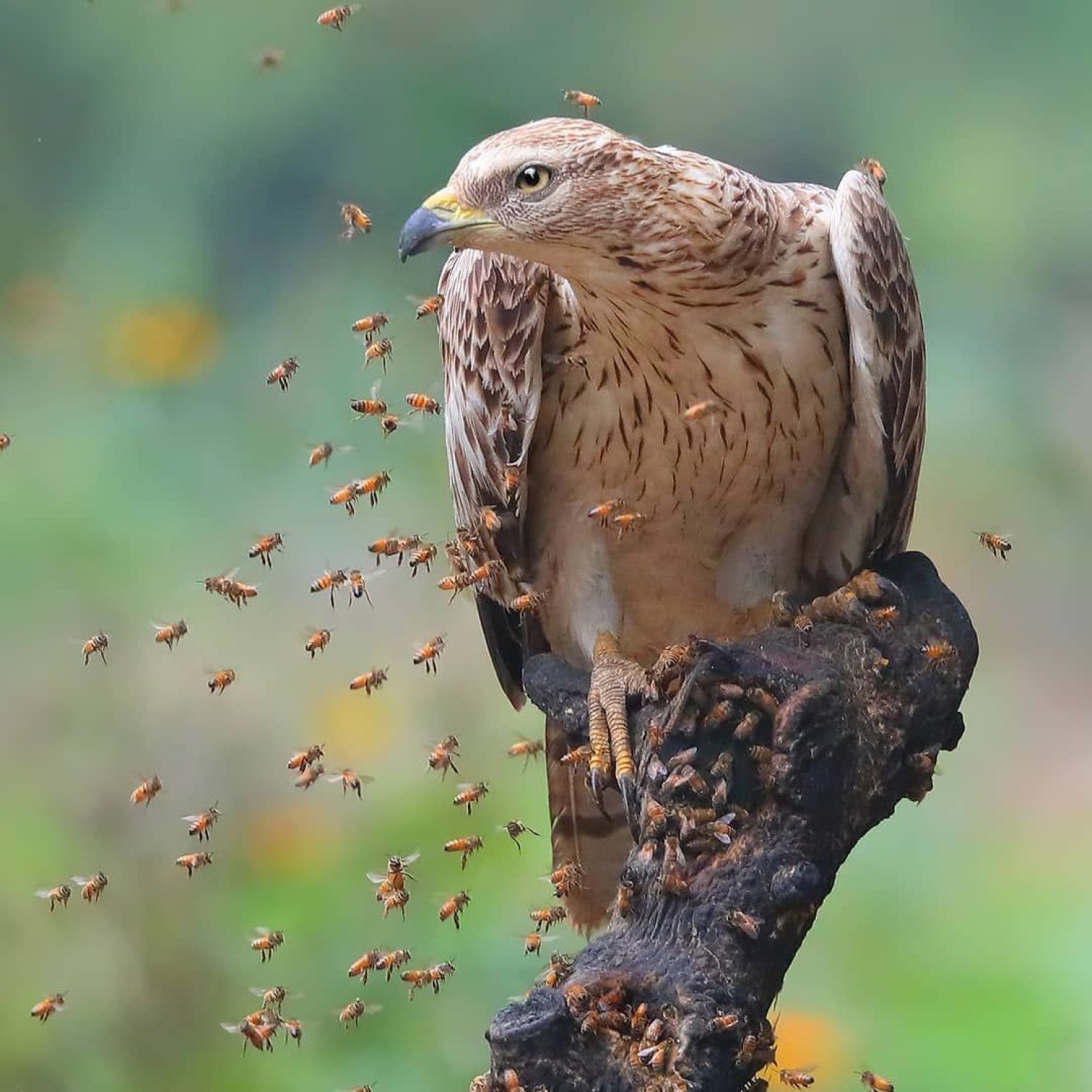
Honey Buzzard
55-60 cm
The Honey Buzzard, found in Central Europe, is a medium-sized bird known for its broad wings. Standing at 55-60 cm in length, this member of the Accipitridae family is a skilled hunter. Its distinct body shape allows it to soar effortlessly through the air and spot prey from great heights. Keep an eye out for this stunning bird of prey during your next hike in the forests of Central Europe.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Honey Buzzard
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Woodlands, forests, and wooded areas
The Incredible Adaptations of the Honey Buzzard
In the world of birds, there are some species that truly stand out with their unique and fascinating characteristics. One such bird is the Honey Buzzard, a medium-sized bird of prey that belongs to the family Accipitridae. Scientifically known as Pernis apivorus, this bird is also commonly referred to as the Honey Buzzard due to its unique feeding method. Found in woodlands, forests, and wooded areas in Europe, Asia, and Africa, the Honey Buzzard has captured the attention of bird enthusiasts all over the world Honey Buzzard. But what sets this bird apart from other birds of prey? Let's delve deeper into the incredible adaptations of the Honey Buzzard.The Honey Buzzard's Appearance and Habitat
The Honey Buzzard is a beautiful bird with a unique coloration. Its body is mostly covered in shades of brown and gray, with a white underside. This coloration helps the bird to blend in with its surroundings and stay hidden from predators. Apart from its color, the Honey Buzzard's body shape is also noteworthy. It has a medium-sized body with broad wings, allowing it to soar high in the sky and travel long distances.This bird can be found in woodlands, forests, and wooded areas, making its home in trees and thickets. They prefer these habitats as they provide ample food sources and shelter for the birds. This makes central Europe, specifically Germany, the country of origin and location for the Honey Buzzard Horned Lizard.
Feeding Method and Adaptations
What makes the Honey Buzzard truly unique and fascinating is its feeding method. Unlike other birds of prey, the Honey Buzzard is a carnivore that mainly feeds on bees and wasps. It has developed incredibly thick and strong skin on its face and neck, which allows it to withstand multiple bee stings while raiding bee hives for honeycomb and brood.Apart from its tough skin, the Honey Buzzard also has a narrow elongated beak that enables it to access the inner parts of the bee hives, where the honey and larvae are located. Its long toes and sharp claws allow it to grip and tear through the honeycomb with ease.
Moreover, the Honey Buzzard is well-known for its highly developed sense of smell. This amazing adaptation allows it to detect bee colonies from above and determine which ones have the most honey. It can also differentiate between different types of bees and wasps, depending on the intensity and type of smell.
Physical and Behavioral Adaptations for Survival
Apart from its unique feeding method, the Honey Buzzard has other physical and behavioral adaptations that have helped it survive in its environment. Its broad wings allow it to glide and soar through the sky, conserving energy while in search of food. It also has a small and narrow head, which reduces wind resistance and aids in flying at high altitudes.Behavior-wise, the Honey Buzzard has developed some interesting habits to survive in its habitat. For instance, during the breeding season, the female bird builds a decoy nest to distract predators from the actual nest. This shows the bird's intelligence and adaptability to its surroundings.
Another striking behavior of the Honey Buzzard is its migratory patterns. They are known to travel long distances during the migration season, sometimes covering up to 1600 km in a single day. This allows them to follow food sources and find suitable nesting habitats.
Insight into Honey Buzzard's Taxonomy
The Honey Buzzard falls under the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata, making it an animal with a backbone and spinal cord. It belongs to the class Aves, meaning it is a bird with feathers. The Honey Buzzard also falls under the order Accipitriformes, which includes other birds of prey such as hawks, eagles, and vultures.Under the family Accipitridae, the Honey Buzzard has evolved specialized adaptations to suit its diet and behaviors. This makes it a part of a diverse and unique family of birds of prey.
Threats and Conservation Efforts
Like most animals, the Honey Buzzard is also facing several threats. One of the major threats is habitat loss due to deforestation and human activities. This reduces the availability of food and nesting sites for the birds. Climate change is also affecting the bird's migration patterns and food sources.To combat these threats, conservation efforts have been put in place. Protected areas have been designated to preserve the woodlands and forests that are the Honey Buzzard’s preferred habitat. Additionally, awareness campaigns have been launched to educate people about the importance of preserving the environment for the survival of the Honey Buzzard and other species.
The Honey Buzzard and its Role in the Ecosystem
Apart from its fascinating adaptations, the Honey Buzzard also plays a crucial role in the ecosystem. As a predator, it helps regulate the population of its prey, mainly bees and wasps, which in turn helps maintain a balance in the ecosystem. The bird's droppings also help fertilize the soil and contribute to nutrient recycling.Moreover, the Honey Buzzard is also an indicator species, meaning its presence or absence can reflect the health of an ecosystem. This makes it essential to protect this bird and its habitat to ensure the overall well-being of the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Honey Buzzard is truly an incredible bird with fascinating adaptations that have allowed it to thrive in its habitat. From its unique feeding method to its physical and behavioral characteristics, this bird of prey has captured the attention and admiration of many. As we continue to learn more about the Honey Buzzard, it is crucial to remember the importance of preserving its habitat and protecting this magnificent bird for future generations to admire and appreciate.
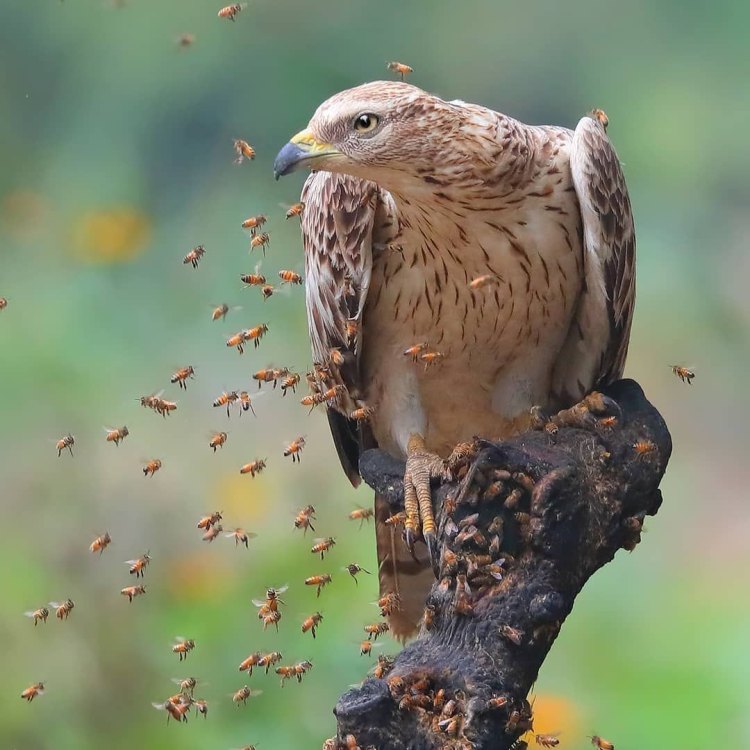

Honey Buzzard
Animal Details Honey Buzzard - Scientific Name: Pernis apivorus
- Category: Animals H
- Scientific Name: Pernis apivorus
- Common Name: Honey Buzzard
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Accipitriformes
- Family: Accipitridae
- Habitat: Woodlands, forests, and wooded areas
- Feeding Method: Carnivore
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, Asia, and Africa
- Country of Origin: Germany
- Location: Central Europe
- Animal Coloration: Brown, gray, and white
- Body Shape: Medium-sized with broad wings
- Length: 55-60 cm
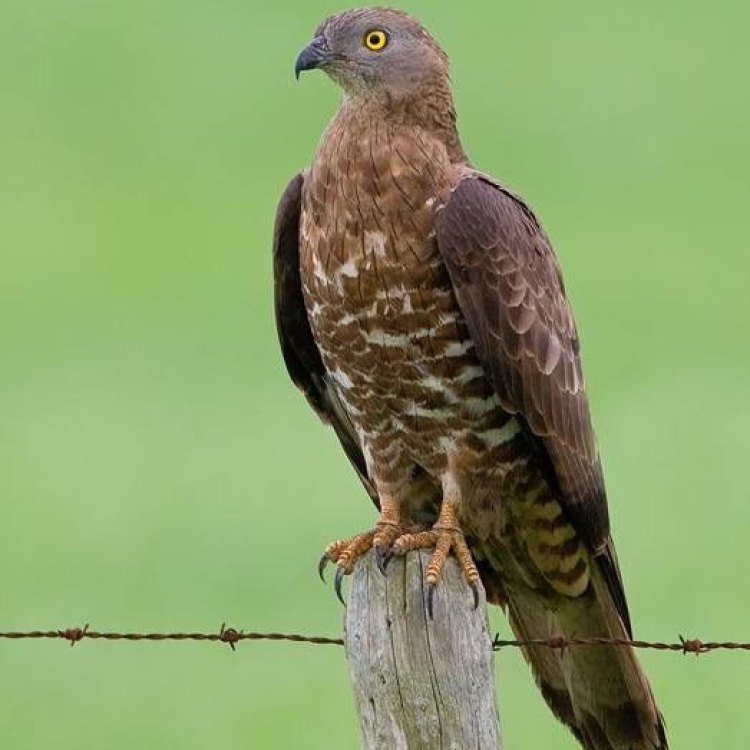

Honey Buzzard
- Adult Size: Medium
- Average Lifespan: 10-12 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Monogamous
- Sound or Call: The call is a piercing 'klee-klee-klee'
- Migration Pattern: Migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary or small groups
- Behavior: Honey Buzzards are known for their unique feeding behavior where they primarily feed on wasp and bee larvae. They are also known to steal food from other birds.
- Threats: Habitat loss, illegal hunting, and poisoning
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Helps control populations of wasps and bees
- Human Use: Honey Buzzards are often admired by birdwatchers
- Distinctive Features: Long wings and a slender body
- Interesting Facts: Honey Buzzards are the only birds of prey that primarily feed on bees and wasps.
- Predator: No known predators
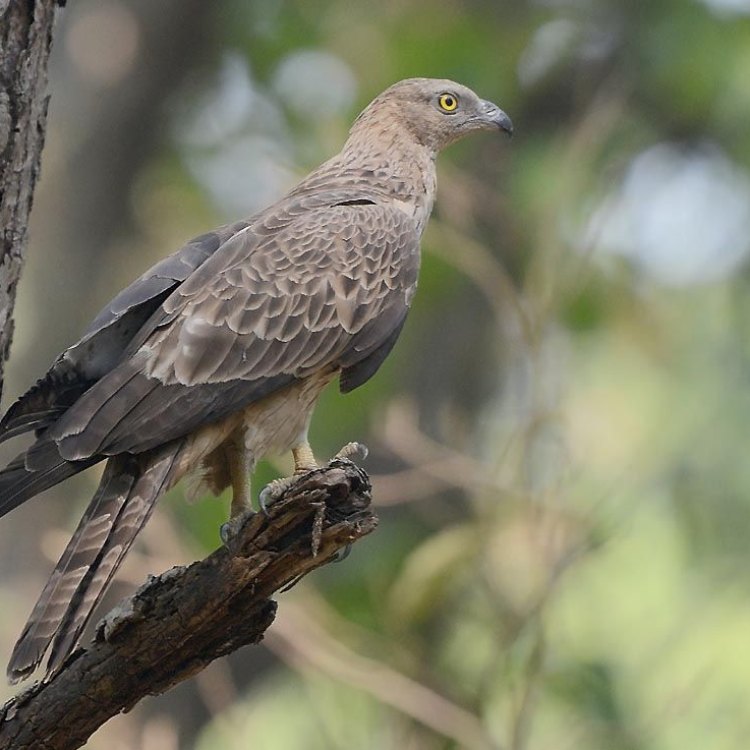

Pernis apivorus
The Fascinating World of the Honey Buzzard
Birds of prey have always captured our imagination with their majestic appearance and powerful hunting abilities. From the swift peregrine falcon to the iconic bald eagle, these birds hold a special place in our hearts and minds. But there is one particular bird of prey that stands out from the rest with its unique features and behavior - the Honey Buzzard.The Honey Buzzard, also known as Pernis apivorus, is a medium-sized bird of prey found in Europe and parts of Asia and Africa PeaceOfAnimals.Com. It is a member of the Accipitridae family, which also includes hawks, eagles, and kites. What separates the Honey Buzzard from its relatives is its specialized adaptation for feeding on wasp and bee larvae, earning it the nickname "wasp hawk."
With an average lifespan of 10-12 years, the Honey Buzzard is a relatively short-lived bird. However, its life cycle is full of interesting behaviors and unique characteristics that make it a fascinating subject for birdwatchers and researchers alike.
The World of the Honey Buzzard - Size, Reproduction, and Behavior
The Honey Buzzard is a medium-sized bird, with an average length of 47-60 cm and a wingspan of 115-150 cm. Its weight can range from 440-880 grams, making it one of the smaller birds of prey. However, its size does not hinder its hunting abilities, as it is swift and agile in flight.The reproductive behavior of Honey Buzzards is sexual, and they are monogamous birds. They form pairs with a mate and stay together for the breeding season Honey Bee. These pairs are known to be fiercely protective of their territory, with both male and female birds participating in nest defense. This level of collaboration and commitment has earned them the reputation of being one of the most devoted bird couples.
During the breeding season, the Honey Buzzards use their unique call to attract and communicate with their mates. The call is a piercing 'klee-klee-klee' and is often heard during the mating rituals and territorial disputes. While this call may not match the melodious songs of other birds, it is distinctive and can be easily recognized.
The Honey Buzzard is a migratory bird and moves to warmer regions during the winter months. It undertakes a long-distance migration, covering thousands of kilometers, and is often seen flying in small groups. However, they are also known to be solitary birds, spending most of their time alone, except during the breeding season.
Feeding Habits and Role in the Ecosystem
The most unique feature of the Honey Buzzard is its feeding behavior. Unlike other birds of prey, it does not hunt for small mammals or birds. Instead, it primarily feeds on wasp and bee larvae, earning it the nickname "wasp hawk."The Honey Buzzard's slender body and long wings allow it to maneuver swiftly through the dense forest canopy, where it primarily hunts. It is known to use its sharp talons to dig into nests and feed on the larvae, avoiding the stings of angry wasps or bees. This behavior has earned the Honey Buzzard a reputation as a "beekeeper's friend" in some parts of Europe, as it helps control the populations of these pesky insects.
Due to their specialized diet, Honey Buzzards have a significant impact on the ecosystem. They play a crucial role in controlling the populations of wasps and bees, which are considered beneficial insects. By preying on their larvae, the Honey Buzzard helps maintain a balance in the ecosystem, preventing a potential explosion in their numbers.
Threats to the Honey Buzzard and Human Use
Despite their critical role in the ecosystem, Honey Buzzards face a variety of threats that endanger their survival. Habitat loss due to deforestation is the most significant threat, as it reduces their primary hunting ground. This loss of habitat also affects their breeding, as they require large, dense forests to build their nests.Illegal hunting and poisoning are also major concerns for Honey Buzzards. These birds have been hunted for centuries for their meat and feathers, and despite being protected by law in many countries, they are still targets of illegal hunting. The use of pesticides and poisons also poses a significant threat to their populations, as they can ingest these toxins while feeding on contaminated insect prey.
Thankfully, due to their large range and relatively stable populations, the Honey Buzzard is classified as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. However, conservation efforts are still necessary to protect these birds and their habitat.
Honey Buzzards are also admired and appreciated by birdwatchers for their unique behavior and appearance. Their impressive flying skills and specialized diet make them a sought-after sighting for nature enthusiasts. Many birdwatching tours and activities focus on spotting these elusive birds, contributing to the local economies and promoting conservation efforts.
Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts
The Honey Buzzard's long wings and slender body are its most distinctive features. These adaptations allow it to fly effortlessly through the dense forest canopy and maneuver quickly while hunting. Its wings are also key to its migration, as it can cover great distances without expending too much energy.Besides their unique feeding behavior, Honey Buzzards also have some interesting facts that make them stand out from other birds of prey. They are the only birds of prey that primarily feed on wasps and bees, and they are also the only bird species in the world to have a reversible outer toe. This unique feature enables them to have a better grip on their insect prey while digging into their nests.
Another interesting fact about Honey Buzzards is that they have no known predators. As adults, they are skilled at defending themselves, and their nests are often hidden in dense tree canopies, out of reach of potential predators. However, their eggs and chicks are vulnerable to attacks from other birds, such as crows and goshawks.
In Conclusion
The Honey Buzzard is a fascinating bird of prey that captivates us with its unique features and behaviors. From its specialized diet to its monogamous, devoted relationships, this bird offers a glimpse into a world seldom seen by humans. While it faces threats to its survival, conservation efforts and the appreciation of birdwatchers offer hope for its continued existence.Next time you hear the piercing 'klee-klee-klee' call of a bird, look up and see if you spot a Honey Buzzard soaring through the skies. If you're lucky, you may witness its impressive hunting abilities or catch a glimpse of its beautiful, slender wings. Remember, these birds are not merely insects predators, but essential players in the delicate balance of our ecosystem. Let us appreciate and protect these majestic birds for generations to come.
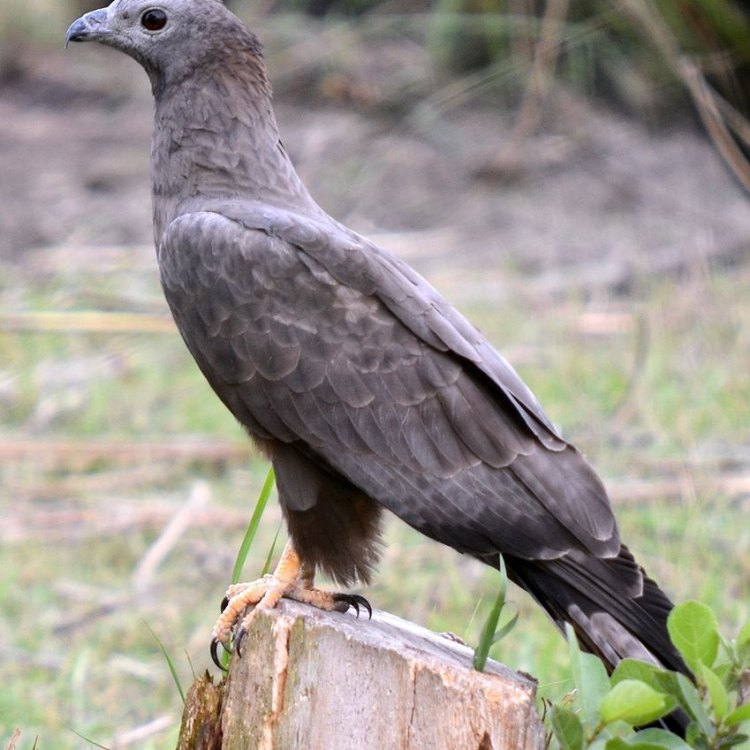

The Incredible Adaptations of the Honey Buzzard
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.