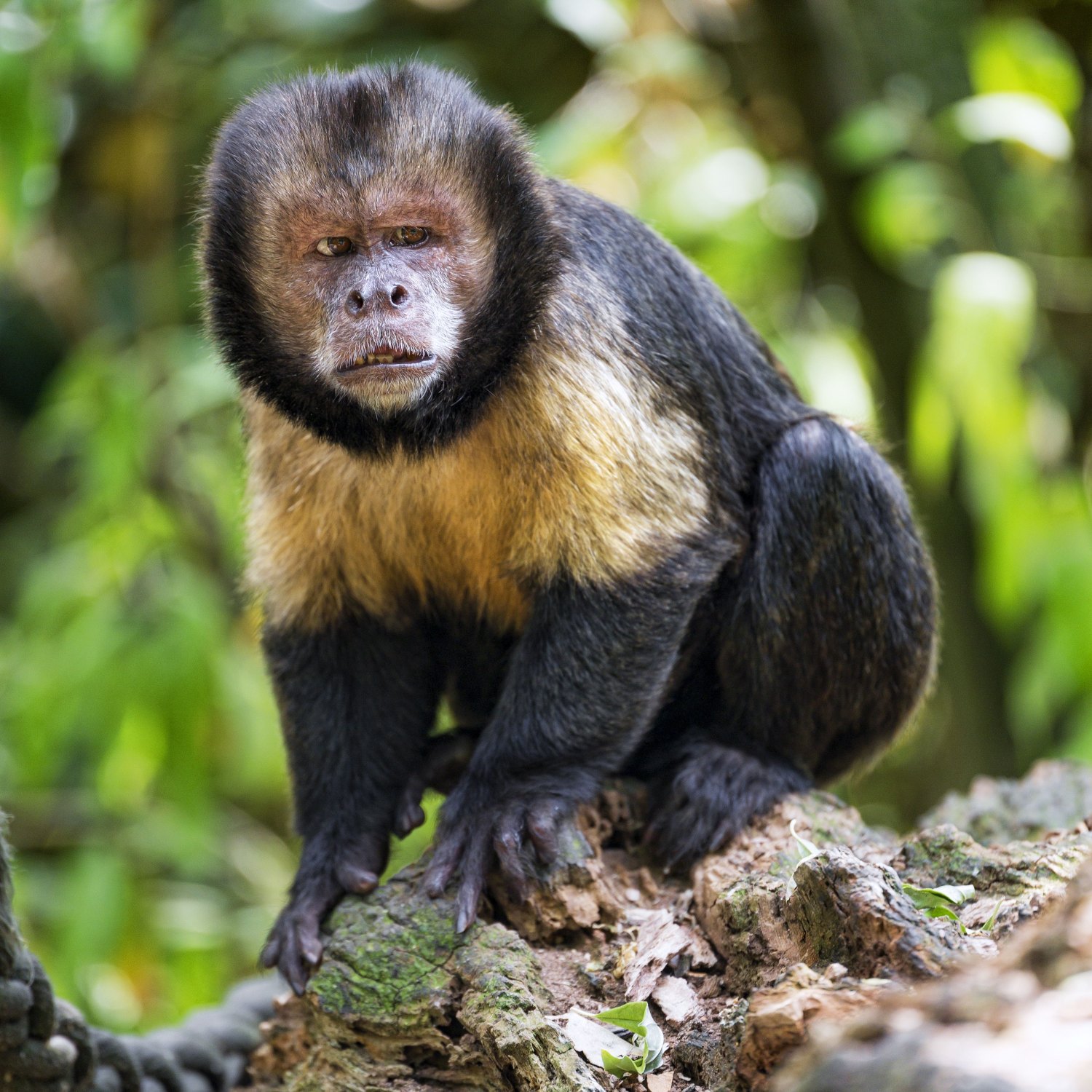
Capuchin
25 to 45 centimeters
Capuchins, small and agile primates found in rainforests, belong to the Cebidae family. Ranging from 25 to 45cm in length, these intelligent animals are a delight to watch. With their curious nature and ability to use tools, they are a key species in maintaining the balance of the rainforest ecosystem. Learn more about these fascinating creatures and their important role in the wild. #Capuchin #Rainforest #Primates
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Capuchin
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Tropical forests, savannas, and mangroves
The Intelligent and Adaptable Capuchin Monkey
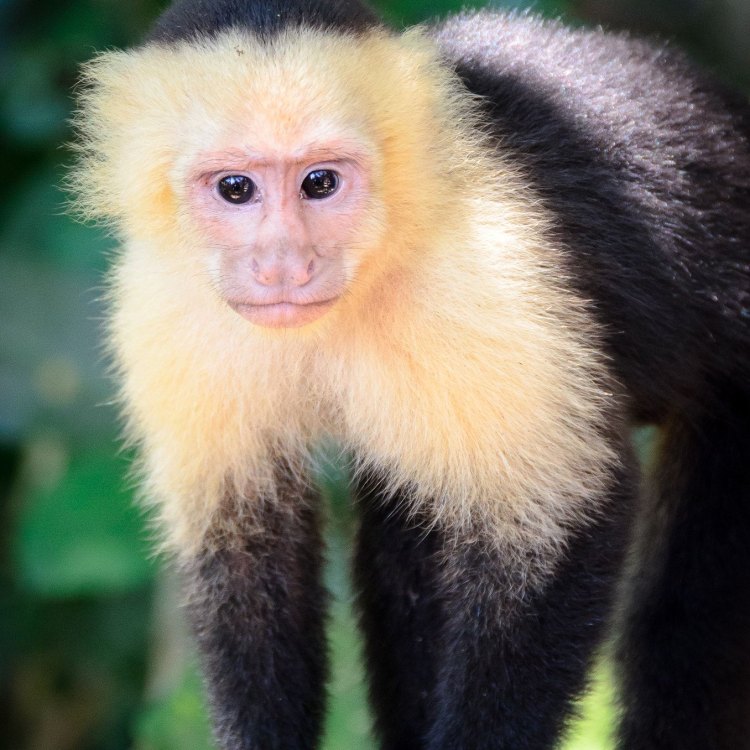
The Capuchin monkey, scientific name Cebus, is a highly intelligent and adaptable primate species that is found across Central and South America. With their distinctive black or brown fur and white or light-colored faces, these monkeys are easily recognizable. But there is much more to these fascinating creatures than their charming appearance.Ancestry and Classification
The Capuchin monkey belongs to the Animalia kingdom and the Chordata phylum Capuchin. They are also classified as members of the Mammalia class and the Primates order. These monkeys belong to the Cebidae family, which also includes other New World primates such as howler monkeys, squirrel monkeys, and tamarin monkeys.Habitat and Distribution
Capuchin monkeys are native to Central and South America, and their range extends from Panama to Argentina. They can be found in tropical forests, savannas, and mangroves, making them incredibly adaptable. However, they are most commonly found in the rainforests of Brazil, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Peru, and Colombia.Physical Characteristics
Capuchin monkeys have a small and agile body shape, with a length ranging from 25 to 45 centimeters and a weight of 1.5 to 4 kilograms. Their fur can vary in color, but they typically have black or brown fur and a distinctive patch of white or light-colored fur on their face, giving them a unique appearance. This patch of fur is why they are often referred to as "organ-grinder" monkeys Corman Shepherd.Diet and Feeding Habits
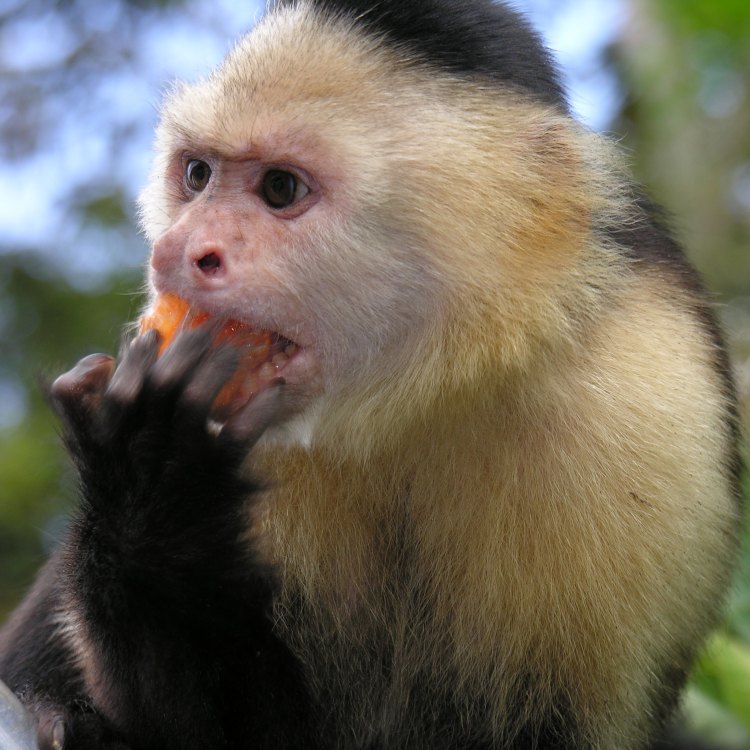
Capuchin monkeys are omnivorous, meaning they have a varied diet. In the wild, they will eat a variety of fruits, flowers, insects, small mammals, and eggs. They are also known to use tools to aid in their food gathering. For example, they have been observed using rocks to crack open hard nuts and shells.These monkeys are also adaptable when it comes to their feeding habits. In areas where food is scarce, they are known to forage during the day and night, while in areas with an abundance of food, they may only forage during the day.
Behaviour and Social Structure
Capuchin monkeys are highly social animals and live in groups of 10 to 20 individuals, known as "troops." Within these troops, there is a dominant male, along with several females and their offspring. However, these troops can also merge with other troops, forming even larger groups.One interesting behavior of these monkeys is that they exhibit a form of altruism known as "reciprocal food sharing." This behavior involves male monkeys giving food to females in exchange for grooming, and it helps to build social bonds within the group.
These monkeys are also known for their intelligence and problem-solving skills. They can be trained to perform tasks and have even been used in some scientific research studies.
Threats and Conservation
While Capuchin monkeys are not considered endangered as a species, some of their subspecies, such as the black-capped capuchin, are facing threats to their survival. Habitat loss due to deforestation and human development is a significant threat to these monkeys. They are also sometimes hunted for the pet trade or for use in traditional medicines.To protect these monkeys, conservation efforts have been put in place, such as creating protected areas and educating local communities on the importance of preserving their natural habitat.
The Role of Capuchin Monkeys in Nature
Capuchin monkeys play a vital role in their ecosystems as seed dispersers, helping to maintain the balance of plant diversity. As they consume fruits and disperse the seeds through their feces, they aid in the growth and renewal of various plant species. They also play an important role in controlling insect populations, acting as natural pest controllers.Fun Facts About Capuchin Monkeys
- Capuchin monkeys have a lifespan of around 15 to 25 years in the wild.- They have a prehensile tail, which means they can grasp and hold onto objects.
- Capuchin monkeys are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of habitats, from rainforests to urban areas.
- They have excellent eyesight and can see a wider range of colors than humans.
- These monkeys are known to exhibit a variety of facial expressions, including smiling, pouting, and even blowing raspberries.
- They are highly vocal and use a variety of vocalizations to communicate with each other.
In Conclusion
The Capuchin monkey is a highly adaptable, intelligent, and social primate species that plays a critical role in its ecosystem. With their distinctive appearance and variety of behaviors, they are a fascinating species to observe and study. It is essential for us to continue conservation efforts to protect these intelligent and adaptable creatures and allow them to thrive in their natural habitats.
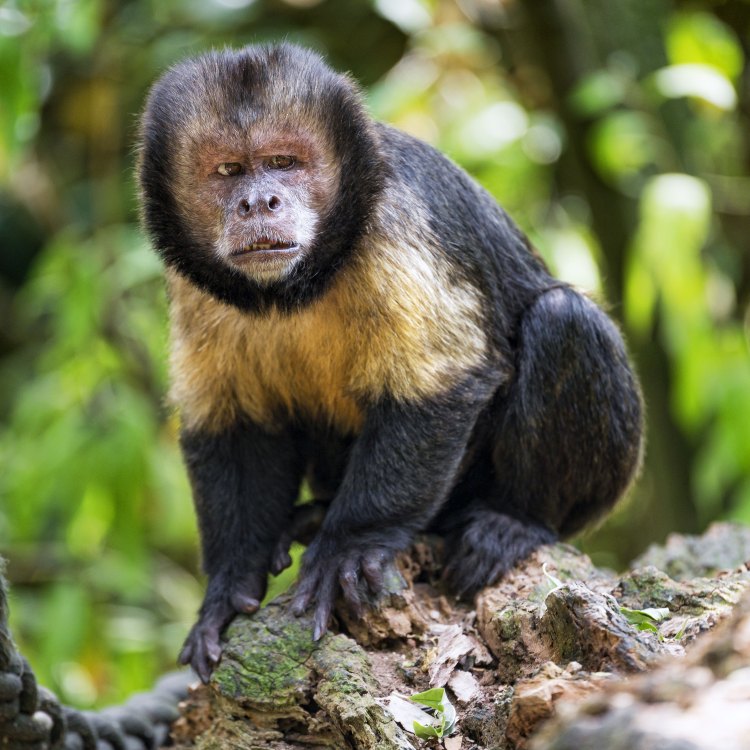

Capuchin
Animal Details Capuchin - Scientific Name: Cebus
- Category: Animals C
- Scientific Name: Cebus
- Common Name: Capuchin
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Family: Cebidae
- Habitat: Tropical forests, savannas, and mangroves
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Central and South America
- Country of Origin: Brazil, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Peru, and Colombia
- Location: Rainforests
- Animal Coloration: Black or brown fur with white or light-colored faces
- Body Shape: Small and agile
- Length: 25 to 45 centimeters
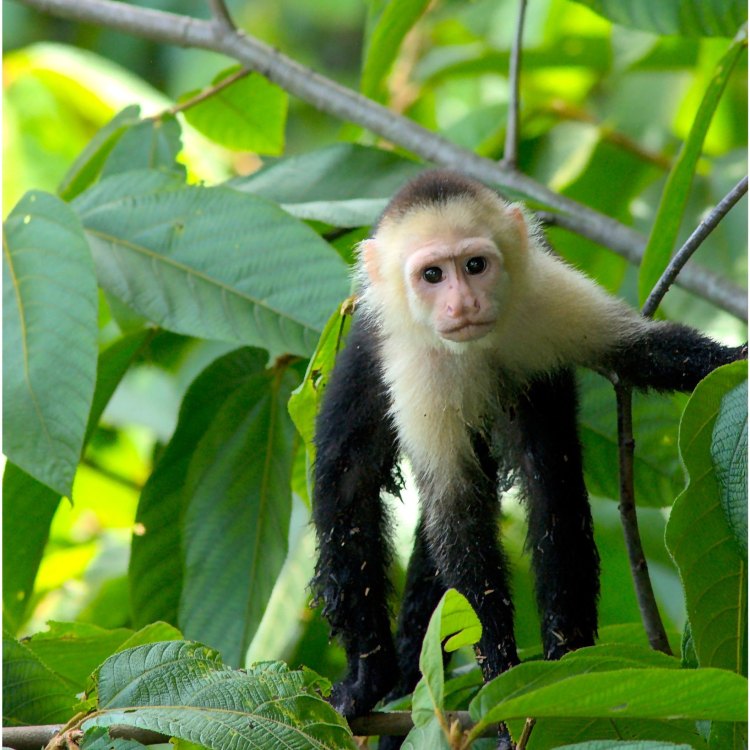

Capuchin
- Adult Size: Small to medium-sized
- Average Lifespan: 25 to 35 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Polygamous mating system
- Sound or Call: Vocalize through various sounds and calls
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Live in large groups called troops
- Behavior: Intelligent and resourceful
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, illegal pet trade
- Conservation Status: Vulnerable
- Impact on Ecosystem: Seed dispersers and pollinators
- Human Use: Used in the entertainment industry and as assistance animals
- Distinctive Features: White or light-colored faces with black or brown fur
- Interesting Facts: They use tools to extract food from hard-to-reach places
- Predator: Jaguars, ocelots, and birds of prey

Cebus
The Fascinating World of Capuchin Monkeys
The animal kingdom is full of diverse and fascinating creatures. Among them, the capuchin monkey stands out with its unique characteristics and behaviors. These small to medium-sized primates, known scientifically as Cebus capucinus, can be found in the tropical forests of Central and South America. Let's take a closer look at what makes these monkeys so special and why we should be concerned about their conservation PeaceOfAnimals.Com.A Look at the Basics
As mentioned, capuchin monkeys are small to medium-sized primates, with adult size ranging from 13 to 22 inches and weighing between 3 to 9 pounds. They have a lifespan of 25 to 35 years in the wild, making them a long-lived species among primates. Capuchins reach sexual maturity between 3 to 4 years old, and their reproductive behavior is sexual, meaning they require a male and a female to mate and produce offspring.One interesting fact about capuchin monkeys is their polygamous mating system. This means that a male will mate with multiple females, and a female can also mate with multiple males during her fertile period. This behavior is common among primates, and it allows for genetic diversity and the passing of strong genes to offspring.
The Social Life of Capuchins
Capuchin monkeys are highly social animals and are known to live in large groups called troops. These troops can have up to 20 members, with a dominant male leading the group. Females tend to stay with their birth troop, while males will move to other troops once they reach sexual maturity Cantil.These intelligent and resourceful monkeys have a complex social structure within their troops. They form close bonds with their family members and exhibit behaviors like grooming, playing, and sharing food. They also have a somewhat hierarchical structure, where the dominant male and female have more privileges and decision-making power.
The Sounds of Capuchins
Capuchin monkeys are vocal animals and communicate through various sounds and calls. They use a combination of vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language to convey different messages. Their vocal repertoire includes grunts, barks, shrieks, and purrs, which they use to warn others of predators, show submission or dominance, and express distress or happiness.Interestingly, males and females have different calls, and a mother and her offspring have a specific vocalization that helps them identify each other. These social and vocal behaviors play an essential role in maintaining the cohesion and organization of capuchin troops.
Behavioral Adaptations
Capuchin monkeys are known for their intelligence and problem-solving abilities. They are incredibly adaptable and have developed various behavioral adaptations to survive in their environment. One of the most impressive behaviors is their use of tools.Capuchins are one of the few non-human species that use tools to extract food from hard-to-reach places. They have been observed using stones to crack open nuts, sticks to dig for insects, and even using leaves as protection against the sun and rain. This behavior is learned through observation and is passed down from generation to generation, showcasing their strong cultural intelligence.
Threats to Survival
While capuchin monkeys have managed to thrive in their natural habitat for thousands of years, their future is now uncertain due to various threats. Habitat loss and fragmentation are the primary threats to their survival. The expansion of agriculture, mining, and urban development has resulted in the destruction of their forest homes, leaving them with smaller and more isolated areas to live in.Another major concern is the illegal pet trade. Capuchin monkeys are highly sought after as exotic pets, and many individuals are captured and sold illegally. This not only affects the monkey's well-being, but it also disrupts their social structures and can lead to genetic issues if bred in captivity.
The Need for Conservation
As a result of these threats, capuchin monkeys are currently listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature's (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. This means that they are facing a high risk of extinction in the wild if significant conservation measures are not taken.Capuchins play an essential role in their ecosystem as seed dispersers and pollinators. They help maintain the balance of their forest home by spreading seeds and aiding in forest regeneration. Their extinction could have a significant impact on the biodiversity of their habitat.
The Human Influence
Apart from being a crucial species in their ecosystem, capuchin monkeys have also been used by humans for various purposes. In some parts of South America, they are hunted for their meat, and in recent years, they have been used in the entertainment industry for TV shows and movies.However, the most significant human use of capuchins is possibly their involvement in the assistance animal industry. With their intelligence and trainable nature, these monkeys have been trained to assist people with disabilities. While this may seem like a noble cause, there are concerns that these animals may not have a suitable life in captivity and may even have been illegally obtained.
The Distinctive Features of Capuchins
Capuchin monkeys have distinct physical features that make them stand out among other primates. One of the most noticeable characteristics is their white or light-colored faces, which gives them a unique and almost human-like appearance. Their bodies are covered in black or brown fur, with a tuft of hair on top of their head resembling a cap, hence their name.Additionally, their prehensile tails, which can be used as a fifth limb, are an essential feature for their survival in the trees. They also have dexterous hands and feet, with opposable thumbs, enabling them to manipulate objects and move nimbly through the trees.
Their Predators in the Wild
Capuchin monkeys may have adapted to survive in their natural habitat, but they are not without predators. Jaguars, ocelots, and birds of prey are the primary predators of capuchins. These animals pose a significant threat, especially to the young and vulnerable members of the troop.Luckily, capuchins have developed various survival tactics, such as living in large groups, using their vocalizations to warn others of potential danger, and their agility to quickly move through the trees and evade predators.
In Conclusion
The capuchin monkey is undoubtedly a fascinating and unique species, with its distinctive features, complex social behaviors, and remarkable adaptations. However, these primates face various threats to their survival, and it is our responsibility to take action and ensure their conservation.We must strive to protect their natural habitat, educate others about the importance of their role in the ecosystem, and discourage the illegal pet trade. With these efforts, we can ensure that these intelligent and resourceful animals continue to thrive in their natural habitat for generations to come. Let us appreciate and celebrate the wonders of the animal kingdom and do our part in preserving its diversity.

The Intelligent and Adaptable Capuchin Monkey
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.