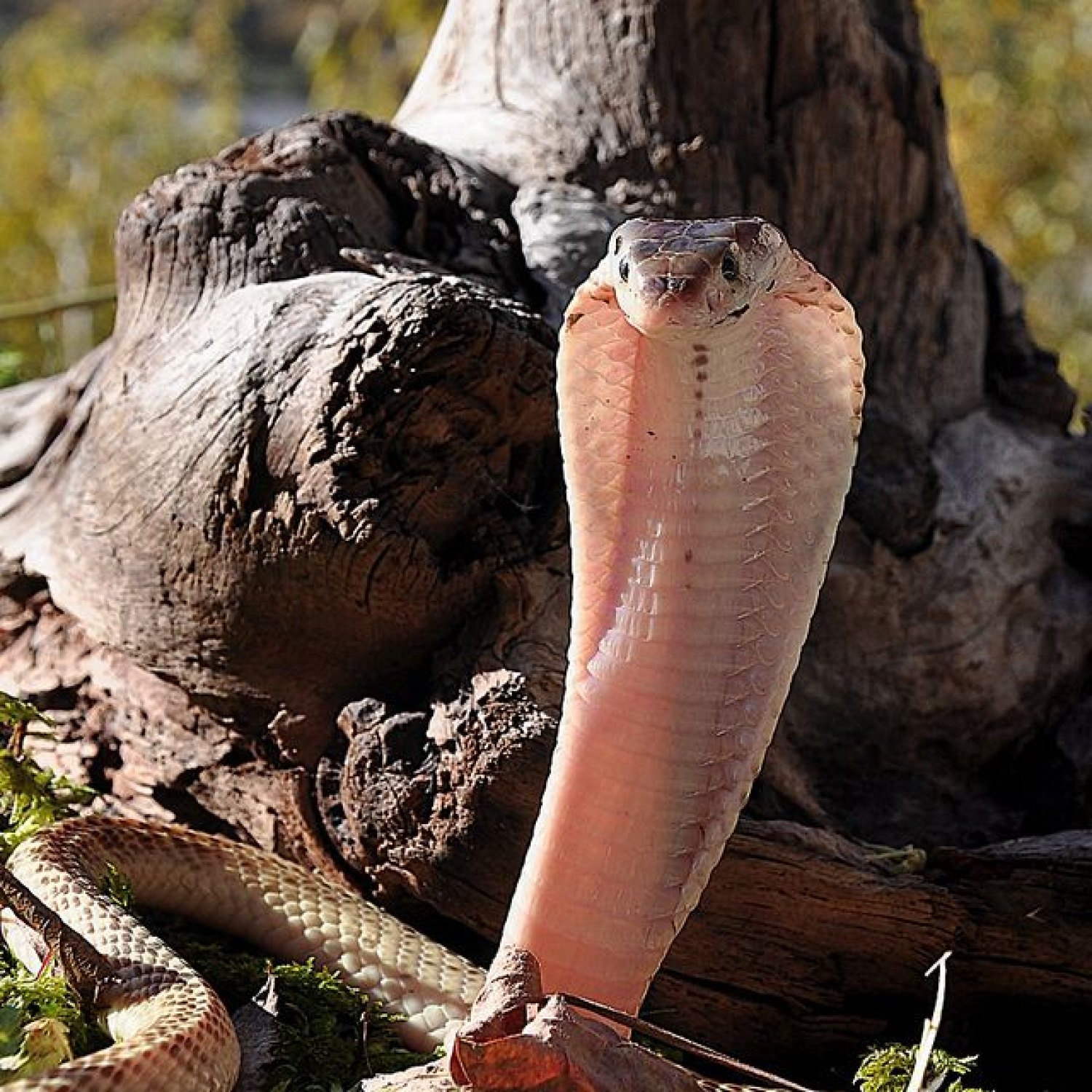
Equatorial Spitting Cobra
1.5 to 2 meters
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra, found in Sumatra, Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia, and Java, is a highly venomous snake known for its unique defense mechanism of spitting venom at potential threats. This slender and elongated snake can reach a length of 1.5 to 2 meters, making it one of the largest cobras in its category. Beware of this powerful predator when hiking in these areas! #EquatorialSpittingCobra #SnakeSafety #WildlifeEncounters
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Equatorial Spitting Cobra
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Tropical Rainforests, Swamps, Marshes
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra: A Tropical Wonderland's Most Dangerous Serpent
The dense, lush rainforests of Southeast Asia are a haven for an incredible array of wildlife, from monkeys and birds to tigers and elephants. But lurking among the vibrant flora and fauna is a creature often feared and misunderstood - the Equatorial Spitting Cobra (Naja sumatrana). With its venomous bite and unique defense mechanism, this snake has earned a notorious reputation in its native habitat.Discovering the Equatorial Spitting Cobra
Naja sumatrana, also commonly known as the Equatorial Spitting Cobra, is native to the Southeast Asian islands of Sumatra, Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia, and Java Equatorial Spitting Cobra. This species belongs to the animal kingdom, phylum Chordata, class Reptilia, and order Squamata. It is a member of the Elapidae family, which also includes other venomous snakes like the King Cobra and Black Mamba.In appearance, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra has a slender, elongated body, with adults typically reaching a length of 1.5 to 2 meters. Its body is covered in dark brown or black scales, often with lighter bands, giving it a striking and intimidating appearance. As with most snakes, the female is typically larger than the male.
A Deadly Weapon in its Venomous Bite
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra’s primary method of defense is its highly venomous bite, which can injure or even kill humans. Its venom is a powerful neurotoxin that attacks the nervous system, leading to paralysis, respiratory failure, and even death in severe cases. However, these snakes are not naturally aggressive and will only bite when they feel threatened or are provoked European Bee Eater.While the venomous bite of the Equatorial Spitting Cobra can be deadly, not all bites result in envenomation. This is because the snake has the ability to regulate the amount of venom it injects, depending on the size and nature of its prey or threat.
Unique Defense Mechanism – Spitting Venom
The name “Spitting Cobra” comes from the Equatorial Spitting Cobra's trademark defense mechanism - spitting venom. When threatened, the snake can spray its venom in a directed stream up to two meters away. This extraordinary ability, unique to spitting cobras, is possible due to the elongated and grooved fangs that allow the venom to be ejected like a spray from a spray bottle.This venom spray is not just a mechanism to deter predators; it can also temporarily blind its attackers or prey, making it easier to escape or strike. In rare cases, if the venom gets into the eyes, it can cause permanent damage or even blindness, highlighting the danger of this capability.
A Habitat Suited for Survival
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra's natural habitat consists of tropical rainforests, swamps, and marshes, where they can thrive in the wet, humid environment. These snakes are excellent swimmers, and their ability to move smoothly through the water allows them to hunt a variety of prey, including fish, frogs, lizards, birds, and other small mammals. Their excellent climbings skills also enable them to hunt in trees and bushes, which is where their preferred prey – rodents and birds – typically reside.One of the most remarkable things about the Equatorial Spitting Cobra's habitat is its resilience. Despite deforestation and the destruction of their natural habitats, these snakes have managed to adapt and survive in human-altered landscapes, making them a constant presence in many Southeast Asian communities.
Distribution and Impact on Human Populations
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra is a native species of Southeast Asia, with its highest concentration in Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. However, as a result of the pet trade, these snakes have also been introduced to other parts of the world, including the United States, where they have become established in certain states like Florida.While not considered an endangered species, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra's impact on human populations is not to be underestimated. Due to their preferred habitat in tropical regions, where humans often live and work, encounters with these snakes are quite common. Loss of habitat has also brought humans and snakes into closer contact, leading to an increase in snake bites. In Malaysia alone, over 10,000 snake bites are reported annually, and the Equatorial Spitting Cobra is responsible for a significant percentage of these cases.
This snake's lethal venom and unique ability to spit venom make it a threat to human populations, which has led to fear and vilification. However, it is essential to remember that these snakes are crucial to their ecosystem, keeping rodent populations in check and playing a vital role in the food chain.
Fascinating Facts about Equatorial Spitting Cobra
- While the venom of the Equatorial Spitting Cobra is dangerous to adult humans, it is not fatal to some local wildlife, such as the Asian monitor lizard, which has developed immunity to it.- Due to their excellent swimming skills, these snakes can also hunt fish underwater.
- In addition to their venomous bite, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra can also deliver a painful, non-lethal bite using its rear fangs. This bite is used primarily for grasping and holding onto prey.
- These snakes are mostly solitary creatures, only coming together during the breeding season.
- The legal export of the Equatorial Spitting Cobra is prohibited in Indonesia, but its capture and sale continue to be a thriving business on the black market.
Preserving the Equatorial Spitting Cobra
Like most wildlife species, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra faces numerous threats, including loss of habitat and persecution by humans. However, conservation efforts are in place to protect these amazing creatures.In Indonesia, the Wildlife Conservation Society works closely with local communities and government agencies to protect species like the Equatorial Spitting Cobra by raising awareness about the importance of these snakes in the ecosystem. The Wildlife Conservation Society also employs techniques like radio telemetry and satellite tracking to study and monitor spitting cobra populations.
On a broader scale, countries like Malaysia and Indonesia have enacted laws to curb the illegal trade of wildlife, including snakes. These laws, combined with education and awareness efforts, have yielded positive results, reducing the demand for exotic wildlife.
In Conclusion
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra is a magnificent creature, perfectly adapted to its tropical environment and crucial to the ecosystem. While its venom and unique defense mechanism may instill fear in some, it is important to understand and appreciate the natural role these snakes play in maintaining a balance in nature. With continued conservation efforts and responsible interaction with these snakes, we can ensure their survival for generations to come.
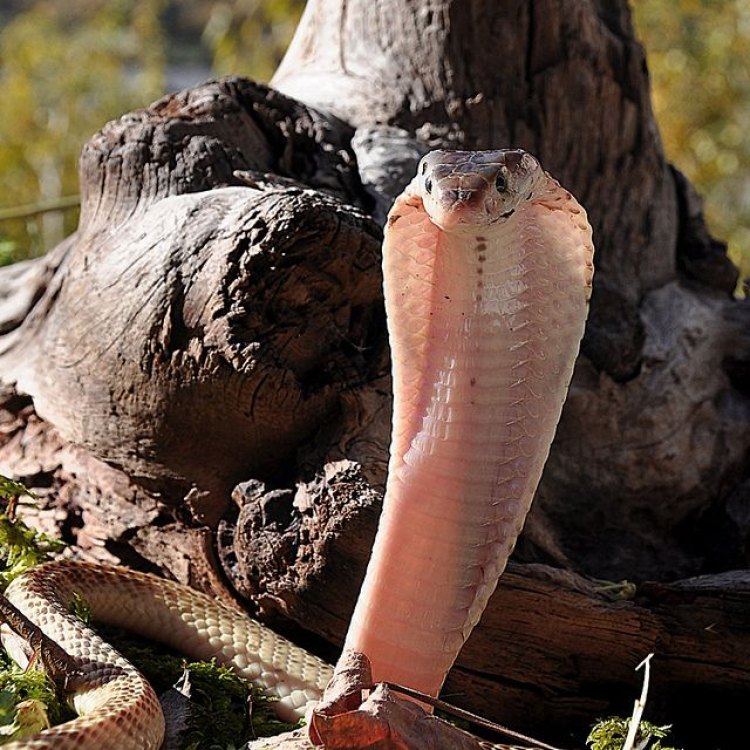

Equatorial Spitting Cobra
Animal Details Equatorial Spitting Cobra - Scientific Name: Naja sumatrana
- Category: Animals E
- Scientific Name: Naja sumatrana
- Common Name: Equatorial Spitting Cobra
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Family: Elapidae
- Habitat: Tropical Rainforests, Swamps, Marshes
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Southeast Asia (Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand)
- Country of Origin: Indonesia
- Location: Sumatra, Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia, Java
- Animal Coloration: Dark brown or black with lighter bands
- Body Shape: Slender and elongated
- Length: 1.5 to 2 meters
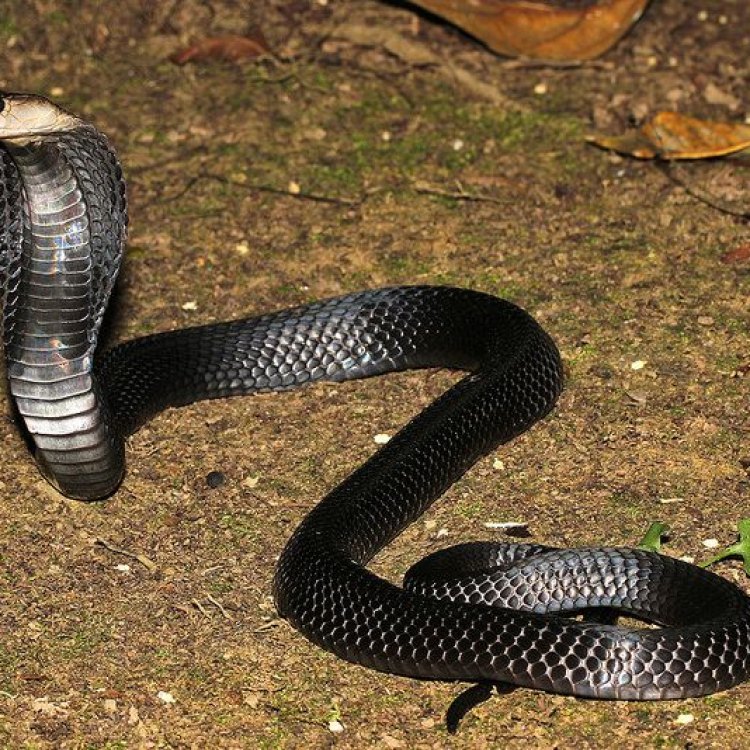

Equatorial Spitting Cobra
- Adult Size: 1.4 to 2 meters
- Average Lifespan: Up to 20 years
- Reproduction: Oviparous (egg-laying)
- Reproductive Behavior: Males fight for breeding rights
- Sound or Call: Hisses and growls
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal, Aggressive when threatened
- Threats: Habitat loss, Illegal wildlife trade, Killing due to fear
- Conservation Status: Vulnerable
- Impact on Ecosystem: Apex predator, helps control prey populations
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Spits venom at threat
- Interesting Facts: Can accurately spit venom up to 2 meters
- Predator: Large predatory birds, snakes
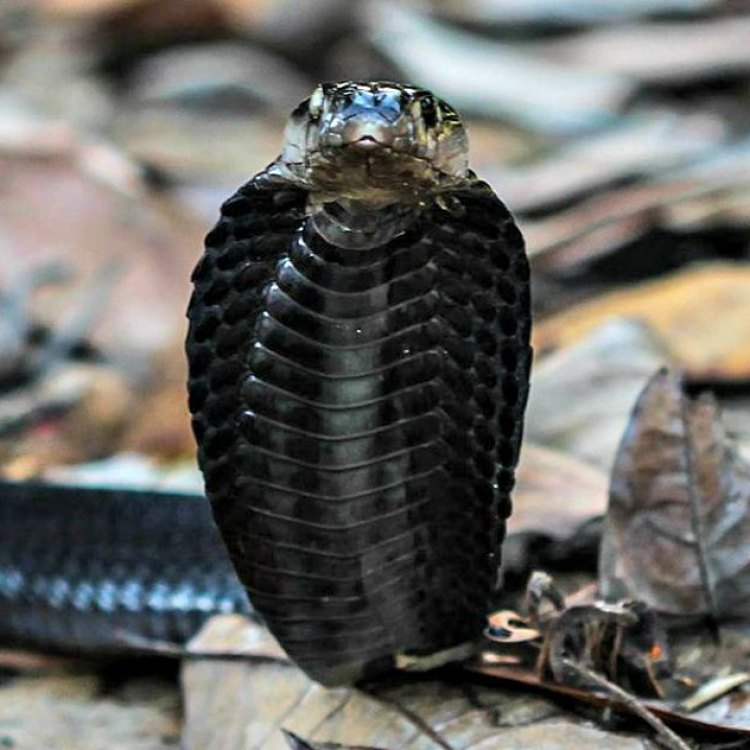

Naja sumatrana
The Mighty Equatorial Spitting Cobra: A Deadly Master of Self-Defense
The equatorial regions of Africa, Asia, and Australia are teeming with a diverse array of wildlife. While many of these species are well-known to the world, there are some that remain elusive and shrouded in mystery. One such creature is the Equatorial Spitting Cobra, a highly venomous and incredibly fascinating snake that is native to these equatorial regions. This article will delve into the unique features and behavior of the Equatorial Spitting Cobra, shedding light on this elusive creature and the vital role it plays in its ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Adult Size and Average Lifespan:
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra, also known as Naja Nivea, is a medium-sized snake that typically grows to 1.4 to 2 meters in length. It has a slender body, with a distinct hood that it expands when threatened. This species' average lifespan is up to 20 years, making it one of the longest-living venomous snakes in the world. With its long and robust life, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra has a significant impact on its environment, being an apex predator that helps maintain balance and control prey populations.
Reproduction and Behavior:
Like many snake species, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra is oviparous, meaning it lays eggs. The female snake can lay up to 15 eggs at a time, and once hatched, the baby snakes are independent and do not rely on their mother for survival. However, this does not mean that these snakes do not engage in social behavior. During breeding season, which typically occurs between April to June, the males will engage in fierce battles for breeding rights with the females Euoplocephalus. This behavior also highlights one of the distinctive features of this species.
Distinctive Features and Self-Defense Mechanism:
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra is known for its ability to accurately spit venom at a threat, making it a formidable predator and self-defense mechanism. This cobra has specialized, grooved fangs that allow it to spray venom up to 2 meters away with pinpoint accuracy. It can also accurately strike and inject venom into its prey when hunting. However, this feature is not only used for hunting and self-defense. The Equatorial Spitting Cobra can also use its venom as a defense mechanism when threatened.
When threatened, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra will first assume a defensive stance, flattening its neck to form its distinctive hood. If the threat persists, it will hiss and growl, signaling that it is ready to attack. If the threat continues to approach, the cobra will forcefully eject its venom towards the threat's eyes, causing severe pain and temporary blindness. While this may seem like a vicious and cruel defense mechanism, it is essential for the survival of this species. In their natural habitat, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra faces many threats, and its venom spit is its only line of defense.
Habitat and Migration Patterns:
The Equatorial Spitting Cobra is known to inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, savannas, grasslands, and even agricultural fields. However, they are particularly fond of bodies of water, such as streams and rivers, where they can hunt for their preferred prey – frogs, toads, and rodents. As a result, they are often found near or in these areas. One interesting fact about these snakes is that they are non-migratory, meaning they do not travel long distances, unlike some of their snake counterparts. They prefer to stay in a relatively small area, making it vital to protect their habitats to ensure their survival.
Threats and Conservation Status:
Like many other species, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra faces numerous threats, primarily due to human activities. Habitat loss is a significant threat to this species as human development continues to encroach on their natural habitats, leaving them with less space to thrive. Additionally, they also face persecution due to fear and illegal wildlife trade. Many people see this snake as a threat, even though it would not attack unless provoked. As a result, many are killed out of fear, which significantly impacts the survival of this species.
Conservation efforts for the Equatorial Spitting Cobra have been minimal, and as a result, this species is currently classified as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. This means that the population of this species is declining, and urgent action is needed to protect and preserve this vital species. If more is not done to protect this snake and its habitat, it may face extinction in the near future, which would have drastic consequences for its ecosystem.
Impact on the Ecosystem:
Despite facing numerous threats, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra plays a critical role in its ecosystem. As an apex predator, it helps control the populations of its prey, preventing overpopulation and maintaining balance in the ecosystem. Additionally, these snakes also serve as a food source for other predators, such as large predatory birds like eagles and other snakes, creating a chain of life that is vital for a healthy ecosystem. It is essential to understand and appreciate the role of this species in its environment to ensure its conservation and survival.
Human Use and Misconceptions:
Interestingly, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra does not have any known use for humans. Unlike other snake species, their venom is not used for medicinal purposes or in traditional practices. However, their venom is used in scientific research to better understand its properties and potential uses. Additionally, as mentioned earlier, these snakes are often perceived as dangerous and aggressive, even though they only attack when provoked. This misconception has resulted in many being killed out of fear, which has contributed to their declining population.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Equatorial Spitting Cobra is a unique and fascinating species that plays a vital role in its ecosystem. From its distinctive features and self-defense mechanisms to its impact on the environment and the threats it faces, this snake is a complex and intriguing creature. As humans, it is our responsibility to protect and preserve the Equatorial Spitting Cobra and its habitat. With conservation efforts and awareness, we can ensure that this remarkable species remains a part of our natural world for generations to come.
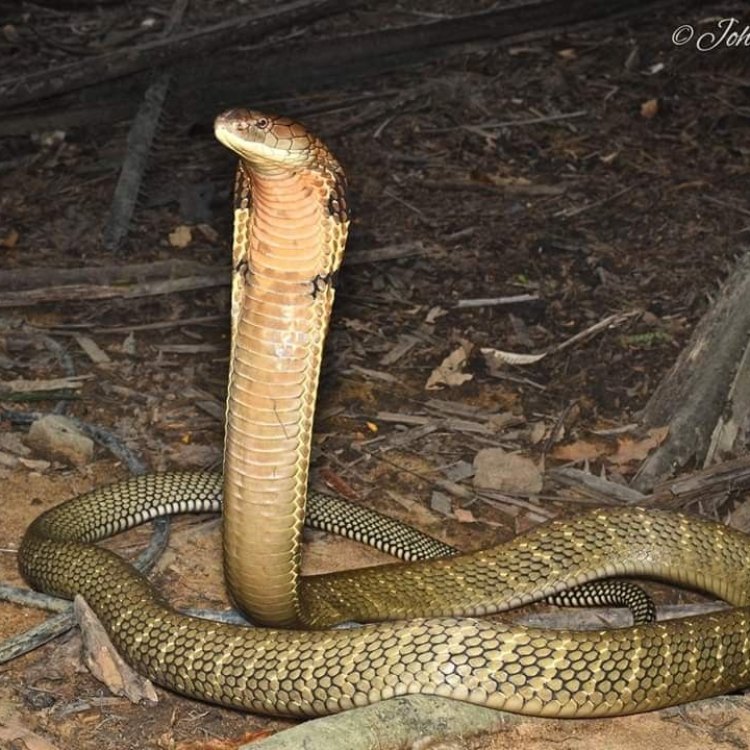

The Equatorial Spitting Cobra: A Tropical Wonderland's Most Dangerous Serpent
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.