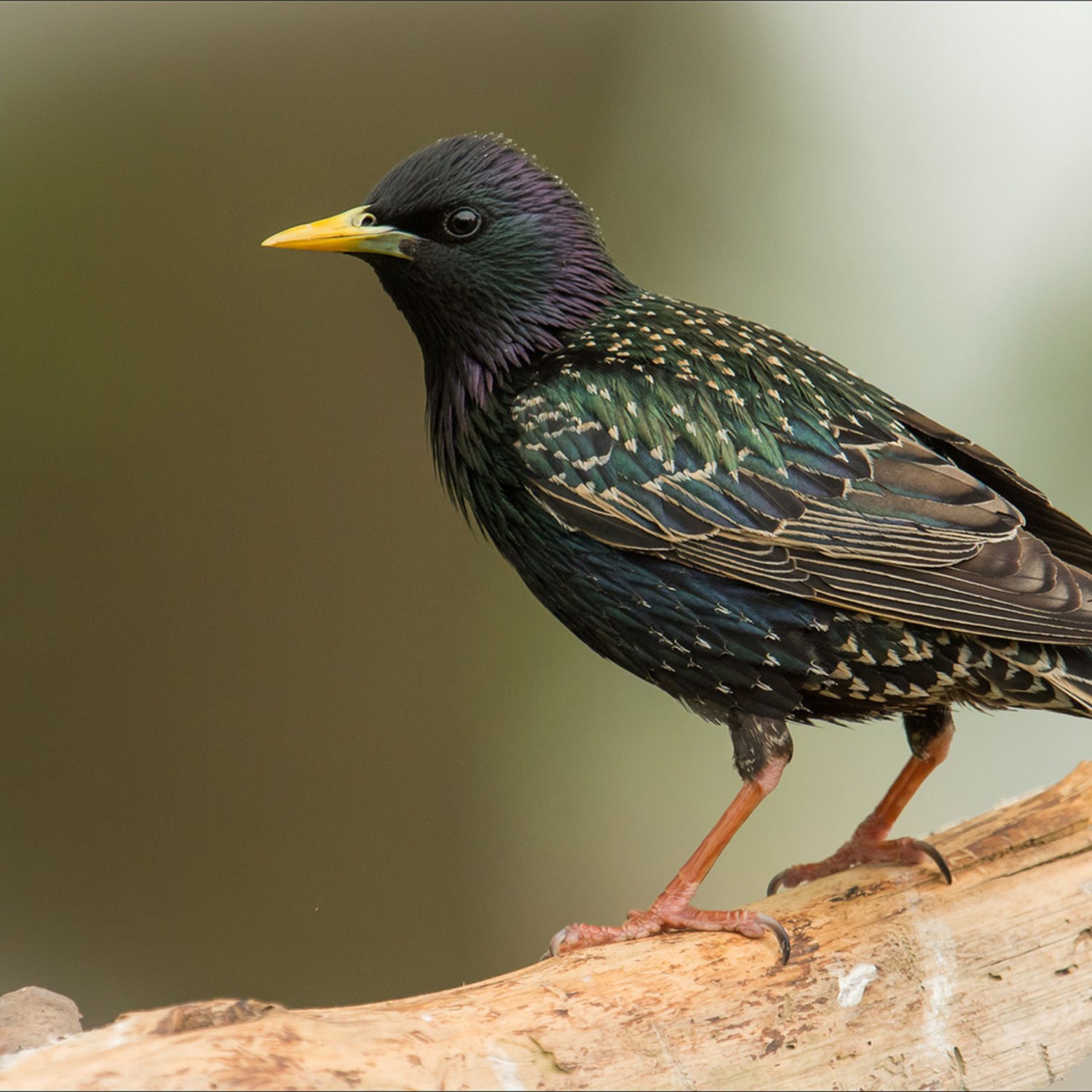
European Starling
19-22 cm
The European Starling is a medium-sized, plump bird found worldwide, belonging to the Sturnidae family. With an average length of 19-22 cm, they are known for their beautiful, iridescent feathers and their melodic song. These birds are highly adaptable and can be found in a variety of habitats, making them a common sight in many countries. However, their population has been declining in some areas due to competition from other invasive species.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: European Starling
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Fields, meadows, open woodlands, farmlands, urban areas
The Phenomenal European Starling: Beauty, Adaptability, and Controversy
Imagine walking through a park or field and suddenly hearing a cacophony of loud, melodic chirping and chattering. Your curiosity leads you to a nearby tree, where you see a large group of birds with sleek black feathers shining in the sunlight. As you get closer, you notice their striking green and purple sheen and realize that you are in the presence of European Starlings.These small to medium-sized birds may seem common and unremarkable at first glance, but upon closer inspection, they reveal a world of fascinating characteristics that have made them both cherished and despised by humans European Starling. From their widespread adaptability to their vibrant coloration, the European Starling has proven to be an intriguing and highly complex creature.
Origins and Distribution
The European Starling, scientifically known as Sturnus vulgaris, has been a part of human history for centuries. Its name is derived from the Latin word "sturnus," which means starling, and the adjective "vulgaris," which means common. Originally native to Europe, these birds were introduced to North America, Australia, and New Zealand in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and have since spread to other parts of the world.Their introduction was controversial and highly debated, as these birds were considered to be a threat to agricultural crops and local bird populations. However, their adaptability and tenacity have enabled them to thrive in their new environments and become one of the most numerous birds in the world.
Today, European Starlings can be found almost everywhere in the world, with the exception of the Arctic and Antarctica. They have become a common sight in fields, meadows, open woodlands, farmlands, and even urban areas, making them highly adaptable and versatile creatures.
Physical Characteristics
At first glance, European Starlings may seem like ordinary black birds, but their appearance holds subtle yet remarkable details that set them apart from other species Eastern Indigo Snake. Their feathers have an iridescent quality, giving off shades of green and purple when exposed to light. This striking coloration is more prominent in males, whose feathers have a glossy, metallic sheen.Their body shape is medium-sized and plump, with a rounded head and a short tail. They have long, pointed wings and a slightly curved bill, which they use for foraging and probing the ground for food. Their size typically ranges from 19 to 22 cm, making them relatively small birds compared to other species.
Feeding and Habitat
One of the reasons for the success and widespread distribution of European Starlings is their omnivorous diet. They have versatile feeding habits and can consume a variety of food sources, including insects, fruits, seeds, and grains. In urban areas, they can also feed on scraps and trash, making them scavengers as well.Their adaptable nature extends to their habitat as well. They can be found in a range of environments, from open fields and meadows to man-made structures, such as buildings and bridges. They are social birds and can often be seen in large flocks, especially during the winter when they congregate in roosting sites to keep warm.
The Controversy and Impact
Despite their adaptability and widespread distribution, European Starlings are also the subject of intense scrutiny and even hatred in some parts of the world. As mentioned earlier, their introduction to non-native regions has caused a significant impact on agricultural crops and local bird populations.In the United States, they are considered an invasive species and are listed as a pest in many areas. Their large numbers and competitive nature have led to the decline of native bird species, and they are often seen as a threat to agricultural and economic interests. Some measures have been taken to control their population, including shooting and nest removal, but these methods have proven to be inefficient in the long term.
On the other hand, in their native Europe, European Starlings are celebrated and cherished for their beauty and intelligence. They are a common sight in gardens and parks, and their cheerful songs and acrobatic flights make them popular among bird watchers and enthusiasts.
Intelligence and Abilities
European Starlings possess remarkable intelligence and impressive skills that have contributed to their successful existence. They are social birds and have intricate communication systems that involve various vocalizations and gestures. They are also capable of mimicking sounds and songs of other birds and even human speech.One of their most impressive abilities is their capacity for problem-solving and learning new skills. In urban areas, they have been observed using their beaks to open trash cans and even turning off lights by pulling on the wires. These clever behaviors show their ability to adapt and survive in human-dominated environments.
Conservation Efforts
Despite their controversial status in some parts of the world, there have been efforts to conserve and protect European Starlings. In their native Europe, they are still considered a common and widespread species. However, in the UK, their numbers have declined significantly in recent years, causing concern for their conservation.Conservation groups and organizations are working to raise awareness about these birds and their ecological importance. Some efforts have also been made to study their behavior and develop more efficient measures for controlling their population without negatively impacting other species.
Conclusion
The European Starling is a remarkable bird with a complex and controversial history. From their origins in Europe to their global distribution, they have proven to be highly adaptable and resilient creatures. Their striking coloration, intellect, and adaptability have both captivated and divided humans, making them a fascinating topic of study and observation.Despite their controversial status, it is undeniable that European Starlings are extraordinary creatures with unique traits that have enabled them to thrive in various environments. As we continue to coexist with these birds, it is essential to strike a balance between conservation efforts and managing their impact, ensuring the protection of both their species and the ecosystem they are a part of.
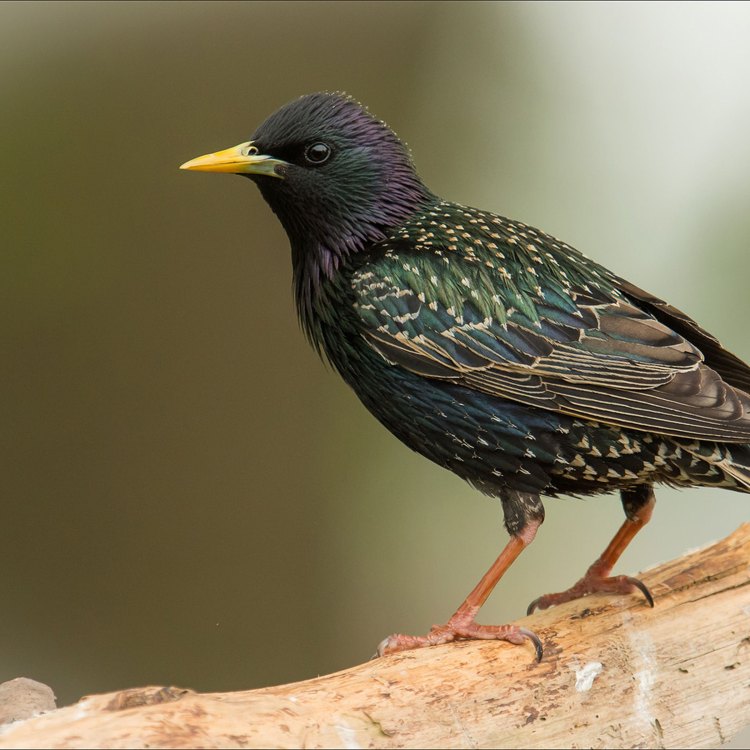

European Starling
Animal Details European Starling - Scientific Name: Sturnus vulgaris
- Category: Animals E
- Scientific Name: Sturnus vulgaris
- Common Name: European Starling
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Passeriformes
- Family: Sturnidae
- Habitat: Fields, meadows, open woodlands, farmlands, urban areas
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, North America, Australia, New Zealand
- Country of Origin: Europe
- Location: Worldwide
- Animal Coloration: Black with iridescent green and purple
- Body Shape: Medium-sized, plump
- Length: 19-22 cm
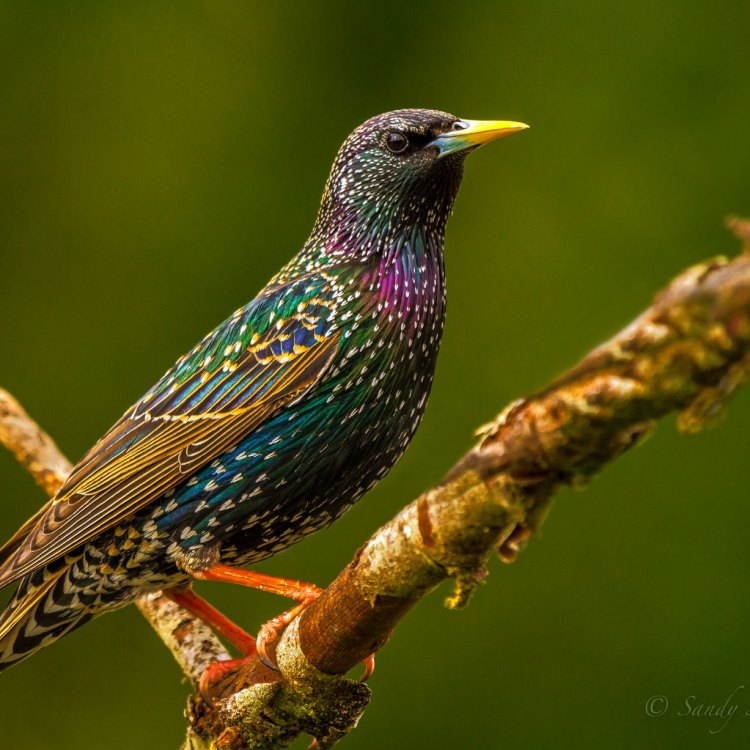

European Starling
- Adult Size: Small to medium
- Average Lifespan: 2-5 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Monogamous
- Sound or Call: Mimics various sounds, including other bird calls
- Migration Pattern: Boreal or partial migrant
- Social Groups: Flocks
- Behavior: Highly social, often forms large flocks
- Threats: Habitat loss, predators, diseases
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Competes with native bird species for nesting sites and food
- Human Use: Introduced to North America for insect control
- Distinctive Features: Sleek black plumage with metallic sheen
- Interesting Facts: Can mimic human speech, one of the most abundant bird species in North America
- Predator: Birds of prey, mammals
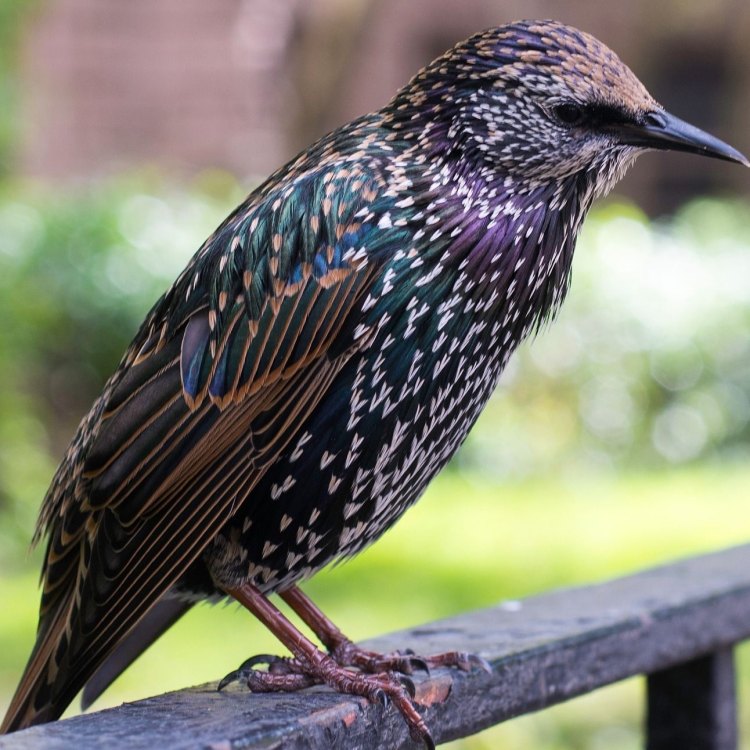

Sturnus vulgaris
The European Starling: A Mimic and Competitor in the Avian World
When one thinks of birds, the majestic eagle or the colorful peacock may come to mind. But there is one bird that often goes unnoticed, despite its abundance and unique characteristics - the European Starling.Native to Europe, Asia, and North Africa, the European Starling belongs to the family of Sturnidae, which includes over 100 species of starlings, mynas, and other birds. Its scientific name, Sturnus vulgaris, translates to "common starling," reflecting its widespread presence in many parts of the world PeaceOfAnimals.Com.
But what makes the European Starling stand out from other bird species? Let's delve deeper into its distinctive features, behavior, and impact on the ecosystem.
A Sleek, Metallic Appearance
At first glance, the European Starling may seem like an ordinary, small to medium sized bird. But upon closer observation, its plumage will catch your eye. Its sleek black feathers are adorned with a metallic sheen, giving it a stunning appearance. The effect is most noticeable in the sunlight, when the bird's feathers reflect various shades of purple, green, and blue.This metallic appearance is due to the arrangement of the starling's feathers, which creates an optical illusion when light bounces off them. Interestingly, the color of the starling's plumage varies depending on the time of year. During breeding season, the male starlings' feathers take on a glossy iridescence, while non-breeding males and females have a more matt appearance.
Mimicry and Communication
One of the most fascinating features of the European Starling is its ability to mimic various sounds, including other bird calls Electric Eel. In fact, they are known for their incredible vocal skills and can imitate almost any sound they hear. This includes human speech, which has earned them the nickname "feathered mimics."This mimicry serves several purposes for the starlings. They use it to attract mates, communicate with their flock members, and defend their territory. Some starlings have even been observed mimicking the sound of another bird species to trick their predators.
But why do starlings mimic other birds? It is believed that this behavior evolved as a defense mechanism against predators. By imitating the calls of other bird species, the starlings confuse their predators and make it difficult for them to identify the bird's exact location.
Monogamous Reproduction and Social Behavior
The reproductive behavior of European Starlings is quite unique. They are monogamous, meaning that they mate for life with one partner. Each spring, the mating pairs build their nest together, usually in tree cavities, but also in crevices of buildings or other structures.During the breeding season, male starlings perform elaborate displays to attract female starlings. These displays involve spreading their wings and feathers, bobbing their head, and singing loudly. Once the pair has bonded, they will work together to raise their young, which typically consists of 4-6 eggs.
Despite being monogamous, European Starlings are highly social birds. They often form large flocks, especially during the non-breeding season. These flocks can consist of thousands of starlings, and their synchronized movements and murmurations are a sight to behold. These large flocks provide protection against predators and also help the starlings find food more easily.
A Boreal Migrant
Unlike many bird species that migrate long distances, European Starlings are considered as either partial or boreal migrants, meaning they only migrate short distances. In areas with colder climates, they will migrate to more temperate regions for the winter, while those in milder climates will only move a short distance from their breeding grounds.Interestingly, the time of the starlings' migration can vary by location. In some areas, they may start migrating as early as August, while in others, they may not migrate until November. This ability to adapt their migration patterns makes them well-suited to different environments.
Impact on the Ecosystem
As with any other species, the European Starling has its role to play in the ecosystem. However, since it is an introduced species in many parts of the world, its impact on the environment is a subject of ongoing debate.In North America, the European Starling was introduced in the late 1800s by a group called the American Acclimatization Society. The society believed that introducing the starling would help control insect pests and benefit agriculture. While this may have been the intention, the consequences have been quite different.
Due to its adaptable nature and aggressive behavior, the starling has become one of the most abundant bird species in North America, with a population estimated to be over 200 million. However, this comes at a cost. The starlings compete with native bird species for nesting sites and food, causing a decline in their populations.
Moreover, the starling's fondness for fruits and grains has made it a nuisance for farmers, who often see their crops destroyed by large flocks of the birds. In addition, its large flocks and droppings can also damage buildings and pose sanitation issues.
Human Use and Conservation Status
Interestingly, the European Starling's introduction to North America has had some positive impacts as well. It has been noted that the presence of starlings has reduced the spread of some harmful insect species, such as the gypsy moth and the Japanese beetle. This has indirectly benefited native bird species, which feed on these insects.In Europe, where the starling is native, it has served as a source of food for humans for centuries. In early times, starlings were even kept as pets because of their ability to mimic human speech. Nowadays, they are mostly considered a game bird and are a popular dish in many European countries.
Despite the impact it has had on the ecosystem, the European Starling is not considered endangered or threatened. In fact, its conservation status is listed as "Least Concern" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is due to its large and stable population and ability to adapt to different environments.
Threats and Predators
However, the European Starling is still facing various threats to its survival. The destruction of its natural habitat due to urbanization and agricultural expansion is a significant concern. In addition, the use of pesticides and other chemicals in agriculture can poison the starlings and reduce their food supply.Like most bird species, the European Starling also faces threats from predators. Birds of prey, such as hawks and falcons, are their main natural predators. However, mammalian predators, such as raccoons and squirrels, have also been known to prey on their eggs and young.
In Conclusion
The European Starling may not have the striking appearance of some other bird species, but its unique features and behavior make it a fascinating creature. Whether mimicking other birds or competing with them for resources, the starling has adapted to its surroundings over time, highlighting its incredible resilience.While its introduction to North America has had consequences on the ecosystem, it also serves as a reminder of the impact human actions can have on the environment. As we continue to find ways to coexist with the starling and other species, let's also strive to protect and preserve their natural habitats for the well-being of all.
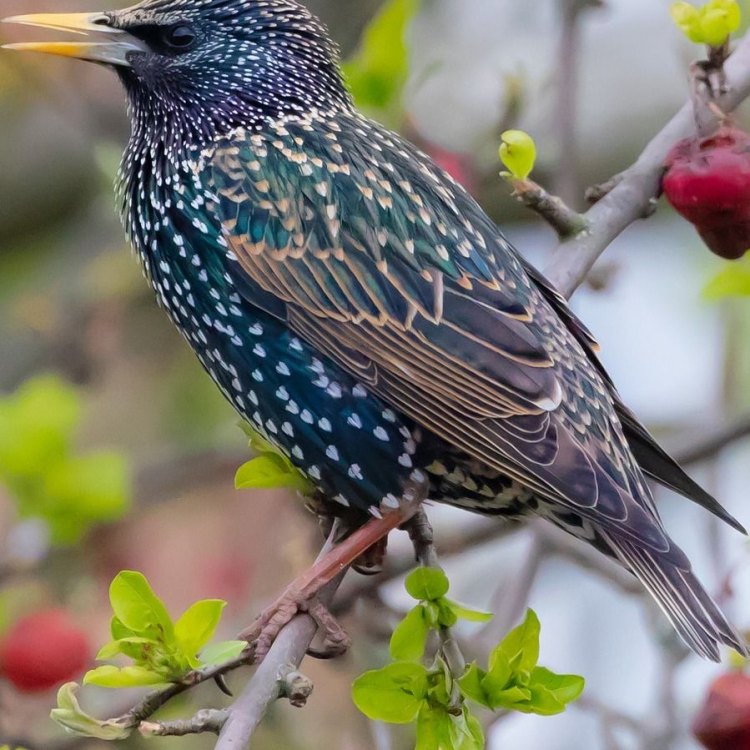

The Phenomenal European Starling: Beauty, Adaptability, and Controversy
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.