Duck
20-28 inches (50-71 cm)
Ducks, members of the Anatidae family, are compact and streamlined birds found in various habitats around the world. With a length of 20-28 inches, these animals are often seen paddling in ponds, lakes, and rivers. Their unique body shape, along with their webbed feet, make them excellent swimmers and divers. Keep an eye out for these adorable creatures on your next nature walk!
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Duck
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers
The Fascinating World of Ducks: Mysteriously Elegant Birds
When we think of ducks, we often envision them gliding gracefully on a pond, quacking softly and searching for food. These mysteriously elegant birds have captured our hearts for centuries, with their vibrant colors, streamlined bodies, and unique behaviors. But what do we really know about these creatures beyond their cute appearance and quacking calls? Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of ducks and discover what makes them one of the most beloved and intriguing birds on the planet.A Quick Introduction: Scientific Name and Classification
Ducks fall under the scientific name Anas platyrhynchos, which means "flat-billed duck" in Greek Duck. They belong to the animal kingdom, phylum Chordata and class Aves, making them closely related to other birds such as chickens and penguins. Ducks belong to the order Anseriformes, which also includes swans and geese. Within this order, ducks are placed in the family Anatidae, which means "waterfowl" in Greek. Within this family, there are over 120 species of ducks, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors.The Special Habitat of Ducks
When we think of ducks, we often imagine them in ponds or lakes, but these birds are quite versatile in their choice of habitat. Ducks can be found in various locations, including wetlands, ponds, lakes, and rivers. They are also found in different regions across the globe, making them a widespread and diverse species. Interestingly, ducks do not have a specific country of origin, as they are found in various habitats in different parts of the world.Omnivorous Creatures with Unique Feeding Methods
Ducks are known to be omnivorous creatures, meaning they feed on both plants and animals Dragonfly. Their diet typically consists of insects, small fish, crustaceans, seeds, and vegetation. The way ducks obtain food is entirely fascinating and unique. They have a specialized bill that allows them to filter food from water, mud, or soil. This bill is lined with small, comb-like structures that help them to sift through food particles while retaining water. This allows them to effectively and efficiently feed on a wide range of food sources.The Vibrant Colors and Patterns of Ducks
Ducks may seem plain in appearance, with their shades of brown, gray, and white, but they are actually quite vibrant and eye-catching. Most species of ducks exhibit sexual dimorphism, meaning males and females have different physical characteristics. Male ducks, also known as drakes, are usually more colorful than females, with vibrant iridescent feathers and striking patterns. This is because male ducks use their appearance to attract females during the breeding season. Female ducks, on the other hand, have more subtle colors, which help them to blend in with their surroundings and protect their young.The Compact and Streamlined Body Shape of Ducks
One of the most distinctive physical features of ducks is their compact and streamlined body shape. This shape is ideal for swimming and diving, as ducks spend a majority of their time in and around water. Their body shape is designed for speed and agility in the water, making them perfectly adapted to their aquatic habitats. Additionally, their webbed feet and waterproof feathers also contribute to their exceptional swimming abilities.The Surprising Length of Ducks
Ducks come in a variety of sizes, with some species being much larger than others. On average, ducks can measure anywhere from 20 to 28 inches (50-71 cm) in length. However, the largest species of duck, the Australian Wood Duck, can measure up to 30 inches (76 cm) in length. On the other hand, the smallest species of duck, the Baikal Teal, only measures around 14 inches (35 cm).The Fascinating Behaviors of Ducks
Apart from their physical characteristics, ducks are also known for their unique behaviors. For example, ducks are social animals and often form strong bondings with their partners. They are highly vocal creatures, with males using a range of calls to attract females and warn off potential predators. They also have a unique way of courtship, where males perform elaborate displays to impress females. Once a pair has bonded, they will stay together for the breeding season, and sometimes even for life.The Impact of Ducks on the Ecosystem
Ducks may seem like simple birds, but they play a crucial role in the ecosystem. As omnivores, they help to regulate the population of invertebrates and small aquatic creatures, thus maintaining a balanced food chain. Moreover, they also play a significant role in seed dispersal, as they consume seeds and distribute them through their droppings. They also help to control the growth of aquatic plants, preventing them from overgrowing and causing imbalances in their habitat.The Threats Facing Ducks
Despite being widespread and adaptable, ducks face several threats to their survival. One of the biggest threats is habitat loss, as wetlands and other habitats they rely on are being destroyed for human development. This loss of habitat also affects their food sources, making it difficult for ducks to find enough food to survive. Additionally, pollution, hunting, and the introduction of non-native species also pose a risk to the survival of ducks.The Conservation Efforts in Place
To protect ducks and their habitats, there are several conservation efforts in place. These include the restoration and protection of wetlands, banning hunting in certain areas, and captive breeding programs to increase the population of endangered species. Moreover, initiatives to reduce pollution and raise awareness about the importance of ducks in the ecosystem are also being implemented. These efforts are vital in ensuring the survival of ducks and preserving their diverse and fascinating species.The Fascinating World of Ducks: A Conclusion
In conclusion, ducks are remarkable creatures that have captured our imagination for centuries. Not only are they beautiful and graceful, but they also play a vital role in the ecosystem. With their versatile habitats, unique feeding methods, and vibrant colors, ducks are a true wonder of nature. However, it is our responsibility to ensure their survival by protecting their habitats and understanding their importance in the ecosystem. So next time you see a duck quacking on a pond, take a moment to appreciate the fascinating and mysterious world that these birds inhabit.

Duck
Animal Details Duck - Scientific Name: Anas platyrhynchos
- Category: Animals D
- Scientific Name: Anas platyrhynchos
- Common Name: Duck
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Anseriformes
- Family: Anatidae
- Habitat: Wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: No specific country of origin
- Location: Various habitats in different countries
- Animal Coloration: Variable, usually in shades of brown, gray, and white
- Body Shape: Compact and streamlined
- Length: 20-28 inches (50-71 cm)

Duck
- Adult Size: Medium-sized
- Average Lifespan: 2-12 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Monogamous
- Sound or Call: Quack
- Migration Pattern: Some species migrate, while others are non-migratory
- Social Groups: Often form flocks
- Behavior: Ducks are known for their swimming and diving abilities
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, hunting
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important for seed dispersal and nutrient cycling in aquatic ecosystems
- Human Use: Hunting, farming, pets
- Distinctive Features: Webbed feet, waterproof feathers, bill adapted for filtering food
- Interesting Facts: Ducks are excellent swimmers and divers. They have the ability to fly long distances and are highly adaptable to different habitats.
- Predator: Various predators depending on the region, including foxes, raccoons, and birds of prey
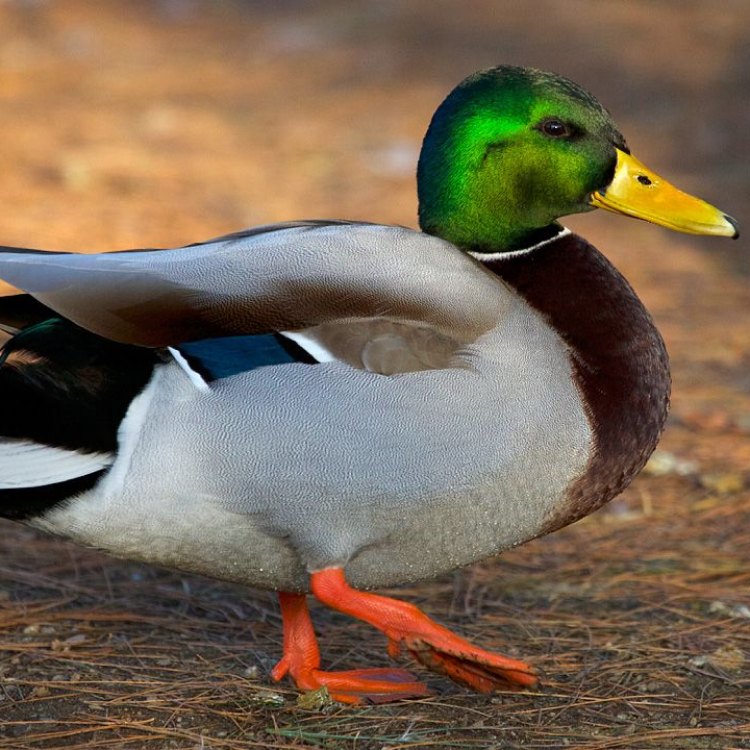

Anas platyrhynchos
The Unique and Fascinating World of Ducks
When we think of ducks, we may picture the iconic Donald Duck or the beautiful and graceful mallards in a park pond. But there is so much more to these feathered creatures than meets the eye. Ducks are a diverse and complex species that have captivated humans for centuries with their intriguing behaviors and distinctive features. In this article, we will explore the world of ducks, from their reproductive behavior to their impact on the ecosystem, and why they are more than just cute and quacking waterfowl PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Adult Size: Medium-Sized
The first thing that comes to mind when thinking of ducks is their size - not too big, not too small. Ducks are considered medium-sized birds, typically ranging from 20-30 inches in length and weighing anywhere from 1-8 pounds. Their size makes them perfect for a variety of environments, from wetlands to grasslands, and even urban areas. Their adaptability and versatility have allowed them to thrive in different habitats around the world.
Average Lifespan: 2-12 Years
The average lifespan of a duck varies depending on the species, with some living only 2 years in the wild and others living up to 12 years in captivity. Factors such as predators, disease, and availability of food and water can all impact the lifespan of a duck. However, the average lifespan for most duck species is around 5-6 years.
Reproduction: Sexual
Like most birds, ducks reproduce sexually through fertilization of eggs. Male ducks, also known as drakes, will compete with each other for the attention of female ducks, also known as hens Dalmatian. Once a female has chosen her mate, they will typically form a monogamous pair for the breeding season. However, some male ducks may mate with multiple females, depending on the availability of resources.
Reproductive Behavior: Monogamous
As mentioned, ducks are known for exhibiting monogamous behavior during the breeding season. They will typically mate with one partner and raise their offspring together. However, this monogamous behavior is not always consistent, and some species may engage in polygamous behavior, having multiple mates at once.
Sound or Call: Quack
The classic "quack" is the most recognizable sound associated with ducks. However, not all ducks make the same sound. Some species have raspy cackles, while others have high-pitched whistles. The "quack" is primarily a female call used to communicate with her offspring, while the male calls tend to be deeper and more varied.
Migration Pattern: Some Species Migrate, While Others Are Non-Migratory
Ducks are known for their migratory patterns, with some species traveling long distances in search of food and suitable breeding grounds. However, not all ducks migrate. Some species, such as the mallard, stay in their breeding grounds year-round, while others, like the teals and shovelers, migrate to different areas seasonally.
Social Groups: Often Form Flocks
Ducks are highly social animals and are often seen in flocks, especially during migration. Flocking helps them defend against predators, find food, and stay warm during colder months. Some species, such as the bufflehead, may form flocks of hundreds or even thousands of individuals during migration. However, during breeding season, ducks tend to be more solitary, only forming small social groups with their mate and offspring.
Behavior: Swimming and Diving Abilities
One of the most distinctive features of ducks is their excellent swimming and diving abilities. Their webbed feet and waterproof feathers enable them to glide effortlessly through water, propelling themselves with powerful paddling movements. They can stay underwater for several minutes, diving up to 40 feet in search of food. These abilities also make them highly efficient at foraging, allowing them to survive and thrive in aquatic environments.
Threats: Habitat Loss, Pollution, Hunting
Like many other species, ducks also face threats to their survival. The primary threat to ducks is habitat loss due to human activities such as land development and pollution. Wetlands, in particular, are crucial habitats for ducks, providing food and shelter. However, with the increase of urbanization and industrialization, these vital areas are rapidly disappearing. Additionally, pollution from chemicals and plastics can harm ducks and their habitat.
Hunting is another significant threat to duck populations. While hunting regulations and conservation efforts have helped in recent years, many duck species are still hunted for sport, food, or commercial purposes. To ensure the conservation and protection of ducks, it is essential to have sustainable hunting practices and proper management of hunting areas.
Conservation Status: Least Concern
Despite the various threats that ducks face, the majority of species are considered of least concern for conservation. This means that their populations are relatively stable, and they are not at significant risk of extinction. However, some species, such as the Laysan duck and the Madagascar teal, are considered vulnerable due to their small and declining populations. With proper conservation efforts and management, we can ensure that ducks continue to thrive and contribute to the ecosystem.
Impact on Ecosystem: Important for Seed Dispersal and Nutrient Cycling in Aquatic Ecosystems
Ducks play a vital role in the ecosystem, especially in wetland habitats. They are considered excellent seed dispersers, with seeds passing through their digestive system and being excreted in different locations, helping to ensure plant diversity and growth. Additionally, ducks contribute to nutrient cycling in aquatic ecosystems by consuming small organisms and releasing waste that enriches the soil and water.
Human Use: Hunting, Farming, Pets
Ducks have been utilized by humans for thousands of years for various purposes. Hunting, farming, and keeping them as pets are just some of the ways that humans have utilized ducks. Their meat and eggs are a staple in many diets, and their feathers are used for insulation and decorations. However, it is essential to ensure ethical and sustainable practices when it comes to using ducks for human purposes.
Distinctive Features: Webbed Feet, Waterproof Feathers, Bill Adapted for Filtering Food
Ducks have many unique physical features that make them stand out in the bird world. Their webbed feet, which can vary in shape and size depending on the species, help them to move efficiently through water. Their waterproof feathers have a natural oil coating that repels water, keeping them dry and warm. And their bill, which varies in shape and size depending on the species' diet, is adapted for filtering food from water and the ground.
Interesting Facts: Highly Adaptable and Excellent Swimmers and Divers
There are over 120 different species of ducks, each with its unique characteristics and behaviors. One interesting fact about ducks is their adaptability. They can thrive in a variety of environments, including freshwater, marine, and even urban areas. Additionally, ducks are excellent swimmers and divers, with some species, such as the canvasback, capable of diving up to 6 minutes and reaching depths of 30 feet.
Predator: Various Predators Depending on the Region, Including Foxes, Raccoons, and Birds of Prey
Ducks may seem like a peaceful and harmless species, but they do have their share of predators. Depending on the region, the predators of ducks can vary. In North America, they may face threats from foxes, raccoons, and birds of prey such as eagles and hawks. In Europe, their main predators include foxes, stoats, and weasels.
The Importance of Appreciating and Protecting Ducks
Ducks are more than just cute and quacking waterfowl. They are an essential part of the ecosystem and play a significant role in seed dispersal, nutrient cycling, and as indicators of environmental health. It is crucial to appreciate and protect these fascinating creatures to ensure their survival and to maintain a healthy balance in the natural world.
In conclusion, ducks are incredible creatures with unique features, behaviors, and contributions to the ecosystem. From their monogamous relationships to their impressive swimming and diving abilities, ducks continue to fascinate and amaze us. As humans, it is our responsibility to protect and conserve duck populations, ensuring that we can continue to learn from and admire these remarkable birds for generations to come.
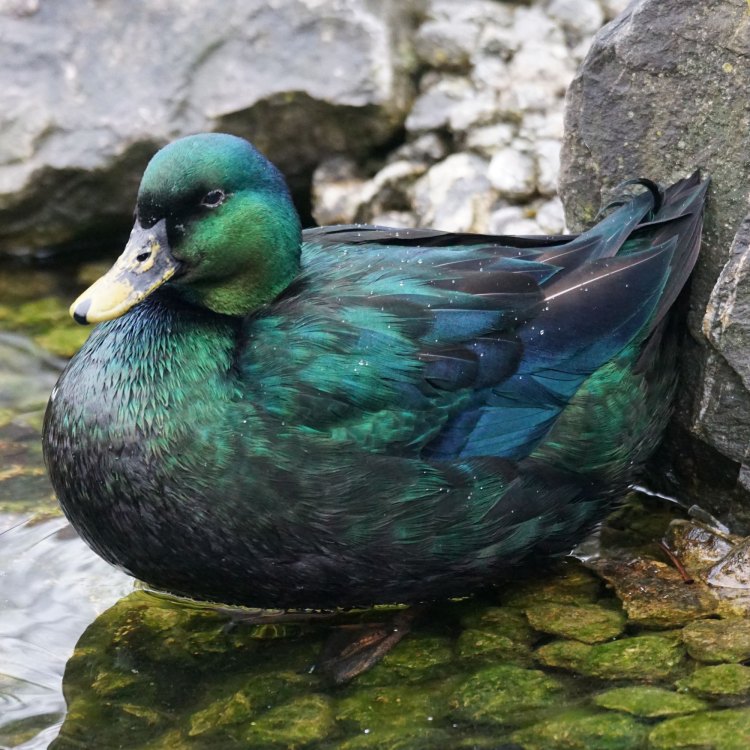

The Fascinating World of Ducks: Mysteriously Elegant Birds
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.