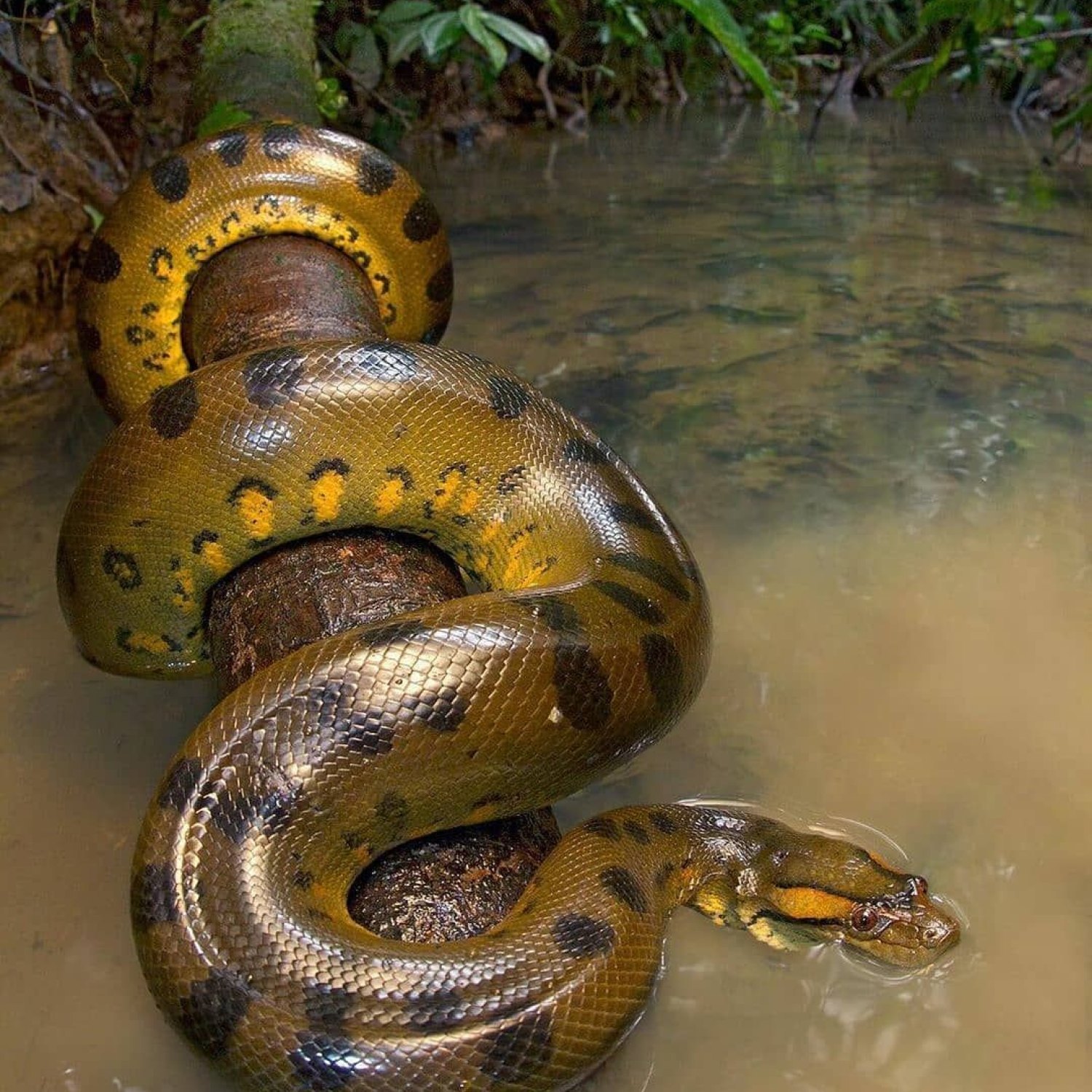
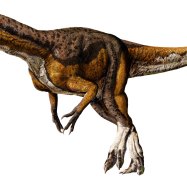
Green Anaconda
Up to 6 meters
The Green Anaconda, known for its impressive length of up to 6 meters, is native to the Amazon River basin and is a member of the Boidae family. Its long and cylindrical body shape allows it to move swiftly through the water. This massive creature is a sight to behold, but be sure to keep a safe distance while exploring its natural habitat! #GreenAnaconda #AmazonRiver #Boidae #AnimalFacts
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Green Anaconda
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Tropical rainforests, swamps, marshes, and slow-moving rivers
The Mighty Green Anaconda: Master of the Amazon River Basin
If you've ever heard tales of giant snakes that haunt the depths of the Amazon River basin, you may have dismissed it as simply a myth. However, the green anaconda (Eunectes murinus) is no mythical creature – it is a real-life giant, and one of the most fascinating and powerful animals found in the rainforests of South America.The Green Anaconda, also known as the common anaconda, is a member of the Boidae family, making it a close relative of other large snake species such as the boa constrictor and the reticulated python. It is a reptile, meaning it is cold-blooded and has scaly skin, and is classified under the phylum Chordata and class Reptilia Green Anaconda. The scientific name of the green anaconda, Eunectes murinus, comes from the Greek words "eu" (meaning good) and "nectes" (meaning swimmer), which translate to "good swimmer", highlighting the snake's incredible aquatic abilities.
This article will take you on a journey to learn more about the green anaconda, from its habitat and feeding habits to its impressive size and unique physical features. So grab your binoculars and join us as we explore the Amazon rainforest and uncover the secrets of the mighty green anaconda.
Habitat and Distribution
The green anaconda is a native to the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in countries such as Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, and Paraguay. Within these countries, the green anaconda can be found in various habitats, including swamps, marshes, and slow-moving rivers. They are also known to inhabit flooded forests during the rainy season, where they can be seen slithering through the murky waters in search of prey.Within the Amazon River basin, the green anaconda is considered a master of its environment, and it is not hard to see why. With an incredible length of up to 6 meters, it can easily camouflage itself among the dense vegetation and murky waters of the rainforest, making it nearly impossible to spot. Their preferred habitat also provides them with ample opportunities to ambush their prey, making it a perfect hunting ground for these formidable predators Gomphotherium.
Feeding and Hunting Habits
Speaking of hunting, the green anaconda is a carnivore, meaning it feeds on a diet consisting mainly of other animals. Their diet primarily includes fish, birds, reptiles, and mammals, such as rodents, capybaras, and even caimans. Unlike other snake species that rely on venom to subdue their victims, the green anaconda relies on its massive size and strength to overpower its prey.When hunting, the green anaconda uses a unique technique known as constriction. This involves biting down on its prey and wrapping its long and muscular body around it to squeeze it until it is suffocated. Once the prey is dead, the green anaconda swallows it whole, head first, using its backward-pointing teeth to help push the prey down its throat.
This feeding method allows the green anaconda to consume prey much larger than its head, making it a top predator in its environment. In fact, adult green anacondas have been known to eat animals as large as deer or pigs, making them true kings of the jungle.
Physical Characteristics
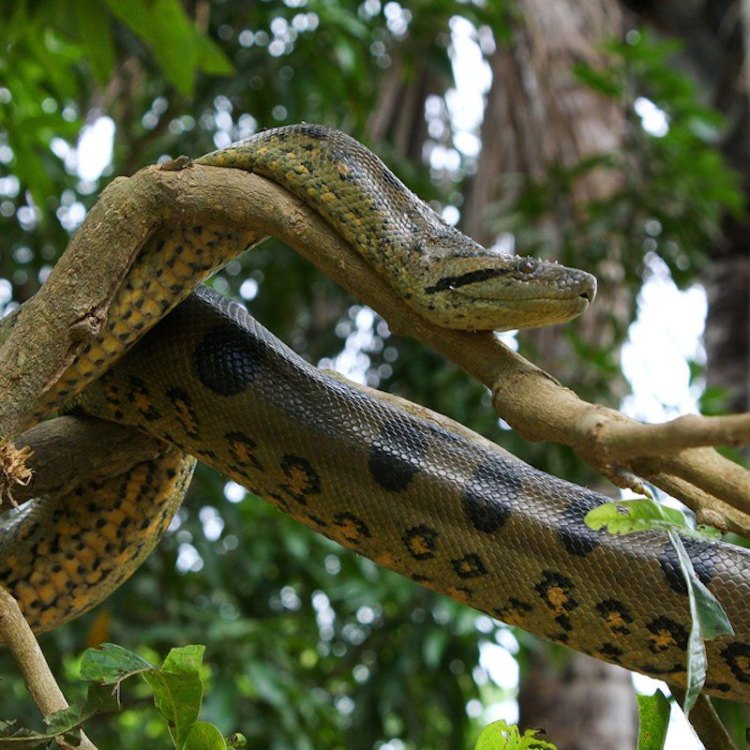
One of the most striking features of the green anaconda is its olive green coloration, which provides excellent camouflage in the rainforest environment. This green coloration is further enhanced by black spots that cover its entire body, giving it a distinctive pattern.The body shape of the green anaconda is also worth mentioning. Unlike most snakes that have a long, slender body, the green anaconda has a long and cylindrical body shape, with a relatively large head and a short, thick tail. This body shape is advantageous for the anaconda, as it allows them to be excellent swimmers and helps them move and maneuver through dense vegetation easily.
Size and Size Comparisons
When it comes to size, the green anaconda is a true giant among snakes. As mentioned earlier, they can reach lengths of up to 6 meters, making them one of the largest snake species in the world. To put this into perspective, the average size of a green anaconda is about the same length as a standard school bus.Compared to other giant snakes such as the reticulated python, the green anaconda comes out on top in terms of sheer size, with the former only reaching lengths of up to 4.5 meters. However, the green anaconda is slightly smaller than the African rock python, which can grow up to 6.5 meters in length. Nonetheless, the green anaconda is still an impressive feat of nature and is a sight to behold in its natural habitat.
Conservation Status and Threats
Despite their intimidating size and powerful hunting abilities, the green anaconda is currently listed as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List. However, this doesn't mean that they are not faced with any threats in the wild.Like most animals in the rainforest, the green anaconda is threatened by deforestation and destruction of its natural habitat. This not only reduces their available hunting and breeding grounds, but it also exposes them to potential conflicts with humans, leading to increased instances of human-animal conflict.
Moreover, the green anaconda is also hunted for its skin and body parts, which are highly valued in the illegal wildlife trade. This has led to a decline in their population in certain areas, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts to protect these majestic creatures for future generations.
In Conclusion
The green anaconda is truly a remarkable animal that continues to fascinate and captivate people around the world. With its impressive size, unique physical features, and powerful hunting abilities, it is no wonder that it is considered the master of the Amazon River basin.From its olive green coloration to its exceptional swimming and constricting abilities, the green anaconda is a true force to be reckoned with in the rainforest. It is our responsibility to protect and preserve these majestic creatures, not only for their survival but also for the balance of the delicate ecosystem that they call home. So let us continue to marvel at the incredible green anaconda and do our part in ensuring its future survival.
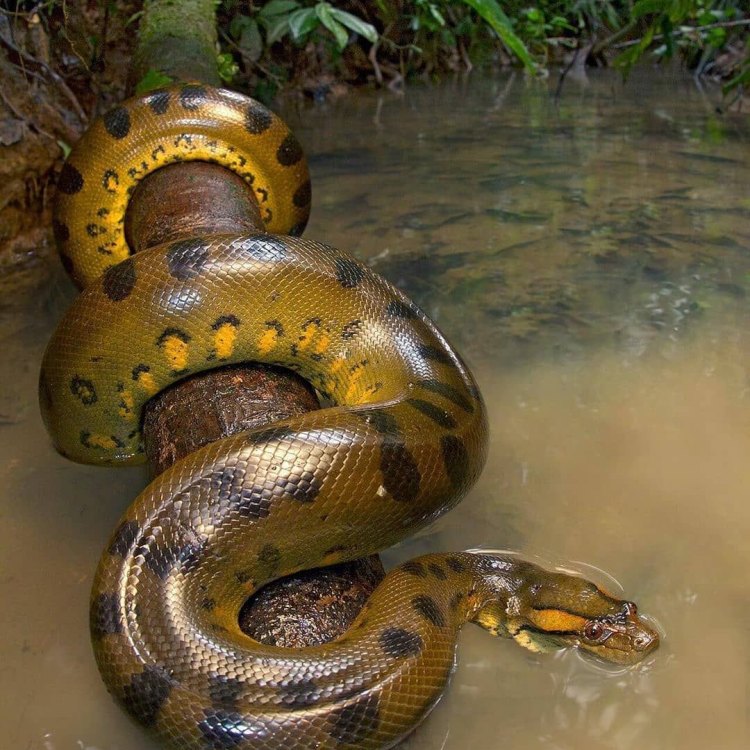

Green Anaconda
Animal Details Green Anaconda - Scientific Name: Eunectes murinus
- Category: Animals G
- Scientific Name: Eunectes murinus
- Common Name: Green Anaconda
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Family: Boidae
- Habitat: Tropical rainforests, swamps, marshes, and slow-moving rivers
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: South America
- Country of Origin: Brazil
- Location: Amazon River basin
- Animal Coloration: Olive green with black spots
- Body Shape: Long and cylindrical
- Length: Up to 6 meters
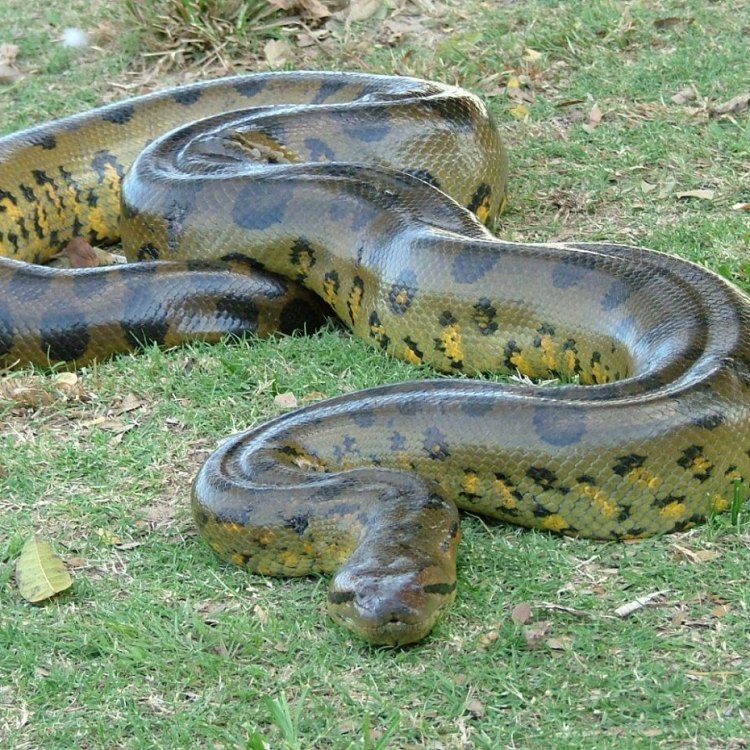

Green Anaconda
- Adult Size: Up to 5.5 meters
- Average Lifespan: Up to 10 years in the wild, up to 30 years in captivity
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs in water; females give live birth to young
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: None
- Social Groups: Solitary except during breeding season
- Behavior: Mostly aquatic and spends much of its time in water
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and hunting
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Apex predator, helps control population of prey species
- Human Use: Hunting for skins, meat, and traditional medicine
- Distinctive Features: Large size, thick body, powerful jaws
- Interesting Facts: One of the largest snakes in the world; capable of swallowing prey larger than its head
- Predator: Humans, jaguars, caimans

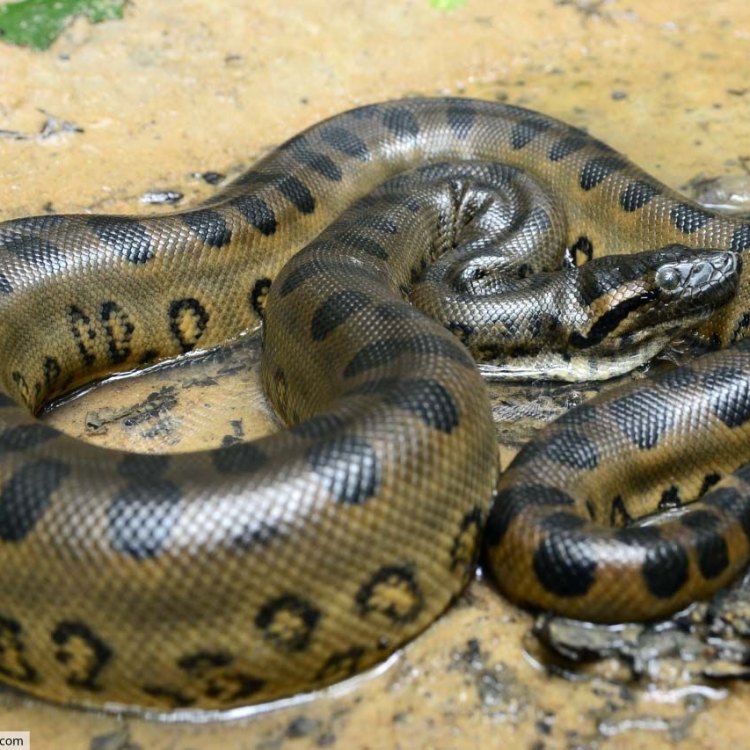
Eunectes murinus
The Mighty Green Anaconda: A Fascinating Apex Predator of the Amazon
Deep in the lush tropical rainforests of South America, hides a creature shrouded in mystery and surrounded by fear – the green anaconda. It is a member of the boa family and is considered one of the largest and most powerful snakes in the world, with a reputation that strikes both awe and terror in human hearts. This magnificent creature is not only an apex predator, but also plays a vital role in the Amazonian ecosystem. In this article, we delve into the unique features and captivating life of the green anaconda PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Size and Lifespan
The green anaconda, scientifically known as Eunectes murinus, can reach lengths of up to 5.5 meters (18 feet) and weigh over 200 kilograms (440 pounds). It is the largest snake species in the world by weight, although it falls slightly behind the reticulated python in terms of length. Its impressive size is a result of their long and thick bodies, adapted for efficient movement through water and squeezing prey.These magnificent creatures can live up to 10 years in the wild, but with proper care and a healthy diet, they can live up to 30 years in captivity.
Reproduction and Behavior
The reproductive behavior of green anacondas is similar to other boa species, with mating occurring in water. Male anacondas will often compete for the attention of a female by engaging in an intense wrestling match, where the strongest and most fit male wins the right to mate with the female.A female anaconda can give birth to up to 100 live offspring, which is quite rare in the world of snakes as most lay eggs. The young are fully formed and capable of swimming and hunting on their own, but they will stay close to their mother for protection for the first few weeks Gila Monster.
Green anacondas are mostly aquatic, spending a significant amount of their time in water. They are excellent swimmers and have the ability to hold their breath for up to 10 minutes, making them efficient hunters in the water. They are also known to bask in the sun on riverbanks to regulate their body temperature.
Despite their intimidating size and power, these snakes are solitary creatures, except during the breeding season. They prefer to live and hunt alone, avoiding potential conflicts with other anacondas.
Threats and Conservation Status
The green anaconda has faced numerous threats, primarily from human activities such as habitat loss, poaching, and hunting. The clearing of forests for agriculture and human settlements has led to a significant decrease in their natural habitat. In addition, they are hunted for their skin, which is used to make leather wallets, belts, and other accessories. Their meat and oil are also considered delicacies in some regions, while their body parts are used in traditional medicine.Fortunately, the green anaconda is classified as “Least Concern” on the IUCN Red List, meaning their population is stable and not currently facing the risk of extinction. However, continued efforts must be made to protect their habitat and regulate hunting and poaching activities.
Impact on the Ecosystem
As apex predators, green anacondas play a vital role in the Amazonian ecosystem. They help to control the population of their prey species, which in turn helps to maintain a balance in the ecosystem. Without these top predators, certain prey species could overpopulate and negatively impact their environment.Additionally, green anacondas provide an important source of food for other predators, including jaguars and caimans. They also help to distribute nutrients in the forest through their regular shedding of skin and digestion of prey.
Human Use and Distinctive Features
Despite their vital role in the ecosystem, green anacondas have also been exploited by humans for various purposes. They are hunted for their valuable skins, meat, and oil, without considering the impact on their population and the ecosystem. In some cultures, green anacondas are held in high regard and are believed to have special medicinal properties, leading to their use in traditional medicine.The most distinctive feature of green anacondas is their sheer size. These large and robust snakes have thick bodies and powerful jaws, making them formidable predators. They are also able to camouflage themselves well, blending in with their surroundings to avoid detection.
Interesting Facts
Besides their impressive size, there are many fascinating facts about green anacondas that make them a truly unique and intriguing species. One of the most incredible facts is their ability to eat prey that is significantly larger than their heads. This feat is possible due to their highly elastic jaws, expandable stomachs, and unique digestive system that allows them to consume prey whole.Green anacondas are also known for their intelligence and problem-solving skills. They can navigate through complex waterways and even climb trees to hunt their prey. These snakes also have a spectacular method of killing their prey – constriction. By methodically squeezing their prey, they cut off blood circulation and prevent their victims from being able to breathe, leading to a swift death.
Predators
Despite their fearsome reputation, green anacondas do have some natural predators. Humans remain their biggest threat, but they may also fall prey to jaguars and caimans. Smaller anacondas may even become prey for larger ones, as their cannibalistic nature is well-documented.In conclusion
In conclusion, the green anaconda is a fascinating and complex creature that holds a vital place in the Amazonian ecosystem. Its impressive size and power may strike fear in the hearts of many, but these creatures are an integral part of the environment and should be respected and protected. By understanding and appreciating their unique features and importance, we can work towards conserving and ensuring the survival of this incredible species for generations to come.

The Mighty Green Anaconda: Master of the Amazon River Basin
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.