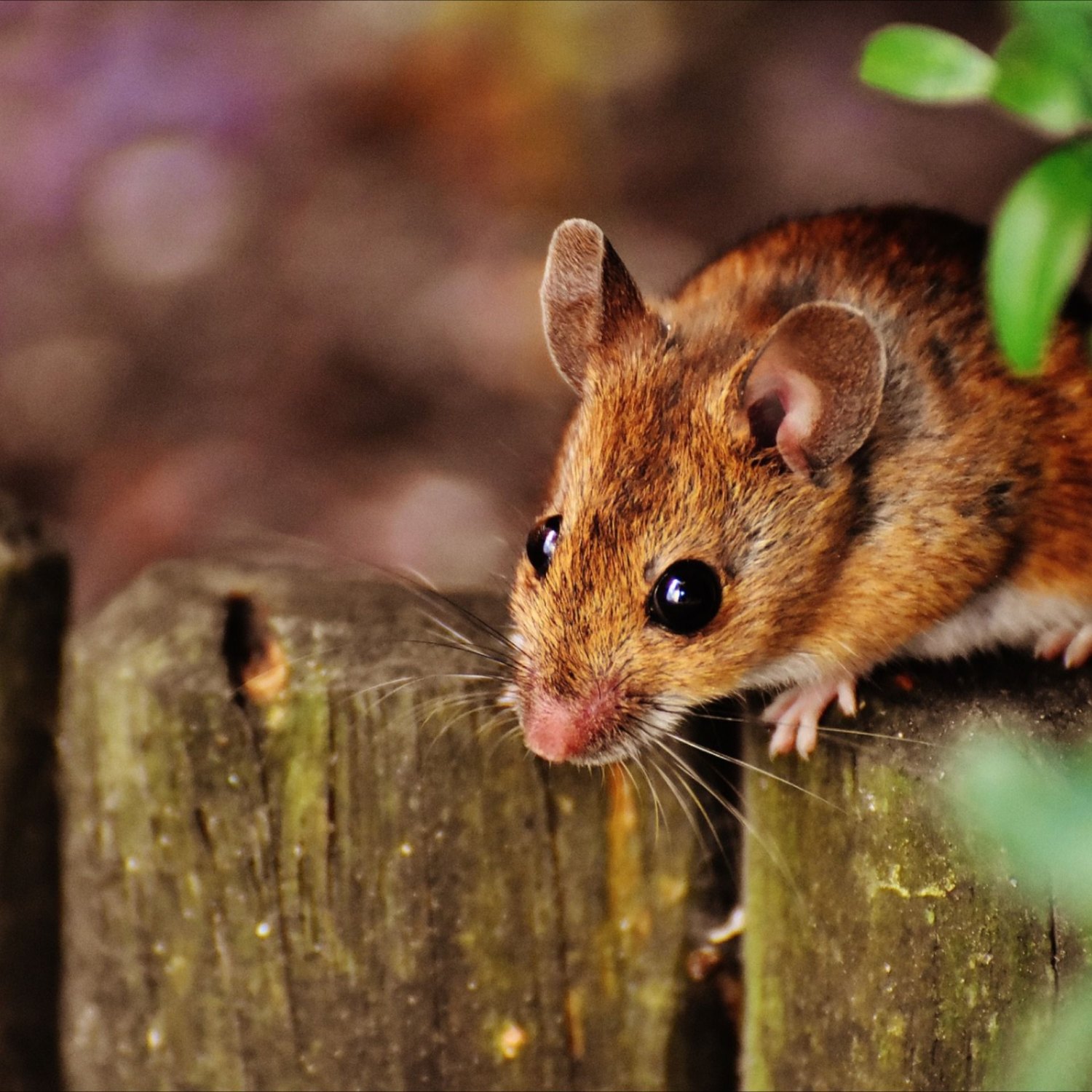
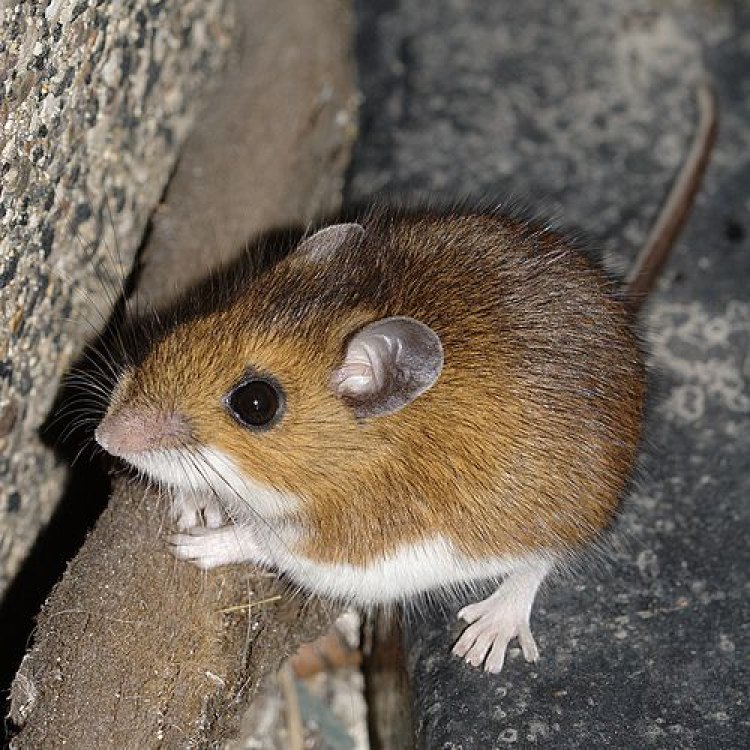
Deer Mouse
3.25 to 4 inches (8 to 10 cm)
The Deer Mouse, a small and slender member of the Cricetidae family, can be found throughout North America. Measuring 3.25 to 4 inches long, this tiny creature is known for its sharp senses and swift movements. #DeerMouse #NorthAmerica #Wildlife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Deer Mouse
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Forests, grasslands, deserts
The Fascinating World of the Deer Mouse: A Closer Look at Peromyscus maniculatus
The natural world is full of unique and fascinating creatures, each with their own special characteristics. From the deserts to the forests, we can find a wide variety of animals that have adapted to their environment in different ways. One such animal is the deer mouse, also known as Peromyscus maniculatus.These small rodents have captured the curiosity and interest of many due to their distinctive appearance and behavior Deer Mouse. In this article, we will take a closer look at the deer mouse, exploring its scientific and common name, kingdom, habitat, feeding method, geographical distribution, and other fascinating features that make it a very special animal.
The Origins of the Deer Mouse
The deer mouse's scientific name, Peromyscus maniculatus, may sound complicated, but it actually gives us some valuable information about this animal. "Peromyscus" comes from the Greek words "peri," meaning "around" and "mys," meaning "mouse." This refers to the round shape of the mouse's head. The second part, "maniculatus," means "with small hands," which is a reference to the mouse's small paws.The deer mouse is also commonly known as the deer mouse, a name given due to its grayish-brown or reddish-brown coloration, which resembles that of a deer. This combination of scientific and common names gives us a glimpse into the unique physical characteristics of this creature.
The Deer Mouse's Place in the Animal Kingdom
The deer mouse belongs to the Animalia kingdom, which means it is a multicellular eukaryote. This also means that it is part of the Chordata phylum, which includes all animals with a spinal cord Dachsador. Deer mice are classified as mammals, specifically under the order Rodentia, which includes more than 2,200 species of rodents.Within the Rodentia order, deer mice belong to the Cricetidae family, which includes over 600 species of rodents. This family is divided into two subfamilies, the Neotominae, and the Arvicolinae. The deer mouse belongs to the Neotominae subfamily, making it closely related to other species of mice, such as the North American wood mouse and the white-footed mouse.
The Deer Mouse's Habitat and Adaptations
Deer mice are found throughout North America, from Alaska to Labrador, and from Central America to Mexico. They are highly adaptable animals and can thrive in various environments, from forests and grasslands to deserts. Their wide range of habitat is a testament to their resilience and ability to survive in diverse conditions.One of the reasons for their success in different environments is their unique physical characteristics. Deer mice have small, slender bodies, with a length of 3.25 to 4 inches and a weight of 0.5 to 1 ounce. This compact size allows them to move quickly and efficiently, which is crucial for their survival in the wild.
The deer mouse's fur is another adaptation that helps it thrive in different habitats. Its grayish-brown or reddish-brown coloration allows it to blend in with its surroundings, providing camouflage and protection from predators. This ability to blend in is also aided by the mouse's small ears, which are not easily noticeable.
The Omnivorous Diet of the Deer Mouse
Deer mice are classified as omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and animals. Their diet primarily consists of seeds, nuts, insects, fruits, and small invertebrates. They are also known to eat other rodents at times, such as baby mice and voles. Their wide variety of food sources makes them resilient to changes in their environment, allowing them to adapt to different food availability in different seasons.Deer mice are known to store food in their burrows during the fall, allowing them to survive the winter when food is scarce. This behavior also helps them stay hidden from predators while feeding, minimizing their risk of being caught.
The Geographical Distribution of the Deer Mouse
As mentioned earlier, the deer mouse is found throughout North America, making it one of the most widely distributed mammals on the continent. They can be found in almost every U.S. state, except for Hawaii, and are also prevalent in Canada and Mexico.One of the reasons for their wide distribution is their ability to thrive in various habitats, as mentioned earlier. Additionally, deer mice reproduce quickly, with females giving birth to litters of four to six pups multiple times a year. This allows them to quickly expand their population and colonize new areas.
Interesting Facts About the Deer Mouse
- Deer mice are nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active at night.- They have excellent hearing and can easily detect predators, such as owls and snakes.
- Deer mice are known for their jumping ability, which helps them escape predators quickly.
- These rodents are also known for their curious and explorative nature, often venturing into new areas in search of food.
- Deer mice are relatively long-lived for rodents, with a lifespan of two to three years in the wild and up to five years in captivity.
In Conclusion
In summary, the deer mouse, also known as Peromyscus maniculatus, is a small and fascinating creature with a lot of unique features. From its wide distribution and adaptability to its omnivorous diet and physical characteristics, the deer mouse is a testament to the diversity and resilience of nature.As we continue to explore and learn about the natural world, we should appreciate and protect these incredible animals and their habitats. Every creature, big or small, plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystem, and the deer mouse is no exception. So, the next time you spot a tiny rodent scurrying past, remember to take a moment to appreciate the incredible creature that it is.
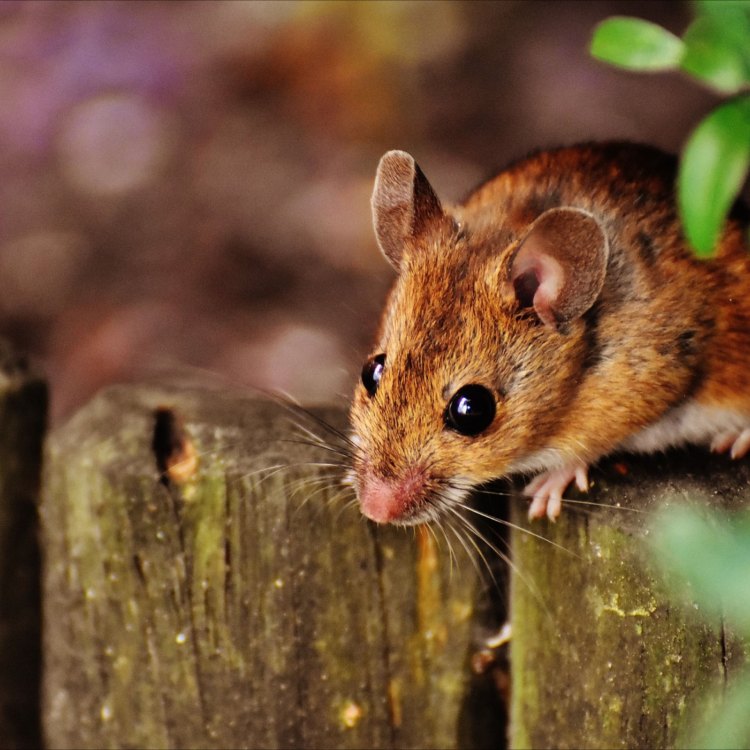

Deer Mouse
Animal Details Deer Mouse - Scientific Name: Peromyscus maniculatus
- Category: Animals D
- Scientific Name: Peromyscus maniculatus
- Common Name: Deer Mouse
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Rodentia
- Family: Cricetidae
- Habitat: Forests, grasslands, deserts
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Country of Origin: United States and Canada
- Location: Throughout North America
- Animal Coloration: Grayish-brown or reddish-brown
- Body Shape: Small and slender
- Length: 3.25 to 4 inches (8 to 10 cm)

Deer Mouse
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 1 to 2 years in the wild
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Polygamous
- Sound or Call: Soft vocalizations, including chirps and squeaks
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary or small family groups
- Behavior: Nocturnal and agile climbers
- Threats: Predators, habitat loss, and climate change
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important prey species
- Human Use: Research in genetics and behavior
- Distinctive Features: Large eyes and long tail
- Interesting Facts: Excellent jumper and can leap up to 8 feet
- Predator: Owls, foxes, snakes, and cats

Peromyscus maniculatus
The Fascinating World of Deer Mice: Small but Mighty Creatures
When we think of small animals, we often underestimate their importance and unique characteristics. One such creature is the deer mouse, a small and unassuming rodent that roams the wild parts of North America. While they may seem like just another tiny mammal, deer mice boast several distinctive features and behaviors that set them apart from other animals. In this article, we will take a closer look at these fascinating creatures and explore their world in detail PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Size and Lifespan
As their name suggests, deer mice are small rodents, with an average adult size of only 2-3 inches long and weighing between 0.6-1.1 ounces. Despite their diminutive size, these mice pack a powerful punch and are known for their ability to leap up to 8 feet in a single bound, thanks to their strong hind legs. This incredible jumping ability is just one of the distinctive features that make deer mice stand out from other mammals.
In the wild, deer mice have an average lifespan of 1 to 2 years. However, some may live up to 4 years in captivity, provided they have a healthy and safe environment. Like many other small mammals, they have a high reproductive rate, which helps maintain their population despite their short lifespan.
Reproduction and Behavior
Deer mice are sexual reproducers, with males and females engaging in courtship behavior before mating Dingo. What’s interesting is that deer mice are polygamous, meaning that males may mate with multiple females during a breeding season. This reproductive behavior is one way in which deer mice increase their chances of offspring survival.
While deer mice are small, they are mighty nocturnal creatures, and this is where their agile climbing skills come into play. They are skilled climbers, able to scale trees, shrubs, and even walls with ease. This behavior allows them to escape predators and search for food, as they are primarily active at night.
Sound and Migration Patterns
Deer mice are not particularly vocal animals, but they do make soft vocalizations, including chirps and squeaks. These vocalizations are an important form of communication within their species, and are used to warn other mice of potential danger, as well as to attract potential mates. However, these calls are often too faint for humans to hear.
In terms of migration, deer mice are non-migratory animals, meaning that they do not cover long distances in search of food or shelter. They are typically solitary animals, but can also live in small family groups, consisting of a male, female, and their offspring. These groups usually do not wander too far from their home range.
Threats and Conservation Status
Like many other small mammals, deer mice face various threats in their natural habitats. Their small size and nocturnal behavior make them vulnerable to predators such as owls, foxes, snakes, and cats. In addition, habitat loss due to human activities and climate change poses a significant threat to their survival.
Despite these challenges, deer mice are currently listed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that their population is stable, and they do not face any immediate threat of extinction. However, conservation efforts are still necessary to monitor and protect their habitats from further damage.
Impact on Ecosystem
While deer mice may not garner as much attention as other charismatic wildlife, they play a crucial role in their ecosystems. As omnivores, they have a diverse diet consisting of seeds, insects, fruits, and small vertebrates. This makes them an important prey species, providing food for various predators and helping maintain the balance within their ecosystems.
In addition, deer mice have also been used in research studies due to their unique genetics and behavior. Scientists have studied their ability to resist the effects of high levels of radiation, which can provide insights into human health issues such as cancer. As small mammals, deer mice are a valuable resource for scientists, contributing to our understanding of the natural world.
Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts
Apart from their excellent jumping and climbing abilities, deer mice have some other distinctive features that make them stand out. They have large eyes and long tails, which helps them navigate their surroundings and maintain balance while climbing.
Despite their small size, deer mice are excellent jumpers and can leap up to 8 feet in a single bound. This is comparable to a human jumping over a two-story building! In addition, they are adept at digging tunnels and constructing elaborate burrows to serve as their homes.
The World of Deer Mice: Awe-Inspiring and Mighty Creatures
In conclusion, the world of deer mice is full of wonder and fascination, with their unique features and behaviors setting them apart from other small mammals. From their reproductive and social behavior to their climbing and jumping abilities, these little creatures are truly mighty and important in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. As humans, it is our responsibility to appreciate and protect these animals, ensuring that their populations continue to thrive in the wild.

The Fascinating World of the Deer Mouse: A Closer Look at Peromyscus maniculatus
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.