
Embolotherium
3-4 meters
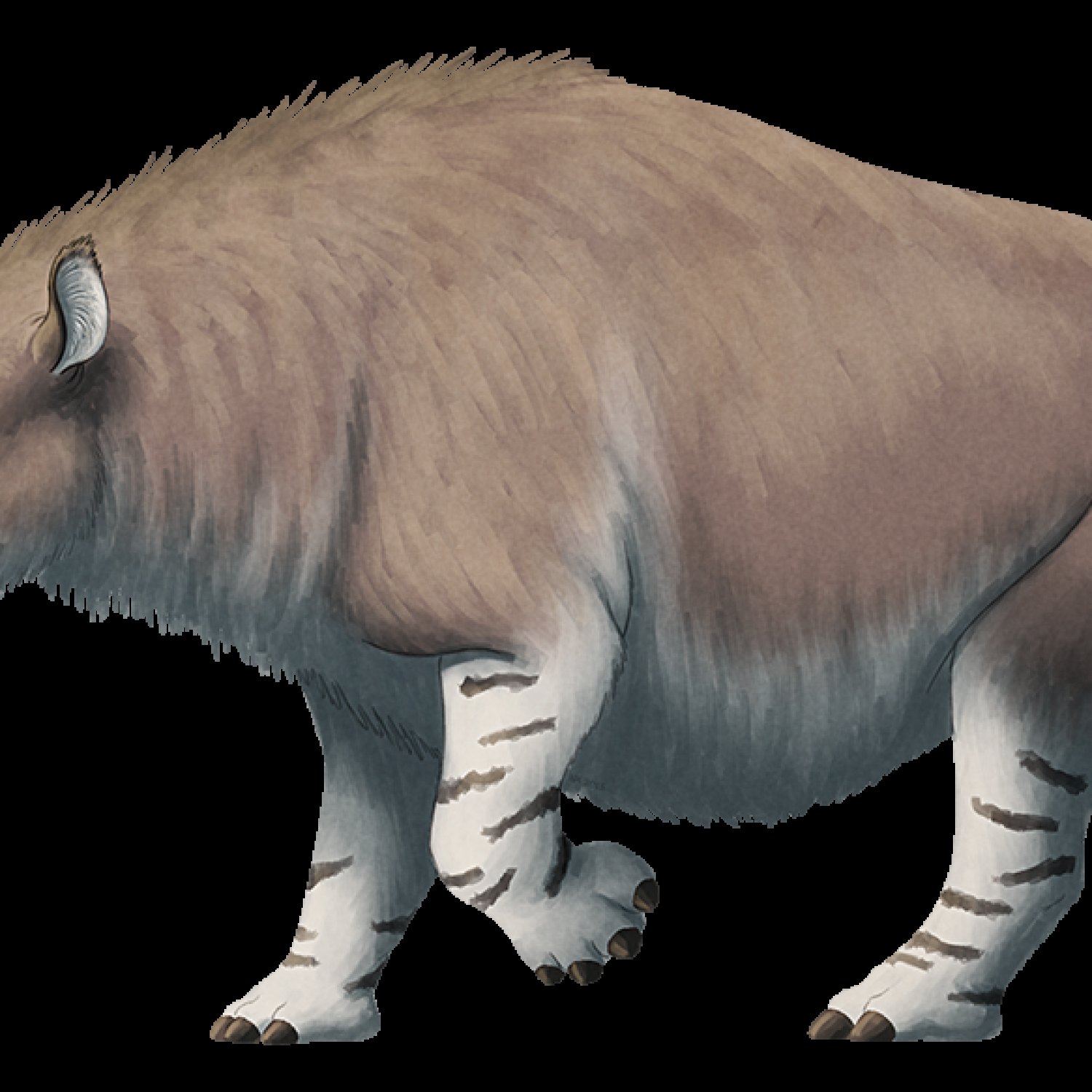
Embolotherium, a large and stocky herbivorous mammal, roamed the Gansu Province in China over 30 million years ago. Belonging to the Amynodontidae family, this animal could reach a length of 3-4 meters. It's no surprise that this impressive creature is commonly referred to by its scientific name, as it brings to mind its unique and majestic appearance. Embolotherium is a fascinating piece of Earth's history that continues to captivate us even today.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Embolotherium
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Grasslands
The Remarkable Embolotherium: A Prehistoric Giant from the Grasslands of Asia
In the world of prehistoric mammals, there were many strange and fascinating creatures. From giant ground sloths to saber-toothed tigers, these animals capture our imagination and make us wonder about the world that existed millions of years ago. However, there is one species that stands out among the rest due to its sheer size and unique features - the Embolotherium.Scientifically known as Embolotherium, this prehistoric giant falls under the animal kingdom, phylum Chordata, and the class Mammalia Embolotherium. It belonged to the Order Perissodactyla, which includes modern-day horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs. This massive mammal was a member of the family Amynodontidae, which is now extinct.
Embolotherium is a fascinating creature that roamed the earth during the Oligocene epoch, which was around 33 to 23 million years ago. It lived in the grasslands of Asia, specifically in the country of origin, China, in the province of Gansu. Its name is derived from the Greek words “embolon,” which means wedge, and “therion,” which means beast. This name perfectly describes its unique feature, which we will discuss further in this article.
Habitat and Distribution
The Embolotherium was a herbivorous animal that inhabited the vast grasslands of Asia. It lived in open areas, where it could find an abundance of vegetation to sustain its large body. During the Oligocene epoch, the climate in this region was warm, and the grasslands were flourishing, creating the perfect environment for this majestic creature European Polecat.
Although the Embolotherium had a widespread distribution, it was mainly found in China's Gansu province. Fossils of this species have also been discovered in Mongolia, Pakistan, and Kazakhstan, indicating that it roamed in a significant part of Asia.
Appearance and Physical Characteristics
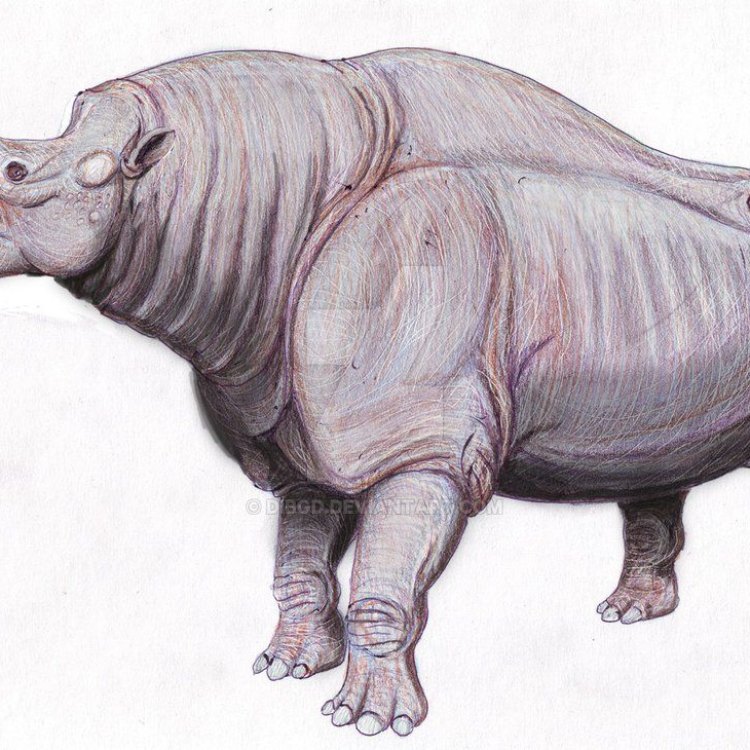
The Embolotherium was a truly impressive animal, standing at an impressive 3 to 4 meters in length and weighing around 2 to 3 tons. Its body shape was large and stocky, with four sturdy legs that supported its massive frame. Its stocky build is one of its most distinctive features, which sets it apart from other members of the Perissodactyla order.
One of the most striking features of the Embolotherium was its head. Unlike modern-day herbivores, which have small heads and elongated snouts for feeding on leaves, this prehistoric giant had a massive, wedge-shaped head. This skull could grow up to 75 cm in length, with large, forward-curving horns on top.
Scientists believe that these horns were used for fighting among males or for display during mating rituals. This feature gives us a glimpse into the competitive nature of these creatures and how they must have lived in groups and engaged in intense battles for dominance.
The Embolotherium was primarily covered in short, dense fur, which was likely brown in color, providing camouflage in its grassland habitat. Its legs were long and sturdy, allowing it to run at impressive speeds despite its massive size.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
As mentioned earlier, the Embolotherium was a herbivorous animal, which means it fed on a plant-based diet. It had a specialized set of teeth that were perfectly suited for chewing tough grass and vegetation, which was abundant in the grasslands where it lived.
Unlike modern-day herbivores that have multiple stomach chambers to aid digestion, the Embolotherium had a simple stomach with a large fermentation chamber. This adaptation allowed it to process and extract nutrients efficiently from the tough plant matter.
Studies have shown that this prehistoric giant was a selective feeder and often sought out the most nutritious plants to consume. Its size also meant that it needed to consume large quantities of food every day, making it an essential part of the grassland ecosystem as it helped maintain the balance of plant life in the region.
Final Thoughts
Embolotherium was truly a remarkable creature that lived during a time when the world was vastly different from what we know today. Its massive size and unique features make it a fascinating subject for scientific research, providing us with valuable insights into the evolutionary history of mammals.
Although it has been extinct for millions of years, the Embolotherium lives on in our imagination and in the fossils that have been discovered. With continued studies and discoveries, we hope to learn more about this prehistoric giant and the world it lived in.
The Embolotherium is a reminder that our planet's history is full of strange and incredible creatures, and it's essential to continue preserving and studying fossil remains to gain a better understanding of our world's past.
The Embolotherium was a herbivorous animal that inhabited the vast grasslands of Asia. It lived in open areas, where it could find an abundance of vegetation to sustain its large body. During the Oligocene epoch, the climate in this region was warm, and the grasslands were flourishing, creating the perfect environment for this majestic creature European Polecat.
Although the Embolotherium had a widespread distribution, it was mainly found in China's Gansu province. Fossils of this species have also been discovered in Mongolia, Pakistan, and Kazakhstan, indicating that it roamed in a significant part of Asia.
Appearance and Physical Characteristics
The Embolotherium was a truly impressive animal, standing at an impressive 3 to 4 meters in length and weighing around 2 to 3 tons. Its body shape was large and stocky, with four sturdy legs that supported its massive frame. Its stocky build is one of its most distinctive features, which sets it apart from other members of the Perissodactyla order.One of the most striking features of the Embolotherium was its head. Unlike modern-day herbivores, which have small heads and elongated snouts for feeding on leaves, this prehistoric giant had a massive, wedge-shaped head. This skull could grow up to 75 cm in length, with large, forward-curving horns on top.
Scientists believe that these horns were used for fighting among males or for display during mating rituals. This feature gives us a glimpse into the competitive nature of these creatures and how they must have lived in groups and engaged in intense battles for dominance.
The Embolotherium was primarily covered in short, dense fur, which was likely brown in color, providing camouflage in its grassland habitat. Its legs were long and sturdy, allowing it to run at impressive speeds despite its massive size.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
As mentioned earlier, the Embolotherium was a herbivorous animal, which means it fed on a plant-based diet. It had a specialized set of teeth that were perfectly suited for chewing tough grass and vegetation, which was abundant in the grasslands where it lived.Unlike modern-day herbivores that have multiple stomach chambers to aid digestion, the Embolotherium had a simple stomach with a large fermentation chamber. This adaptation allowed it to process and extract nutrients efficiently from the tough plant matter.
Studies have shown that this prehistoric giant was a selective feeder and often sought out the most nutritious plants to consume. Its size also meant that it needed to consume large quantities of food every day, making it an essential part of the grassland ecosystem as it helped maintain the balance of plant life in the region.
Final Thoughts
Embolotherium was truly a remarkable creature that lived during a time when the world was vastly different from what we know today. Its massive size and unique features make it a fascinating subject for scientific research, providing us with valuable insights into the evolutionary history of mammals.Although it has been extinct for millions of years, the Embolotherium lives on in our imagination and in the fossils that have been discovered. With continued studies and discoveries, we hope to learn more about this prehistoric giant and the world it lived in.
The Embolotherium is a reminder that our planet's history is full of strange and incredible creatures, and it's essential to continue preserving and studying fossil remains to gain a better understanding of our world's past.

Embolotherium
Animal Details Embolotherium - Scientific Name: Embolotherium
- Category: Animals E
- Scientific Name: Embolotherium
- Common Name: Embolotherium
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Perissodactyla
- Family: Amynodontidae
- Habitat: Grasslands
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Asia
- Country of Origin: China
- Location: Gansu Province
- Animal Coloration: Brown
- Body Shape: Large and stocky
- Length: 3-4 meters

Embolotherium
- Adult Size: Similar to a rhinoceros
- Average Lifespan: Unknown
- Reproduction: Viviparous
- Reproductive Behavior: Unknown
- Sound or Call: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Unknown
- Social Groups: Unknown
- Behavior: Unknown
- Threats: Extinct
- Conservation Status: Extinct
- Impact on Ecosystem: Unknown
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Large size and long tusk-like canine teeth
- Interesting Facts: Embolotherium was one of the largest mammals to have ever lived on land.
- Predator: Unknown
Embolotherium
Uncovering the Mysterious Embolotherium: The Giant Rhinoceros-like Mammal Lost in Time
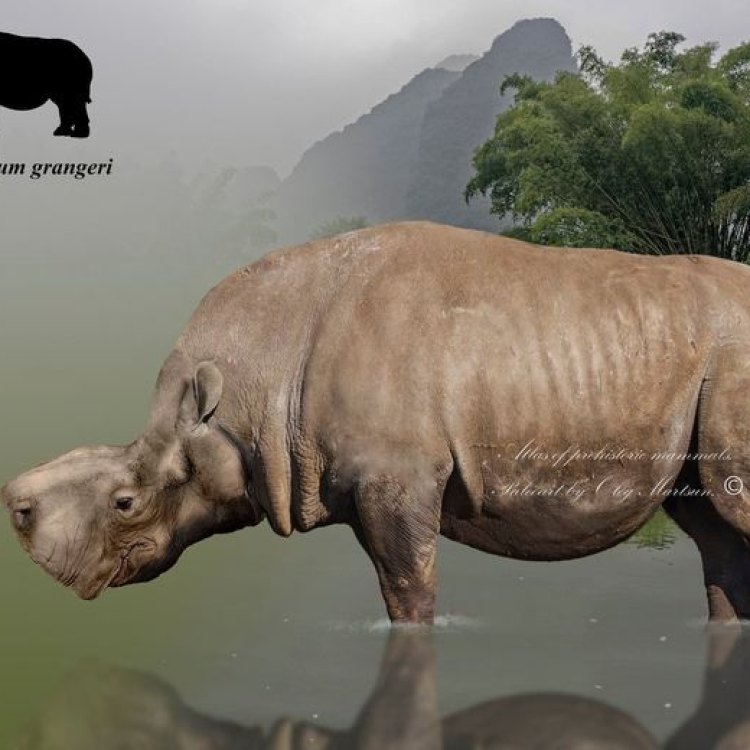
Millions of years ago, during the Eocene epoch, a massive mammal roamed the land with its imposing presence. This colossal creature, known as Embolotherium, was one of the largest land mammals to ever exist. Despite its impressive size and unique features, very little is known about this enigmatic animal. In this article, we dive into the depths of history to discover the fascinating facts about Embolotherium and unravel the mystery that surrounds this extinct species PeaceOfAnimals.Com.The Giant of the Eocene Epoch
Embolotherium, also known as the Eocene Entelodont, was a member of the family Entelodontidae, which included other extinct species such as Daeodon and Archaeotherium. This massive mammal is estimated to have lived between 37 and 27 million years ago, during the late Eocene epoch. Its fossil remains have been found in areas such as China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan. The name Embolotherium is derived from the Greek words “embolon,” meaning wedge, and “therion,” meaning wild beast, referring to its wedge-shaped bones and fierce appearance.Size and Physical Appearance
One of the most distinctive features of Embolotherium was its massive size, similar to that of a rhinoceros. This mammal could grow up to 8.5 feet (2 Eagle Ray.6 meters) tall at the shoulder and reach a staggering weight of over 2.5 tons. Its overall body shape and structure were also similar to that of a rhinoceros, with a large, stocky body, short legs, and a barrel-shaped torso. However, unlike its chunky rhinoceros counterparts, Embolotherium possessed a relatively longer neck and a more elongated skull.Another unique characteristic of Embolotherium was its long tusk-like canine teeth, which could grow up to 15 inches (38 cm) long. These sharp, curved teeth were situated in the front of its mouth and were used to tear into food and defend against potential predators. Its massive jaw muscles and bony sheath protecting its teeth also indicate that Embolotherium had a strong bite force.
Reproduction and Behavior
Though very little is known about the reproductive behavior of Embolotherium, it is believed that these giant mammals were viviparous, meaning they gave birth to live young. It is presumed that the female Embolotherium gave birth to a single calf at a time due to the large size of the offspring.As for their behavior, experts suggest that Embolotherium was a solitary animal, as no evidence has been found to support the presence of social groups or herds. However, given their large size, it is possible that they may have formed temporary pairs or groups during breeding seasons.
Mysterious Sound and Migration Patterns
Despite the extensive study of Embolotherium’s fossil remains, there is no information on their sound or call. It is possible that they may have made low grunting sounds similar to those of their relatives Daeodon and Archaeotherium, which were known to be vocal animals. However, this remains a mystery that may never be fully uncovered.Another aspect that researchers have been unable to determine is the migration patterns of Embolotherium. Due to their large size and possible solitary behavior, it is unlikely that they migrated in large herds. However, their movement patterns and range of habitat remain a topic of speculation.
The Hunt for Clues: Threats, Extinction, and Conservation Status
As with many other extinct species, the exact cause of Embolotherium’s extinction remains a mystery. There are numerous theories, including climate change, competition for resources, and possible disease outbreaks. However, there is no evidence to support any of these hypotheses conclusively.What is known is that Embolotherium had become extinct by the end of the Eocene epoch, around 27 million years ago. Fossil remains found in the Gashunyinade Formation in Mongolia showed evidence of significant climate change, which could have contributed to their demise. These ancient mammals were at the top of the food chain and had no known predators, making their extinction even more puzzling.
Unfortunately, because of the limited fossils found and our lack of understanding of the species, Embolotherium is classified as extinct, with an unknown conservation status. It serves as a reminder of the need to continuously study and protect the remaining species on our planet to prevent them from succumbing to the same fate.
Impact on the Ecosystem and Human Use
The impact of Embolotherium on the ecosystem during its time on Earth is still unknown. As top predators, they may have had some influence on controlling other herbivore populations, but there is no evidence to support this theory. Their massive size and long teeth also indicate that they may have had a significant role in seed dispersal, similar to that of modern-day rhinos.As for human use, there is no evidence to suggest that Embolotherium was ever utilized by ancient humans for food, clothing, or any other purpose. However, their impressive size and unique features make them a fascinating subject for paleontologists and animal enthusiasts alike.
Interesting Facts about Embolotherium
As we continue to learn more about this massive mammal, there have been some intriguing facts that have surfaced about Embolotherium. Here are a few that are sure to pique your curiosity:- Researchers believe that Embolotherium was the inspiration for the fictional creature “Bulborb” in the popular video game series, “Pikmin.”
- The name “Entelodont” means “perfect tooth,” which was given to the family of Embolotherium and related species due to their sharp, efficient teeth.
- It is believed that Embolotherium’s tusk-like teeth were not used for chewing, but rather as a defense mechanism against predators.
- The only known fossil of a young Embolotherium was found in a fragmentary state, leading experts to suggest that it was most likely crushed by its mother after giving birth.
- The closest living relative to Embolotherium is the pig, which is believed to have evolved from the same ancestor.
In Conclusion
The story of Embolotherium is one of mystery and wonder. Despite our efforts to uncover its secrets, this colossal mammal will continue to fascinate and intrigue us for years to come. Its impressive size, unique features, and enigmatic existence make it a valuable piece in the puzzle of Earth’s history. As we continue to explore and learn more about our planet, there is no doubt that more information about Embolotherium and other extinct species will come to light,

The Remarkable Embolotherium: A Prehistoric Giant from the Grasslands of Asia
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












