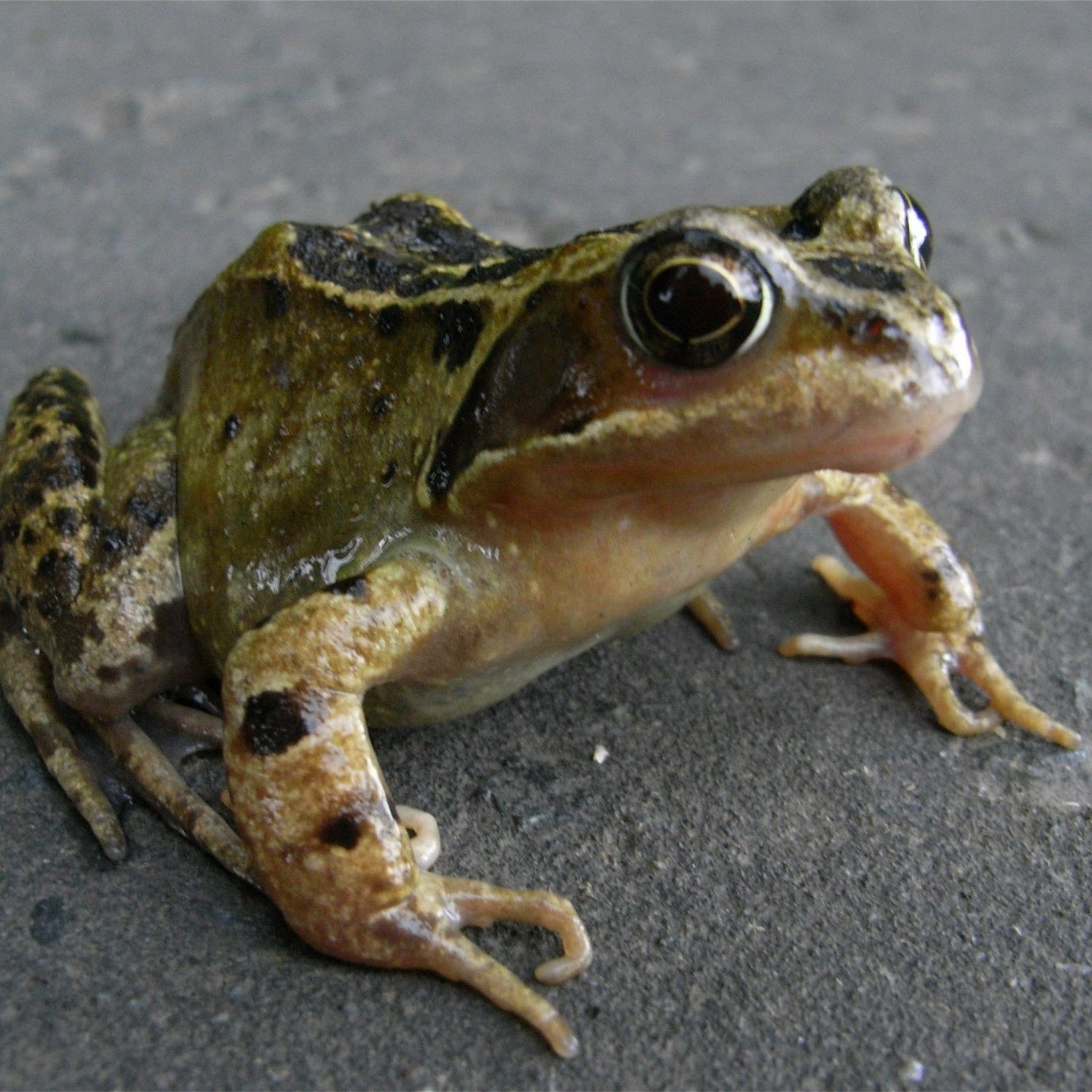
Common Frog
6 to 9 centimeters
The Common Frog, also known as Rana temporaria, is a small and slender amphibian that can be found in various countries in Europe and Asia. With a length of 6 to 9 centimeters, it has a distinctive smooth skin and long hind legs, making it an excellent jumper. Belonging to the Ranidae family, these cute creatures are a common sight in ponds and wetlands, and are an important indicator of a healthy ecosystem.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Common Frog
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Ponds, lakes, marshes, and wetland areas
Discover the Fascinating World of the Common Frog
The animal kingdom is full of creatures large and small, each with their unique characteristics that captivate the imagination. From the fierce and mighty lion to the colorful and graceful butterfly, animals have captured our attention throughout history. One of the most fascinating creatures that often goes unnoticed is the common frog, scientifically known as Rana temporaria.While we may dismiss frogs as ordinary creatures, glossing over them as we skip rocks in ponds or flip through nature channels on TV, they are remarkable animals that have an interesting story to tell Common Frog. In this article, we will dive into the world of the common frog, learning about its habitat, behavior, and unique characteristics.
Meet the Common Frog - A Member of the Amphibian Family
As the name suggests, the common frog is, indeed, a very common animal that can be found in various locations worldwide. It belongs to the kingdom Animalia, the phylum Chordata, and the class Amphibia. It is a part of the order Anura, which includes all frogs and toads. The common frog is a member of the family Ranidae, which includes other pond-dwelling frogs such as the bullfrog and green frog.One of the essential characteristics that distinguish amphibians from other animals is their ability to live both on land and in water. This means that the common frog can be found in a variety of habitats, making its home in ponds, lakes, marshes, and wetlands in Europe, Asia, and parts of North Africa. It is fascinating to note that the natural distribution of this species is constantly changing as human activities, such as habitat destruction, affect their populations.
A Carnivorous Lifestyle
Like most frogs, the common frog is a carnivorous creature, which means it feeds on other animals Cecropia Moth. They are known to prey on small insects, spiders, worms, and even small fish or tadpoles. Their feeding method involves using their long sticky tongue to catch their prey in a swift motion. Their diet is critical to maintaining the balance of the ecosystems they inhabit, as frogs are both predator and prey.Interestingly, the common frog has a unique way of catching its prey. It uses its eyes to detect movement and then extends its sticky tongue at a rapid speed to catch its meal. However, their hunting method is not always successful, which means frogs have to rely on their camouflage to hide from predators.
The Colors and Shapes of the Common Frog
Often, when we think of frogs, we envision them as green or brown creatures with dark spots or markings. While this is true for some common frogs, their coloration can vary widely, depending on their habitat and geography. This variation in coloration allows them to blend in with their surroundings, making them difficult to spot for predators.In terms of their body shape, common frogs have a slender body with smooth skin, which is vital for their survival. The smooth skin helps them to absorb oxygen and moisture, allowing them to breathe and stay hydrated even when they are out of the water. Additionally, their long hind legs are an essential feature for their locomotion, allowing them to jump and swim with ease.
A Size That Can Surprise
The common frog may seem like a small and insignificant creature, but its size can surprise you. On average, they measure between 6 to 9 centimeters in length, with females being slightly larger than males. However, in some cases, the common frog can grow up to 11 centimeters in length. Their small stature makes them vulnerable to predators, which is why their ability to camouflage and jump great distances is critical for their survival.The Importance of the Common Frog in Our Ecosystem
Frogs are often considered to be a vital part of our ecosystem, and for a good reason. They play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the food chain, both as predators and prey. As carnivorous creatures, they help control insect populations, and as prey animals, they are a source of food for larger predators. Additionally, frogs serve as indicators of environmental health, and their presence or absence can signal potential issues in their habitats.Furthermore, common frogs also contribute to nutrient cycling in their habitats. As they feed on smaller animals, their excretion releases nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus into the ecosystem, which helps maintain soil quality and supports plant growth.
The Threats Facing the Common Frog
Despite their adaptability and resilience, common frogs face several threats in their natural habitats. One of the most significant challenges is habitat destruction and fragmentation due to human activities. As wetlands and natural water sources are destroyed for development, the common frog loses its home and breeding grounds, impacting their populations.Moreover, pollution, such as chemicals and pesticides, can also harm frogs, as they absorb these substances through their permeable skin. It can lead to health issues and decrease their ability to reproduce, causing population declines.
Lastly, the introduction of non-native species and diseases can be detrimental to common frogs. Non-native predators, such as fish, can prey on tadpoles and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem. In some cases, diseases spread by non-native species can also affect the health of local frog populations.
Conservation Efforts for the Common Frog
To protect the common frog and its habitat, conservation organizations, and researchers are working tirelessly to understand its ecology and behavior. Through research and monitoring, they can track frog populations and identify potential threats early on.Furthermore, efforts are being made to preserve wetland habitats and restore degraded areas to provide suitable breeding grounds for frogs. Education and awareness programs are also crucial in educating the public about the importance of frogs and their conservation.
Conclusion
The common frog may seem like an ordinary creature, but it plays a vital role in our ecosystem. Its ability to adapt to changing environments and the important ecological functions it performs make it an essential animal to protect. By learning more about the common frog, we can appreciate these remarkable creatures and take steps to ensure their survival for generations to come.
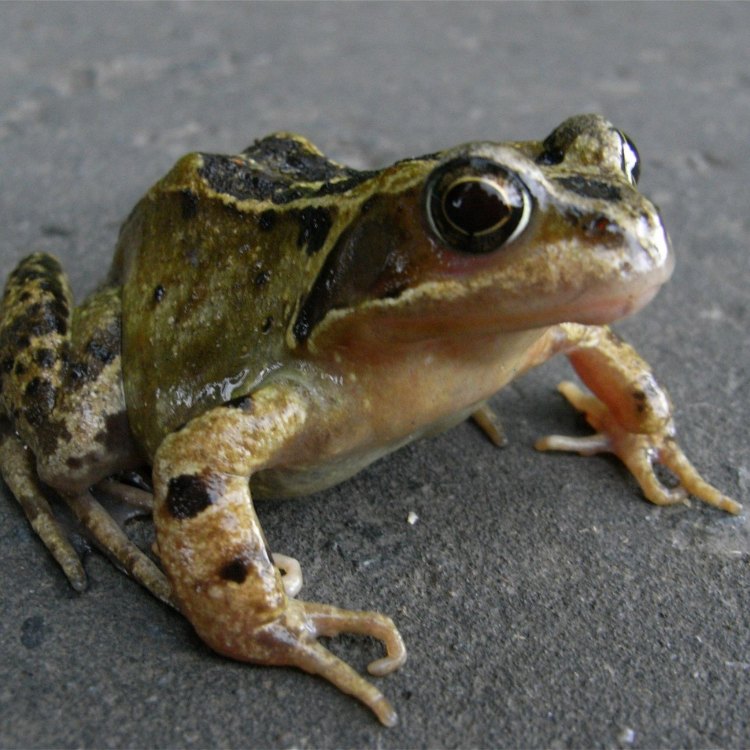

Common Frog
Animal Details Common Frog - Scientific Name: Rana temporaria
- Category: Animals C
- Scientific Name: Rana temporaria
- Common Name: Common Frog
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Amphibia
- Order: Anura
- Family: Ranidae
- Habitat: Ponds, lakes, marshes, and wetland areas
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, Asia, and parts of North Africa
- Country of Origin: Varies depending on the specific population
- Location: Various countries in Europe and Asia
- Animal Coloration: Variable, usually green or brown with dark spots or markings
- Body Shape: Slender body with smooth skin and long hind legs
- Length: 6 to 9 centimeters

Common Frog
- Adult Size: 6 to 9 centimeters
- Average Lifespan: 4 to 10 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males attract females with vocalizations and perform courtship rituals
- Sound or Call: Males produce a distinctive croaking sound during breeding season
- Migration Pattern: Some populations migrate to breeding sites
- Social Groups: Solitary, but aggregate at breeding sites
- Behavior: Mostly nocturnal, spends majority of time in water
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, disease, and predation
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important predator of insects and other small invertebrates
- Human Use: Occasionally kept as pets, used for scientific research
- Distinctive Features: Webbed feet, bulging eyes, and visible eardrums (tympanum)
- Interesting Facts: Can change color to match their surroundings, hibernate during winter
- Predator: Birds, reptiles, mammals, and larger amphibians
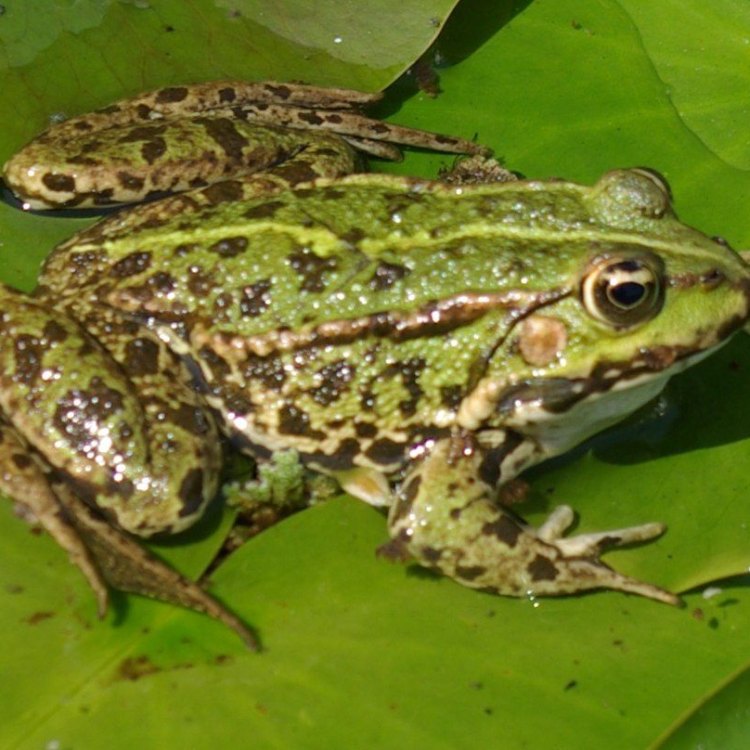

Rana temporaria
The Intriguing World of the Common Frog: A Closer Look at its Life, Behavior, and Impact
Amphibians are often underrated and overlooked creatures, but they play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems. Among these amphibians is the Common Frog, also known as the European Common Frog or the European Common Brown Frog. These humble creatures may seem simple and unremarkable at first glance, but they hold within them a world of fascinating traits and behaviors. Let's take a closer look at the Common Frog and explore its life, behavior, and impact on the environment PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Average Size and Lifespan
The Common Frog, scientifically known as Rana temporaria, is a relatively small amphibian, measuring between 6 to 9 centimeters in length. This size may vary depending on the environmental conditions and the availability of food, but it is an average size for most adult Common Frogs. As for their lifespan, these creatures can live anywhere between 4 to 10 years, making them a long-living species compared to other amphibians.Reproduction and Reproductive Behavior
Like most frogs, the Common Frog's reproductive cycle involves mating and laying eggs. These frogs are sexual, meaning they require a male and a female to reproduce. During mating season, which typically occurs between March and September, male frogs produce a distinctive croaking sound to attract females. These vocalizations can be heard from a considerable distance and are used to establish mating territories.Once a male has attracted a female, they engage in courtship rituals, which involve the male clinging onto the female's back until she lays her eggs in a water body. Male frogs are known for their diligence in protecting the eggs and tadpoles from harm, and they will even carry tadpoles on their backs to keep them safe Central Ranges Taipan.
The Role of Sound in Breeding
The Common Frog's vocalizations are an essential aspect of their reproductive behavior and are used to attract females and communicate with other males. This unique croaking sound is produced by the male frog blowing air through its vocal sacs, resulting in a distinct and often loud call. These vocalizations are also used to establish dominance and maintain territories during mating season.Migration Patterns and Social Groups
While most Common Frogs are solitary creatures, they do come together in large numbers during the breeding season. This communal behavior is necessary for successful mating, as it increases their chances of finding a suitable mate. Some populations of Common Frogs also migrate to breeding sites, which are often specific ponds or bodies of water, to lay their eggs.Nocturnal Behavior and Habitat
The Common Frog is mostly nocturnal, meaning they are active during the night and rest during the day. This behavior is attributed to their sensitive skin, which is prone to drying out in the sun. These frogs spend the majority of their time in or near water bodies, as their skin requires a moist environment to breathe and stay hydrated. They are excellent swimmers and can stay underwater for long periods, using their webbed feet to propel themselves through the water.Threats to the Common Frog and Conservation Status
Like many other animal species, the Common Frog faces various threats to its survival. Habitat loss, pollution, disease, and predation are the main factors responsible for the declining population of these creatures. Habitat loss occurs due to urbanization and the draining of wetlands, which are important breeding sites for Common Frogs. Pollution also affects these creatures, as chemicals and contaminants in water bodies can harm or kill them. In addition, diseases such as chytrid fungus pose a significant threat to amphibians, including the Common Frog.Despite these challenges, the Common Frog is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List, meaning it is not currently facing any major threats to extinction. However, continued efforts are needed to monitor and protect their populations, especially in areas where their numbers are declining.
The Impact of Common Frogs on the Ecosystem
Despite their small size, Common Frogs play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems. As important predators of insects and other small invertebrates, they help control their populations, preventing them from becoming overpopulated and damaging the environment. In addition, their tadpoles play a significant role in nutrient cycling in water bodies, helping to maintain their health and cleanliness.Human Use and Interesting Facts
Common Frogs are occasionally kept as pets, but they are not a popular choice due to their nocturnal and aquatic nature. However, they are often used for scientific research, as their sensitive skin and reproductive cycle make them a useful species for studying the impact of pollution and other environmental factors on amphibians.One of the most fascinating things about Common Frogs is their ability to change color to match their surroundings. This trait, known as camouflage, helps them blend in and avoid detection by predators. In addition, these frogs hibernate during the winter months, burying themselves in the mud at the bottom of ponds and bodies of water to survive the cold temperatures.
Natural Predators of the Common Frog
Unfortunately, the Common Frog's small size and vulnerable nature make them prey to various animals, including birds, reptiles, mammals, and larger amphibians. Birds, such as herons and hawks, are known to feed on these frogs. Reptiles, such as snakes and lizards, also hunt them, along with mammals like foxes and badgers. Even larger amphibians, such as water snakes and newts, pose a threat to the Common Frog.In conclusion, the Common Frog is an intriguing creature with a unique life cycle, reproductive behavior, and role in the ecosystem. Despite facing challenges, it continues to thrive in many parts of Europe and is a vital part of our natural world. By learning more about these fascinating creatures, we can appreciate and protect them, ensuring their survival for years to come.
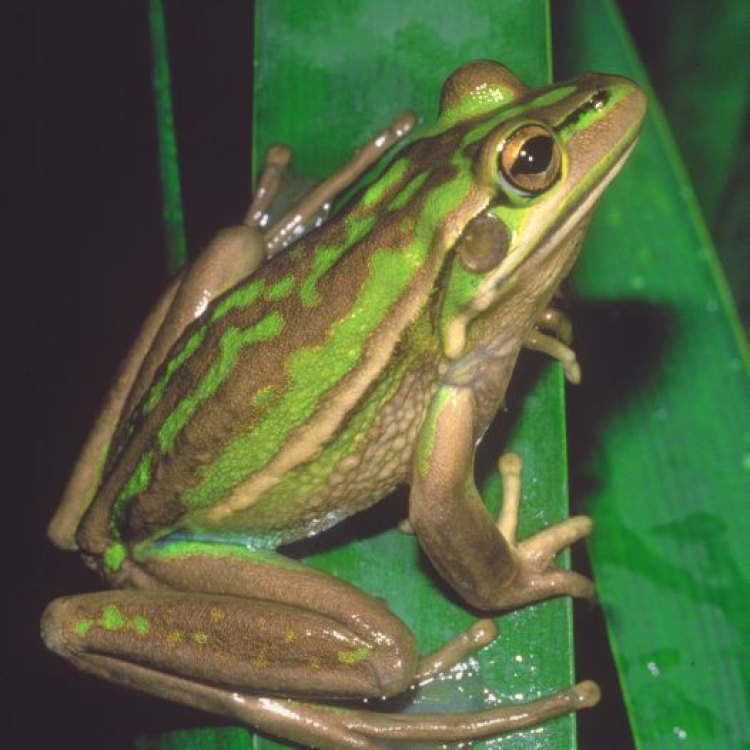

Discover the Fascinating World of the Common Frog
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.