Lamprey
About 12 inches to 40 inches
Lampreys are unique animals in the petromyzontidae family with an eel-like body shape. Ranging in size from 12 to 40 inches, they can be found in rivers, streams, and oceans. Despite their scary appearance, they're harmless to humans and play an important role in their ecosystem. Keep an eye out for these fascinating creatures in their underwater habitats! #lamprey #petromyzontidae #aquaticlife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Lamprey
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Freshwater and marine
A Fascinating Look into the World of Lampreys: The Underdogs of Marine Life
Lampreys are often overlooked in the world of marine life. While they may not be as well-known as dolphins or sharks, these creatures are just as fascinating and deserving of our attention. From their unique feeding methods to their interesting habitat, there is so much to learn and appreciate about these underdogs of the marine world.The scientific name for lampreys is Petromyzontidae, which comes from the Greek words "petra" meaning stone and "myzo" meaning suck Lamprey. This accurately describes their feeding method, which we will delve into later. These ancient creatures have been around for over 360 million years and belong to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, and class Cyclostomata. They are also part of the order Petromyzontiformes and family Petromyzontidae.
What is a Lamprey?
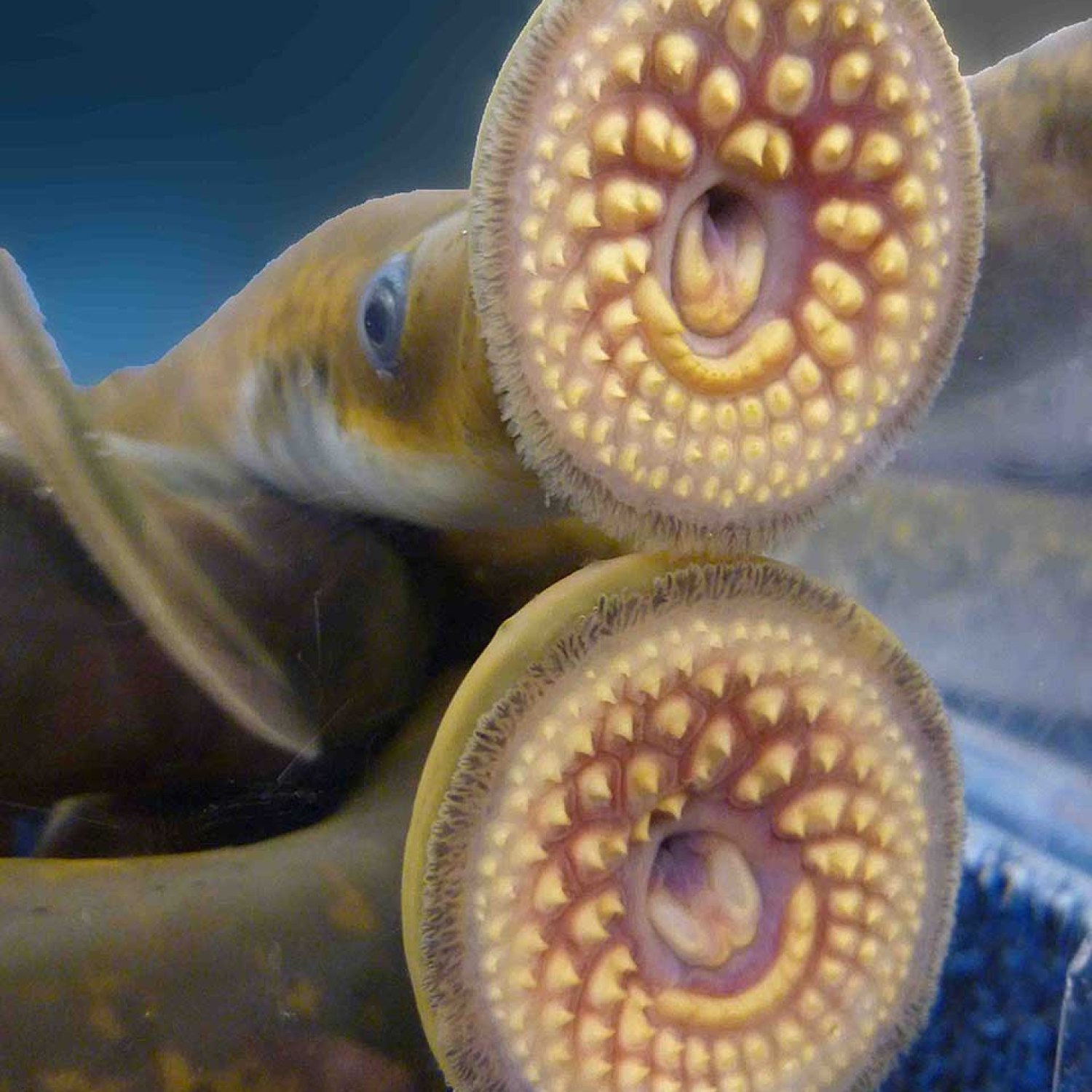
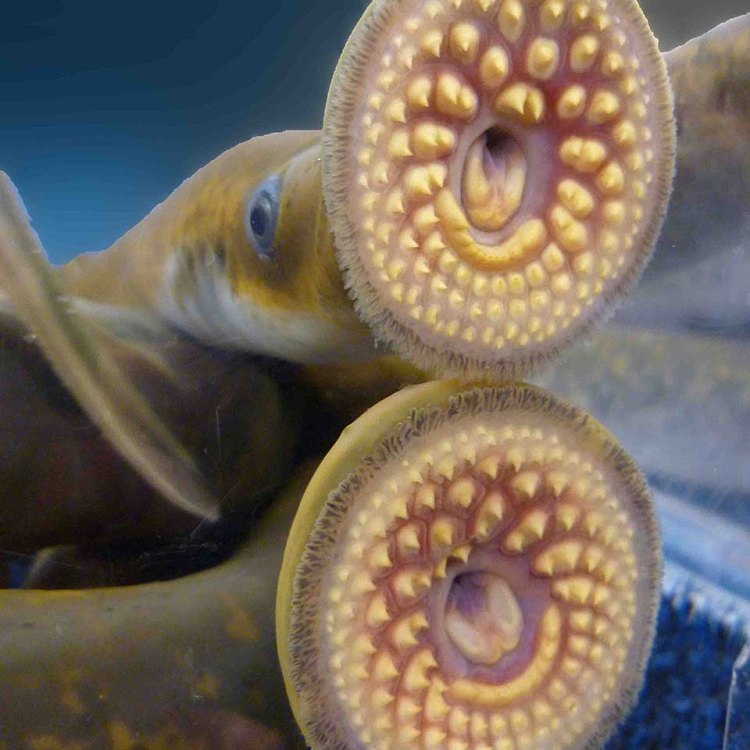
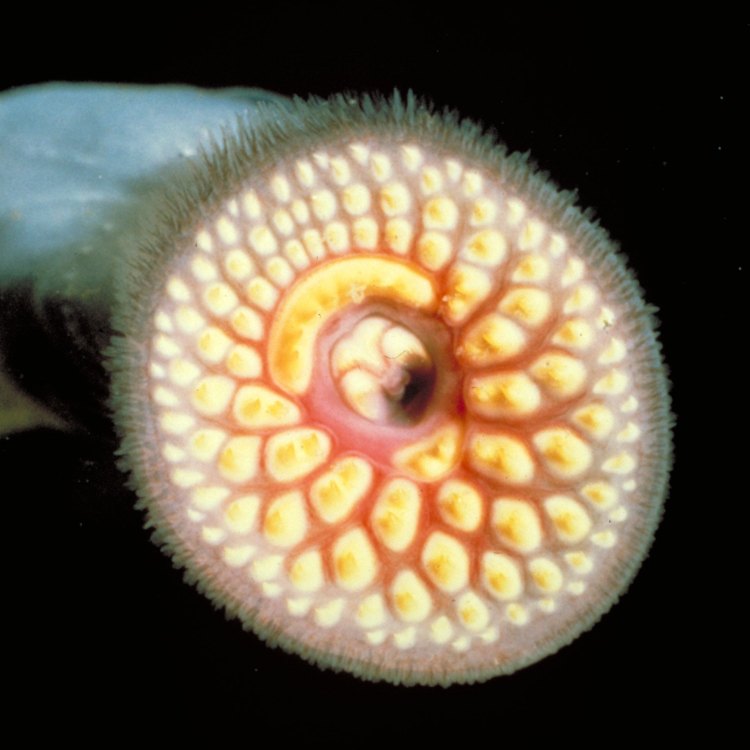
Lampreys are jawless fish, which means they do not have a jawbone like most other fish. Instead, they have a circular, tooth-filled mouth that they use to latch onto other fish and suck out their blood. They are typically found in freshwater and marine habitats, making them versatile creatures.They vary in size, with some species growing as small as 12 inches and others reaching up to 40 inches in length. Their body shape is similar to an eel, with a long, cylindrical body and smooth, scaleless skin. They can come in various colors, including shades of gray, brown, and black, depending on the species Leopard Seal.
A Parasitic Feeding Method
One of the most intriguing aspects of lampreys is their feeding method. As mentioned earlier, they have a circular mouth with sharp, curved teeth that they use to latch onto other fish and suck their blood. This parasitic feeding method has earned them the nickname "vampire fish." However, not all lampreys feed this way. Some species are non-parasitic and feed on small particles, plankton, and other marine creatures.Their unique feeding method has made them infamous in some areas, often portrayed as villains in certain cultural works. Still, it's important to remember that this is a natural part of their survival, and they play an essential role in the ecosystem.
Habitat and Distribution
Lampreys can be found worldwide, with different species inhabiting different regions. Some live in freshwater, while others prefer the ocean. They are often found in rivers, streams, and oceans with fast-flowing currents and clean, oxygen-rich water. They are also known to migrate long distances, sometimes crossing multiple countries to reach their desired habitat.Lampreys have been found in various countries worldwide, making it challenging to pinpoint their country of origin. There are over 40 known species of lampreys, with each having their unique distribution patterns and preferred habitats.
The Key to Survival
Lampreys may seem like creatures of the deep, lurking in the shadows and preying on unsuspecting fish. However, they, too, have predators and face challenges that threaten their survival. Pollution, habitat destruction, and overfishing are just a few of the threats that lampreys face in the modern world.But, despite these challenges, lampreys have been able to survive and adapt for millions of years. This is due in part to their unique life cycle, which consists of a larval, parasitic, and adult stage. The larvae live in freshwater for several years before undergoing metamorphosis into the parasitic stage, where they attach themselves to other fish and suck their blood. When they reach maturity, they return to their freshwater habitat to spawn and start the cycle all over again.
The Importance of Lampreys
Lampreys may not be as well-known as some of their marine counterparts, but they play a crucial role in the ecosystem. As larvae, they help to filter and clean the water, keeping it healthy for other creatures. As adults, they act as an important food source for other predatory fish, helping to maintain a healthy balance in the marine world.Additionally, lampreys have a long and fascinating history, making them important to scientific research. Due to their ancient lineage, they are often studied to understand evolution and the origins of various marine species.
The Future of Lampreys
Unfortunately, like many other marine creatures, lampreys are facing threats to their survival. Human activities such as overfishing and pollution have significantly impacted their population in recent years. However, measures are being taken to protect and conserve these creatures for future generations.Some countries, such as Canada and the United States, have banned commercial fishing of lampreys and have implemented regulations to protect their habitats. Conservation efforts are also being made in Europe, where lampreys are an important cultural and commercial resource.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lampreys may not be as well-known as some of their marine counterparts, but they are just as important, if not more. These ancient creatures have survived for millions of years, adapting to various habitats and facing numerous challenges. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem and are an important part of our planet's biodiversity.It's time to give these underdogs of the marine world the recognition and appreciation they deserve. With ongoing efforts to protect and conserve their species, we can ensure that future generations will get to witness the fascinating world of lampreys. So, the next time you see one of these creatures, remember the unique and vital role they play in our oceans.
Lamprey
Animal Details Lamprey - Scientific Name: Petromyzontidae
- Category: Animals L
- Scientific Name: Petromyzontidae
- Common Name: Lamprey
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Cyclostomata
- Order: Petromyzontiformes
- Family: Petromyzontidae
- Habitat: Freshwater and marine
- Feeding Method: Parasitic
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: Various countries
- Location: Rivers, streams, and oceans
- Animal Coloration: Gray, brown, or black
- Body Shape: Eel-like
- Length: About 12 inches to 40 inches

Lamprey
- Adult Size: Up to 2 feet long
- Average Lifespan: Up to 10 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: External fertilization
- Sound or Call: Silent
- Migration Pattern: Some species migrate between freshwater and saltwater
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Threats: Habitat destruction, water pollution, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Varies depending on species
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important role as a prey species and ecosystem engineer
- Human Use: Food (in some cultures), bait, research
- Distinctive Features: Circular mouth with rasping teeth, lack of jaws, suckers for attachment
- Interesting Facts: Lampreys have been around for over 360 million years, they are considered living fossils
- Predator: Various fish species, birds, and mammals

Petromyzontidae
The Mysterious and Ancient World of Lampreys
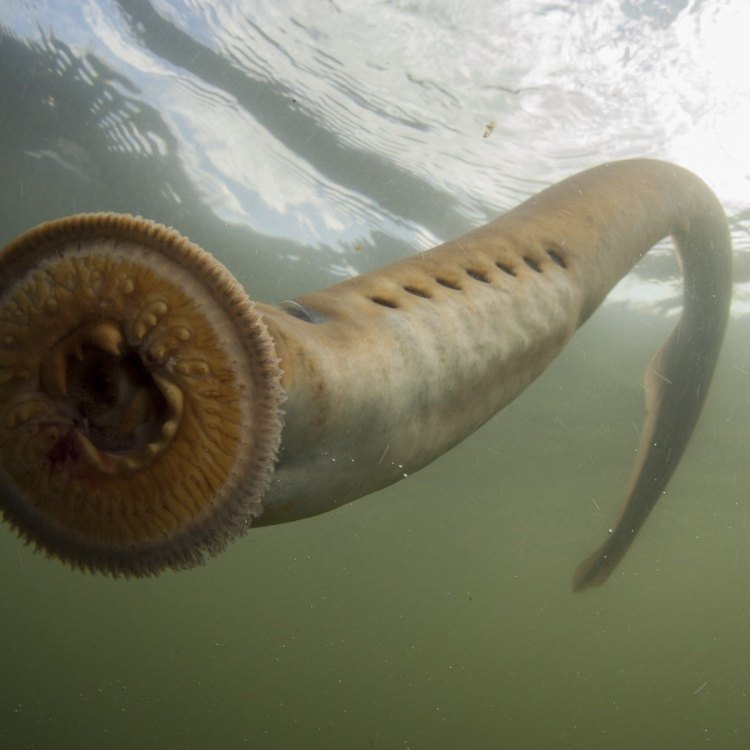
Deep in the waters of lakes, rivers, and oceans, there exists a creature that has been around for over 360 million years – the lamprey. These eel-like fish have long fascinated scientists and have captured the imaginations of writers and artists throughout history. With their unique features, mysterious behavior, and important role in ecosystems, lampreys are truly one of nature's marvels.Lampreys belong to the order Petromyzontiformes, which consists of over 40 species PeaceOfAnimals.Com. These ancient fish are found in both freshwater and saltwater environments across North America, Europe, and Asia. Let's dive into the fascinating world of lampreys and uncover their distinctive features, behavior, threats, and conservation efforts.
Anatomy and Distinctive Features
Lampreys range in adult size from a few inches to up to 2 feet long. They have a long, slender body and are typically a brownish-gray color. One of their most distinctive features is their circular mouth, which is lined with rows of sharp, rasping teeth used for sucking onto their prey. Unlike other fish, lampreys do not have jaws, but they do have a protruding tongue with more teeth used for rasping into their prey's flesh.Another unique feature of lampreys is their two round, sucker-like discs located on their head. These suckers are used for attachment to surfaces and are also helpful in navigating through water currents.
Behavior and Reproduction
Lampreys are solitary creatures and are mainly active at night, making them nocturnal Lesser Scaup. They are also known for their ability to migrate between freshwater and saltwater environments, with some species traveling hundreds of miles for spawning purposes. This migration pattern is essential for reproduction, as lampreys practice external fertilization, meaning the female lays her eggs on the riverbed, and the male releases his sperm over them.Interestingly, lampreys do not produce any sounds or calls, which is uncommon for fish. They also have a unique reproductive behavior called ammocoetes stage, where they transform from their larval stage to adulthood. During this stage, they live in the sediment of a freshwater river or stream and feed on organic matter until they are ready to migrate to the ocean.
Threats to Lampreys
Unfortunately, like many other species, lampreys face numerous threats to their survival. One of the biggest threats is habitat destruction, as humans continue to alter and destroy natural habitats for development purposes. This destruction disrupts lampreys' migration patterns and can result in a decline in their population.Water pollution is another significant threat to lampreys' survival. As they are sensitive to water quality, any pollution can harm and even kill them. Polluted water also affects their prey, which can lead to a decrease in food availability for lampreys.
Overfishing is also a significant threat to lampreys, as they are often caught unintentionally in fishing nets meant for other species. This, coupled with the fact that they are slow-growing and late-maturing, puts them at risk of overexploitation.
Conservation Status and Impact on Ecosystems
The conservation status of lampreys varies depending on the species. Some are listed as endangered, while others are classified as least concern. However, due to the ongoing threats they face, efforts are being made to conserve and protect these ancient fish. For example, in the Great Lakes region, a binational management plan has been established to monitor and manage lamprey populations.Despite their often negative portrayal, lampreys play an important role in ecosystems. As a prey species, they are a vital part of the food chain, providing food for various fish species, birds, and mammals. Lampreys also act as ecosystem engineers, as their feeding behavior and movements can shape the structure of their habitats.
Human Use and Interesting Facts
In some cultures, lampreys are considered a delicacy and are used as food. They are also used as bait for fishing, particularly in Europe and North America. Lampreys have also been used as a research subject due to their unique anatomy and behavior.Aside from their use by humans, lampreys have many fascinating facts that make them even more intriguing. As mentioned earlier, they have been around for over 360 million years and are considered living fossils, making them one of the oldest species on Earth. They are also closely related to hagfish, another ancient and often misunderstood fish species.
Predators and Surprising Adaptations
Like most animals, lampreys have their share of predators. Various fish species, such as trout and salmon, feed on lampreys. Birds, such as herons, have also been known to prey on them, as well as mammals, including seals and otters. These predators are attracted to lampreys' circular mouth and use it as a way to grab and consume them.To adapt to their potential predators, lampreys have developed some surprising defenses. For example, some lamprey species can secrete a toxic mucus when they feel threatened, causing predators to release them. Others have the ability to burrow into sediment when faced with danger, making them difficult to catch.
Appreciating the Mysterious Lamprey
Despite their intimidating appearance, lampreys are truly fascinating creatures that have been around for millions of years. These ancient fish have adapted to their environments and play an important role in ecosystems. However, they also face many threats that could lead to their decline.It is essential to appreciate and understand the unique features and behavior of lampreys while also taking steps to protect and conserve them. By doing so, we can ensure that these mysterious creatures continue to thrive and contribute to the diverse and fragile ecosystems they call home.

A Fascinating Look into the World of Lampreys: The Underdogs of Marine Life
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












