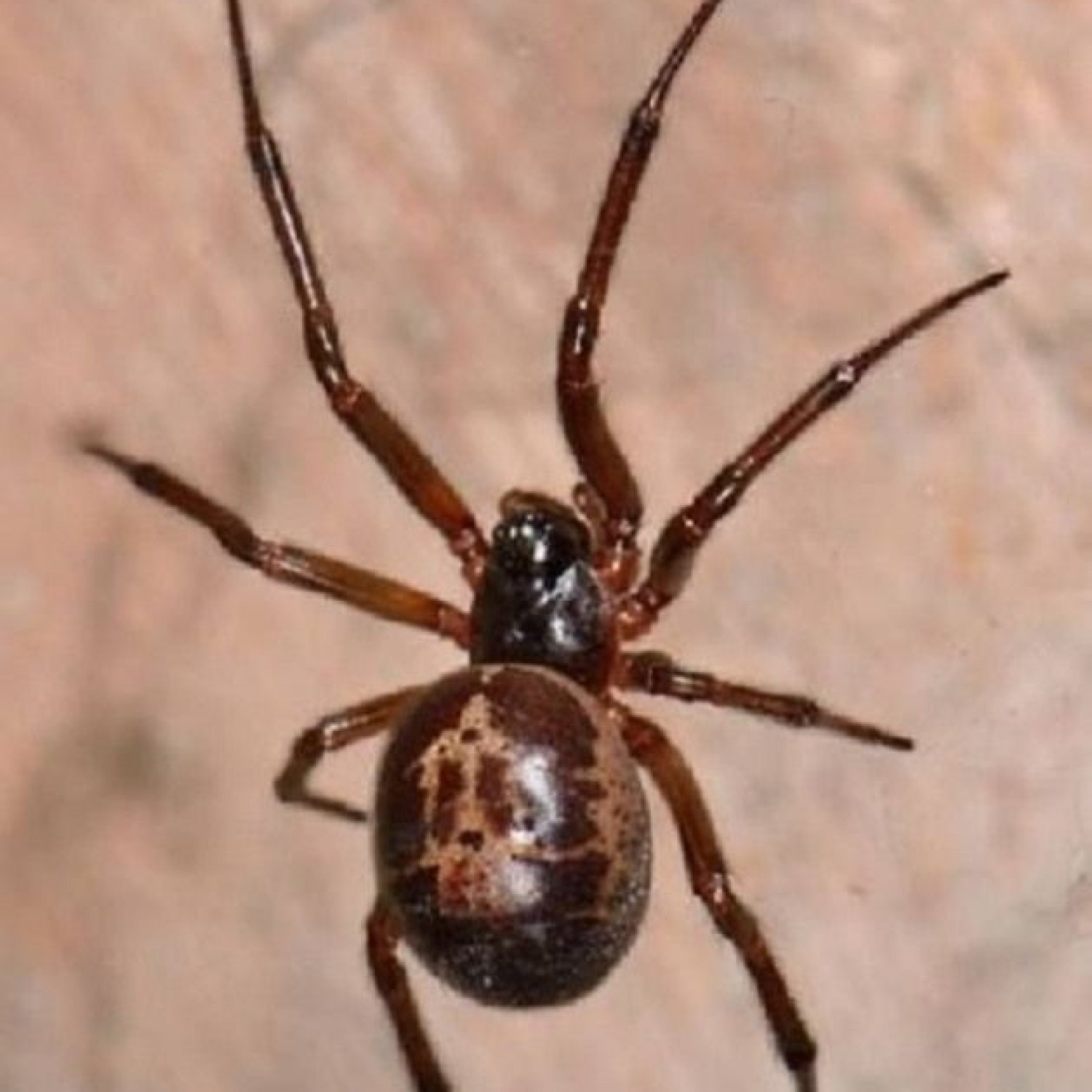
False Widow Spider
10 - 15 mm
The False Widow Spider, found worldwide, can grow to 10-15mm in length and is part of the Theridiidae family. Known for its medium-sized, round abdomen and long legs, it can be found both indoors and outdoors. Despite its name, this spider's bite is usually mild and rarely causes serious harm to humans. #FauxSpiderFacts
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: False Widow Spider
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Urban areas, gardens, woodland, fields
The Fascinating World of the False Widow Spider
Among the many creatures that roam the earth, few are as misunderstood and feared as spiders. Oftentimes, the mere mention of their name is enough to send shivers down our spines. However, not all spiders are dangerous, venomous killers. In fact, some are fascinating creatures that play a crucial role in our ecosystem False Widow Spider. One such spider is the False Widow Spider, scientifically known as Steatoda.Kingdom: Animalia
False Widow Spiders belong to the Kingdom Animalia, the largest and most diverse group of organisms on our planet. They are part of the animal family, alongside creatures such as mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects.Phylum: Arthropoda
Within the Animal Kingdom, False Widow Spiders fall under the Phylum Arthropoda. This is a group of animals that are characterized by their segmented bodies, jointed limbs, and external skeletons. Examples of other arthropods include crabs, lobsters, and insects.Class: Arachnida
The Class Arachnida comprises creatures with eight legs, simple eyes, and no antennae. In addition to spiders, this class also includes scorpions, ticks, and mites.Order: Araneae
False Widow Spiders are part of the Order Araneae, which encompasses all types of spiders Field Cuckoo Bumblebee. This order is distinguished by the presence of two body segments (cephalothorax and abdomen) and six to eight eyes.Family: Theridiidae
The False Widow Spider belongs to the Theridiidae family, commonly known as comb-footed spiders. This family includes over 2,000 species, with the False Widow Spider being one of the most well-known.Habitat and Distribution
The False Widow Spider is a cosmopolitan species. This means that it can be found all over the world, including Europe, North America, Africa, and Asia. However, its country of origin is England. They have spread to other parts of the world through human activities, such as trade and transportation.In terms of habitat, these spiders are incredibly adaptable. They can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, gardens, woodland, and fields. They are also known to make their homes indoors, in sheds, garages, and other dark, enclosed spaces.
Feeding Habits
False Widow Spiders are predators, meaning that they hunt and eat other living things. They primarily feed on insects, but they have been known to catch and consume larger prey, such as other spiders and even small lizards. Despite their reputation as venomous killers, their bites are not typically fatal to humans and are only used to immobilize their prey.Appearance and Characteristics
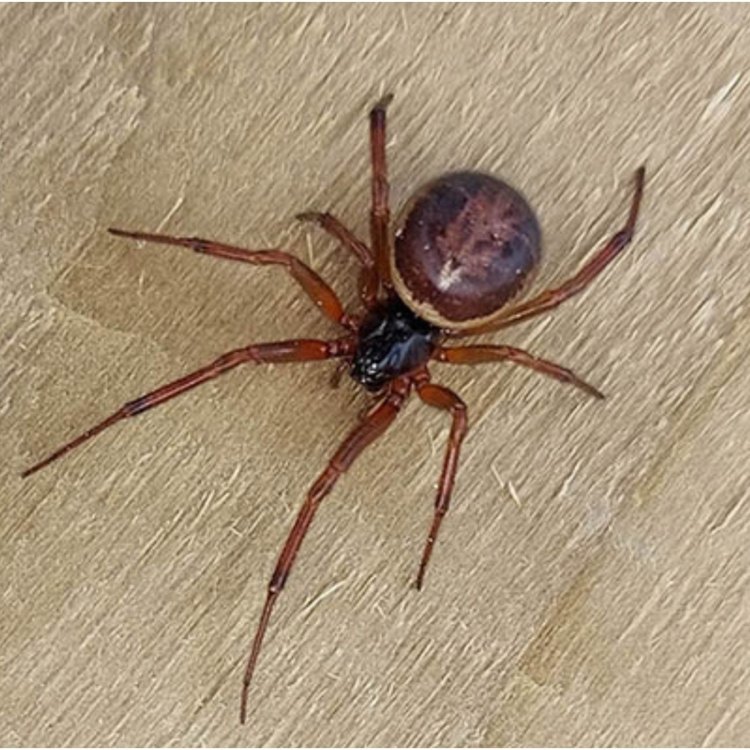
One of the most distinctive features of the False Widow Spider is its coloration. They are typically dark brown to black, with cream-colored markings on their abdomens. These markings are often in the shape of an hourglass or skull, contributing to their fearsome reputation. However, not all False Widow Spiders have these markings, and some may have a completely black or brown body.In terms of body shape, False Widow Spiders are medium-sized and have a round abdomen. Their legs are long and slender, giving them an intimidating appearance. On average, these spiders range from 10 to 15 mm in length, with females being slightly larger than males.
Myths and Misconceptions
The False Widow Spider has gained a notorious reputation as one of the most venomous spiders in the UK. However, this is not entirely accurate. While they do possess venom, it is not considered dangerous to humans. Venom is a means of protection and is only used by these spiders when they feel threatened. Most bites from False Widow Spiders result in minor irritation and swelling, similar to a bee sting.Another common misconception is that these spiders are aggressive and will attack humans. In reality, they are quite shy and will only bite as a last resort. Like most spiders, they prefer to avoid human contact and will only bite if provoked or accidentally trapped against the skin.
The Importance of False Widow Spiders
Despite their fearsome appearance and reputation, False Widow Spiders play a crucial role in our ecosystem. As predators, they help control the population of insects, including pests that can damage crops and spread diseases. In this way, they are beneficial to humans and the environment.The Rise of the False Widow Spider
Over the past few years, there has been a noticeable increase in False Widow Spider sightings in the UK. This has led to much concern and fear among the public, with many believing that these spiders are multiplying at an alarming rate. However, this is not entirely accurate.The increase in False Widow Spider sightings can be attributed to a change in their behavior. These spiders have adapted to urban environments and are now commonly found in areas with human activity. This includes homes, gardens, and buildings. Previously, they were more prevalent in rural areas, where they would live in sheds and barns.
Dealing with False Widow Spiders
While False Widow Spiders are not as dangerous as they are often portrayed, it is still important to take precautions when dealing with them, especially if you have children or pets. Here are some tips for managing False Widow Spiders in your home and garden:- Seal any cracks and crevices in your home to prevent spiders from entering.
- Keep your home clean and clutter-free, as spiders are attracted to dark, cluttered spaces.
- Regularly dust and vacuum to remove spiders and their webs.
- If you find a False Widow Spider indoors, carefully remove it using a glass and piece of paper, then release it outside.
- When working in the garden, wear gloves to avoid accidental bites from spiders.
- If you are concerned about potential spider bites, seek medical advice.
The Power of Perception
The False Widow Spider is a prime example of how perception can shape our understanding and attitudes towards a particular species. While they may appear intimidating and fearsome, they are an essential part of our ecosystem and play a valuable role in maintaining a balance in nature. By educating ourselves and breaking free from misconceptions and stereotypes, we can learn to coexist with the creatures that share our planet. So the next time you come across a False Widow Spider, take a moment to appreciate its fascinating features and remember that it is just as much a part of this world as we are.
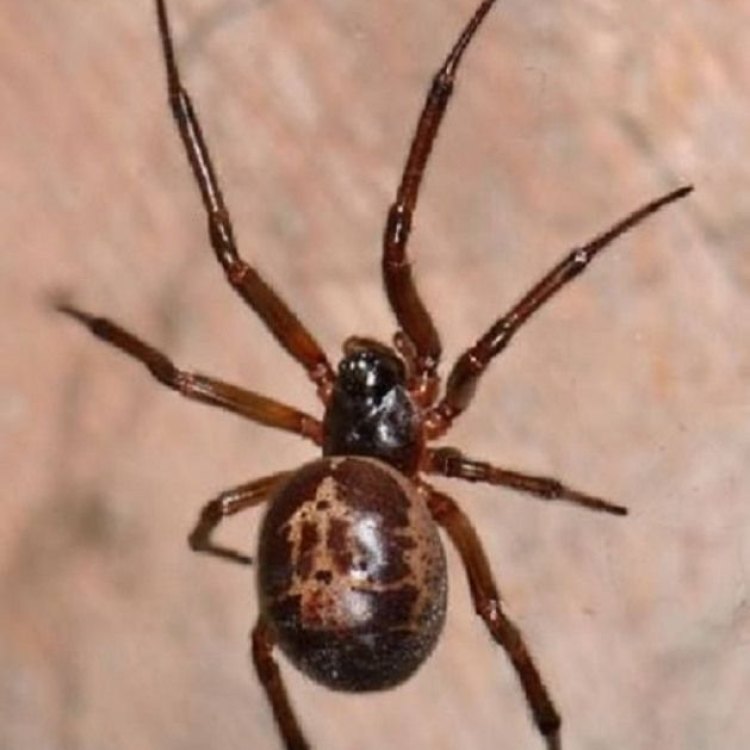

False Widow Spider
Animal Details False Widow Spider - Scientific Name: Steatoda
- Category: Animals F
- Scientific Name: Steatoda
- Common Name: False Widow Spider
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Arachnida
- Order: Araneae
- Family: Theridiidae
- Habitat: Urban areas, gardens, woodland, fields
- Feeding Method: Predator
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, North America, Africa, Asia
- Country of Origin: England
- Location: Indoors, outdoors
- Animal Coloration: Dark brown to black with cream-colored markings
- Body Shape: Medium-sized, round abdomen, long legs
- Length: 10 - 15 mm
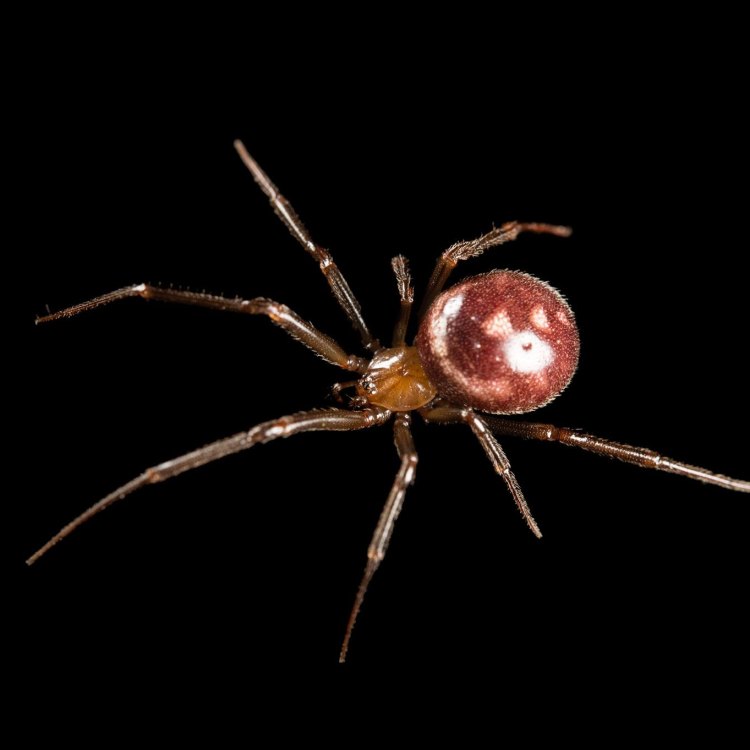

False Widow Spider
- Adult Size: 15 - 20 mm
- Average Lifespan: 1 - 3 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males perform courtship rituals before mating
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal, builds tangled webs in dark corners
- Threats: Human fear and persecution
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Predator of insects
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Distinctive cream-colored markings on abdomen
- Interesting Facts: Can deliver a painful bite, but usually not life-threatening
- Predator: Birds, other spiders

Steatoda
The Fascinating World of the False Widow Spider: A Unique and Misunderstood Arachnid
Tucked away in the shadows, weaving intricate webs in the dark corners of our world, is a creature that elicits fear and fascination – the False Widow spider. While its name may evoke images of dangerous and deadly spiders, the reality is quite different. These small but mighty arachnids offer a unique and intriguing glimpse into the world of spiders.So, who exactly are the False Widow spiders, and why are they causing such a stir? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of these misunderstood creatures and uncover their unique features and attributes PeaceOfAnimals.Com.
The Basics: Size, Lifespan, and Reproduction
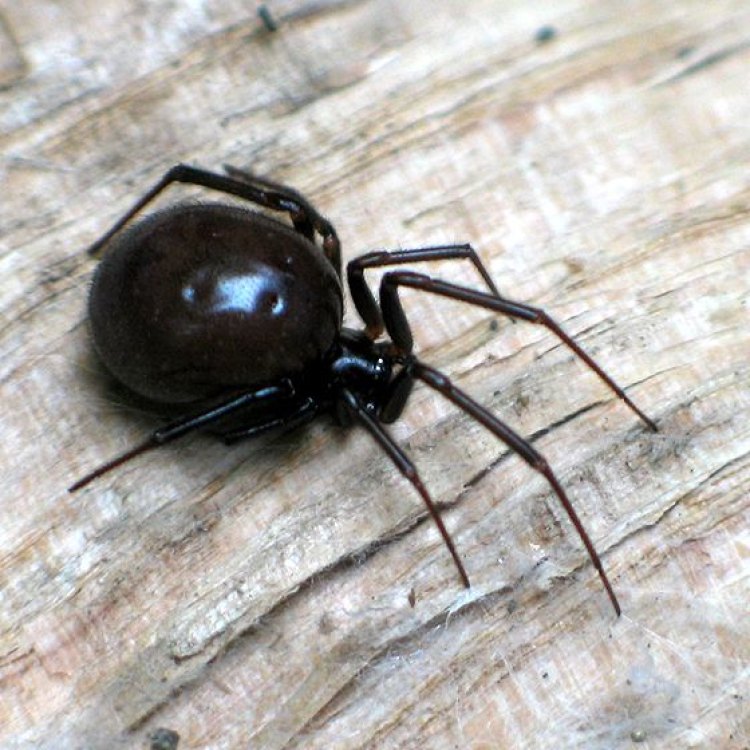
The False Widow spider, also known as Steatoda nobilis, is a species of spider that belongs to the Theridiidae family. They are found in various parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. While there are over 1,100 known species of False Widow spiders, the most notorious ones are the black widow look-alikes found in Europe and North America.As adults, the False Widow spider can reach a size of 15-20 millimeters, which is smaller than a typical house spider. They have a dark brown body with distinctive cream-colored markings on their abdomen, which makes them easily identifiable. However, these markings are not always present, and some individuals may have an all-brown appearance.
On average, False Widow spiders have a lifespan of 1-3 years, which is relatively long compared to other spider species. Interestingly, their reproductive behavior is sexual, with males performing elaborate courtship rituals before mating. Once the eggs are fertilized, the female will typically lay them in a sac or wrap them in silk to protect them until they hatch Field Spaniel.
Behavior and Social Groups
False Widow spiders are creatures of the night and are mostly active during the night. They are solitary creatures and do not exhibit any social behaviors or form groups like other spiders. Instead, they prefer to live alone, hiding and building their tangled webs in dark corners in human-made structures or outdoors.While some spider species migrate to search for food or more suitable habitats, False Widow spiders are non-migratory. They stay in one location throughout their lifespan, unless disturbed or threatened.
Interestingly, False Widow spiders do not make any sound or call, making them a silent predator. They rely on their keen senses to capture their prey, which includes insects such as moths, flies, and beetles.
Threats and Conservation Status
When talking about False Widow spiders, it’s impossible not to mention the fear they strike in humans. Their dark brown color, sharp fangs, and association with the notorious black widow spider often lead to myths and misconceptions. However, the truth is that False Widow spiders are not aggressive towards humans and will only bite if provoked.Their bites are known to be painful and may cause swelling and irritation, but they are rarely life-threatening. It is also worth noting that False Widow spiders have venom, but it is much less potent compared to black widow spiders, making them less dangerous to humans.
Unfortunately, due to this fear and persecution, False Widow spiders have gained a reputation as a dangerous and deadly species, leading to their conservation status not being evaluated. However, it's essential to understand that these spiders play a vital role in our ecosystem as predators of insects. Without them, there could be an overabundance of pests and insects, which could have a detrimental impact on our environment and agriculture.
Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts
Apart from their distinctive markings and behavior, there are a few other notable features that make False Widow spiders unique. As mentioned earlier, they are often confused with black widow spiders due to their appearance, but there are some distinct differences. False Widow spiders have a larger abdomen and smaller legs compared to black widows. They also lack the characteristic hourglass-shaped red markings found on the underside of black widow spiders.In addition, False Widow spiders are skilled builders and use their web to capture prey and protect their eggs. Unlike other spiders that use their web to catch insects, False Widow spiders use it as a barrier, creating a tangled and messy web that can deter predators. They also have a natural oil-based layer on their bodies that makes them almost waterproof, ensuring that their web stays intact during rain or wind.
Interestingly, False Widow spiders also possess a unique ability to reset their body clocks, allowing them to adapt to the changing daylight hours. This is especially useful for spiders that live in urban areas, where artificial lights can disrupt their natural body rhythms.
Predators and Human Use
Given their small size and ability to hide and blend in with their surroundings, False Widow spiders are preyed upon by various predators. Some of their natural predators include birds, lizards, and other spider species. They are also known to engage in cannibalism, with larger spiders preying on smaller ones.While False Widow spiders do not have any known benefits for humans, their venom has been studied for potential use in medicine. It has been found to contain proteins that could potentially be used to treat blood clots and high blood pressure. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential medical benefits of False Widow spider venom.
Unraveling the Mysteries of the False Widow Spider
As we have discovered, False Widow spiders are unique and fascinating creatures that have been wrongly portrayed as dangerous and deadly. With their distinctive features, behavior, and abilities, they offer a glimpse into the peculiar world of spiders, and their presence is beneficial for maintaining a balanced ecosystem.So, the next time you spot a False Widow spider spinning its tangled web in the corner of your room, don’t be quick to squash it out of fear. Instead, take a moment to appreciate its beauty and important role in our environment. By understanding and respecting these creatures, we can coexist with them peacefully, without the need for unnecessary fear or persecution.

The Fascinating World of the False Widow Spider
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.