Cephalaspis
Up to 60 cm (24 inches)
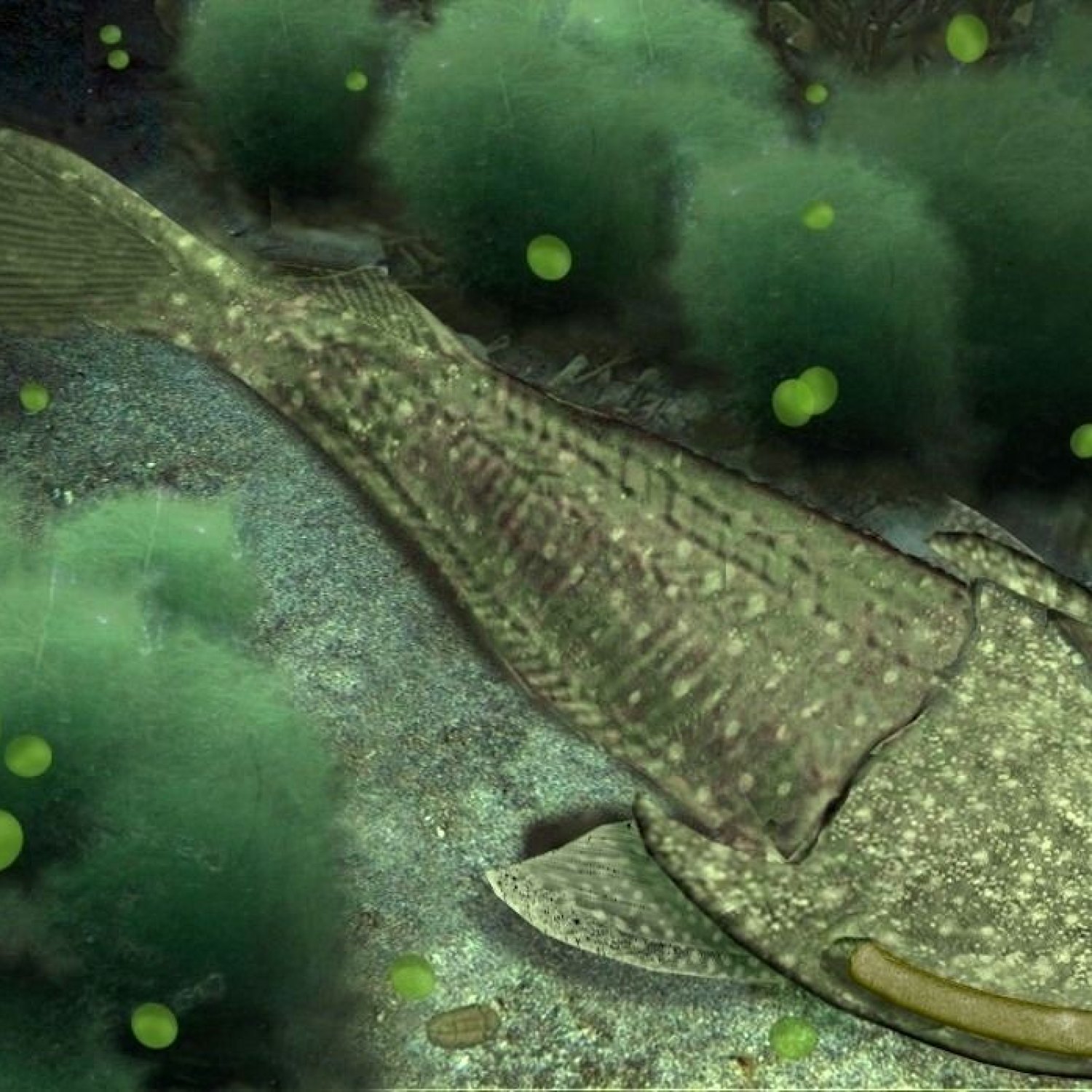
Cephalaspis, a type of primitive fish, can be found in rocks, riverbeds, and shores with its flattened body and bony plate covering its head. These creatures, belonging to the Cephalaspidae family, can grow up to 60 cm (24 inches) in length. Explore these fascinating animals and discover their evolution and role in the ecosystem. #Cephalaspis #prehistoricfish #riverbeds #sea life
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Cephalaspis
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Freshwater
The Fascinating World of Cephalaspis: A Prehistoric Fish
Deep in the rivers and shores of Europe and North America, there once swam a unique and fascinating creature - the Cephalaspis. This ancient fish, whose name means "head shield," was well-adapted to its freshwater habitat and had a distinctive appearance that set it apart from other fish of its time.Introduction to Cephalaspis
Cephalaspis, also known as "bony fish," is a prehistoric fish that roamed the waters during the Devonian period, approximately 400 million years ago. While its scientific and common names may be the same, this fish had many distinctive features that made it stand out in the aquatic world Cephalaspis.Taking a Closer Look at Cephalaspis
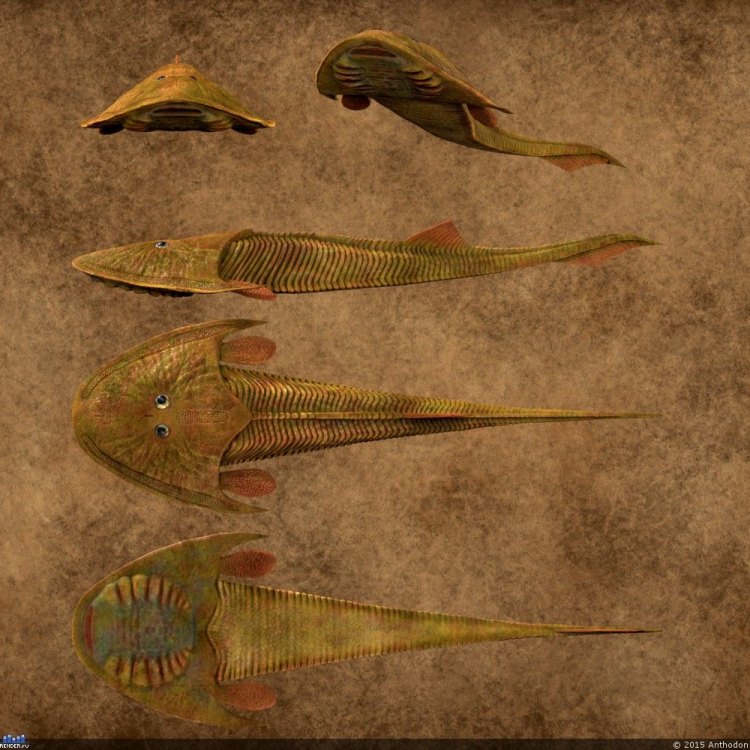
Cephalaspis belongs to the Animalia kingdom and Chordata phylum, making it an animal with a spinal cord. It is part of the Placodermi class, a group of armored fish that were one of the first vertebrates to evolve jaws.The fish's order is Cephalaspidiformes, and it belongs to the Cephalaspidae family. The name of this family is derived from the Greek words "kephale," meaning head, and "aspis," meaning shield, perfectly describing the unique feature of Cephalaspis.
These fish lived in freshwater habitats, preferring to dwell in calm and shallow waters. They were carnivorous, preying on smaller fish and invertebrates, using their sharp teeth to catch their meals.
Cephalaspis had a wide geographical distribution, with fossils found in various locations in Europe and North America. However, the country of origin of this fish is believed to be the United Kingdom.
Appearance of Cephalaspis
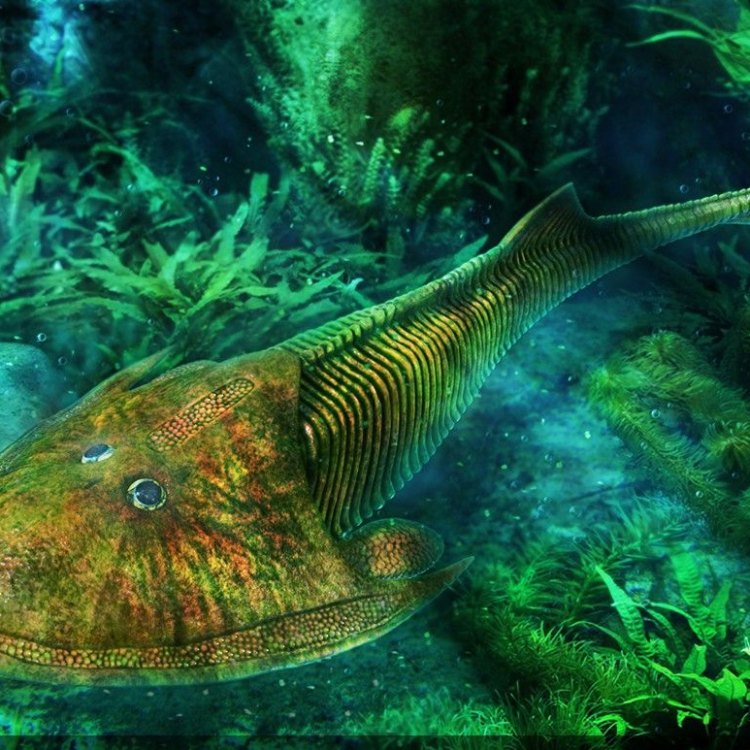
One of the most distinctive features of Cephalaspis was its mottled brown or olive drab coloration, making it blend in with its surroundings Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. This coloration served as a form of camouflage, helping it to avoid predators and sneak up on prey.But the most striking aspect of this fish's appearance was its flattened body, covered by a bony plate that extended over its head like a shield. This plate served as a form of armor, protecting the fish from predators and providing support for its large head.
The head of Cephalaspis was relatively large, with two well-developed eyes on either side. This placement of its eyes suggests that this fish had good eyesight and was probably an active predator.
Cephalaspis also had a unique body shape, with its head and body tapering towards its tail. It had fins on either side of its body, which it used for locomotion and balance.
Size and Habitat of Cephalaspis
Cephalaspis was a medium-sized fish, with some species reaching up to 60 cm (24 inches) in length. This fish was well-adapted to its freshwater habitat, using its flattened body and fins to navigate through shallow waters.They could be found in a variety of freshwater habitats, including streams, lakes, and rivers. Cephalaspis preferred to live in areas with plenty of rocks, riverbeds, and shores, which provided them with shelter and food sources.
The Legacy of Cephalaspis
Despite being extinct for millions of years, Cephalaspis has left a lasting impact on the world of science. Fossils of this fascinating fish have been found in various locations, providing scientists with valuable insights into the evolution of vertebrates.One of the most significant contributions of Cephalaspis is the fact that it was one of the earliest vertebrates to evolve jaws. This adaptation allowed them to become apex predators, paving the way for the evolution of more complex and diverse fish.
Conclusion
The story of Cephalaspis is one that is shrouded in mystery and wonder. This prehistoric fish, with its unique armor and sharp teeth, roamed the waters during a time when life on Earth was still evolving. Its legacy lives on, providing us with a glimpse into the ancient world and the incredible creatures that once inhabited it.
Cephalaspis
Animal Details Cephalaspis - Scientific Name: Cephalaspis
- Category: Animals C
- Scientific Name: Cephalaspis
- Common Name: Cephalaspis
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Placodermi
- Order: Cephalaspidiformes
- Family: Cephalaspidae
- Habitat: Freshwater
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, North America
- Country of Origin: United Kingdom
- Location: Rocks, riverbeds, and shores
- Animal Coloration: Mottled brown or olive drab
- Body Shape: Flattened body with a bony plate covering the head
- Length: Up to 60 cm (24 inches)

Cephalaspis
- Adult Size: unknown
- Average Lifespan: unknown
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: unknown
- Sound or Call: unknown
- Migration Pattern: unknown
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: active during the day
- Threats: unknown
- Conservation Status: Extinct
- Impact on Ecosystem: unknown
- Human Use: unknown
- Distinctive Features: Bony head covering with two large eyes
- Interesting Facts: One of the earliest known jawed vertebrates
- Predator: unknown

Cephalaspis
The Mysterious Cephalaspis: Exploring the Early Days of Jawed Vertebrates
The world beneath our oceans is full of countless mysteries waiting to be unraveled. In the depths of prehistoric waters, there once swam a strange and unique creature known as Cephalaspis. Its name, derived from the Greek words for "head" and "shield," aptly describes its most distinctive feature – a bony head covering with outstretched ridges and two large eyes. This ancient creature is one of the earliest known jawed vertebrates, evolving before most of the diverse aquatic species we see today PeaceOfAnimals.Com. Let's dive into the enigmatic world of Cephalaspis and discover the secrets of this intriguing fish.Uncovering the Basics of Cephalaspis
The Cephalaspis lived during the Late Devonian Period, over 360 million years ago. With an adult size still unknown, scientists can't pinpoint its exact physique, but it is believed to have a flattened body with a rounded head, similar to a stingray. Its flattened shape likely allowed it to blend in with its surroundings, making it a stealthy predator or a camouflaged prey.Unfortunately, due to the lack of preserved fossils, we have limited information about the average lifespan and reproductive behavior of Cephalaspis. However, as a sexual species, it is likely that they reproduced through spawning, where males fertilize the eggs externally in the water. As for their reproductive behavior, little is known, but scientists speculate that they may have been solitary creatures, coming together only to mate.
Another aspect of Cephalaspis's behavior that remains a mystery is its sound or call. It is possible that they made some sort of sound, either to communicate with each other or as a means of echolocation, but without any evidence, we can only speculate Carpet Python.
Living the Solitary Life
Cephalaspis is believed to have been solitary creatures, meaning they lived and hunted alone. This behavior would have made them self-sufficient and less in need of social bonds. However, as with most aquatic species, their larval stage may have involved living and traveling in groups before breaking off into individual adults.One characteristic that sets Cephalaspis apart is its diurnal behavior, meaning it was most active during the day. This is in contrast to most prehistoric fish that were nocturnal, possibly due to their need for camouflage. But as a daytime hunter, the Cephalaspis would have needed keen eyesight to spot prey and avoid being preyed upon itself.
Elusive Threats and Extinction
The natural predator of Cephalaspis remains unknown, but it's likely that they fell victim to larger aquatic predators of the time, such as the notorious Dunkleosteus. With its strong and sharp jaws, it would have been able to easily crack open the bony head covering of the Cephalaspis, making it an easy meal.Unfortunately, the exact cause of Cephalaspis's extinction is also a mystery. Like many other prehistoric species, it is believed that a combination of factors such as environmental changes, competition for resources, and the appearance of new predators, all contributed to their decline. Despite their elusive demise, one thing is clear – the Cephalaspis is no longer a part of our ecosystem, and we are left to wonder about its impact on the environment.
A Creature of Many Surprises
One of the most interesting facts about Cephalaspis is their unique place in the evolutionary history of jawed vertebrates. Along with its close relative, the Pteraspis, it is believed to be one of the earliest fish to possess a jaw, a characteristic that played a crucial role in the diversification and success of future aquatic species. Without the jawed vertebrates, we may not have the diverse sea creatures we see today.Additionally, scientists have found evidence of Cephalaspis living in both freshwater and saltwater environments, showing their adaptability and resilience. This fact, coupled with their bony head covering, also suggests that they may have been able to migrate from one habitat to another, unlike other prehistoric fish that were confined to either freshwater or saltwater.
Lost to the Depths of History
Sadly, the Cephalaspis is now extinct, and we can only study their existence through the fossils and remains left behind. But, as with all things lost to time, there is still so much we can learn from this mysterious creature. Their unique features and behavior provide a glimpse into the early days of jawed vertebrates and how they adapted and evolved over time.While we may never fully understand the life of the Cephalaspis, we can admire its fascinating features and imagine what the world was like during its time. As we continue to explore the depths of our oceans, who knows what other mysteries and wonders we will uncover. But for now, the Cephalaspis remains a mysterious and intriguing part of our past.

The Fascinating World of Cephalaspis: A Prehistoric Fish
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












