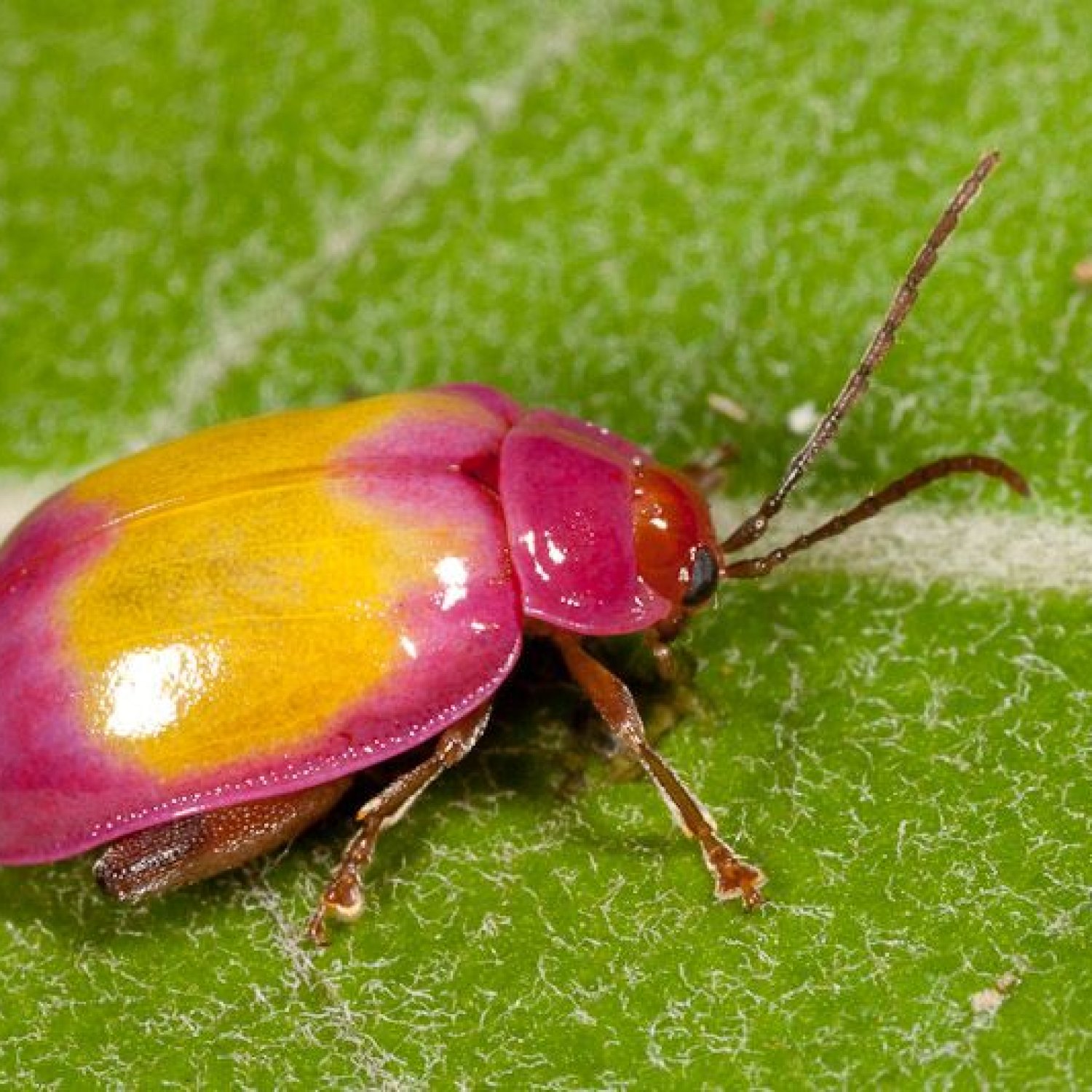
Flea Beetle
2-10 mm
Flea Beetles are small, oval-shaped insects that belong to the Chrysomelidae family. Ranging from 2 to 10 mm in length, they can be found in various regions. These pesky insects are known for their jumping abilities and can damage crops and plants. Protect your garden by keeping an eye out for these tiny pests! #pestcontrol #garden #insects
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Flea Beetle
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Grasslands, meadows, gardens, and agricultural fields
The Incredible Flea Beetle: A Tiny Insect with Mighty Capabilities
Have you ever seen a beetle that jumps like a flea? Meet the flea beetle, an insect so small and yet so impressive in its abilities. Scientifically known as Altica spp., this tiny creature belongs to the Animalia kingdom and the Arthropoda phylum. With its unique physical appearance and incredible features, the flea beetle has captured the fascination of entomologists and gardeners alike Flea Beetle.The flea beetle is commonly known as the flea beetle, but it goes by several other names as well, such as chrysomelid beetle, jumping beetle, and leaf beetle. It belongs to the insecta class and the coleoptera order, which includes all the beetles in the world. It is part of the chrysomelidae family, which includes over 37,000 species of beetles and is considered one of the most diverse beetle groups in the world.
These tiny insects have a widespread habitat, making them one of the most common insects in the world. They can be found in various regions, including grasslands, meadows, gardens, and agricultural fields. There is no specific country of origin for the flea beetle as it is found all over the world, making it a truly cosmopolitan insect.
One of the most fascinating things about the flea beetle is its feeding method. These tiny creatures are herbivorous, meaning they feed on plants. They may be small, but they have a big appetite, and their feeding habits can cause significant damage to crops and plants Florida Panther. They are particularly drawn to members of the nightshade family, such as tomatoes, eggplants, and potatoes.
Unlike other beetles that have large mandibles for chewing, the flea beetle has small, sharp mouthparts. They use these pointy mandibles to feed on leaves, causing small, round holes in them. While these holes do not significantly harm the plants, the combined damage from a large number of flea beetles can be detrimental to crops and gardens.
The flea beetle's most unique and remarkable feature is its ability to jump like a flea. Despite its small size, it has powerful hind legs that allow it to jump up to 30 times its body length. This incredible jumping ability is what gives the insect its common name, the flea beetle. These jumps are not only for show but also serve as an escape mechanism when it feels threatened.
The flea beetle is known for its beautiful and vibrant coloration. They come in a variety of shades, including green, blue, black, brown, and metallic. These radiant colors serve as a warning to predators, indicating that they are toxic and should not be eaten. Some species of flea beetles also have unique patterns on their wings, making them even more visually appealing.
In terms of physical attributes, the flea beetle has a small, oval-shaped body that measures between 2-10 mm in length. The body is divided into three distinct parts, the head, thorax, and abdomen. The head houses the beetle's eyes, antennae, and mouthparts, while the thorax contains the legs and wings. The abdomen is where the insect's digestive and reproductive organs are located.
Being a small and delicate insect, the flea beetle has several natural predators, including birds, spiders, and other insects. However, it has developed some remarkable defense mechanisms to protect itself from these predators. The most common defense mechanism is to jump away from danger, aided by its powerful hind legs. They are also known to produce a foul odor when threatened, further deterring predators.
The flea beetle also has a unique way of reproducing. The female flea beetle lays her eggs in the soil surrounding host plants, and the larvae emerge in just a few days. These larvae then feed on the plant roots before turning into pupae. Once they reach the pupal stage, they remain in the soil until they emerge as adults. The life cycle of the flea beetle can vary from a few weeks to several months, depending on the species and the environment.
Being a small but mighty insect, the flea beetle has caught the attention of scientists and researchers, particularly those interested in Natural Language Processing (NLP). By studying its physical attributes, behaviors, and interactions with its environment, researchers can gain valuable insights into the natural world. The study of the flea beetle can also help in understanding larger processes, such as evolution and ecology.
In addition to the scientific community, flea beetles have also captured the interest of gardeners and farmers. These tiny insects can cause significant damage to crops and plants, leading to economic losses. As a result, there have been various efforts to control flea beetle populations through the use of pesticides or natural predators, such as parasitic wasps.
In conclusion, the flea beetle may be small, but it is a true powerhouse in the insect world. Its ability to jump, its beautiful coloration, and its unique defense mechanisms make it a fascinating and impressive creature. As scientists continue to study this tiny insect, we can only hope to uncover more of its amazing capabilities and contributions to the natural world. So, the next time you come across a tiny, jumping beetle, take a moment to appreciate the incredible flea beetle and its mighty powers.
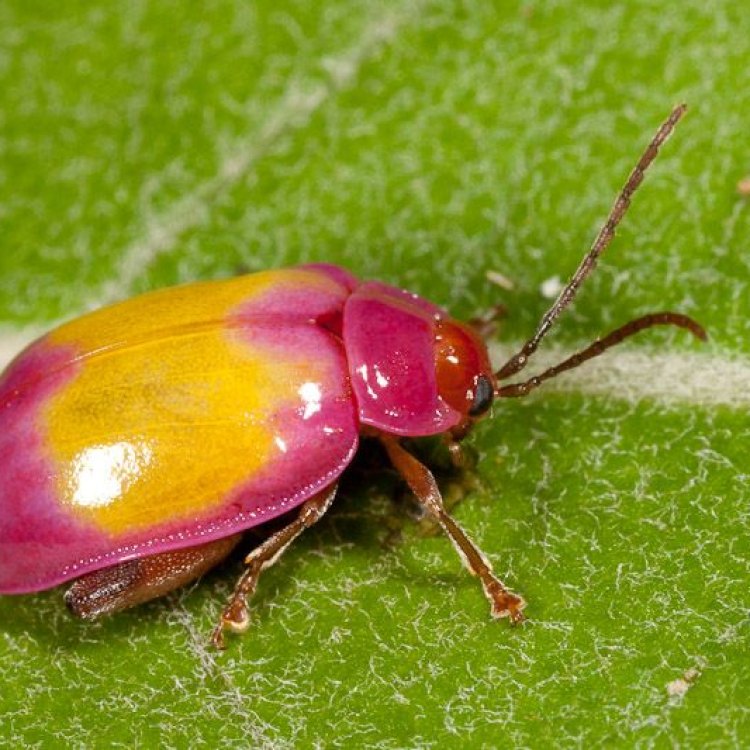

Flea Beetle
Animal Details Flea Beetle - Scientific Name: Altica spp.
- Category: Animals F
- Scientific Name: Altica spp.
- Common Name: Flea Beetle
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Family: Chrysomelidae
- Habitat: Grasslands, meadows, gardens, and agricultural fields
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: Unknown
- Location: Various regions
- Animal Coloration: Green, blue, black, brown, or metallic
- Body Shape: Small, oval-shaped
- Length: 2-10 mm

Flea Beetle
- Adult Size: 2-10 mm
- Average Lifespan: Several weeks to several months
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs on host plants
- Sound or Call: No
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Active during the day
- Threats: Predators, pesticides
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: May damage crops and plants
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Strong hind legs for jumping
- Interesting Facts: Can jump up to 100 times their body length
- Predator: Birds, spiders, other insects
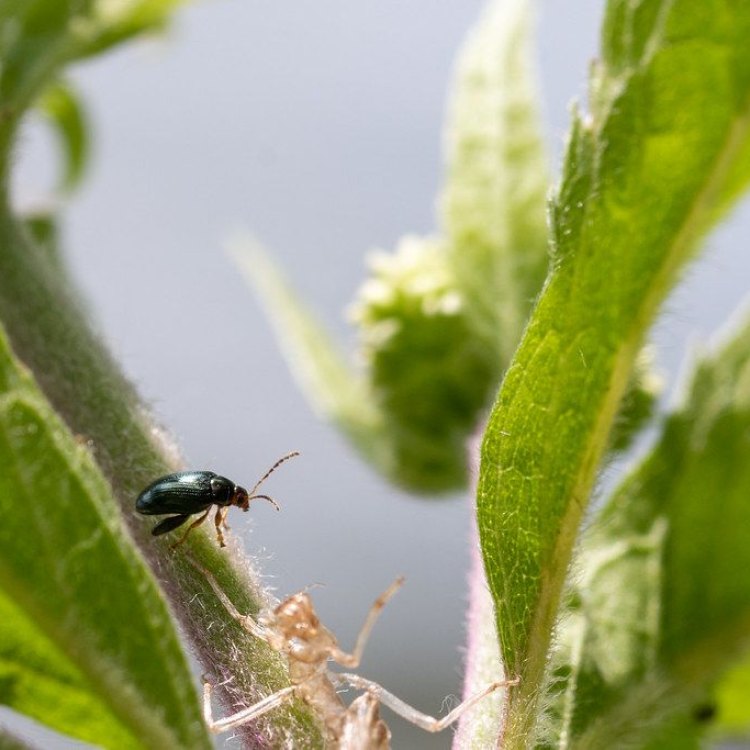

Altica spp.
The Hardy and Mischievous Flea Beetle
When we think of beetles, we often imagine slow and grounded creatures slowly crawling around. But there is one type of beetle that breaks this stereotype – the flea beetle. These tiny insects may have a small size, but their agility and resilience make them mighty in the insect world.Flea beetles belong to the family Chrysomelidae, which consists of about 3,000 species worldwide PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They are known for their jumping abilities, and their hind legs are their prized possessions. They use these legs to launch themselves up to 100 times their body length, making them one of the greatest jumpers in the insect world.
So, what makes the flea beetle unique? In this article, we will delve into the life and habits of these small but mighty creatures and explore their impact on the ecosystem.
The Life of a Flea Beetle
The size of an adult flea beetle ranges from 2-10 mm, with a lifespan of several weeks to several months. While some may consider their size a disadvantage, flea beetles have mastered the art of survival and have adapted to their environment.Flea beetles have a sexual mode of reproduction, where mating occurs on the host plants. The female beetle lays eggs on the underside of leaves, which hatch into larvae in a span of few days. These larvae then feed on the host plant, causing potential damage to the plant's health.
While adult flea beetles are solitary creatures, they may congregate in large numbers when the conditions are favorable Falcon. They are also active during the day, making them easier to spot and study.
The Dynamics of Flea Beetle Behavior
As mentioned earlier, flea beetles are agile jumpers, thanks to their strong hind legs. But what makes them jump? These tiny insects have a flight response, and when threatened, they use their powerful legs to propel themselves off the ground and onto a nearby plant or leaf. This behavior not only helps them escape predators but also aids in their dispersal to find new food sources.Apart from their incredible jumping abilities, flea beetles also have a unique camouflage mechanism. Some species have a shiny blue or green color while others have stripes or dots, making them blend in with their surroundings. This helps them camouflage and avoid detection by predators.
While they may appear cute and harmless, flea beetles can cause damage to crops and plants. They feed on the leaves, chewing through them and leaving holes, thus weakening the plant's health. This behavior can be destructive and cause significant economic losses to farmers and gardeners.
The Threats Faced by Flea Beetles
No matter how agile and resilient they may be, flea beetles face threats in their daily lives. Their small size makes them vulnerable to predators such as birds, spiders, and other insects. They also face the danger of pesticides used in agriculture, which can harm them and even kill them in large numbers.Moreover, flea beetles are not resistant to environmental changes, and any disruption in their habitat can impact their survival. Their non-migratory behavior also limits their ability to relocate to a new environment, making them even more vulnerable to changes.
The Impact on the Environment
Flea beetles may be small in size, but their presence can have a significant impact on the environment. As mentioned earlier, they can cause damage to crops and plants, which can have a ripple effect on the ecosystem. For example, if a large population of flea beetles feeds on a specific plant, it can result in a scarcity of that plant, affecting other animals, such as birds and insects, that may feed on it.Similarly, the use of pesticides to control flea beetle populations can also harm other beneficial insects, disrupting the natural balance in the ecosystem. This is why it is crucial to carefully study and understand the behavior and impact of flea beetles before taking any measures to control their population.
Human Use of Flea Beetles
Contrary to popular belief, flea beetles have no known significance in human use. They do not have any medicinal or commercial value and are not used in any product or food. However, scientists and researchers do study their behavior to understand their impact on the environment better.Interesting Facts about Flea Beetles
Apart from being strong jumpers and having a unique camouflage, flea beetles have some other intriguing features as well. Here are some interesting facts about these little insects:- Flea beetles can jump up to 100 times their body length, making them some of the best jumpers in the insect world.
- They are active during the day and rest at night.
- They are most active in warm and humid conditions.
- Some species of flea beetles feed exclusively on a single plant species, while others have a wider range of host plants.
- Flea beetles are commonly found in agricultural fields, gardens, and wooded areas.
A Fallible Species: Why Flea Beetles Need Our Attention
While flea beetles may seem insignificant to us, they play a crucial role in the ecosystem. Their behavior and impact need to be closely studied and monitored to prevent any potential threats to the environment.For example, the use of pesticides to control flea beetle populations can harm other beneficial insects, such as bees, which are crucial pollinators in the ecosystem. As humans, it is our responsibility to understand and protect all species, no matter how small or insignificant we may perceive them to be.
In Conclusion
Flea beetles may be small in size, but their agility and resilience make them mighty in the insect world. Their unique jumping abilities, camouflage, and behavior make them fascinating creatures to study. However, their impact on crops and plants and the ecosystem as a whole cannot be ignored.It is crucial to strike a balance between controlling their populations and preserving their natural habitat to ensure their survival and maintain the natural balance in the environment. As we continue to learn more about these tiny creatures, let us also do our part in protecting and preserving their existence on our planet.
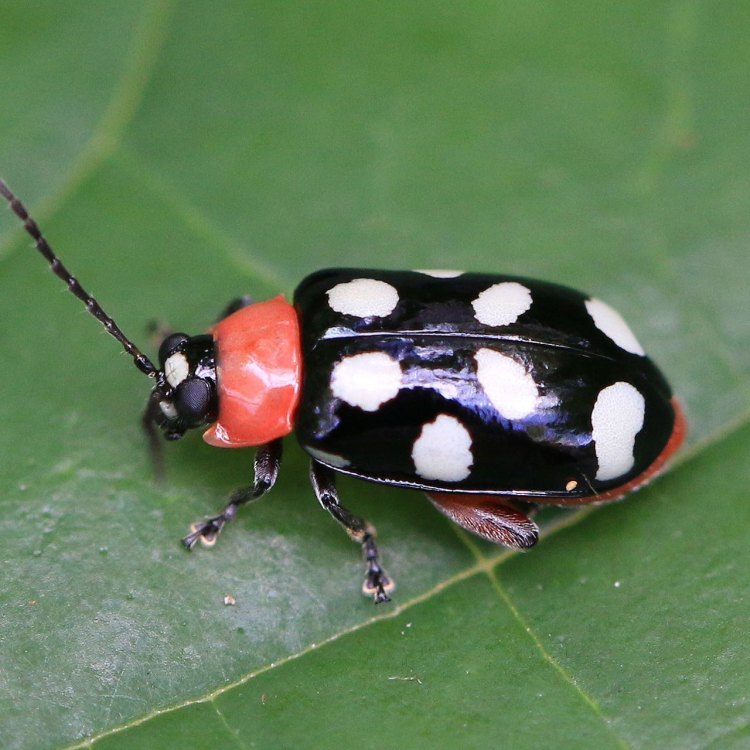

The Incredible Flea Beetle: A Tiny Insect with Mighty Capabilities
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.