Eel Catfish
Up to 70 centimeters
The eel catfish is a fascinating creature found in coral reefs, estuaries, and mangroves. With a length of up to 70 centimeters, it belongs to the Plotosidae family and has an elongated and slender body shape. Keep an eye out for this unique and mesmerizing fish on your next trip to the coast! #eelcatfish #marineanimals #coralreefs
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Eel Catfish
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Marine and brackish water
The Amazing Adaptations of the Eel Catfish
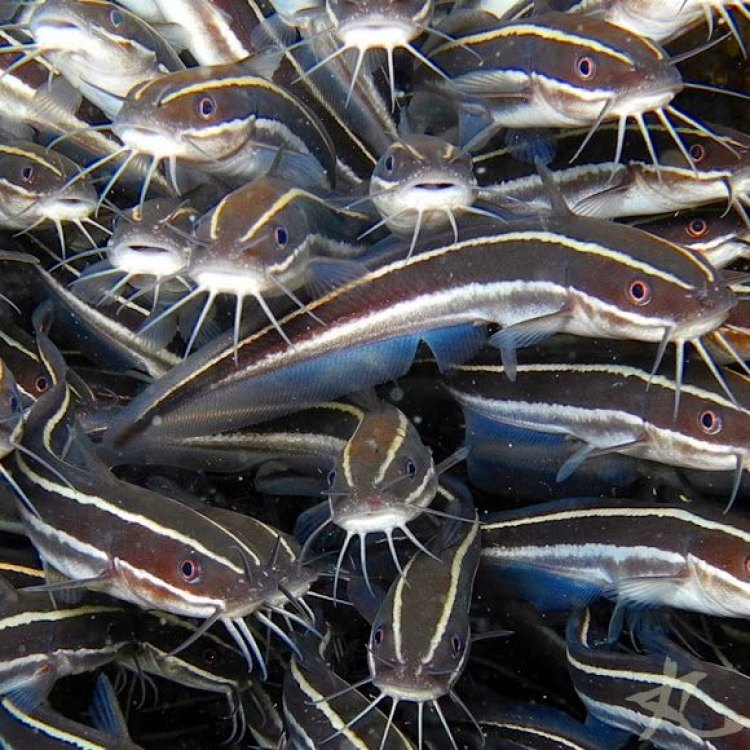
Plotosus lineatus, commonly known as the Eel Catfish, is a fascinating and unique species that inhabits the Indo-Pacific region, particularly in Australia. This fish belongs to the order Siluriformes, which includes more than 3000 species of catfishes. Although it shares similar characteristics with catfish, the Eel Catfish is quite distinctive from other species. In this article, we will dive into the amazing adaptations and features of this interesting fish Eel Catfish.The Habitat and Distribution
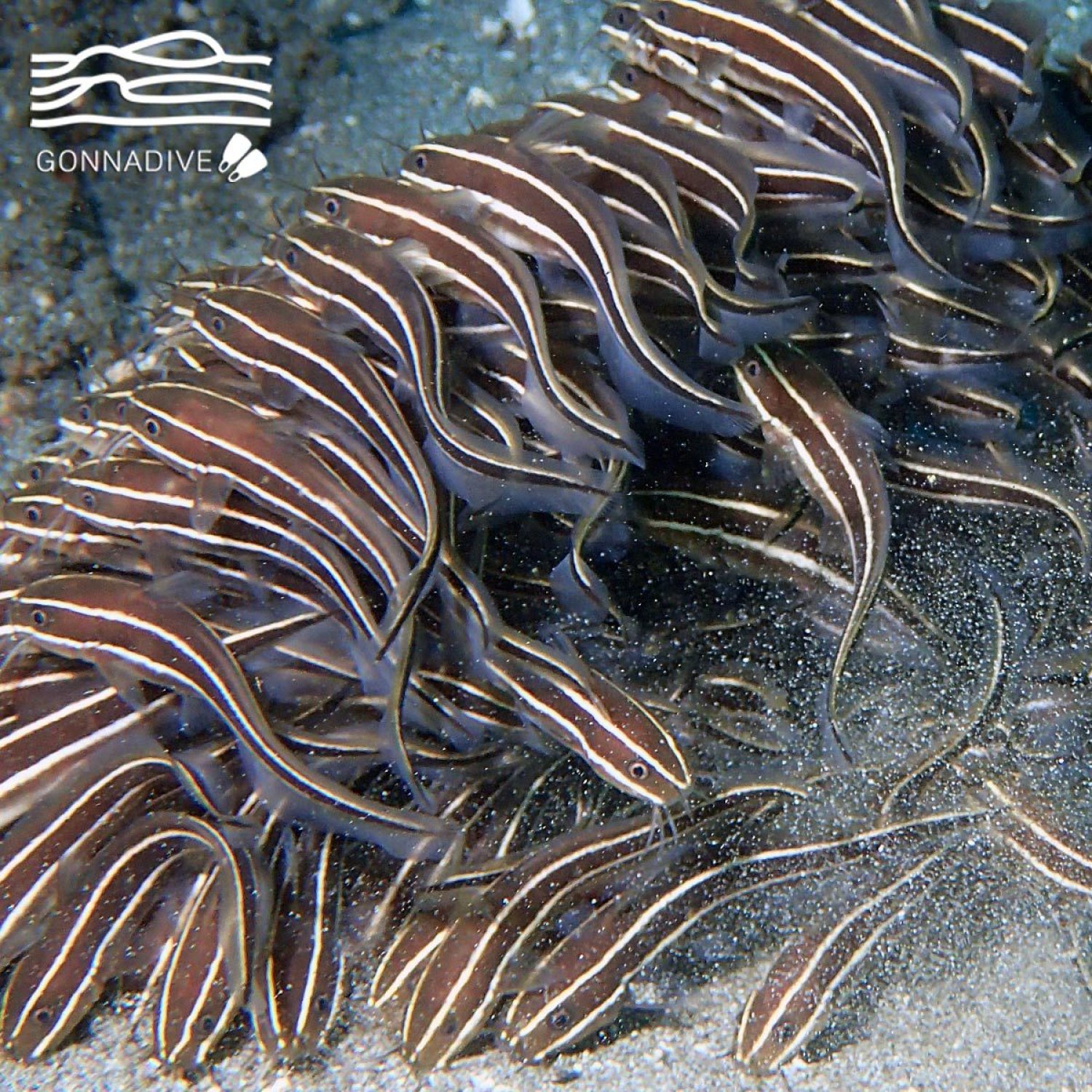
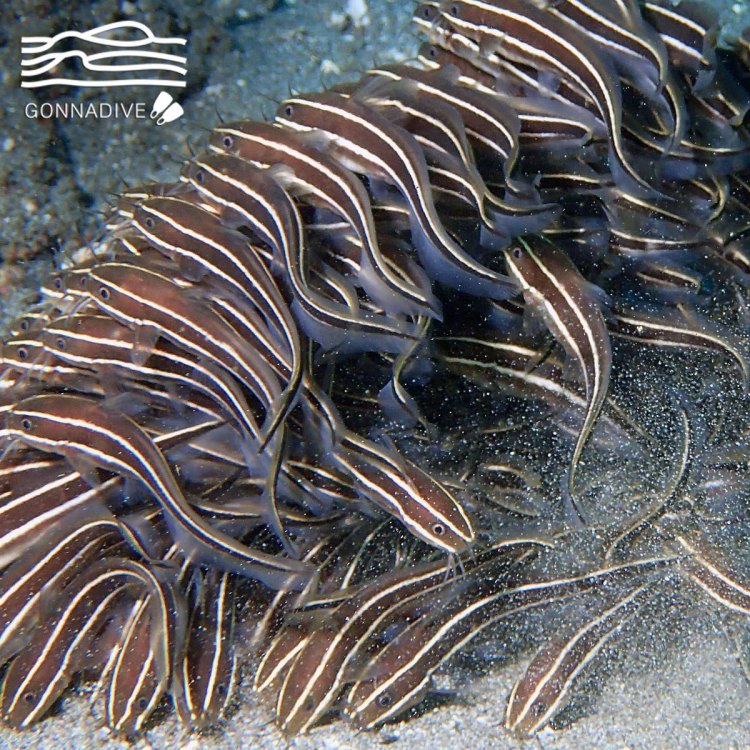
The Eel Catfish can be found in various marine and brackish water environments, such as coral reefs, estuaries, and mangroves. These habitats provide the perfect conditions for the Eel Catfish to thrive. They prefer areas with sandy or muddy bottoms, where they can hide and hunt for food. Their geographical distribution spans from the Indian Ocean to the western Pacific, with their highest concentration in Northern Australia.The Physical Description
The Eel Catfish has a unique and intriguing body shape, unlike any other catfish species. Its elongated and slender body can reach a length of up to 70 centimeters. It is covered in a thick, slimy layer of mucus, making it difficult for predators to catch them. This slimy coating also aids in their smooth movement through the murky waters.One of the most distinctive features of the Eel Catfish is its bluish-gray coloration with vertical black bands Egyptian Goose. This coloration helps them camouflage and blend in with their surroundings, making them less visible to predators. They also have a pair of long barbels near their mouths, which they use to sense food and navigate their environment.
The Feeding Behavior
The Eel Catfish is a carnivorous species, meaning they primarily feed on other animals. They have a voracious appetite and are opportunistic eaters, meaning they will consume any prey they come across. Their diet consists of small fish, crustaceans, and other invertebrates. They have powerful jaws and sharp teeth, which they use to catch and crush their prey. Due to their bottom-dwelling nature, they often burrow in the sand and wait for unsuspecting prey to swim by before attacking.The Adaptations for Survival
The Eel Catfish has a wide array of unique and fascinating adaptations that help them survive in their environment. These adaptations have evolved over thousands of years, making them perfectly suited to their surroundings.Firstly, their elongated and slender body makes them well adapted for maneuvering through small spaces and swimming through the murky waters of their habitat. Their slimy skin also aids in their smooth movement and provides protection against predators.
Their coloration is also a vital adaptation for survival. The bluish-gray color with vertical black bands allows them to camouflage and blend in with their surroundings, making them less visible to predators. The Eel Catfish also has the ability to change color to match their environment, making them even harder to spot.
The pair of long barbels near their mouths is another crucial adaptation for the Eel Catfish. These barbels are loaded with sensory cells that allow them to sense vibrations in the water and locate food. This adaptation is especially useful in the murky waters and helps them find prey more easily.
The Importance of the Eel Catfish
The Eel Catfish may not be as well-known as other species, but they play a significant role in their ecosystems. They are essential predators and help control the population of smaller fish and invertebrates in their habitat. They also serve as prey for larger fish and birds, thus playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their environment.In some countries, the Eel Catfish is also a popular food fish. This species is commercially harvested and sold in markets, contributing to the economy and providing a source of food for people. However, due to their decline in numbers and vulnerability to overfishing, strict regulations have been implemented to protect this species.
The Conservation Efforts
The Eel Catfish has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List, which indicates that their population is stable. However, certain threats, such as habitat destruction and overfishing, pose a risk to this species. As a result, several conservation efforts have been put in place to protect the Eel Catfish and its habitat.One of the most significant conservation efforts is the protection of coral reefs, estuaries, and mangroves, which are the primary habitats of the Eel Catfish. These habitats are sensitive and easily damaged by human activities, such as pollution and coastal development. By protecting these areas, we can also protect the Eel Catfish and other species that depend on these habitats for survival.
In Conclusion
The Eel Catfish, with its unique adaptations and features, is truly an incredible species. It has evolved over thousands of years to survive in its environment, making it perfectly adapted for its niche. This fascinating fish serves as a predator and prey in its ecosystem, playing a vital role in maintaining the balance of its environment. With proper conservation efforts, we can ensure the survival of the Eel Catfish and continue to marvel at its remarkable adaptations.

Eel Catfish
Animal Details Eel Catfish - Scientific Name: Plotosus lineatus
- Category: Animals E
- Scientific Name: Plotosus lineatus
- Common Name: Eel Catfish
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Siluriformes
- Family: Plotosidae
- Habitat: Marine and brackish water
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Indo-Pacific region
- Country of Origin: Australia
- Location: Coral reefs, estuaries, and mangroves
- Animal Coloration: Bluish-gray with vertical black bands
- Body Shape: elongated and slender
- Length: Up to 70 centimeters

Eel Catfish
- Adult Size: 40-70 centimeters
- Average Lifespan: 15-20 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Egg-laying
- Sound or Call: No specific sounds or calls
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Threats: Habitat degradation, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Maintains population balance by feeding on small crustaceans and fish
- Human Use: Commercially harvested as food
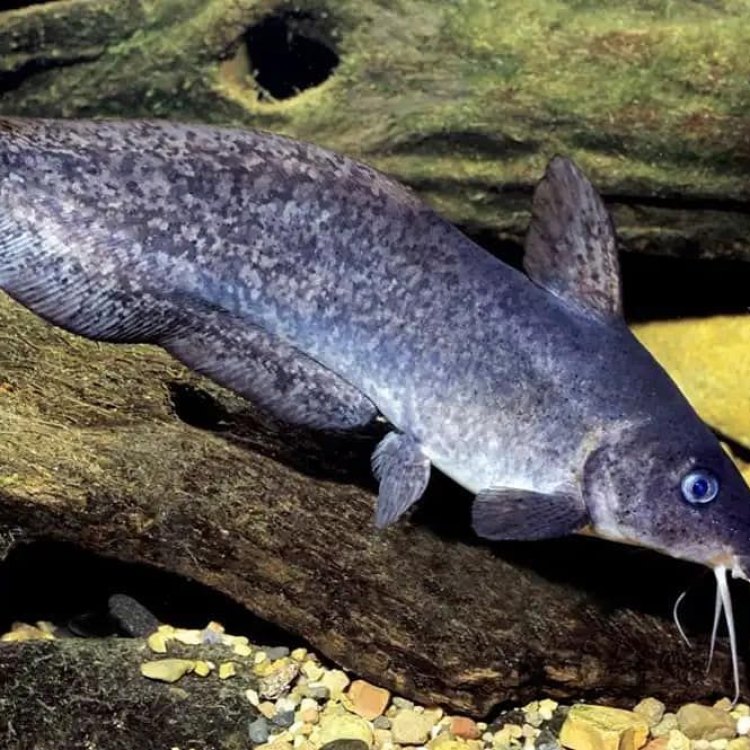
- Distinctive Features: Long, eel-like body with a catfish-like head
- Interesting Facts: Eel catfish have venomous spines on their pectoral and dorsal fins
- Predator: Larger predatory fish

Plotosus lineatus
The Fascinating World of Eel Catfish: A Unique Species with Venomous Spines
When we think of catfish, we often envision the large, whiskered bottom-feeders found in freshwater lakes and rivers. But did you know that there is a catfish that looks like an eel? Introducing the eel catfish, a unique species that combines the features of both eels and catfish. In this article, we will dive into the world of these fascinating creatures, their characteristics, behavior, and the impact they have on their ecosystem.One glance at an eel catfish and you may mistake it for an eel due to its long, slender body PeaceOfAnimals.Com. However, these catfish have a distinctive head that resembles that of a typical catfish, with barbels near its mouth used for sensory purposes. They can reach a size of 40-70 centimeters as adults and have an average lifespan of 15-20 years.
Reproduction and Behavior
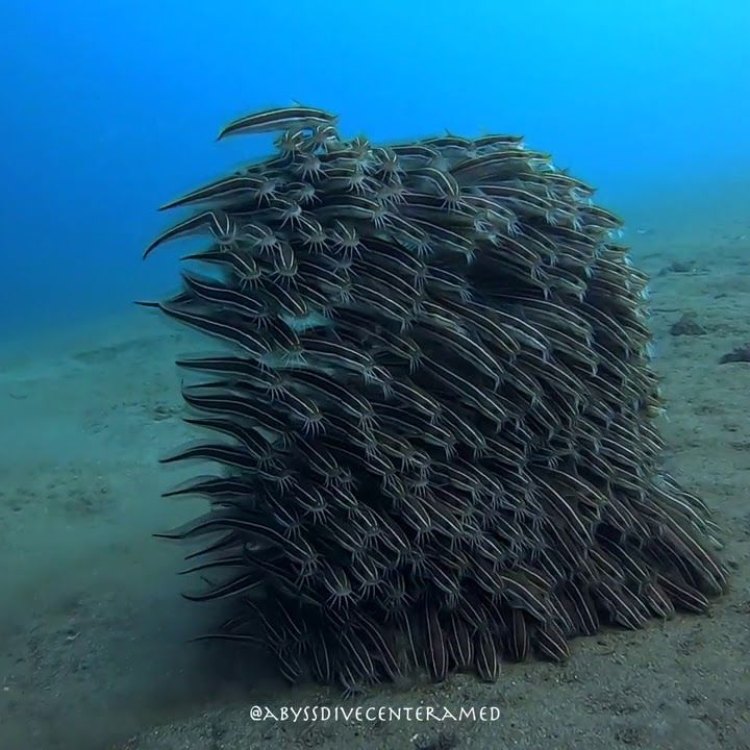
Like most fish, eel catfish reproduce sexually. This means that fertilization occurs internally, and the females lay eggs. However, unlike many other catfish species, eel catfish do not build nests to lay their eggs. Instead, they scatter them throughout their habitat, which is typically in shallow, muddy waters.Eel catfish are solitary creatures and prefer to live alone. They are also nocturnal, meaning they are most active during the night. This behavior, combined with their secretive nature, makes it challenging to study and observe them in their natural habitat Epidexipteryx.
Threats and Conservation Status
Habitat degradation and overfishing are the two main threats facing eel catfish. As a bottom-dwelling species, they are heavily impacted by pollution and human activities that alter their habitat. Additionally, they are commercially harvested as a food source in some areas, further depleting their already declining population. Unfortunately, due to their elusive nature, there is limited data on their current population and distribution, making it difficult to assess their conservation status. As a result, they are listed as "Not Evaluated" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.Impact on Ecosystem
Eel catfish play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem. They are opportunistic feeders and will consume a variety of small crustaceans and fish. By doing so, they help control the population of these prey species, preventing them from becoming overabundant and disrupting the food chain. Without this balancing act, the ecosystem would struggle to function effectively, highlighting the importance of preserving and protecting eel catfish populations.Human Use and Distinctive Features
Eel catfish are commercially harvested as a food source in some parts of the world, including Southeast Asia. In some cultures, they are also used in traditional medicine as a treatment for various ailments. However, due to their venomous spines, they must be handled carefully during the harvesting process.One of the unique features of eel catfish is their venomous spines, located on their pectoral and dorsal fins. While not lethal to humans, these spines can inflict a painful wound if handled or stepped on. This serves as a defense mechanism against potential predators, including larger predatory fish.
Interesting Facts
Aside from their distinctive appearance and venomous spines, there are many other intriguing facts about eel catfish that are worth noting. For example, they have the ability to live in low-oxygen environments, allowing them to survive in waters where other fish cannot. They also have a modified swim bladder that acts as a respiratory organ, allowing them to take in oxygen from the air above the water's surface.Another interesting fact is that despite their eel-like appearance, eel catfish are actually classified as part of the catfish family, Callichthyidae. This family includes other unique and fascinating fish, such as armored catfish and the popular aquarium fish, Corydoras catfish.
In Conclusion
The eel catfish is a truly unique and intriguing species, combining the features of both eels and catfish. Despite their elusive nature, they play a vital role in their ecosystem and highlight the delicate balance of the natural world. As with many other aquatic species, they face threats from human activities and require conservation efforts to protect their population. Next time you come across an eel catfish, remember its fascinating characteristics and the importance of preserving its existence.

The Amazing Adaptations of the Eel Catfish
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.