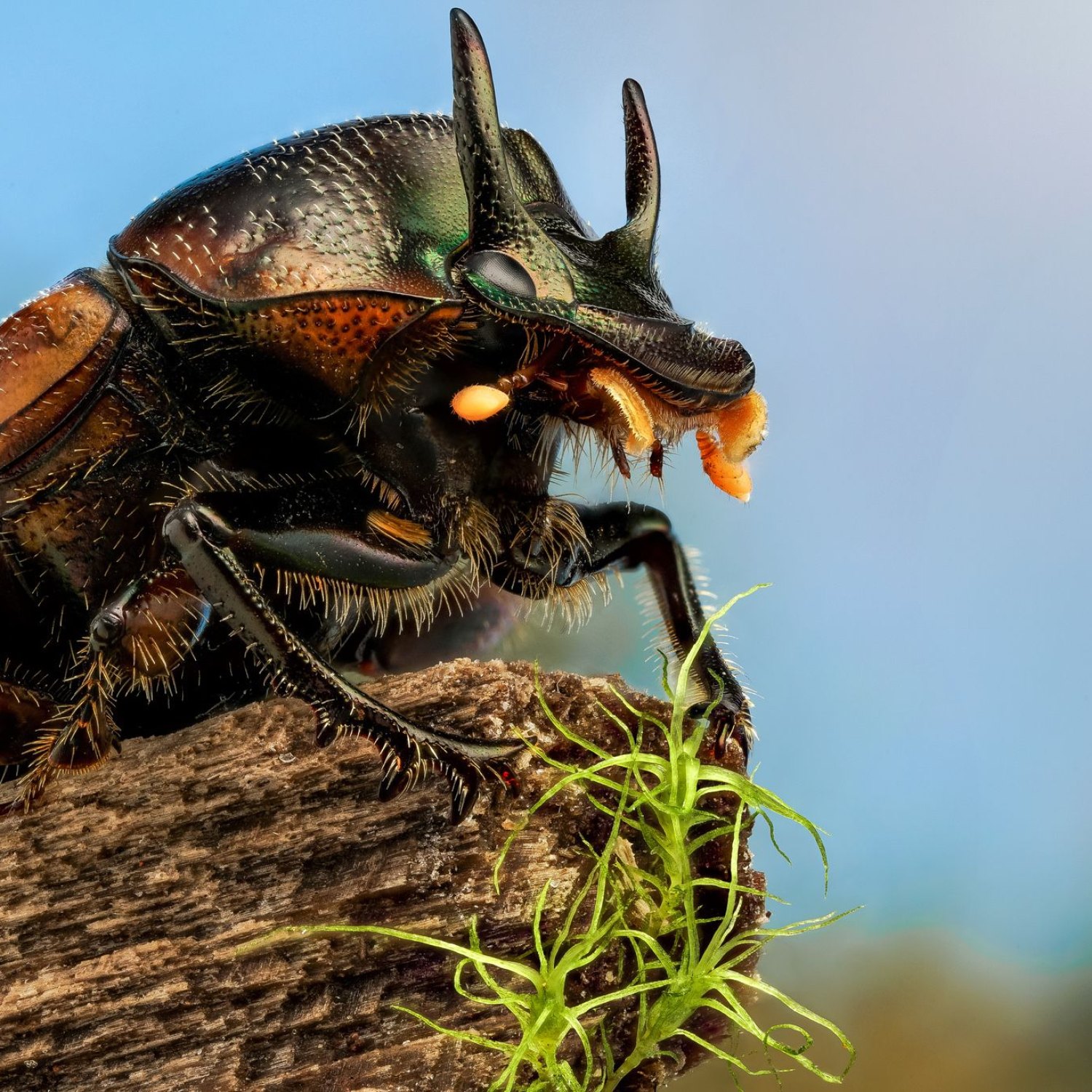
Dung Beetle
2-3 centimeters
Dung beetles, found worldwide, are a family of scarab beetles known for their incredible strength and unique body shape - dorsoventrally flattened and oval-shaped. Measuring at 2-3 cm, these hardworking insects play an important role in helping to decompose animal waste, making them vital to keeping our ecosystems clean and healthy. Despite their small size, they are essential for maintaining a balanced environment. #dungbeetles #scarabbeetles #ecosystemheroes
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Dung Beetle
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Various habitats, including grasslands, forests, and deserts
The Mighty Dung Beetle: Nature's Unsung Hero
Imagine walking through a vast savannah, with the sun shining brightly overhead, birds singing in the distance and a gentle breeze blowing through the grass. As you take in the beauty of nature, you might notice a small beetle happily rolling a ball of dung across the ground. This seemingly insignificant creature is the dung beetle, a fascinating and essential part of our ecosystem.A Classification Like No Other
While we may commonly refer to them as dung beetles, their scientific name is Coleoptera, derived from the Greek words coleos meaning sheath and pteron meaning wing Dung Beetle. This classification is due to the tough shell-like outer wings that protect their delicate inner wings and serve as a means of defense against predators.Dung beetles fall under the Animalia kingdom, making them one of the millions of species that are a part of this diverse group of organisms. They belong to the Phylum Arthropoda, which includes insects, spiders, and crustaceans, and the Class Insecta, which comprises the largest group of arthropods.
Dung beetles are further classified under the Order Coleoptera, which literally translates to 'sheathed wing', while their family name is Scarabaeidae. This family consists of more than 30,000 species worldwide, with the dung beetle being just one of them.
A Habitat for All
One of the remarkable features of dung beetles is their ability to thrive in various habitats, including grasslands, forests, and deserts. While some species may have a preference for a specific environment, many can adapt and thrive in any suitable location. However, their population density may vary depending on the abundance of dung in a particular area.Even more impressive is their ability to occupy every continent on earth, with the exception of Antarctica Dobsonfly. These tiny creatures have managed to spread and establish themselves in different countries worldwide, making them a truly global species.
Feeding Method: Nature's Recyclers
As their name suggests, dung beetles primarily feed on dung, earning them the title of 'nature's recyclers.' These tiny insects play a vital role in decomposing animal waste, ensuring that nutrients are returned to the soil. With the help of other decomposers like bacteria and fungi, dung beetles break down dung into smaller particles, allowing it to be absorbed by plants and enriching the soil.Not only do they contribute to nutrient cycling, but dung beetles also help control the population of dung-breeding insects, thus reducing the risk of disease spread. Their presence also contributes to a cleaner and healthier environment, making them an essential part of our ecosystem.
The Colors of Nature
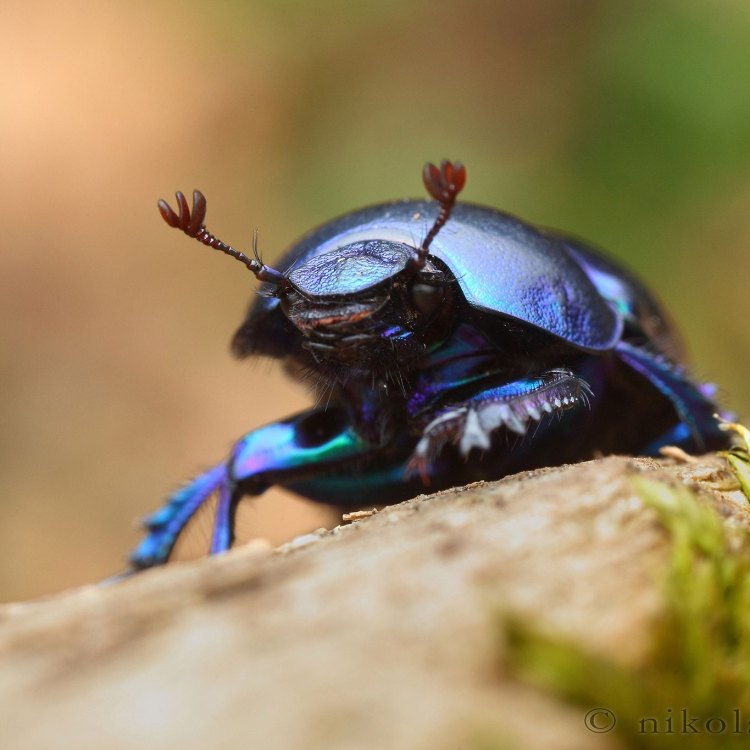
The coloration of dung beetles varies depending on the species, and they come in a range of colors from black to brown to vibrant hues. For example, the rainbow scarab (Phanaeus vindex) displays a metallic green or purple coloration, while the dance fly (Sisyphus fissiceps) has a distinctive yellow and black pattern.These colors serve several purposes, one of which is to attract mates. Male dung beetles, in particular, may display bright colors to attract females and signal their strength and health. Additionally, the colors may serve as a defense mechanism against predators by mimicking other dangerous insects. This varied coloration adds to the beauty and diversity of our natural world.
A Unique Body Shape
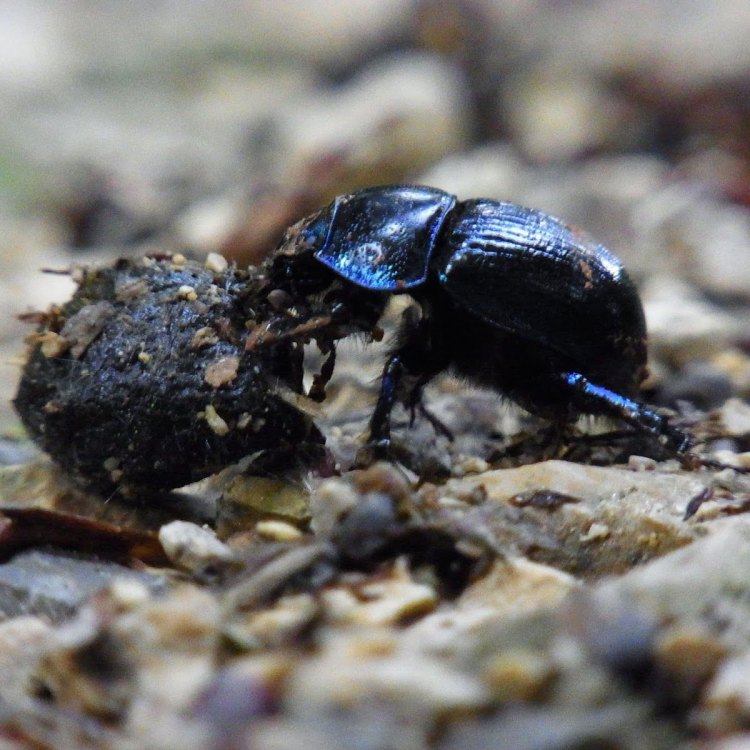
Dung beetles have a unique body shape that sets them apart from other insects. They are dorsoventrally flattened, meaning they have a flattened body from top to bottom, and oval-shaped. This body shape is well-suited for their primary activity of rolling dung balls, as it provides the necessary strength and stability for the task.Their legs are also specialized for their way of life, with the front pair being used for rolling dung, the middle pair for steering, and the hind pair for digging to bury the dung ball. This unique body structure allows them to efficiently carry out their vital role in nature.
The Mighty But Mighty Small
Despite its small size, the dung beetle is a mighty creature. On average, they measure between 2-3 centimeters in length and weigh only around 3-5 grams. However, they can carry dung balls up to ten times their own weight, which is equivalent to a human carrying a small car. This feat of strength is remarkable and showcases the incredible abilities of this tiny insect.An Essential Contributor to Our Ecosystem
It's undeniable that dung beetles are an essential part of our ecosystem. Without them, dung would pile up, causing an imbalance in nutrient cycling and even affecting the health of plants and animals. Their role in keeping our environment clean and healthy is often overlooked, but it's one that cannot be ignored.However, despite their importance, dung beetles are facing several challenges that threaten their existence.
Climate change and the fragmentation of habitats are some of the significant challenges that these insects face. As the climate changes, their habitats may become unsuitable, leading to a decline in population. The fragmentation of their habitats also has a negative impact, as it limits their movement and dispersal, making them more vulnerable to genetic isolation and eventual extinction.
Additionally, the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides can be harmful to dung beetles, as they often feed on plants and insects that may have come in contact with these chemicals. The loss of natural habitats and the use of chemicals are all threats to these fascinating creatures that play such a crucial role in our environment.
The Future of the Dung Beetle
It's crucial that we recognize the importance of dung beetles and take proactive measures to protect and preserve their habitats. Initiatives such as creating corridors that connect fragmented habitats and reducing the use of chemicals can go a long way in ensuring the survival of these vital insects.Furthermore, more research and study can shed light on the various species of dung beetles and their role in our ecosystem. This information can be used to implement effective conservation strategies and promote awareness of the importance of these tiny yet mighty creatures.
In conclusion, the humble dung beetle may not be the most visually appealing or popular creature in the animal kingdom, but its significance cannot be understated. From maintaining a healthy and balanced ecosystem to providing a unique and beautiful addition to nature's palette, these tiny insects are undoubtedly nature's unsung heroes. Let us all do our part in protecting these remarkable creatures and ensuring their continued existence for generations to come.
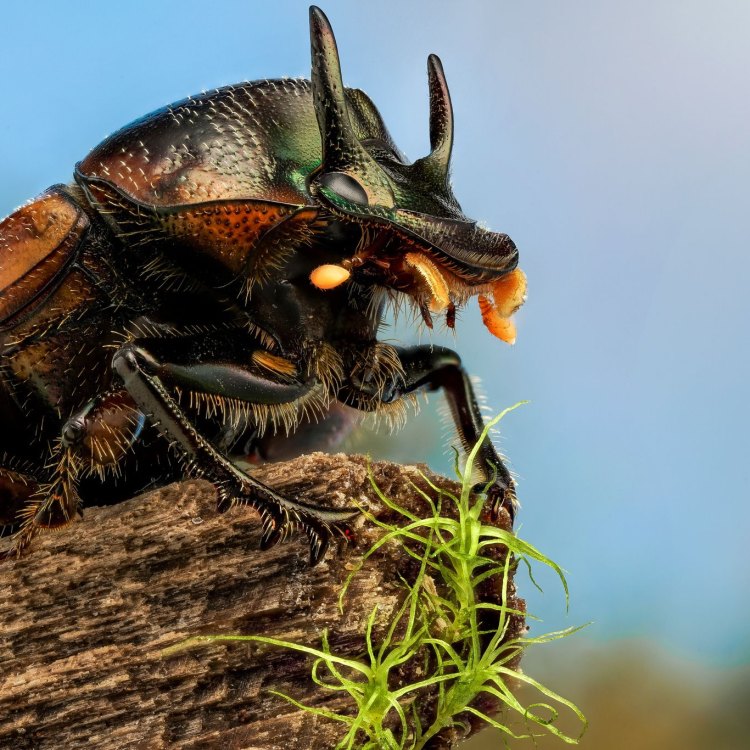

Dung Beetle
Animal Details Dung Beetle - Scientific Name: Coleoptera
- Category: Animals D
- Scientific Name: Coleoptera
- Common Name: Dung Beetle
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Family: Scarabaeidae
- Habitat: Various habitats, including grasslands, forests, and deserts
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Found on every continent except Antarctica
- Country of Origin: Unknown
- Location: Worldwide
- Animal Coloration: Varies depending on species, can be black, brown, metallic green, or vibrant colors
- Body Shape: Dorsoventrally flattened and oval-shaped
- Length: 2-3 centimeters
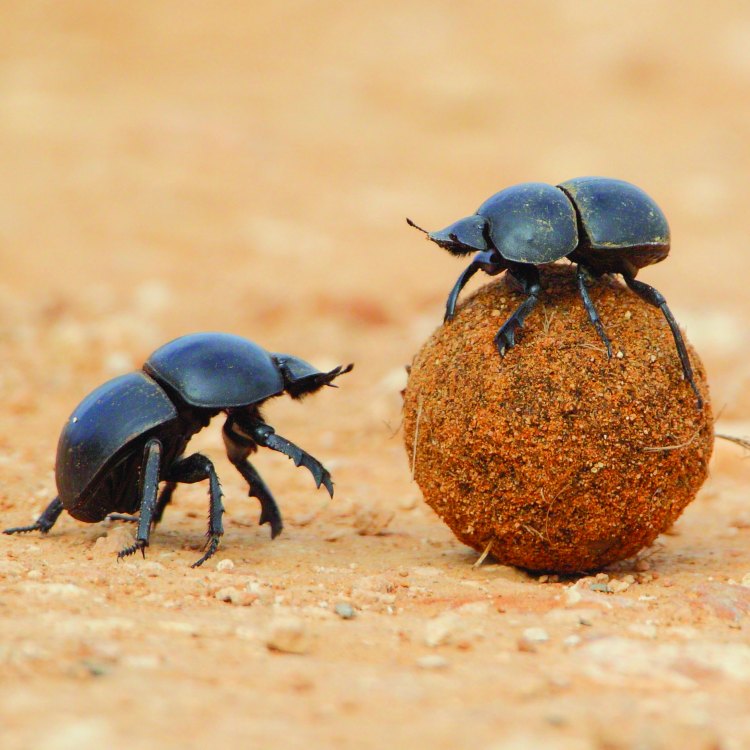

Dung Beetle
- Adult Size: Varies depending on species, can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters
- Average Lifespan: 1-3 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males create dung balls for courtship and may fight over mating opportunities with females
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: No specific migration pattern
- Social Groups: Some species live in colonies while others are solitary
- Behavior: Dung beetles are known for their habit of rolling and burying dung balls as a food source and for reproduction
- Threats: Loss of habitat, pesticide use, pollution, and climate change
- Conservation Status: Varies depending on species, some are of least concern while others are endangered
- Impact on Ecosystem: Dung beetles play a crucial role in nutrient recycling and soil fertility
- Human Use: Used in agriculture to control pest populations and improve soil quality
- Distinctive Features: Strongly developed hind legs for rolling dung, horn-like structures on their heads
- Interesting Facts: Dung beetles can navigate by using the Milky Way as a reference point
- Predator: Various predators including birds, mammals, and reptiles

Coleoptera
The Mighty Dung Beetle: Nature's Hidden Treasure
Nature is full of diverse and intriguing creatures, each with unique features and behaviors that contribute to the delicate balance of our ecosystem. One such creature, often overlooked and underestimated, is the humble dung beetle.These small but mighty insects belong to the family Scarabaeidae, which includes over 5,000 species worldwide. They can be found in almost every corner of the world, from North and South America to Africa and Asia PeaceOfAnimals.Com. Despite their small size, dung beetles play a crucial role in the ecosystem, and their distinctive characteristics are worth exploring.
Dung beetles come in a variety of sizes, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Their coloration varies, with some species sporting metallic hues of green, gold, and purple, while others are dull brown or black. They have a compact body with a hard exoskeleton, and their most striking feature is their pair of strongly developed hind legs.
These unique hind legs serve a specific purpose – rolling and burying dung balls. Yes, you read that right. Dung beetles feed on animal feces, which they collect, roll, and bury underground. This behavior has earned them their name and reputation as "nature's janitors."
So, why do these insects have such an unusual diet? Is it just a matter of convenience? The answer, surprisingly, lies in their reproductive behavior Dwarf Gourami.
Dung beetles have a sexual mode of reproduction, with males competing for mating opportunities with females. They use the process of dung-rolling and -burying as part of their courtship ritual. Males create perfectly round dung balls and roll them away, showcasing their strength to potential mates. Females then select their mates based on their ability to roll the biggest and best dung balls.
This behavior can also lead to fierce competition between males, who may engage in battles over a prized dung ball. These battles can be quite intense, with the use of their horn-like structures on their heads and strong hind legs to push and shove their way to victory.
But aside from their strange diet and reproductive habits, what else makes dung beetles unique? Well, unlike many other animals, dung beetles do not produce any sound or calls. So, if you happen to stumble upon a dung beetle in the wild, you are likely to hear nothing but silence.
Furthermore, dung beetles do not follow a specific migration pattern. While some may live in colonies, especially in tropical regions, others are solitary creatures. They can be found in a wide range of habitats, from farmland and grasslands to forests and deserts.
But like many other creatures, dung beetles face various threats. Loss of habitat due to deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural practices poses a significant risk to their survival. Pesticide use and pollution also harm their populations. Additionally, climate change has impacted their distribution and reproductive behavior, affecting their ability to find food and suitable mates.
According to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the conservation status of dung beetles varies, with some species being of least concern while others are endangered. The heavily researched African Dung Beetle, for example, is classified as endangered due to its declining populations.
So, what exactly is the importance of dung beetles in our ecosystem? The answer may surprise you.
Firstly, as mentioned earlier, dung beetles play a crucial role in nutrient recycling. By collecting and burying animal feces, they contribute to the breakdown of organic matter and the release of essential nutrients back into the soil. This process is especially crucial in grasslands, where the presence of dung beetles helps promote plant growth and soil fertility.
Moreover, dung beetles are essential for controlling pest populations in agriculture. By feeding on feces, they also consume disease-causing pathogens, reducing the risk of spreading illness among other animals, including humans.
These insects are also used in traditional medicine and are rich in antioxidants, making them popular in some cultures. In areas with high dung beetle populations, farmers often collect and sell them to pharmaceutical companies for research and medicine production.
And if all of the above isn't fascinating enough, here's one last unique feature of dung beetles – their ability to navigate using the Milky Way.
Recent research has shown that dung beetles are the first known insect species to use the Milky Way as a reference point for navigation. This skill is particularly helpful for them to navigate at night when they are more active, as it helps them roll their dung balls in a straight line and avoid getting lost.
However, as with any other animal, dung beetles also have predators, including birds, mammals, and reptiles. To evade these predators and protect their precious food source, some species have developed a clever defense mechanism. They roll their dung balls into underground tunnels, where they can feed in safety.
In conclusion, the dung beetle may seem like an insignificant, dirty insect, but it is far from it. These small creatures are instrumental in maintaining the health and balance of our ecosystem. So, the next time you come across a dung beetle, take a moment to appreciate its unique features and the crucial role it plays in our environment. After all, it's nature's hidden treasure.

The Mighty Dung Beetle: Nature's Unsung Hero
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.