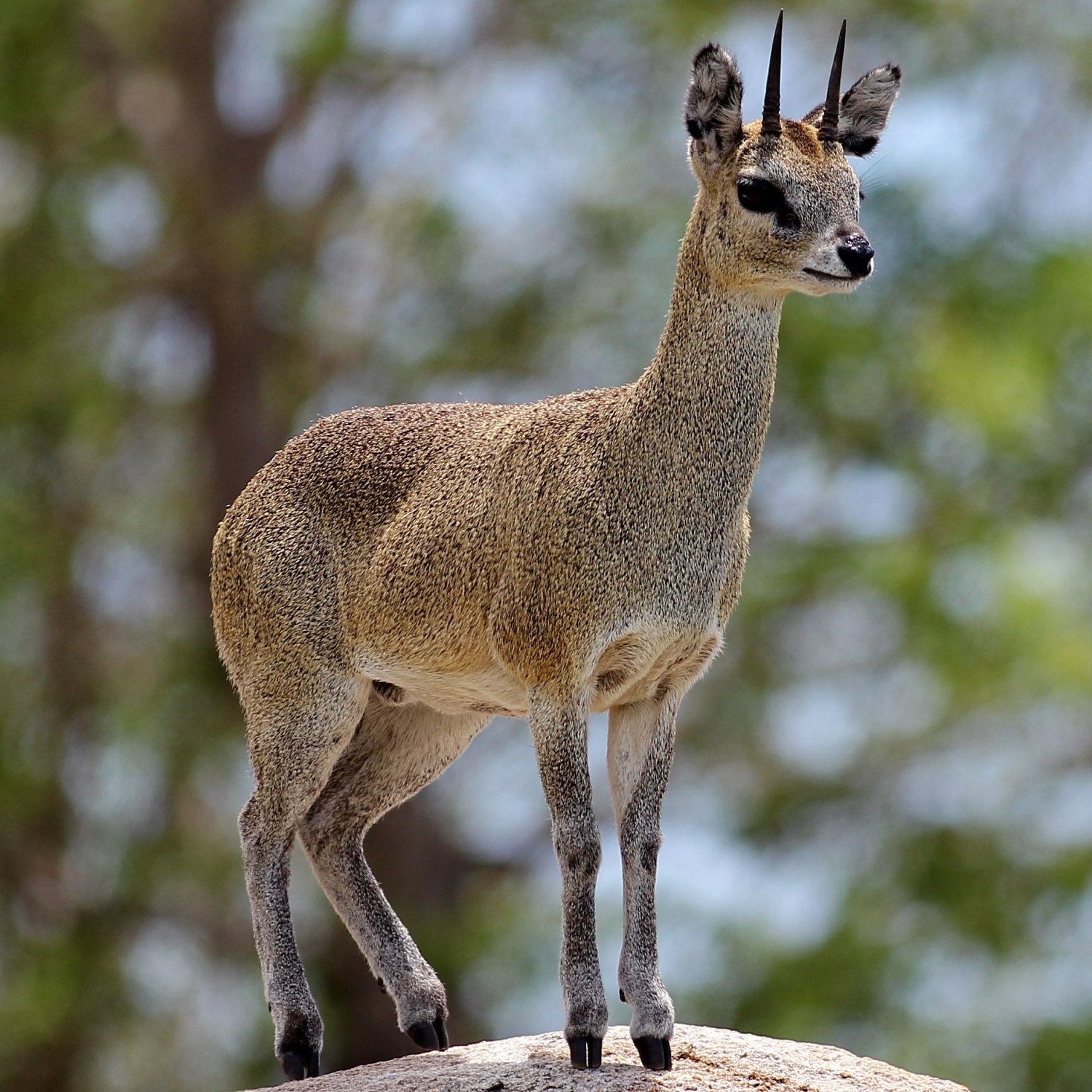
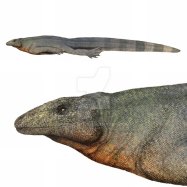
Klipspringer
75-100 cm
Introducing the Klipspringer, a small and compact antelope found in the savannas, grasslands, and mountains. With a length of 75-100 cm, this member of the Bovidae family gets its name from its unique ability to effortlessly leap and clip over rocks and boulders. Keep an eye out for these agile animals on your next outdoor adventure. #Klipspringer #SavannaAnimals #Mountaineering
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Klipspringer
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Rocky outcrops and cliffs
The Graceful Klipspringer: A Rare Gem of the African Savanna
The African savanna is home to a diverse array of wildlife, from towering giraffes to majestic lions. Among these impressive creatures lies a small, elusive antelope that is often overlooked - the klipspringer. With its unique adaptations and hidden beauty, the klipspringer is a fascinating animal that deserves a closer look.Scientifically known as Oreotragus oreotragus, the klipspringer is a member of the Bovidae family, which includes antelopes, goats, and sheep Klipspringer. Its name derives from the Afrikaans word "klip" meaning rock, and "springer" meaning jumper, aptly describing this animal's habitat and behavior.
A Rocky Habitat
The klipspringer's preferred habitat is rocky outcrops and cliffs in savannas, grasslands, and mountainous regions. This unique habitat allows the klipspringer to escape predators and access food sources that other animals cannot reach.Their hooves are specially adapted to navigate rocky terrain, with a rubber-like covering that provides extra grip and prevents them from slipping. This adaptation also allows them to jump nimbly from one rock to another, giving them the appearance of effortlessly "walking on air."
Herbivorous Feeding Habits
As with most antelopes, the klipspringer's primary source of food is vegetation. They are primarily herbivorous, feeding on grasses, leaves, and fruits. However, their unique habitat limits their food choices, so they have adapted to a diet of hearty and fibrous plants that grow on rocky outcrops.Being small and agile allows the klipspringer to reach vegetation that other animals cannot, giving them an advantage in finding food Kiang. They also have a specialized digestive system that enables them to break down tough and woody plants efficiently.
African Distribution
The klipspringer is endemic to sub-Saharan Africa, with a wide distribution across the continent. They can be found in countries such as South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Tanzania, and Kenya, among others. Their distribution is limited to areas with rocky terrain, making them a rare sight in the savanna.In South Africa, the klipspringer is often seen in the Drakensberg Mountains, while in Kenya, they can be spotted on Mount Kilimanjaro. Due to their elusive nature and habitat preferences, it is challenging to gather accurate population numbers. However, they are not considered a threatened species, with a stable population throughout their range.
A Colorful Camouflage
Klipspringers are relatively small, with a body length of 75-100 cm and a weight of 18-40 kg, making them one of the smallest antelopes in Africa. Despite their compact size, they have an impressive coloration that allows them to blend seamlessly into their rocky habitat.Their fur is short and has a coarse texture, ranging from brown, gray, to reddish hues. Their undersides and faces are white, and they have distinctive black markings on their faces, similar to a mask. This coloration helps them blend into the rocks, making them almost invisible when seen from a distance.
The Klipspringer's Unique Adaptations
Apart from their hooves and digestive system, the klipspringer has a few other interesting adaptations that help them survive in their harsh habitat.One such adaptation is their scent glands on their feet, which are used for communication. They can leave their scent behind as they navigate rocky terrain, marking their territory and warning off other klipspringers.
They are also able to survive in areas with limited water sources. Their kidneys are adapted to conserve water, and they can obtain enough water from their diet, making them well suited to their arid habitat.
A Rare Gem
The klipspringer is undoubtedly a rare gem of the African savanna, with its unique adaptations and elusive nature. However, the inaccessibility of their rocky habitat means that they are not often seen by humans, making studying them a challenge.Their small population and limited distribution also make it essential to protect their habitat and ensure their survival. Fortunately, conservation efforts have been put in place to protect their rocky homes and raise awareness about their conservation status.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite being well-suited to their rocky habitat, the klipspringer still faces some challenges that threaten their survival. Human activities such as mining and development encroach upon their rocky homes, diminishing their food sources and disrupting their daily routines.Habitat fragmentation also presents a significant threat, as it can lead to isolation of populations and a decrease in genetic diversity. It is vital for conservation efforts to focus on protecting the klipspringer's habitat and promoting sustainable development practices to ensure their continued existence.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, the klipspringer may not be as well-known or charismatic as other African animals, but it is undoubtedly a remarkable creature living in a unique habitat. Its adaptations and behavior make it a fascinating subject for study, and its elusive nature adds to its allure.As we continue to learn more about the klipspringer and work towards its conservation, let us remember to appreciate and value these rare gems of the African savanna.
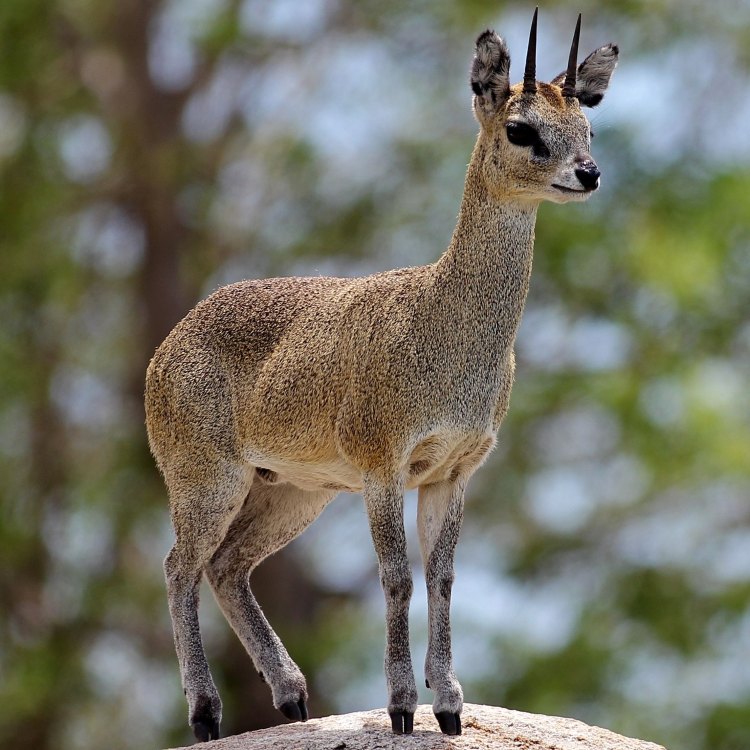

Klipspringer
Animal Details Klipspringer - Scientific Name: Oreotragus oreotragus
- Category: Animals K
- Scientific Name: Oreotragus oreotragus
- Common Name: Klipspringer
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Artiodactyla
- Family: Bovidae
- Habitat: Rocky outcrops and cliffs
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Sub-Saharan Africa
- Country of Origin: Multiple countries in Africa
- Location: Savannas, grasslands, and mountainous regions
- Animal Coloration: Brown, gray, or reddish
- Body Shape: Small and compact
- Length: 75-100 cm
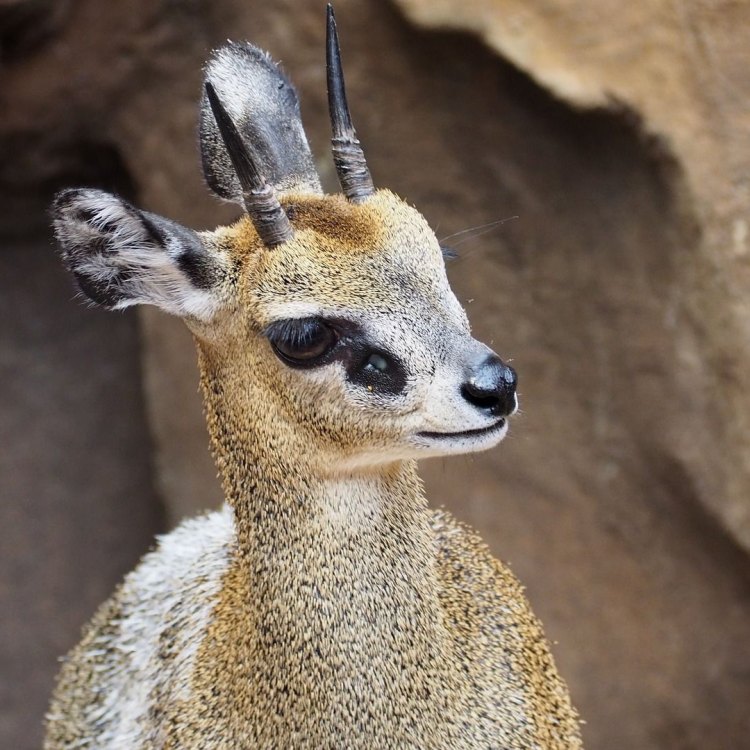

Klipspringer
- Adult Size: 12-15 kg
- Average Lifespan: 10-12 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Polygynous
- Sound or Call: Loud whistle or bark
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Pairs or small family groups
- Behavior: Territorial and secretive
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, hunting
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Eats grass and leaves, helps with plant dispersal
- Human Use: Hunted for meat and sport
- Distinctive Features: Well-developed scent glands and short stout legs
- Interesting Facts: Able to climb steep cliffs and rocks with ease
- Predator: Leopard, jackal, and large eagles
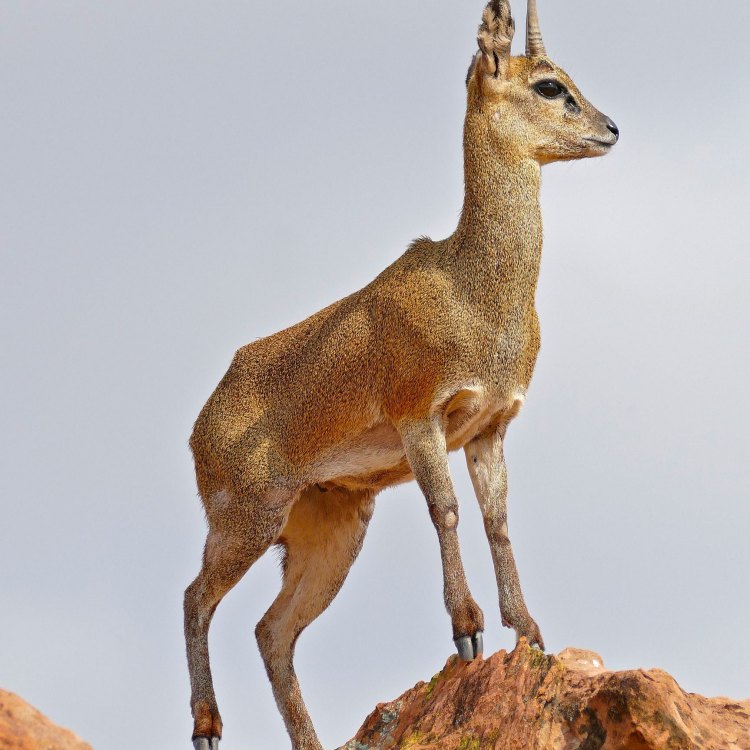

Oreotragus oreotragus
A Look Into the Fascinating World of the Versatile Klipspringer
The African savanna is home to a diverse range of wildlife, from the mighty elephant to the graceful giraffe. But among all these iconic animals, there is one small, yet fascinating creature that often goes unnoticed - the klipspringer. With its unique features and behavior, the klipspringer is truly a remarkable species that deserves more attention and recognition. In this article, we will take a closer look at this versatile and elusive creature, and discover what makes it stand out in the wild PeaceOfAnimals.Com.What is a Klipspringer?
The klipspringer, scientifically known as Oreotragus oureotragus, is a small antelope that is found in eastern and southern Africa. Its name, which means "rock jumper" in Afrikaans, perfectly describes its ability to navigate through rocky terrain with ease. Despite its small size, the klipspringer is a tough and agile creature, well-adapted to its rocky habitat.
Physical Characteristics
Size-wise, the klipspringer is not your average antelope. They have a stocky and compact build, standing at just over 2 feet tall at the shoulder. Adult klipspringers can weigh between 12-15 kilograms, with females being slightly smaller than males. Their most distinctive physical features are their short, stout legs, and well-developed scent glands beneath the eyes. These glands produce a strong musky scent that is used for territorial marking and attracting mates.
Klipspringers have a short and dense coat that varies in color from grey-brown to reddish-brown King Shepherd. This provides them with good camouflage against their rocky surroundings. They also have a mane of long, black hair that runs along their back, and a white chin and throat, giving them a distinct appearance. Both males and females have horns, which they use for defense and territorial disputes. However, the male's horns are usually thicker and longer than females.
Reproductive Behavior and Family Life
Klipspringers are solitary creatures, and the only time they come together is during mating season. They reproduce sexually, with a gestation period of around 7 months, giving birth to a single offspring. The newborn calf is born with a thicker coat to protect it from the rocky terrain and is able to walk within hours of its birth.
One unique aspect of klipspringers' reproductive behavior is their polygynous nature. This means that males will mate with multiple females and have no part in raising the offspring. Females, on the other hand, are responsible for caring for and protecting their young until they are old enough to fend for themselves.
Social Groups and Territorial Behavior
Klipspringers are typically solitary animals, but they can form pairs or small family groups. These groups consist of a mother and her offspring, or a male and female during mating season. They are highly territorial and will fiercely defend their territory from other klipspringers of the same sex.
One interesting behavior of klipspringers is their secretive nature. They prefer to live in secluded areas, away from predators and other animals. They are most active at dawn and dusk, and during the hotter parts of the day, they will retreat to the shade or shelter of rocky outcrops.
Sound and Communication
Even though klipspringers are solitary animals, they still have ways of communicating with each other. They have a loud whistle or bark that they use to alert others of danger or to communicate with their young. Their well-developed scent glands are also an important means of communication, as they use their musky scent to mark their territory and attract mates.
Threats and Conservation Status
Like many other species in the African savanna, klipspringers face various threats in their natural habitat. One of the biggest threats is habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities such as farming and development. This disrupts their natural behavior and can lead to a decline in their population. Another threat is hunting, both for their meat and for sport.
However, despite these threats, klipspringers are currently listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. This is due to their widespread distribution and adaptable nature, as they can survive in a variety of habitats. Conservation efforts are also being made to protect their natural habitat and raise awareness about the importance of preserving this unique species.
Impact on the Ecosystem
Klipspringers may be small, but they play an important role in their ecosystem. As herbivores, they mainly feed on grass and leaves, helping to keep vegetation in balance. They also aid in plant dispersal by eating fruits and seeds and then passing them through their digestive system, spreading them to different areas.
Their well-developed scent glands and territorial behavior also have a significant impact on their ecosystem. By marking their territory, they help maintain a balance in the population of other species, preventing overgrazing in specific areas.
Human Use
While klipspringers are not a commonly hunted species, they are still targeted by local communities for their meat and by trophy hunters. This poses a threat to their already vulnerable population. However, they are also admired for their agility and grace, and some lodges and camps in their habitat offer sightings and photography opportunities for tourists.
Interesting Facts
- One of the most impressive abilities of the klipspringer is its unique hoof structure, which allows them to easily navigate and climb steep cliffs and rocks.
- Unlike most other antelope species, klipspringers do not need to drink water regularly. They can obtain all the moisture they need from the plants they eat.
- In some cultures, the horns of klipspringers are believed to have medicinal properties and are used in traditional medicine.
Predators of the Klipspringer
Klipspringers may have well-developed physical and behavioral adaptations, but they are not invincible. They have a few natural predators, including leopards, jackals, and large eagles. To avoid being detected by these predators, they rely on their excellent camouflage and evasive maneuvers.
The Versatile Klipspringer - An Unsung Hero of the African Savanna
In a world full of powerful and iconic animals, it’s easy to overlook the small and elusive klipspringer. But as we’ve discovered, these unique creatures have many interesting features and behaviors that make them stand out in the wild. From their agile nature to their important role in the ecosystem, the klipspringer is truly a versatile and remarkable species that deserves our attention and protection. Let's hope that we can continue to coexist with these fascinating animals and preserve their natural habitats for future generations to appreciate.
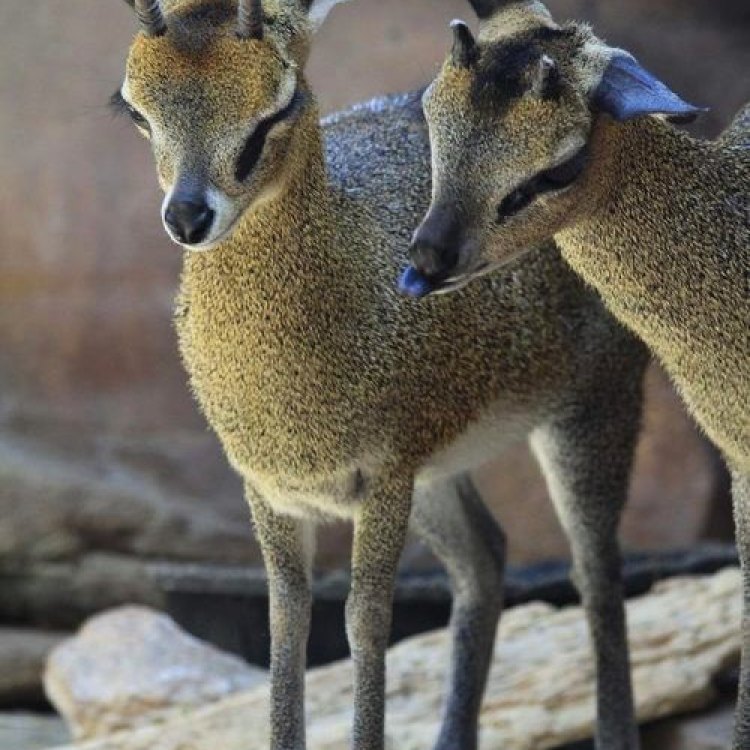

The Graceful Klipspringer: A Rare Gem of the African Savanna
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.