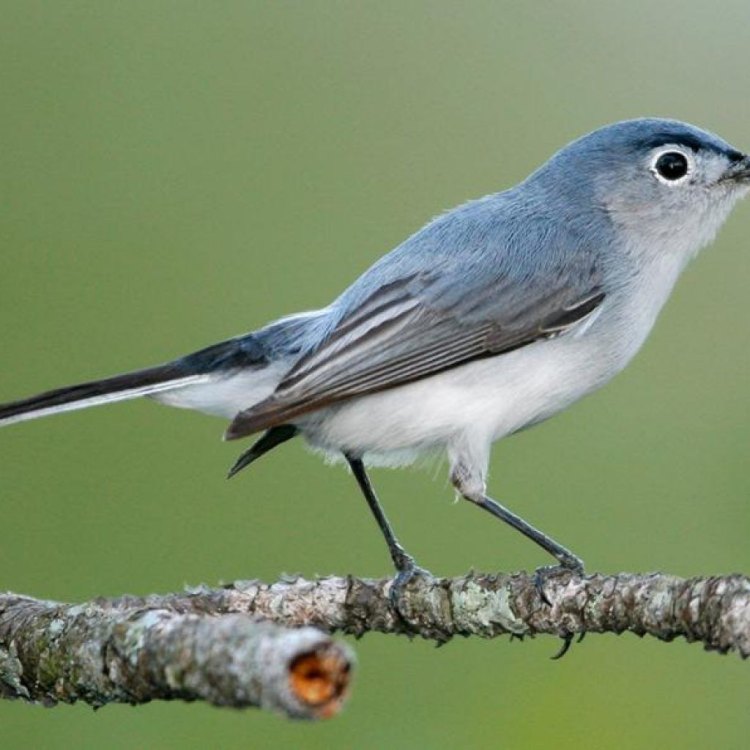
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher is a small and slender bird with a long tail found in eastern and central parts of the US, Mexico, and the Bahamas. With a length of 10.5 to 13 cm, this bird belongs to the family Polioptilidae and is often spotted darting through trees in search of insects. Its striking blue-gray color and distinctive white eye-ring make it a must-see for birdwatchers. #BlueGrayGnatcatcher #Birds #US #Mexico #Bahamas #Polioptilidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Woodlands, forests, thickets, and scrublands
Rising Above the Woods: Discovering the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
Amid the hustle and bustle of our daily lives, it can be easy to forget about the world around us. We often fail to notice the beauty of nature and the myriad of creatures that inhabit it. But if we take a step back, slow down, and observe, we can uncover the wonders of the animal kingdom – creatures like the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher.Scientifically known as Polioptila caerulea, the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher may have a small and unassuming appearance, but it is a bird that stands out in the world of ornithology Blue Gray Gnatcatcher. With its striking blue-gray coloration and unique feeding behavior, this tiny bird has captured the attention of bird enthusiasts and researchers alike.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher, from its taxonomy to its habitat and behavior. So, let's spread our wings and take flight into the world of one of the most captivating birds in North and Central America.
Taxonomy
Before we take a closer look at the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher, let's first understand its place in the animal kingdom. The Kingdom Animalia comprises all animals, and Phylum Chordata includes all animals with a notochord, or spinal cord. The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher falls under the class Aves, which consists of birds, and the order Passeriformes, which includes over half of all bird species.Family and Scientific Name
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher belongs to the Polioptilidae family, which contains small insect-eating birds with a slender body shape and long tail. Its scientific name, Polioptila caerulea, is derived from the Greek words "polios" for gray and "ptilos" for feathers, referring to its distinctive blue-gray coloration.Habitat and Geographic Distribution
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher is primarily found in woodlands, forests, thickets, and scrublands, making its home in the branches of trees and shrubs Blue Jay. It is most commonly found in the eastern and central parts of the United States, as well as Mexico and the Bahamas, during its breeding season.This migratory bird follows a "leap-frog" migration pattern, meaning that they do not migrate to the same location each year. Instead, they move to a different location in the south during the winter and return north for the breeding season. This behavior allows them to follow the abundance of their preferred food source – insects.
Feeding Method
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher's primary source of energy is insects, making it an insectivorous bird. It utilizes a unique feeding technique known as "hover gleaning," in which it hovers in the air and plucks insects from the foliage.Their long tail serves as a stabilizer, allowing them to maintain balance while hovering, and their thin and pointed bill is ideal for catching insects. The small and slender body shape of the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher also aids in agile movements and quick changes in direction, making it a skilled predator of insects.
Appearance
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher may be small, but it is noticeable due to its striking coloration. The upperparts of its body are predominantly blue-gray, while its underparts are white. It has a faint white eye-ring, a black eyeline, and a long, thin black bill. Its tail, as the name suggests, is long and gray, with white outer feathers.The male and female Blue Gray Gnatcatchers have similar plumage, making them difficult to distinguish from each other. However, during the breeding season, males may have a slightly more intense blue-gray coloration than females.
Size and Weight
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher may be small, but it has a mighty presence. It measures between 10.5 to 13 cm (4.1 to 5.1 inches) in length, with a wingspan of approximately 18 cm (7.1 inches). However, their most impressive feature is their weight. Despite their small size, they can weigh anywhere between 6 to 10 grams, which is equivalent to a few paperclips.A Tiny Bird with Big Impact
Despite its small size, the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher has a big impact on its ecosystem. As an insectivorous bird, it plays a crucial role in controlling insect populations, thereby helping to maintain the balance of its habitat. They also serve as a vital food source for larger predators, such as raptors.In addition to its role in the ecosystem, the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher has also become an indicator species for the population health of its habitat. Changes in the abundance of this bird species can signal changes in the overall health of their environment, making them a crucial member of the ecosystem.
Threats and Conservation
While the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher is not currently considered a threatened species, it faces several threats to its population. Habitat loss and fragmentation due to deforestation and urbanization are a significant concern, potentially disrupting their breeding and foraging habits.Additionally, pests and parasites, such as ticks and nest predators like snakes and raccoons, pose a threat to their survival. Climate change and severe weather events can also impact their migratory patterns and food availability.
To protect the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher and its habitat, conservation efforts are in place, including preserving and restoring critical habitats and educating the public about the importance of this species. Bird enthusiasts and researchers also play a vital role in monitoring and studying this species to better understand its needs and behaviors.
Final Thoughts
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher may seem like just another tiny bird in the vast bird kingdom, but it has proven to be a fascinating and important species. From its unique feeding behavior to its role in maintaining the balance of its habitat, this bird has captured the hearts and minds of many.As we continue to learn about and appreciate the natural world, let us not forget about the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher and its fellow inhabitants of our planet. Through conservation efforts and an appreciation for all creatures, big and small, we can ensure a healthy and diverse ecosystem for future generations to come. So, the next time you hear a tiny chirping in the trees, take a moment to look up – it might just be a Blue Gray Gnatcatcher, reminding us to slow down and appreciate the beauty of the natural world.

Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
Animal Details Blue Gray Gnatcatcher - Scientific Name: Polioptila caerulea
- Category: Animals B
- Scientific Name: Polioptila caerulea
- Common Name: Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Passeriformes
- Family: Polioptilidae
- Habitat: Woodlands, forests, thickets, and scrublands
- Feeding Method: Insectivorous
- Geographical Distribution: North and Central America
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Eastern and central parts of the United States, Mexico, and the Bahamas
- Animal Coloration: Blue-gray on the upperparts and white on the underparts
- Body Shape: Small and slender with a long tail
- Length: 10.5 to 13 cm (4.1 to 5.1 inches)
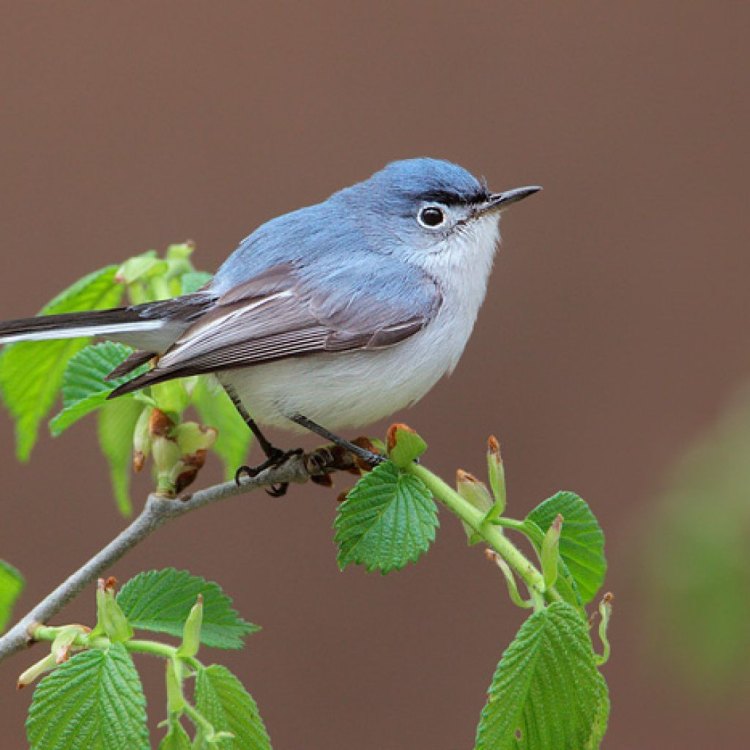

Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 5 to 8 years
- Reproduction: Monogamous
- Reproductive Behavior: Builds a cup-shaped nest using spider silk and lichens
- Sound or Call: High-pitched calls and song
- Migration Pattern: Migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary or in pairs during breeding season
- Behavior: Active and acrobatic
- Threats: Habitat loss and nest parasitism by Brown-headed Cowbirds
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Plays a role in insect control
- Human Use: Observation and study
- Distinctive Features: Long tail with white tips and a thin, pointed bill
- Interesting Facts: The Blue-gray Gnatcatcher is known for catching small insects in mid-air by performing elaborate acrobatic maneuvers.
- Predator: Snakes, birds of prey
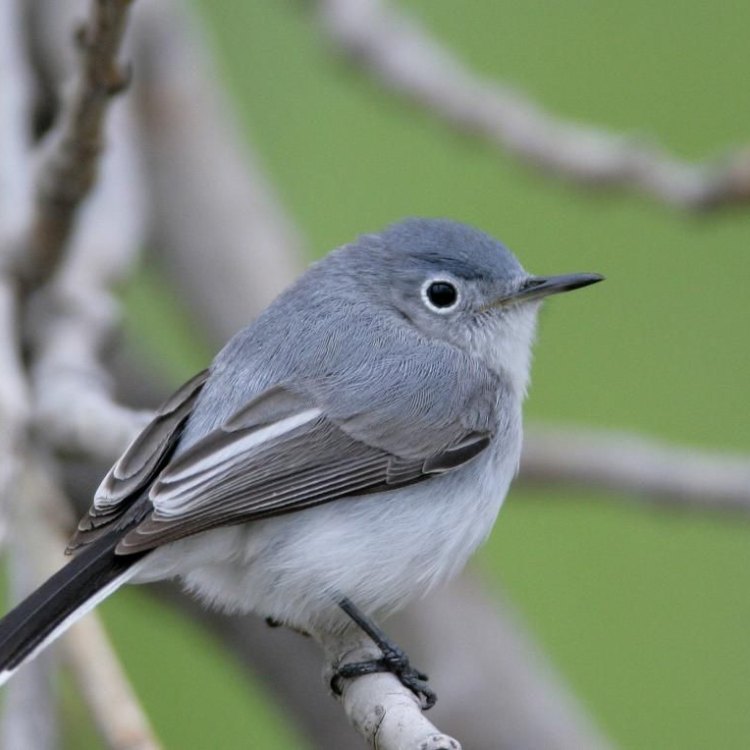

Polioptila caerulea
The Blue Gray Gnatcatcher: A Small Bird With a Big Impact
From the moment you first lay eyes on a Blue Gray Gnatcatcher, you can't help but be enchanted by its small size and distinctive features. These tiny birds, averaging only 4.5 inches in length and weighing less than half an ounce, are a common sight in many parts of North America. But don't be fooled by their small size – the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher plays a big role in our ecosystems and has some fascinating behaviors and traits PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Adult Blue Gray Gnatcatchers are truly small birds, but their impact on their surroundings is anything but insignificant. They have an average lifespan of 5 to 8 years, during which time they play an essential role in insect control. These birds primarily feed on small insects, such as flies, moths, and wasps, making them valuable predators in our ecosystems.
Reproduction for Blue Gray Gnatcatchers is a monogamous affair. During the breeding season, which typically runs from April to August, these birds form pairs and defend their territory together. They build their cup-shaped nests using spider silk and lichens, a unique and impressive feat that requires intricate weaving skills.
But it's not just the building of the nest that makes these birds stand out. Blue Gray Gnatcatchers have distinctive reproductive behaviors too. The male gnatcatcher will fly around the nest area, singing and performing elaborate acrobatic maneuvers to woo his mate Belgian Laekenois. These displays can be quite entertaining to observe, as they showcase the bird's agility and grace.
In terms of appearance, the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher is easily recognizable. As the name suggests, they have a blue-gray coloration on their wings, back, and head, with white underparts. Their long tail has white tips, and their thin, pointed bill is perfectly adapted for catching small insects in mid-air. They also have a unique white eye-ring that sets them apart from other small birds.
But what truly sets the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher apart is its high-pitched calls and song. These birds have a repertoire of sounds, including a soft "speeee" call and a distinctive "zhreeee" song. Their vocalizations can often be heard before they are seen, making them a challenging yet rewarding bird to spot and identify.
Blue Gray Gnatcatchers are also migratory birds, with their breeding range covering most of North America, from southern Canada to central Mexico. They then migrate south during the winter months to Central America and the Caribbean, where they can be found in habitats such as mangroves, tropical forests, and humid lowlands.
Despite their small size, these birds are incredibly active and acrobatic. They rarely stay in one spot for long and are constantly on the move, hopping from branch to branch and hanging upside down to catch insects. To observe them, you'll need to keep a close eye on their movements and be quick with your binoculars!
Blue Gray Gnatcatchers are typically solitary birds, but during the breeding season, they are found in pairs. They are known to be very territorial and will defend their territory and nesting sites from other birds, including predators and potentially even humans.
Speaking of predators, Blue Gray Gnatcatchers face many threats in the wild. Their habitats, such as woodland and scrubland, are under constant pressure from human development, leading to habitat loss for these birds. In addition, their nests are often parasitized by Brown-headed Cowbirds, who lay their eggs in the gnatcatchers' nests, forcing these small birds to raise larger, more aggressive cowbird chicks. This parasitism often results in lower reproductive success for the gnatcatchers.
Despite these challenges, the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher's conservation status is currently listed as "Least Concern" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is thanks in part to the great work of conservation organizations, such as the National Audubon Society, who work to protect and preserve the habitats of these and other bird species.
Humans also play a significant role in the lives of Blue Gray Gnatcatchers. These birds are popular among birdwatchers and bird enthusiasts, who often observe and study them in their natural habitats. Their striking appearance and interesting behaviors make them a favorite subject for photographers, artists, and nature lovers alike.
But what truly makes the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher a remarkable bird is its adaptability and resilience. Despite the threats they face, these birds continue to thrive and play a crucial role in our ecosystems. Their small size and often inconspicuous behavior may make them easy to overlook, but they have a big impact on the world around us.
In conclusion, the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher may be small, but it is a bird worth paying attention to. From their unique reproductive behaviors to their acrobatic antics and important role in insect control, these birds are an essential part of our natural world. So the next time you spot one flitting through the trees, take a moment to appreciate this tiny, yet remarkable, creature.
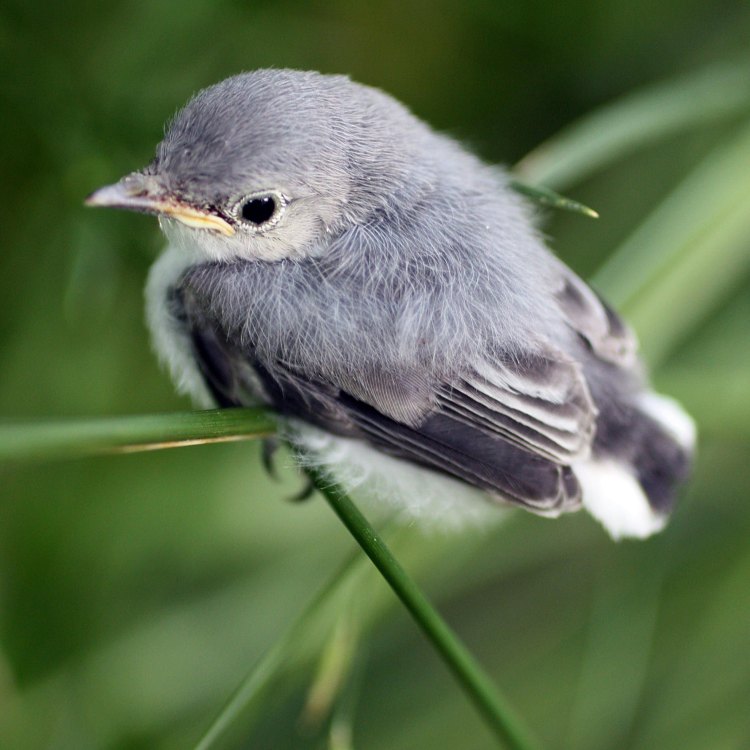

Rising Above the Woods: Discovering the Blue Gray Gnatcatcher
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.