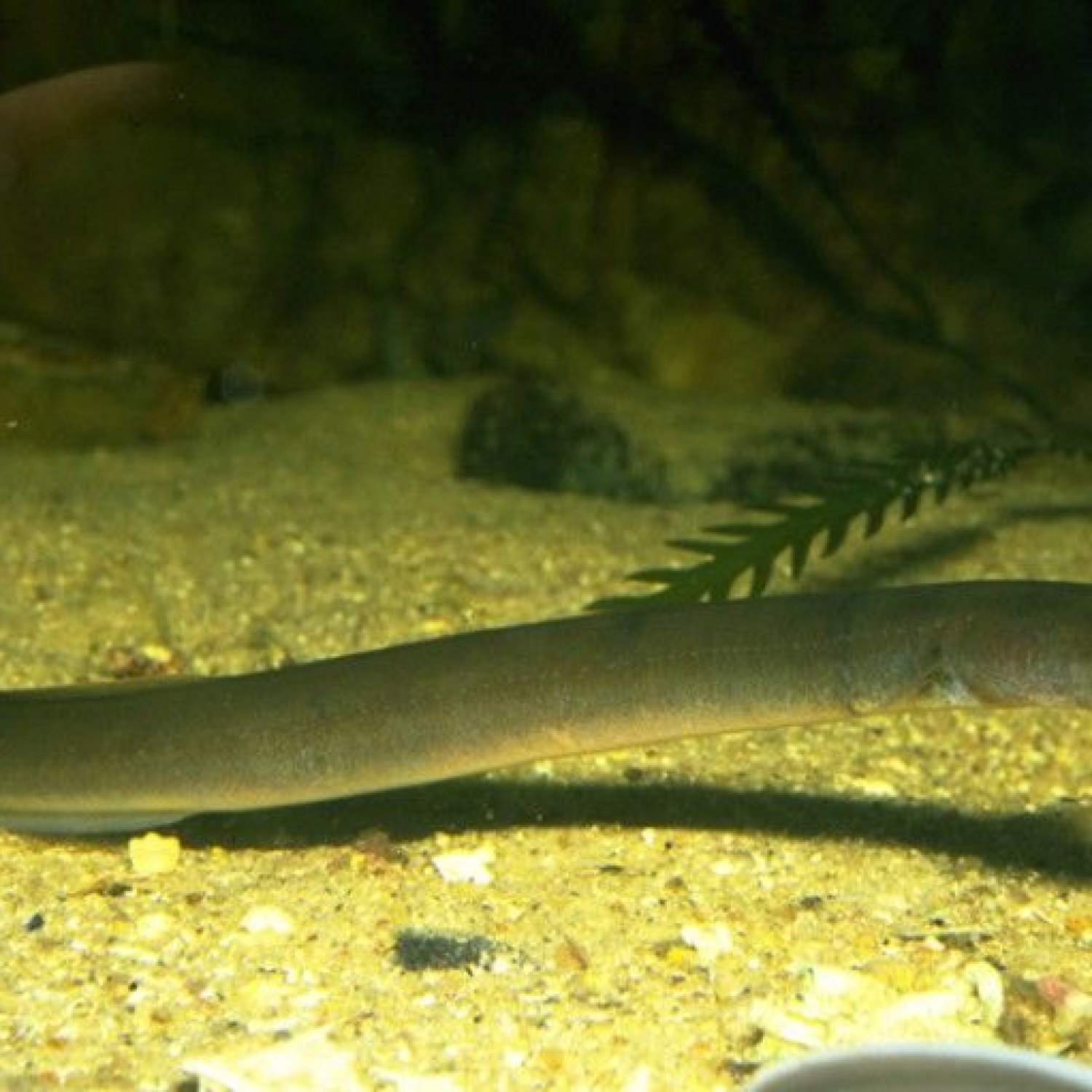
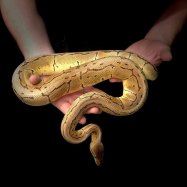
Freshwater Eel
Can grow up to 5 feet in length
The freshwater eel, known for its snake-like body shape, can reach up to 5 feet in length, making it one of the longest freshwater fish. Found in rivers, lakes, and estuaries, these eels belong to the family Anguillidae. Their unique biology and behavior make them popular subjects for scientific research. #FreshwaterEel #Anguillidae #SnakeLikeBody
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Freshwater Eel
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Freshwater
Freshwater Eel: The Slithering Beauty of the Aquatic World
The underwater world is full of intriguing and fascinating creatures, and among them is the Freshwater Eel. This slithering beauty is a unique species that has captured the attention of researchers and enthusiasts for centuries. Its scientific name is Anguilla anguilla, and it belongs to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, and class Actinopterygii. As an important member of the aquatic ecosystem, the Freshwater Eel has several interesting features and characteristics that make it stand out Freshwater Eel. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of Freshwater Eels and explore its habitat, behavior, and significance.The Habitat and Distribution of Freshwater Eels
Freshwater Eels have a vast geographical distribution, and they can be found in Europe, northern Africa, and western Asia. They are native to multiple countries, including the United Kingdom, France, Spain, Egypt, and Turkey. One of the reasons for their widespread distribution is their ability to adapt to different environmental conditions. They can survive in freshwater bodies such as rivers, lakes, and estuaries, making them a common sight in various aquatic habitats.One of the most intriguing aspects of the Freshwater Eel's habitat is its ability to migrate between freshwater and saltwater bodies. They have a unique lifecycle, where they hatch in the ocean and then swim hundreds of miles to enter freshwater rivers and lakes. They live in freshwater bodies for most of their adult life, and when it's time to breed, they return to the ocean, where they spawn and die. This unique life cycle has made Freshwater Eels a subject of interest for researchers studying animal migration Freshwater Sunfish.
The Unique Appearance of Freshwater Eels
Freshwater Eels have a distinctive snake-like appearance, which makes them stand out from other aquatic species. Their body is long and cylindrical, with a dorsal fin that runs through most of their body length. They have a mesmerizing olive green to brown coloration, with a yellow or white underbelly. This coloration helps them camouflage with their surroundings, making them less visible to predators.One of the most fascinating features of Freshwater Eels is their ability to change colors. They have specialized cells called chromatophores, which allow them to change their color to match their environment. It not only helps them to hide from predators, but also makes them more efficient hunters, as they can blend in with the background and surprise their prey.
Diet and Feeding Strategy
Freshwater Eels are carnivorous creatures, and they have a unique feeding strategy. Being nocturnal creatures, they spend most of their daytime hiding and resting in the crevices of rocks or under logs. As the sun sets, they emerge from their hiding spots and become active hunters. They have a keen sense of smell, which helps them locate their prey. They feed on a variety of aquatic creatures, including fish, crustaceans, worms, and snails.As ambush predators, Freshwater Eels have a unique way of capturing their prey. They use their powerful jaws to deliver a quick, unexpected bite, often catching their prey by surprise. They also have a second set of jaws called pharyngeal jaws, which helps them grab and swallow their prey whole. This unique ability of Freshwater Eels has made them feared and respected predators in the aquatic world.
The Significance of Freshwater Eels
The Freshwater Eel is not just another species in the aquatic world; it plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. As predators, they help control the population of their prey, ensuring the survival of other species. Additionally, their migration between freshwater and saltwater habitats allows for the distribution of marine nutrients to inland water bodies, which contributes to the overall health of these ecosystems.Apart from their ecological significance, Freshwater Eels also have cultural and economic importance. In many countries, they are considered a delicacy and are served in various traditional dishes. Their unique ability to migrate between different habitats also makes them an important species for recreational and commercial fishing industries. However, overfishing and habitat destruction have led to a decline in Freshwater Eel populations, highlighting the need for conservation efforts.
The Fascinating World of Freshwater Eels and Science
Freshwater Eels have been a subject of scientific research for centuries, and they continue to unlock new mysteries about this fascinating species. One of the most significant findings is related to their reproductive habits. It was once believed that Freshwater Eels reproduced asexually and that they reproduced on their own. However, recent studies have revealed that Freshwater Eels have a complex breeding process that involves males and females mating in the open ocean.In addition to reproduction, scientists have also been studying the migration patterns of Freshwater Eels. By tracking their movements, researchers have been able to gain insights into their behavior and the environmental factors that influence their migrations. This information is crucial for the preservation of this species, as it helps identify potential threats and conservation measures.
In Conclusion
Freshwater Eels are truly fascinating creatures that have intrigued humans for centuries. From their unique lifecycle to their incredible hunting abilities, they have captured the attention of researchers and enthusiasts around the world. As ambassadors of the aquatic ecosystem, they play a vital role in maintaining the balance of these fragile environments. It is essential to understand and appreciate the significance of Freshwater Eels and work towards their conservation to ensure their survival for future generations to come. So, the next time you come across a Freshwater Eel, take a moment to admire its beauty and marvel at the wonders of the aquatic world.
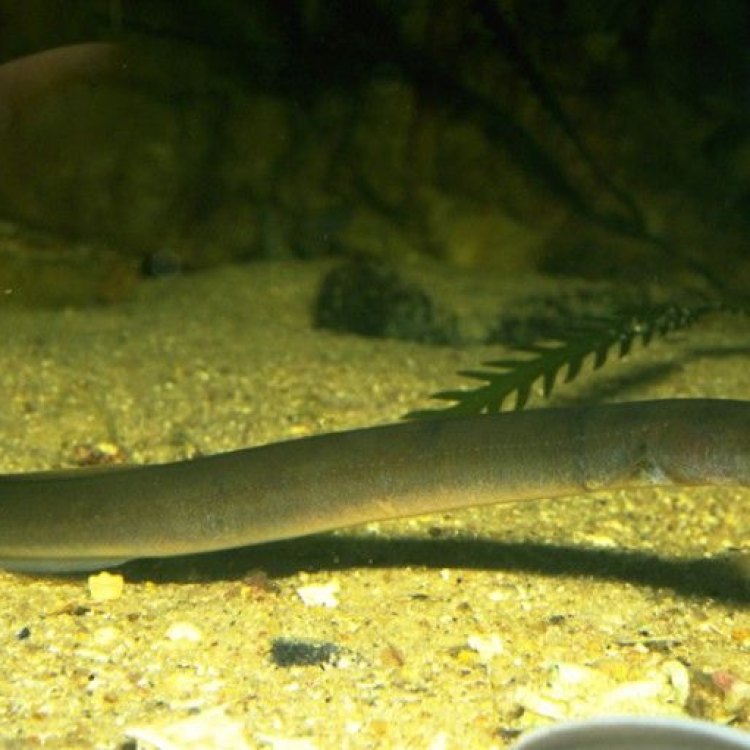

Freshwater Eel
Animal Details Freshwater Eel - Scientific Name: Anguilla anguilla
- Category: Animals F
- Scientific Name: Anguilla anguilla
- Common Name: Freshwater Eel
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Anguilliformes
- Family: Anguillidae
- Habitat: Freshwater
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, northern Africa, and western Asia
- Country of Origin: Multiple countries
- Location: Rivers, lakes, and estuaries
- Animal Coloration: Olive green to brown
- Body Shape: Snake-like
- Length: Can grow up to 5 feet in length
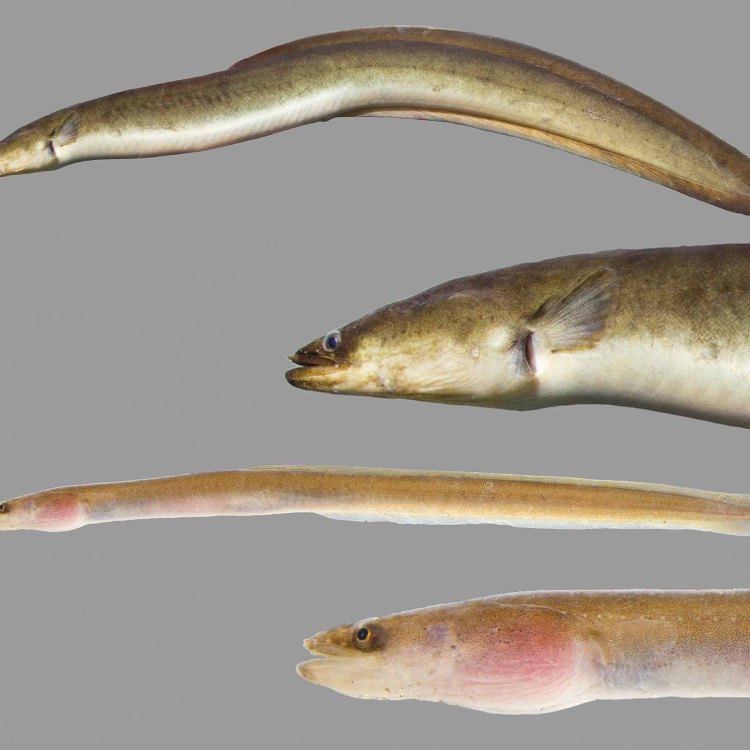

Freshwater Eel
- Adult Size: 2-4 feet
- Average Lifespan: 10-20 years
- Reproduction: Catadromous (breeds in saltwater)
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs during the migration to the sea
- Sound or Call: No specific sound or call
- Migration Pattern: Catadromous (migrates from freshwater to saltwater)
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal, hides during the day
- Threats: Habitat loss, overfishing, pollution
- Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important role in freshwater ecosystems
- Human Use: Fishing, culinary delicacy
- Distinctive Features: Long, slender body with no scales
- Interesting Facts: Capable of traveling long distances over land and even climbing small obstacles
- Predator: Various aquatic and semi-aquatic predators
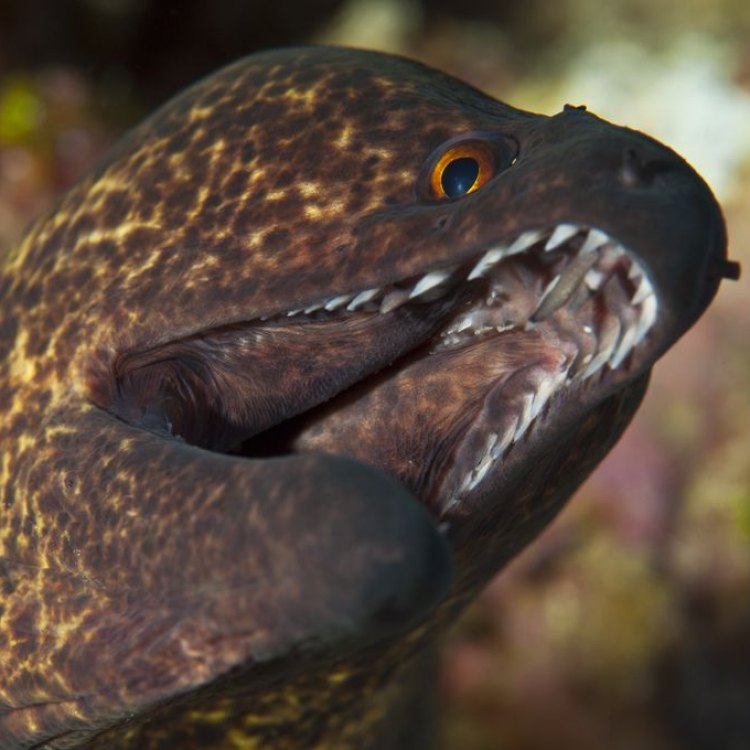

Anguilla anguilla
The Mysterious and Endangered Freshwater Eel: A Fascinating Creature of the Water
The freshwater eel (Anguilla anguilla), also known as the European eel, is a unique and mesmerizing creature that has captured the curiosity of humans for centuries. With its long, slender body and elusive behavior, the freshwater eel has been the subject of numerous mythological and cultural beliefs throughout the world. However, despite its intriguing nature, the freshwater eel is facing a critical threat of extinction, making it a species that needs our attention and protection.In this article, we will delve into the world of the freshwater eel, exploring its distinctive features, behavior, threats, and impact on the ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com. So, let's dive in and discover the mysterious and endangered freshwater eel.
The Size, Lifespan, and Reproduction of the Freshwater Eel
The average size of a fully grown freshwater eel ranges from 2-4 feet, making it a relatively small species compared to other types of eels. However, what it lacks in size, it makes up for in its remarkable lifespan. The freshwater eel has an average lifespan of 10-20 years, with some individuals living up to 40 years in captivity.
Interestingly, the freshwater eel follows a unique reproductive behavior called catadromy, where it breeds in saltwater but spends most of its life in freshwater. This means that the freshwater eel hatches from eggs in the Sargasso Sea in the Atlantic Ocean and then migrates to freshwater rivers and streams to grow and mature. However, when it's time to reproduce, the eels make the reverse journey back to the sea. This behavior makes them a vital link between freshwater and saltwater ecosystems.
Reproductive Behavior and Social Groups of the Freshwater Eel
During the migration to the sea for breeding, the freshwater eels exhibit a peculiar reproductive behavior Fallow Deer. Unlike other eels that spawn in groups, the freshwater eels are solitary creatures and mate individually. The process of mating is still not fully understood by scientists, but it is believed that the male eels release sperm into the water, and the female eels absorb it through their skin.
The freshwater eel also does not produce any specific sound or call during mating, making it a silent and mysterious process. After the mating season, the eels will return to their freshwater habitats and wait for their eggs to hatch, which can take up to a year.
Nocturnal and Solitary Behavior of the Freshwater Eel
The freshwater eel is a master of stealth and prefers to remain hidden during the day. It is primarily a nocturnal creature, meaning it is most active at night. This behavior is important for the eel's survival as it allows them to avoid predators and conserve energy. During the day, the eel will hide in burrows or under rocks and then emerge at night to hunt for food.
The freshwater eel is also a solitary creature, and each individual prefers to live alone. However, they do share their habitat with other eel species, such as the American eel. Despite living in the same environment, these eels do not interact with each other, further adding to the mystery of their behavior.
Threats to the Freshwater Eel's Survival
Unfortunately, the freshwater eel is facing a severe threat of extinction due to various factors. The main threat to their survival is habitat loss. As human populations continue to grow, freshwater habitats such as rivers and streams are being altered or destroyed for agriculture, industrial development, and urbanization. This destruction of their habitat makes it challenging for the eels to migrate or find suitable breeding grounds.
Overfishing is another significant threat to the freshwater eel. Due to its popularity as a culinary delicacy, eel populations have been heavily exploited, leading to a decline in their numbers. This is concerning as eels take a long time to reach maturity and have a low reproductive rate, making it difficult for them to recover from heavy fishing pressure.
Pollution is also a significant issue for the freshwater eel. As they spend most of their life in freshwater, they are highly susceptible to pollutants such as pesticides, heavy metals, and plastic waste, which can accumulate in their body and harm their health. This pollution not only affects eels but also the entire freshwater ecosystem they are a part of.
The Conservation Status and Importance of the Freshwater Eel
Given the various threats faced by the freshwater eel, it is not surprising that its conservation status is currently listed as "critically endangered" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that it is at high risk of extinction in the wild if no action is taken to protect and conserve its population.
Despite its small size, the freshwater eel plays a crucial role in the ecosystem. As an apex predator, the eel helps to control the population of its prey species, maintaining a balance in the freshwater food chain. They also act as a seed disperser, as they consume fruit and then carry the seeds to other locations, aiding in the dispersal of plant species. Therefore, the loss of freshwater eels would have a significant impact on the ecosystem and its functioning.
The Human Use and Fascination with the Freshwater Eel
Humans have been fascinated with the freshwater eel for centuries. The ancient Greeks believed that eels were born from the earth, while the Egyptians worshiped them as a symbol of fertility. In Japan, eels have been considered a delicacy, and their consumption has been a part of their cultural tradition for many years. The freshwater eel is also popular in many European countries, where it is often served smoked or grilled.
However, with the decline in eel populations, many countries have started to regulate their fishing and consumption. In some regions, it is illegal to fish for eels, and there are ongoing efforts to control their exploitation and promote sustainable fishing practices. This reflects the growing awareness of the importance of conserving this unique and endangered species.
Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts about the Freshwater Eel
The freshwater eel's appearance is what makes it stand out from other eel species. Unlike most eels, the freshwater eel does not have scales, and their skin is smooth and slimy. They also have a long, slender body, which allows them to slither through crevices and small openings in their search for food.
One of the most fascinating facts about the freshwater eel is its ability to travel long distances over land. When migrating to the sea, they can cross obstacles such as dams and even climb wet rocks using their strong, muscular bodies. This remarkable feat has been observed in Germany, where eels have been recorded traveling over 100 miles on land to reach the ocean.
Predators of the Freshwater Eel
As with any other species, the freshwater eel also has predators in its natural habitat. Various aquatic and semi-aquatic predators, such as otters, larger fish, and birds, prey on the eel. However, due to its elusive nature, the freshwater eel has developed some defense mechanisms to protect itself. They can secrete a slippery substance from their skin, making them difficult to catch, and they also have the ability to swim backward, which confuses their predators.
In Conclusion
The freshwater eel is an enigmatic and endangered creature that deserves our attention and protection. With its unique behavior, vital role in the ecosystem, and interesting features, the freshwater eel is a captivating species that adds to the diversity of our planet. It is crucial for us to take action to conserve and protect their population to ensure their survival for years to come. Let us appreciate and admire the mysterious and fascinating freshwater eel and help in preserving its existence.
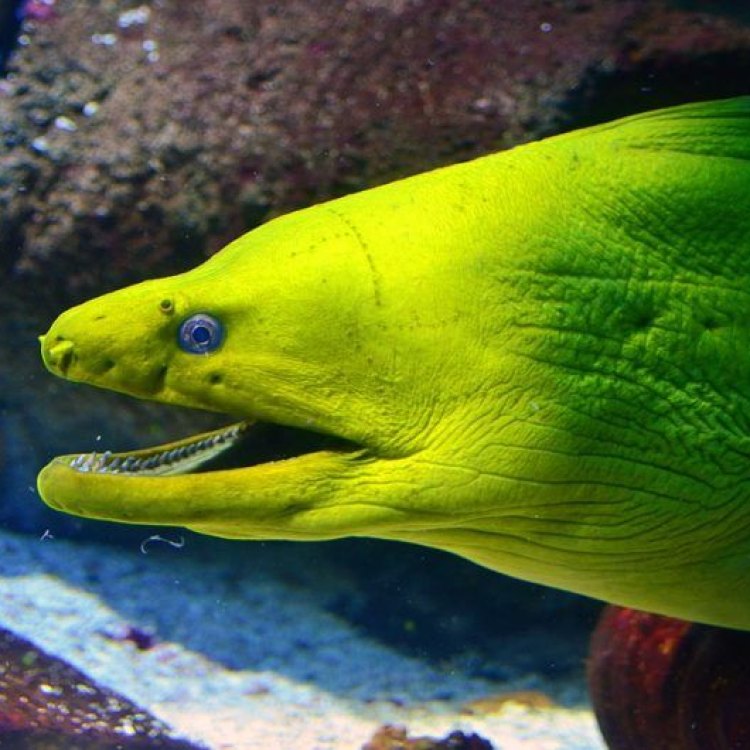

Freshwater Eel: The Slithering Beauty of the Aquatic World
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.