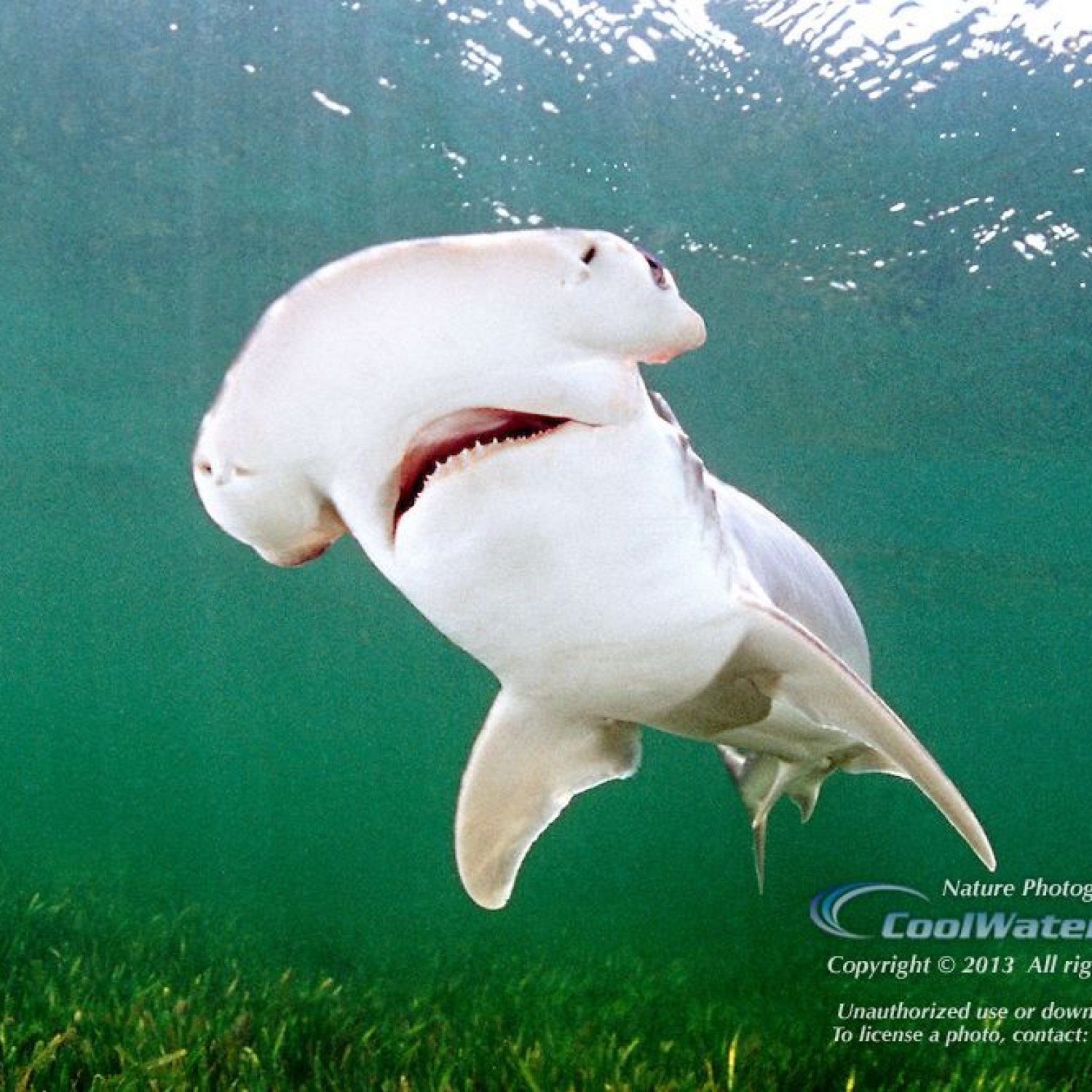

Bonnethead Shark
2 to 5 feet
The Bonnethead Shark is a fascinating creature found in the Atlantic Ocean. With a hammer-shaped head and slender body, it ranges from 2 to 5 feet in length. Belonging to the Sphyrnidae family, it is known for its unique appearance and agile swimming abilities. Learn more about this remarkable animal and its home in the ocean. #BonnetheadShark #AtlanticOcean #Sphyrnidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Bonnethead Shark
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Coastal waters, estuaries, and bays
Unlocking the Secrets of the Bonnethead Shark: Nature's Omnivore
Have you ever heard of a shark that eats plants? Most people would be taken aback by this idea, as sharks are known for their ferocious carnivorous nature. However, there is one species of shark that breaks this stereotype – the Bonnethead Shark.Found in the Western Atlantic, from the United States to Brazil, the Bonnethead Shark (Sphyrna tiburo) is a truly unique creature. It belongs to the class Chondrichthyes, which includes sharks, rays, and chimeras, and is part of the hammerhead shark family, Sphyrnidae Bonnethead Shark. But what makes this shark so fascinating? Let's dive in and explore the wonders of the Bonnethead Shark.
The Physical Appearance of the Bonnethead Shark
As the name suggests, the most distinctive feature of the Bonnethead Shark is its head, which is shaped like a shovel or a bonnet. This distinct shape is due to its flattened front end of its skull. This unique feature is not just for appearances – it serves a purpose. The wide head helps the shark to detect and capture prey more easily, making it an efficient hunter. Unlike its larger relatives, the Great and Scalloped Hammerhead Sharks, the Bonnethead's head is smaller and more rounded, making it the smallest of the hammerhead species.The Bonnethead Shark has a slender, torpedo-shaped body, which is common among most shark species. It ranges from 2 to 5 feet in length and can weigh anywhere from 20 to 35 pounds. The shark's body is covered in gray or brownish-gray skin, which helps it blend in with its sandy surroundings Bichon Frise. This natural camouflage is important for the shark's survival as it allows it to surprise its prey and avoid predators.
The Only Known Omnivorous Shark
One of the most intriguing and unique features of the Bonnethead Shark is its diet. Unlike most sharks that are known to be fierce carnivores, the Bonnethead Shark is the only known species of shark that is omnivorous. This means that it not only consumes meat, but it also feeds on plant matter.The Bonnethead Shark's diet consists of a variety of small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other invertebrates that are commonly found in coastal waters, estuaries, and bays. However, what sets this shark apart is its ability to digest and obtain nutrients from seagrasses, which make up a significant portion of its diet. This unique dietary adaptation allows the Bonnethead Shark to thrive in areas where its usual prey may be scarce.
The Bonnethead Shark's Social Behavior
Another intriguing aspect of the Bonnethead Shark is its social behavior. Unlike most sharks that are solitary creatures, the Bonnethead Shark has been observed to exhibit social behavior and form groups. These groups typically consist of 7-8 sharks, with larger groups forming during the breeding season.The reason behind this social behavior is still unknown, but there are a few theories. Some experts believe that the sharks may come together to hunt for food, while others believe it could be for mating purposes. Whatever the reason may be, this social behavior showcases the complexity and flexibility of shark behavior, and it challenges the common stereotype of sharks being solitary and anti-social creatures.
The Habitat and Geographical Distribution of the Bonnethead Shark
As mentioned earlier, the Bonnethead Shark can be found in coastal waters, estuaries, and bays. These areas are typically shallow, with sandy bottoms where the shark can easily blend in. This habitat preference is also linked to its diet, as these areas are rich in seagrass and other plants that make up a significant portion of its diet.The Bonnethead Shark is primarily found in the Western Atlantic, from the United States to Brazil. However, it can also be found in the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, and as far south as Argentina. This wide range of distribution is a testament to the adaptability and resilience of this species.
Conservation and Threats to the Bonnethead Shark
Despite its unique features and widespread distribution, the Bonnethead Shark faces various threats that could potentially endanger its survival. The sharks are often caught as bycatch and are targeted by commercial and recreational fishing. They are also hunted for their fins, which are used in shark fin soup, a delicacy in some cultures.Furthermore, the destruction of coastal habitats and pollution also poses a threat to the Bonnethead Shark. These sharks rely on healthy and diverse habitats to thrive, and any disruptions to their environment can have severe consequences. If these threats are not addressed, the population of the Bonnethead Shark could decline, leading to their endangerment.
In Conclusion
The Bonnethead Shark is a fascinating and unique creature that challenges our perceptions of sharks. Its omnivorous diet, social behavior, and distinct physical features make it a truly remarkable species. However, the threats it faces cannot be ignored, and conservation efforts need to be implemented to ensure its survival.As we continue to discover more about this species, we can learn valuable lessons about the resilience and adaptability of nature. The Bonnethead Shark is a reminder that there is still so much left to explore and understand about the world around us. So, let's continue to unlock the secrets of the Bonnethead Shark and appreciate the marvels of nature.
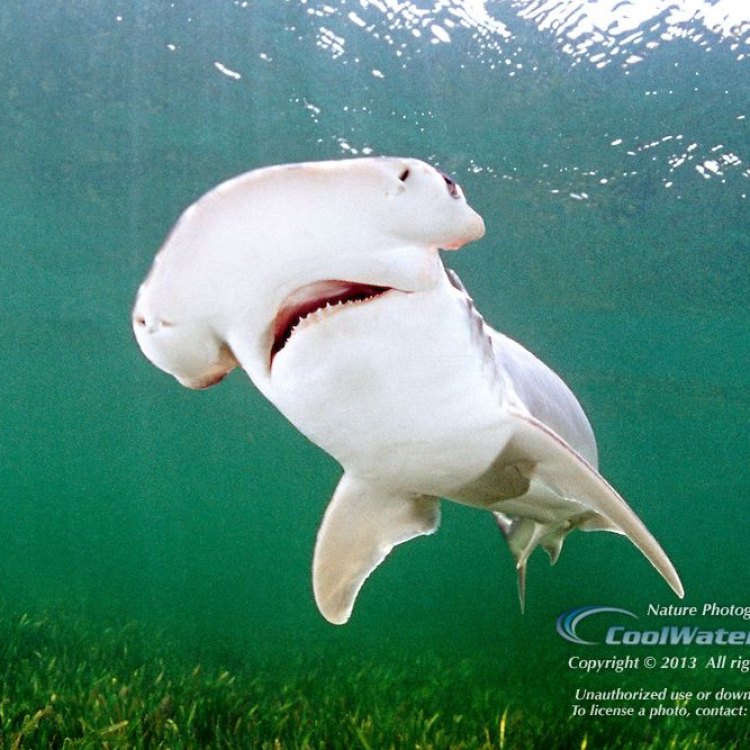

Bonnethead Shark
Animal Details Bonnethead Shark - Scientific Name: Sphyrna tiburo
- Category: Animals B
- Scientific Name: Sphyrna tiburo
- Common Name: Bonnethead Shark
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Sphyrnidae
- Habitat: Coastal waters, estuaries, and bays
- Feeding Method: Omnivore
- Geographical Distribution: Western Atlantic, from the United States to Brazil
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Atlantic Ocean
- Animal Coloration: Gray or brownish-gray
- Body Shape: Hammer-shaped head and slender body
- Length: 2 to 5 feet

Bonnethead Shark
- Adult Size: 3 to 4 feet
- Average Lifespan: 10 to 14 years
- Reproduction: Viviparous (give birth to live young)
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs during the spring and summer
- Sound or Call: No specific sound or call
- Migration Pattern: Migration patterns not well understood
- Social Groups: Solitary or small groups
- Behavior: Active and agile swimmers, not aggressive towards humans
- Threats: Habitat loss, overfishing, and pollution
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Maintain balance in marine ecosystems as predators
- Human Use: Commercial and recreational fishing
- Distinctive Features: Hammer-shaped head, long flattened body
- Interesting Facts: Bonnethead sharks are the smallest species of hammerhead sharks
- Predator: Larger sharks and marine mammals
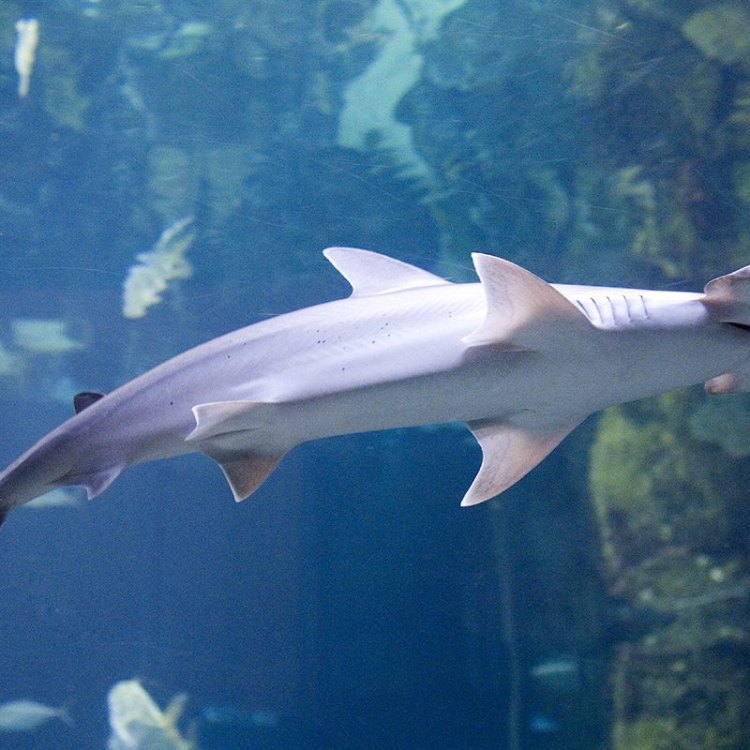
Sphyrna tiburo
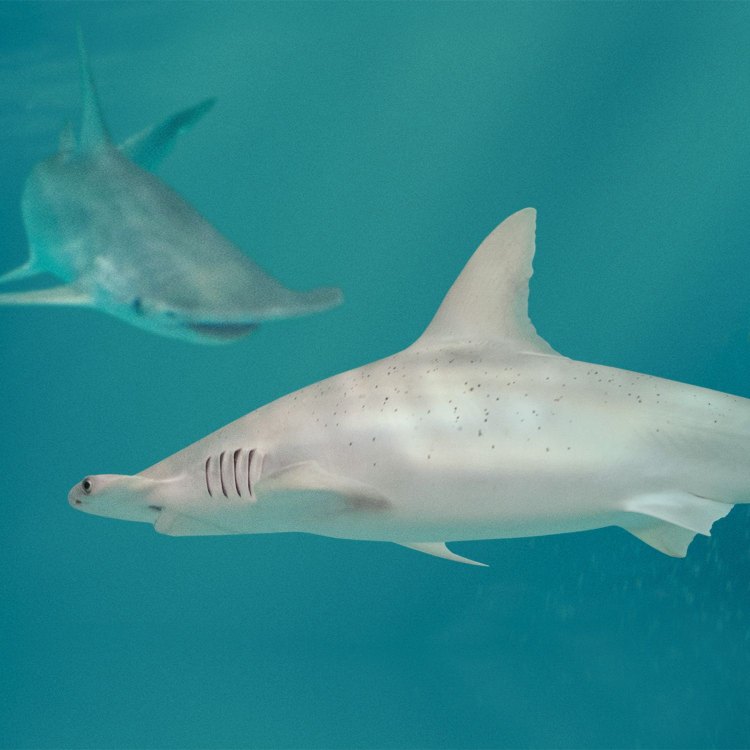
The Fascinating World of the Bonnethead Shark
The underwater world is full of mysterious and intriguing creatures, and one such creature is the Bonnethead shark. With its unique appearance and behavior, this small hammerhead shark has captured the attention of marine enthusiasts and scientists alike. In this article, we'll dive into the world of the Bonnethead shark and explore its distinctive features, interesting facts, role in the ecosystem, and potential threats.Adult Bonnethead sharks can grow up to 3 to 4 feet in length, making them the smallest species of hammerhead sharks PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They have a lifespan of 10 to 14 years, which may seem relatively short compared to other shark species, but their time on this planet is crucial for maintaining balance in marine ecosystems.
These sharks are found in the coastal waters of the Americas, from North Carolina in the United States to southern Brazil. They are commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean Sea, and parts of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. The Bonnethead shark is a stunning creature with a long flattened body and a distinctive hammer-shaped head. But their unique appearance is just one of the many fascinating things about them.
Reproduction
Like other shark species, Bonnethead sharks are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. This reproductive method is common among large predatory sharks to ensure the survival of their offspring. But what sets Bonnethead sharks apart is their reproductive behavior.
Mating occurs during the spring and summer months when mature females migrate to shallow waters to give birth Black Headed Python. Unlike in other shark species, where males aggressively pursue females, Bonnetheads have a unique mating behavior. Males will approach the female's head and bite, which is most likely a courtship ritual rather than aggressive behavior. This peculiar behavior has earned male Bonnethead sharks the nickname "headbutting Casanovas."
Sound or Call
Sharks are known for their silent nature, and the Bonnethead shark is no exception. These sharks do not have a specific sound or call to communicate with each other. Instead, they use body language and chemical signals to communicate and navigate their underwater world.
Migration Patterns
The migration patterns of Bonnethead sharks are not well understood as they are a relatively understudied species. However, some evidence suggests that they may undertake seasonal migrations to and from shallow coastal waters for breeding and feeding purposes.
Social Groups
Bonnethead sharks are solitary creatures, meaning they usually swim alone. However, they have been observed forming small groups during their breeding season. These groups comprise a dominant male and several females, and occasionally, non-dominant males.
Behavior
Bonnethead sharks are known for their active and agile swimming abilities, often seen gracefully gliding through the water. They are typically non-aggressive towards humans and are not known to pose a significant threat to humans.
Their diet mainly consists of small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks, which they prey on using their hammer-shaped heads. This unique head shape allows them to use their wide-set eyes to scan the seafloor for food while maintaining a low profile to sneak up on prey. They also have specialized teeth that are perfect for crushing and grinding hard-shelled prey.
Threats
Despite their docile nature towards humans, Bonnethead sharks face several threats that put their existence at risk. Habitat loss, overfishing, and pollution are among the top threats facing this species.
Like other shark species, Bonnetheads play a crucial role in maintaining balance in marine ecosystems as predators. Removing them from the ecosystem can have significant ripple effects on the entire food chain. And with the increasing demand for shark fins and meat, overfishing has become a significant threat to their population.
Conservation Status
Fortunately, the Bonnethead shark is currently listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List, which means they are not at risk of extinction. However, it's essential to remember that their conservation status can change if we do not take the necessary measures to protect this species.
Human Use
Bonnethead sharks have been commercially and recreationally fished for their meat, fins, and oil. Their meat is considered a delicacy in some countries, and their fins are used in shark fin soup, a traditional dish in many Asian cultures. Additionally, Bonnethead sharks are caught as bycatch in commercial fishing nets, further contributing to their decline.
But as the awareness of their importance in the marine ecosystem grows, there are more efforts to protect and sustainably manage their populations. Some countries have also implemented fishing regulations and quotas to ensure the sustainable use of this species.
Distinctive Features
One of the most distinctive features of Bonnethead sharks is their hammer-shaped head, which sets them apart from other species of sharks. This unique head shape has several purposes, including detecting prey, navigation, and as mentioned earlier, sneaking up on prey.
Interesting Facts
Apart from their unconventional mating behavior and hammer-shaped heads, there are many more interesting facts about Bonnethead sharks that make them stand out in the shark world.
For starters, their small size and harmless nature make them an excellent choice for aquariums, where they can thrive in captivity. They have also been observed displaying problem-solving abilities, such as using their heads to push open a hidden food compartment in an experimental tank.
In Conclusion
The Bonnethead shark may not be as well-known as its larger hammerhead relatives, but it certainly has its own unique features and charm. From its peculiar reproductive behavior to the important role it plays in marine ecosystems, this species of shark deserves our attention and protection.
As humans, it's our responsibility to learn about, appreciate, and protect the diverse creatures that inhabit our oceans. Whether through responsible fishing practices, reducing pollution, or supporting conservation efforts, we can all do our part to ensure that the Bonnethead shark and other marine species continue to thrive in their natural habitats.

Unlocking the Secrets of the Bonnethead Shark: Nature's Omnivore
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












