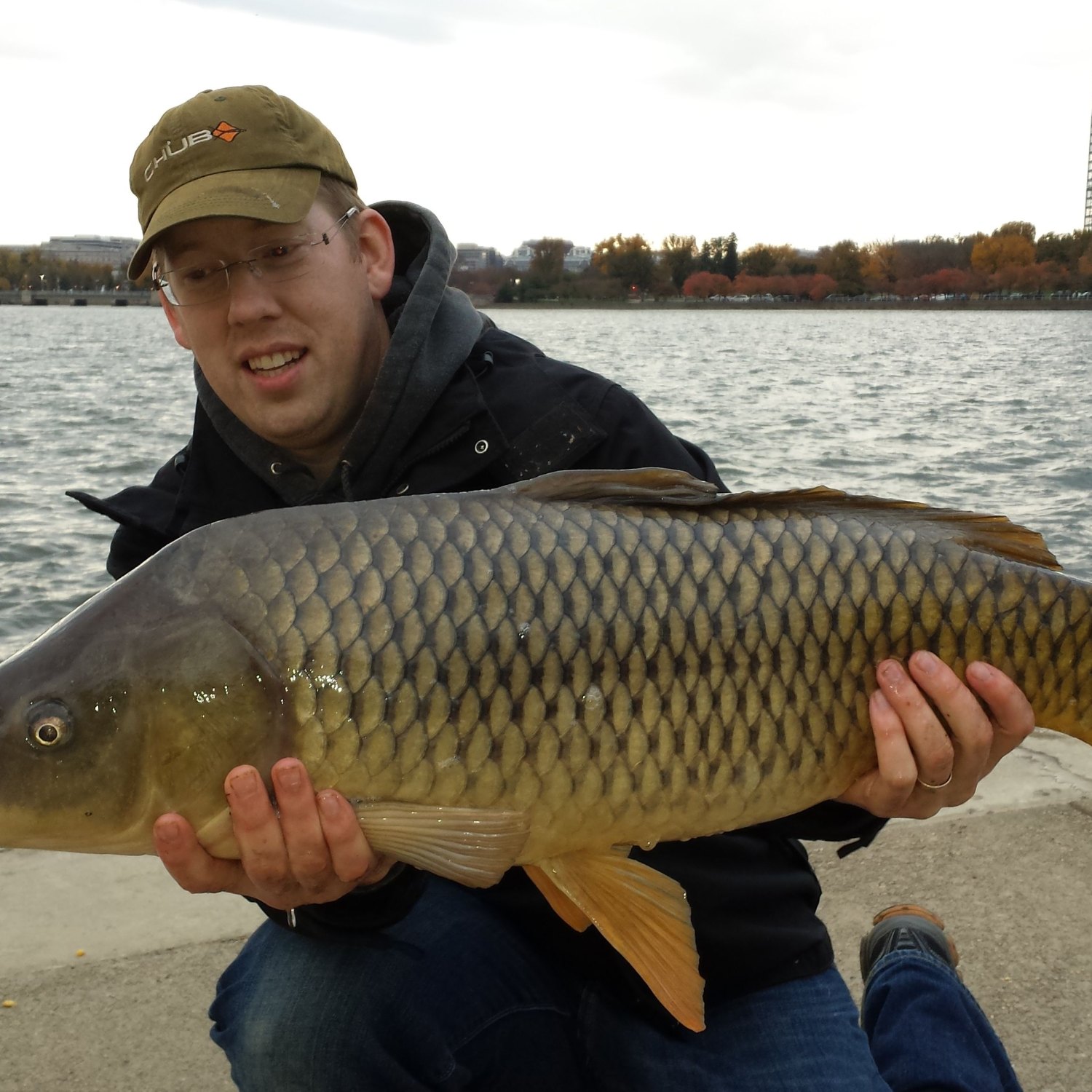
Carp
40 - 80 cm
Did you know the Carp, also known as the 'Golden Fish' is a popular freshwater fish found in ponds, lakes, and rivers? With its torpedo-shaped body and average length of 40-80 cm, it belongs to the Cyprinidae family. These majestic creatures make a great addition to any aquatic ecosystem! #Carp #FreshwaterFish #Ponds #Lakes #Rivers #Cyprinidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Carp
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Freshwater
The Mighty Carp: An Omnivorous Fish in Freshwater
The peaceful and serene freshwater habitats of Eurasia are home to a powerful and adaptable species known as Carp. Scientifically named Cyprinus carpio, this fish falls under the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, and class Actinopterygii. It belongs to the order Cypriniformes and the family Cyprinidae. But enough of the scientific jargon, let's dive deeper into the world of Carp and explore its interesting features Carp.Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Carp are primarily freshwater dwellers, preferring to live in shallow and still waters such as ponds, lakes, and slow-flowing rivers. Their natural habitats span across Eurasia, with a primary concentration in Eastern Europe and China. However, due to human intervention, these hardy fish have been introduced to several other regions, including North America and Australia.Origins in China
Carp have a long and rich history, with their origins tracing back to ancient China. As early as 2500 BC, Carp were being cultivated as a food source in Chinese ponds and lakes. Over time, they spread across Asia and Europe, becoming a staple food for many cultures. This demonstrates the resilience and adaptability of Carp as a species.Appearance and Body Shape
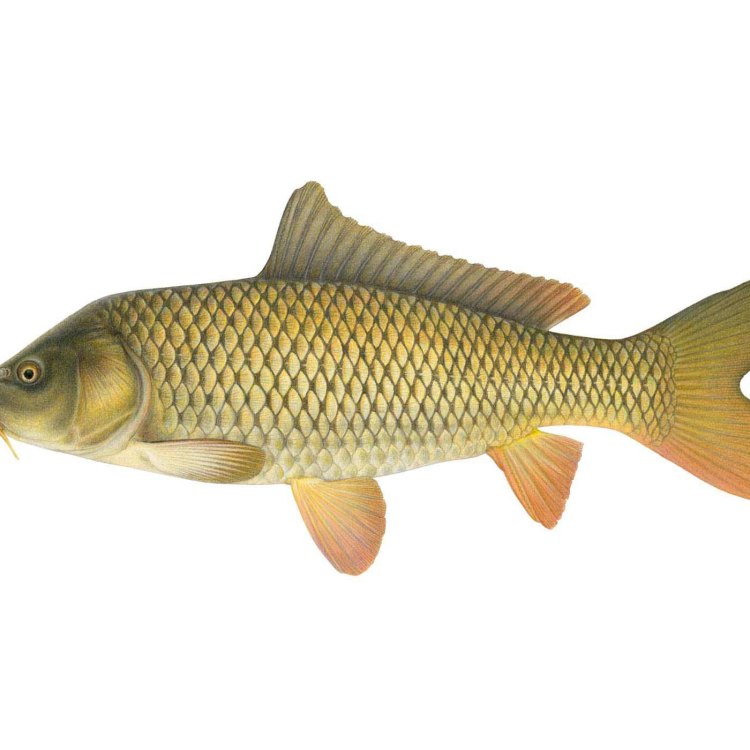
Carp have a torpedo-shaped body, with a slightly flattened head and a forked tail. They can grow up to 40-80 cm in length and weigh anywhere between 2-14 kg Cochin Chicken. However, this size and weight can vary significantly depending on environmental factors such as food availability and competition with other fish species.Distinctive Coloration
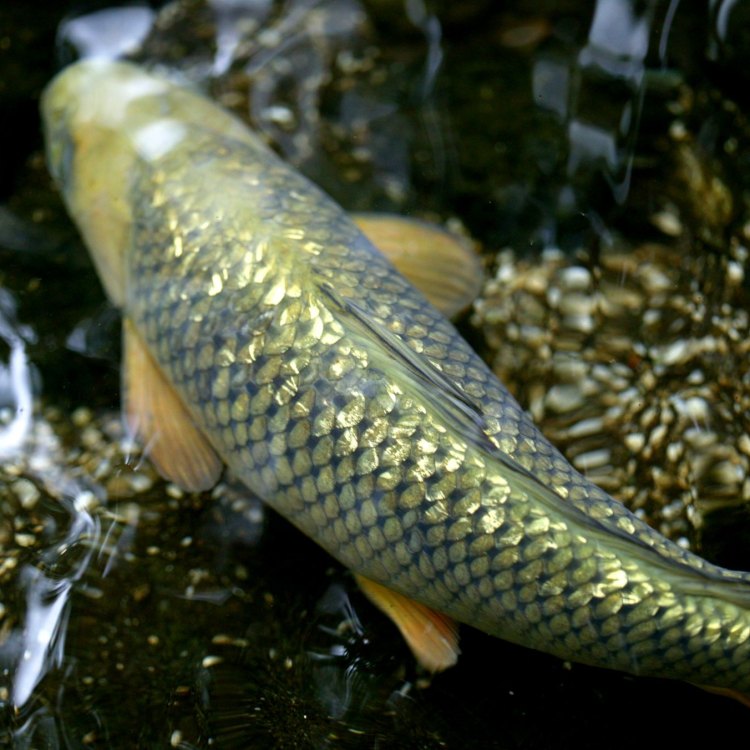
One of the most striking features of a Carp is its coloration. They can come in various shades of green, brown, and golden. The coloration is not only for aesthetic purposes but also serves as camouflage, allowing them to blend in with the murky waters of their habitat. Carp can also change their coloration to adapt to different environments, making them the ultimate survivors.Omnivorous Feeding Method
Carp are known as opportunistic feeders, meaning they will eat whatever is available. They have a diverse diet that includes aquatic plants, insects, crustaceans, and small fish. This omnivorous feeding method allows them to survive in a variety of habitats, making them a crucial part of the freshwater ecosystem.Adaptability and Resilience
One of the most impressive features of Carp is their adaptability and resilience. They can survive in a wide range of water temperatures, oxygen levels, and water conditions. This makes them ideal for commercial fish farming, as they can thrive in man-made ponds and tanks. Carp can also survive in polluted waters, making them vital for the cleanup of contaminated lakes and rivers.The Carp's Role in Culture and Tradition
Carp have been an integral part of many cultures and traditions, particularly in Asia and Europe. In China, Carp symbolizes good luck, abundance, and perseverance. During Chinese New Year, fish-shaped lanterns are released into the water to represent the wish for a prosperous new year. In Japan, Carp is known as Koi and is seen as a symbol of strength and determination. In Europe, Carp is a traditional Christmas dish, and many European countries hold Carp fishing competitions during the holiday season.The Challenges Faced by Carp
Although Carp are adaptable and resilient, they face many challenges in the wild. One of the most significant threats to Carp populations is overfishing. Carp is a popular food source in many cultures, and their large size and abundance make them an easy target for fishermen. In some regions, Carp are considered an invasive species, and efforts are being made to control their numbers to protect native fish species.The Benefits of Carp Farming
While Carp populations in the wild may be declining, Carp farming has seen a significant increase in recent years. Carp farming not only provides a sustainable source of food but also has several other benefits. Carp are efficient converters of feed, meaning they require less food compared to other farmed fish species. They also have a high growth rate, making them an economically viable option for fish farmers. Additionally, Carp farming does not require the use of antibiotics or chemicals, making it an environmentally friendly option.Carp and Natural Language Processing
Carp may seem like a simple and ordinary freshwater fish, but they possess unique features that have fascinated humans for centuries. Their resilience, adaptability, and distinct coloration make them an intriguing subject for Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on understanding and processing human language. Studying the language used to describe Carp's characteristics can provide valuable insights into how humans perceive and communicate about this species.Conclusion
In conclusion, Carp may not be the most glamorous or well-known fish, but they are a crucial part of freshwater ecosystems and human culture. Their resilience, adaptability, and unique coloration have allowed them to thrive in a wide range of environments. As we continue to explore and research these fascinating creatures, we can gain a better understanding of their role in the natural world and appreciate the beauty and complexity of this omnivorous fish.
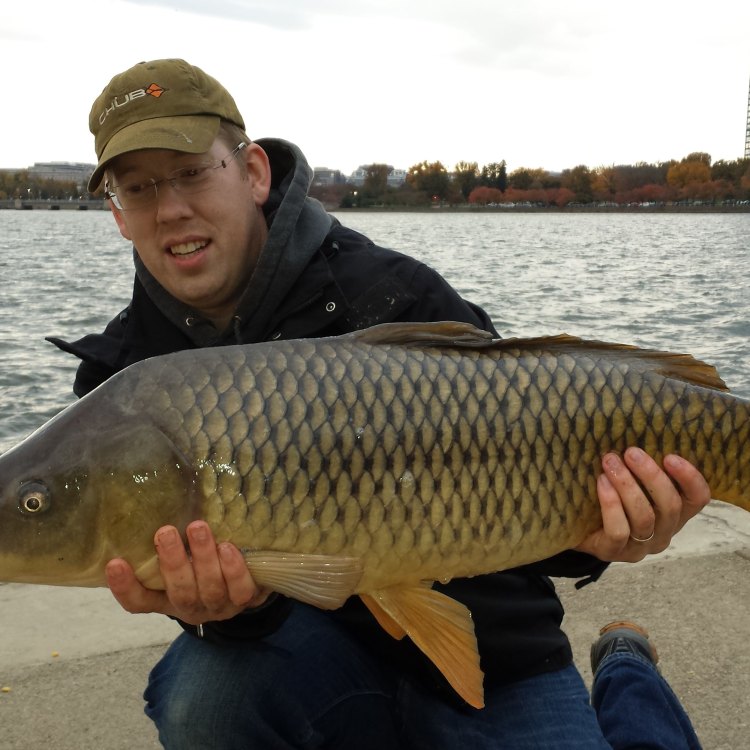

Carp
Animal Details Carp - Scientific Name: Cyprinus carpio
- Category: Animals C
- Scientific Name: Cyprinus carpio
- Common Name: Carp
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Cypriniformes
- Family: Cyprinidae
- Habitat: Freshwater
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Eurasia
- Country of Origin: China
- Location: Ponds, lakes, rivers
- Animal Coloration: Green, brown, golden
- Body Shape: Torpedo-shaped
- Length: 40 - 80 cm

Carp
- Adult Size: Up to 120 cm
- Average Lifespan: 20 - 30 years
- Reproduction: Egg-laying
- Reproductive Behavior: Spawning in groups
- Sound or Call: No sound
- Migration Pattern: None
- Social Groups: Schools
- Behavior: Bottom feeders, active during day
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Can disturb sediment, affect water quality
- Human Use: Aquaculture, sport fishing
- Distinctive Features: Barbels, large scales
- Interesting Facts: Carp are one of the oldest fish species domesticated by humans, Carp have been introduced to various parts of the world as an invasive species
- Predator: Humans, birds, larger fish

Cyprinus carpio
The Fascinating World of Carp: An Ancient Fish Species with Unique Characteristics and Global Impact
Carp, or Cyprinus carpio, is a type of freshwater fish that has been around for millions of years. It is one of the oldest species of fish to be domesticated by humans and has a significant impact on the ecosystems it inhabits. With their distinctive features, interesting reproductive behavior, and various human uses, carp has become a fascinating subject of study for scientists and a popular species for anglers.In this article, we will dive into the world of carp, exploring its size, lifespan, reproductive behavior, social groups, distinctive features, and impact on the ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com. We will also take a look at the various human uses of carp and the threats it faces in today's world.
A Species Like No Other: Size, Lifespan, and Reproductive Behavior
Carp are large freshwater fish, with adults reaching up to 120 cm in length and weighing up to 45 kg. Their average lifespan is between 20 to 30 years, making them a long-lived species compared to other freshwater fish.One of the most interesting aspects of carp is their reproductive behavior. Carp are egg-laying fish, and their reproductive behavior is known as spawning in groups. During the spawning season, which usually occurs in the spring, male carp develop tubercles on their head and gills, which are used to stimulate the female during courtship. Females can lay up to a million eggs at a time, which is a vital factor in the success of the species.
Carp are also known for their distinctive lack of sound or calls. Unlike other fish species, carp do not produce any vocalizations, making them a rather silent species Caribou. This is due to their lack of vocal cords, a unique characteristic that sets them apart from other aquatic creatures.
Social Behavior and Habitat
Carp are typically found in groups known as schools, which can consist of hundreds of individuals. These social groups are essential for the species' survival because they provide protection from predators and aid in finding food.When it comes to behavior, carp are bottom feeders, meaning they feed on the bottom of the waterbed. They are also active during the day, with their feeding patterns being most active at dawn and dusk. Carp use their strong sense of smell and touch to forage for food, primarily consisting of insects, crustaceans, and plant matter.
Carp can be found in a variety of habitats, from shallow, slow-moving water bodies to deep, fast-flowing rivers. They prefer clear waters with soft bottoms, and they are most commonly found in temperate regions of North America, Europe, and Asia.
Distinctive Features: Barbels and Large Scales
Carp are easily identifiable by their distinctive features. They have two long barbels, or sensory organs, protruding from the corners of their mouth, giving them a catfish-like appearance. These barbels help them locate food on the bottom of the waterbed and are a useful evolutionary adaptation for survival.Another notable feature of carp is their large scales. They have a tough, armored skin covered in large scales that provide protection from predators. These scales also help carp regulate their body temperature, maintaining a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment.
The Global Impact of Carp: Invasive Species and Ecosystem Disturbance
In modern times, carp has had a significant impact on ecosystems worldwide. Due to their hardy nature and large reproductive capabilities, carp have been introduced to various parts of the world as an invasive species. This has caused problems for native fish populations and other aquatic species, as carp tend to outcompete them for resources.Moreover, carp's bottom-feeding behavior can disturb sediment, affecting water quality and causing harm to other aquatic species. In some ecosystems, the increase in carp populations has led to a decrease in native plant and invertebrate populations, resulting in significant ecological imbalances.
Human Uses: Aquaculture and Sport Fishing
Despite the negative impact of carp on some ecosystems, they also have a long history of human exploitation. Carp were one of the first fish species to be domesticated by humans, with evidence dating back to ancient China as early as 5000 BC. Today, carp is still a popular fish for human consumption, and it is considered a delicacy in many parts of the world.In addition to being raised in aquaculture for food, carp is also a popular sport fish. They are known for their strength and resilience, making them a challenging catch for anglers. This has led to the creation of carp fishing tournaments and increasing tourism in areas where carp fishing is popular.
Threats to Carp: Habitat Loss, Overfishing, and Pollution
Despite their adaptability and resilience, carp face several threats in their natural habitats. The most significant threat is habitat loss, as many water bodies and rivers have been destroyed or polluted due to human activities. This results in a loss of suitable habitat for carp and can also lead to a decrease in their food sources.Overfishing is another major threat to carp populations. Due to their popularity as a food source and sport fish, carp have been heavily exploited, resulting in a decline in their populations in some regions.
Pollution is also a significant threat to carp, as they are sensitive to changes in water quality. Pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemical pollutants can cause harm to carp populations and affect their reproductive success.
Conservation Status
Despite the many threats to their survival, carp is currently listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. This is due to their widespread distribution and adaptability to various habitats.However, several organizations and agencies are working towards conserving carp populations and their habitats. Efforts such as habitat restoration, regulation of fishing practices, and awareness campaigns about the negative impact of releasing carp into natural water bodies are crucial in maintaining the balance of carp populations and their ecosystems.
The Future for Carp: A Species Worth Protecting
Carp may not be as well-known or beloved as other fish species such as salmon or trout, but they play a crucial role in ecosystems and have a fascinating history of coexistence with humans. As we continue to face challenges such as habitat loss and pollution, it is essential to recognize the importance of preserving and protecting carp populations.Despite their resilience and adaptability, carp still require our active efforts towards conservation. By promoting sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution levels, and protecting their habitats, we can ensure that future generations will continue to enjoy the fascinating and unique world of carp.

The Mighty Carp: An Omnivorous Fish in Freshwater
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.