Leopard Shark
Up to 6.5 feet (2 meters)
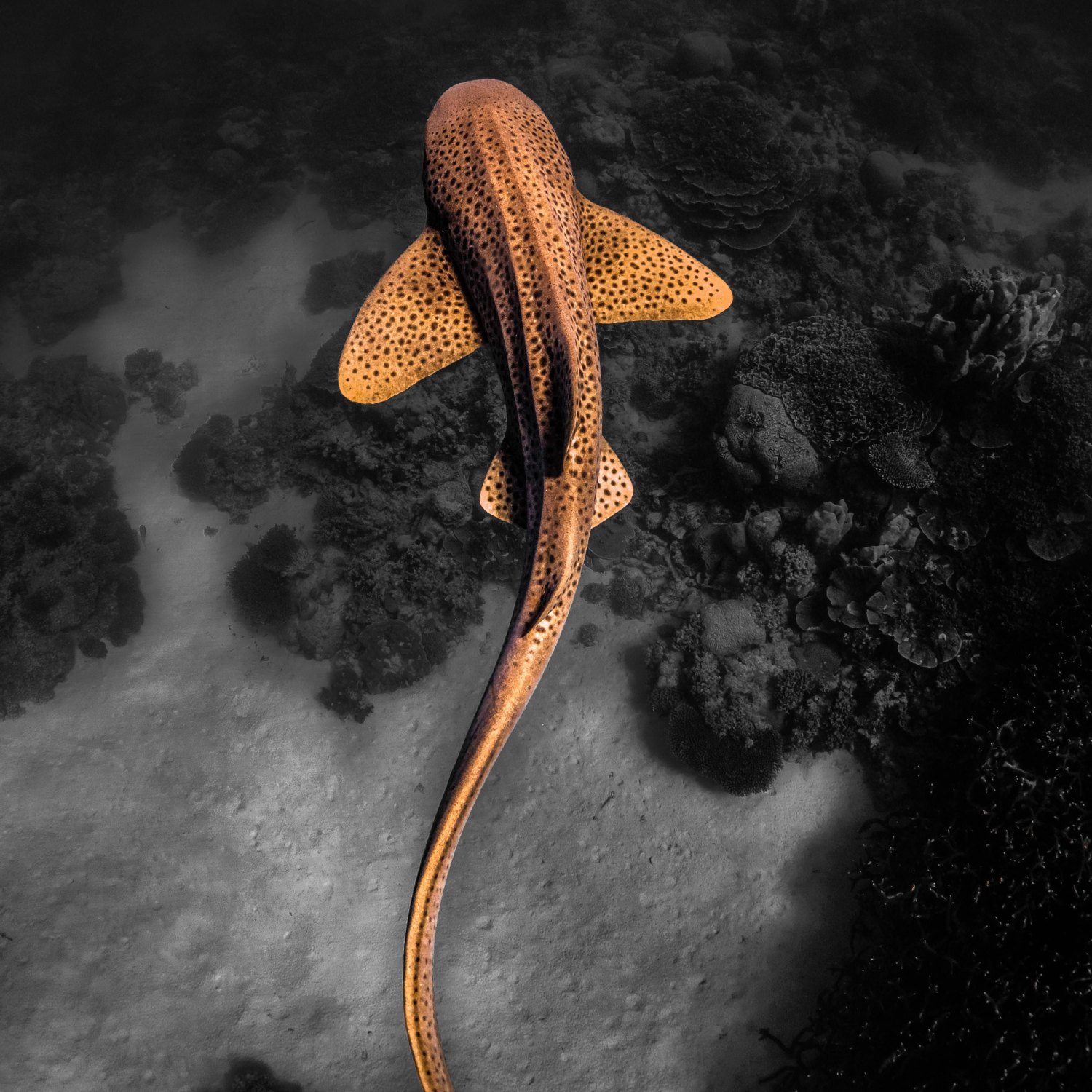
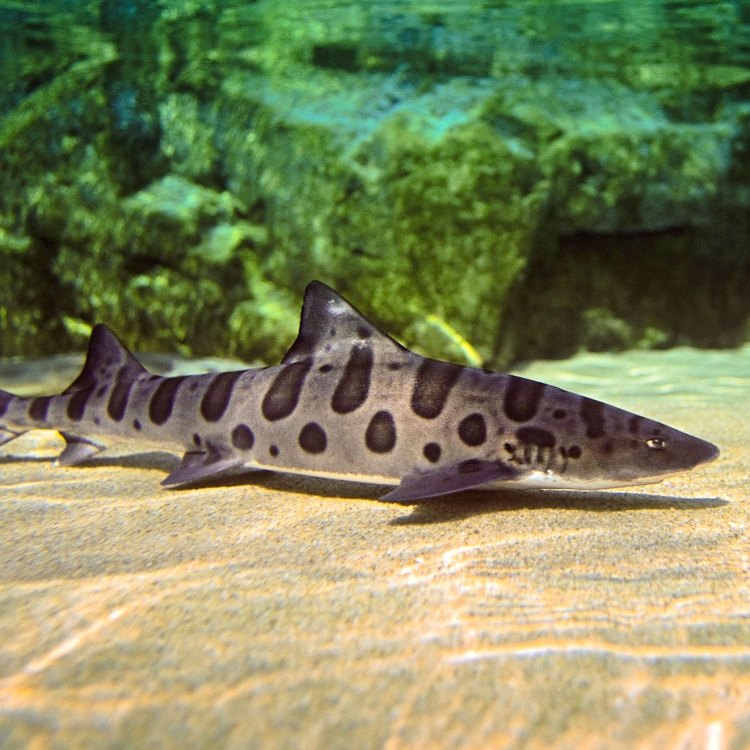
The Leopard Shark, found in California, is a stunning sight with its sleek, slender body and broad pectoral fins. Growing up to 6.5 feet, it belongs to the Triakidae family and can be easily identified by its flattened head. These majestic creatures are a must-see for any animal lover exploring the waters of the United States.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Leopard Shark
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Coastal waters, bays, estuaries
The Unique and Beautiful Leopard Shark: A Fascinating Member of the Animal Kingdom
The ocean is home to countless species of fishes, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions to the delicate ecosystem. One such species is the leopard shark, scientifically known as Triakis semifasciata. This article will dive deep into the fascinating world of the leopard shark, exploring its physical features, behavior, habitat, and more.A Closer Look at the Leopard Shark's Taxonomy and Distribution
The leopard shark belongs to the family Triakidae, a group of sharks commonly known as the houndsharks Leopard Shark. These sharks are characterized by their elongated bodies, flattened heads, and large pectoral fins. The leopard shark, specifically, is part of the order Carcharhiniformes, which includes over 270 species of sharks, such as the familiar great white and tiger sharks.These sharks reside in the Chordata phylum, which includes all animals with a spinal cord. Within this phylum, they belong to the class Chondrichthyes, a diverse group of fishes that possess skeletons made of cartilage instead of bone. This class also includes other well-known species such as stingrays and skates.
The leopard shark is mainly found in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, specifically along the coast of California in the United States. They have also been spotted in the coastal waters, bays, and estuaries of other countries such as Mexico and Japan. Their abundance in the waters of California has earned it the title of state shark, and it is a popular sight among divers and snorkelers in the area.
Appearance and Adaptations of the Leopard Shark
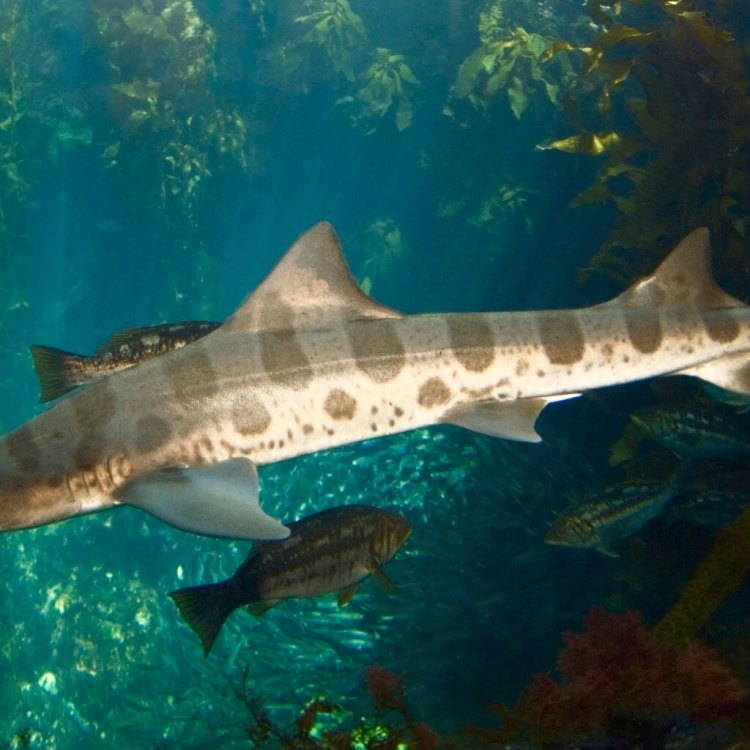
As the name suggests, the leopard shark is known for its unique coloration Lion. Its body is mostly gray or dark brown, with a series of distinct black spots and saddles that give it the appearance of a leopard. These spots are not only for decorative purposes but also serve as a form of camouflage, allowing the shark to blend in with the sandy ocean floor.Apart from its striking appearance, the leopard shark also possesses unique physical adaptations that aid in its survival. Its slender, elongated body and broad pectoral fins allow it to swim gracefully and efficiently through the water. This body shape is also an advantage when hunting, as it enables the shark to maneuver easily and catch its prey.
One of the most notable traits of the leopard shark is its ability to breathe while remaining still. This is due to a specialized respiratory structure called spiracles, located behind its eyes. These spiracles allow the shark to pump water over its gills even while resting, ensuring a steady supply of oxygen.
Feeding and Behavioral Patterns of the Leopard Shark
As with most sharks, the leopard shark is a carnivore, feeding mainly on fish, squid, and crustaceans. However, they are not aggressive hunters and pose little danger to humans. Instead, they rely on stealth and speed to catch their prey.The leopard shark is a nocturnal species, meaning they are most active at night. They are also solitary creatures, although they are occasionally seen in small groups during their breeding season. They are generally non-aggressive towards humans and are known to be docile creatures, making them a popular attraction among divers and snorkelers.
Apart from their feeding patterns and behavior, leopard sharks are also known for their unique reproductive capabilities. Unlike most sharks, they possess both internal and external fertilization methods. Male sharks use claspers, a pair of specialized organs, to transfer sperm to the female's reproductive tract. Females then lay their eggs in protective cases called mermaids' purses, which are found among kelp forests and other marine plants.
Conservation Status and Threats to the Leopard Shark
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) currently classifies the leopard shark as a near-threatened species. While they are not facing immediate danger of extinction, their population is decreasing due to various threats such as overfishing and habitat destruction.One of the main threats to leopard sharks is the destruction of their natural habitat, such as the pollution of coastal waters, which are crucial for their survival. They are also affected by indiscriminate fishing methods, including trawling and gillnetting, which often result in the accidental capture of these gentle creatures.
Fortunately, there are ongoing efforts to protect and conserve the leopard shark. In the United States, it is illegal to fish for leopard sharks without a permit, and there are strict regulations in place to ensure the sustainability of their population. Additionally, organizations such as the California Department of Fish and Wildlife have launched initiatives to monitor and protect these sharks' breeding grounds.
Conclusion
The leopard shark is a unique and fascinating species that contributes to the diversity and balance of our ocean's ecosystem. From its distinct coloration and physical adaptations to its behavior and conservation efforts, this shark has captured the hearts of many marine enthusiasts. As we continue to learn more about these incredible creatures, it is crucial to work towards their protection and preservation for generations to come.
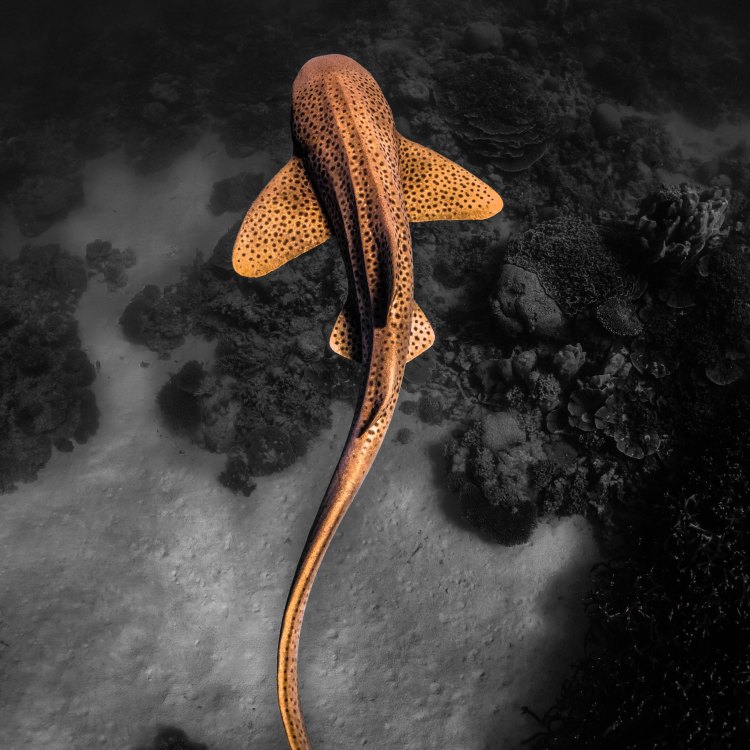

Leopard Shark
Animal Details Leopard Shark - Scientific Name: Triakis semifasciata
- Category: Animals L
- Scientific Name: Triakis semifasciata
- Common Name: Leopard Shark
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Triakidae
- Habitat: Coastal waters, bays, estuaries
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Eastern Pacific Ocean
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: California, United States
- Animal Coloration: Gray or dark brown body with distinct black spots and saddles
- Body Shape: Slender, elongated body with a flattened head and broad pectoral fins
- Length: Up to 6.5 feet (2 meters)
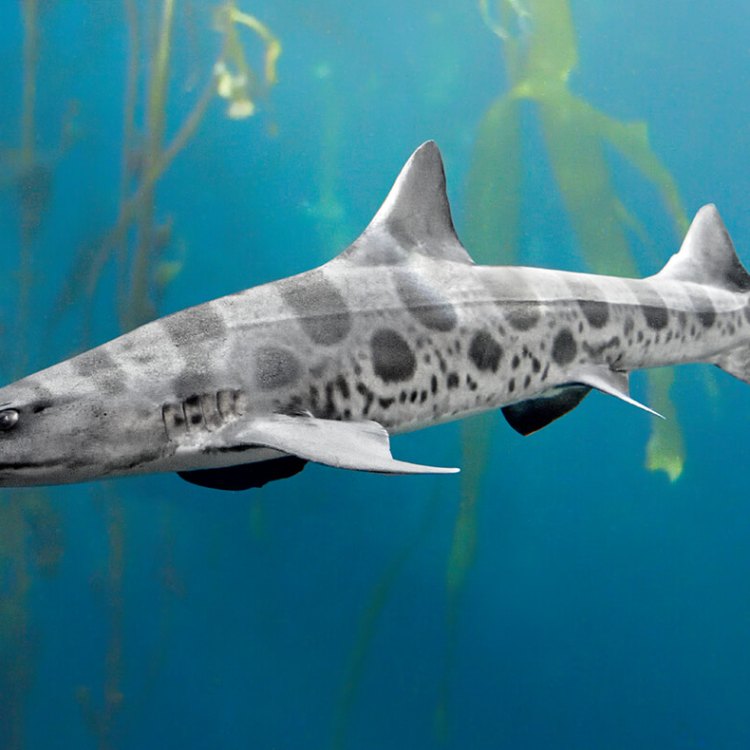

Leopard Shark
- Adult Size: 4.9 - 5.9 feet (1.5 - 1.8 meters)
- Average Lifespan: 20-30 years
- Reproduction: Oviparous
- Reproductive Behavior: Female leopard sharks lay egg cases called mermaid's purses
- Sound or Call: No known sound or call
- Migration Pattern: Seasonal migration along the coast
- Social Groups: Solitary or form small groups
- Behavior: Nocturnal and bottom-dwelling
- Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Near Threatened
- Impact on Ecosystem: Leopard sharks play a role in controlling prey populations and maintaining ecosystem balance
- Human Use: Fished for food, displayed in aquariums
- Distinctive Features: Distinct black spots and saddles on body
- Interesting Facts: Leopard sharks are harmless to humans and are often seen in shallow coastal waters
- Predator: Larger sharks, sea lions

Triakis semifasciata
The Fascinating World of the Leopard Shark: Exploring Its Life, Behavior, and Importance in the Ecosystem
The ocean is a vast and mysterious place, home to countless species of marine life. Among them, is the magnificent leopard shark, a creature with distinctive markings and intriguing behaviors. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of leopard sharks, from their physical characteristics and behaviors to their crucial role in the ecosystem and their interaction with humans.Adult leopard sharks typically reach a length of 4 PeaceOfAnimals.Com.9 to 5.9 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters), making them a fairly average-sized shark. Despite their size, they can live for an impressive 20 to 30 years. These sharks are found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, ranging from southern Oregon in the United States to southern Baja California in Mexico. They are also commonly found in the eastern Pacific Ocean, ranging from as far north as San Francisco Bay to as far south as Mazatlan, Mexico.
One of the most striking features of leopard sharks is their unique black spots and saddles on their body. These markings are what give them their name, as they resemble the spots and patterns of a leopard Loris. These spots may vary in size and shape and can be seen all over their body, from their dorsal fins to their tail.
But despite their ferocious-sounding name and markings, leopard sharks are actually quite harmless to humans. They are known to be docile and rarely attack humans unless provoked or threatened. This makes them a popular species for divers and snorkelers to encounter, often seen in shallow coastal waters.
So, what makes these sharks such interesting creatures? Let's take a closer look at their behavior and reproduction.
Leopard sharks are solitary animals, but they are also known to form small groups with other leopard sharks. During the day, they can be found resting on the ocean floor, often in sandy or muddy areas. They are bottom-dwelling sharks, meaning they spend most of their time close to the ocean floor, hunting for prey.
Their hunting behavior is also unique. Leopard sharks are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night. They use their strong sense of smell to detect prey, which includes small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. They are also known to dig through the substrate on the ocean floor with their snouts, searching for food. This behavior has earned them the nickname "sand sharks."
But when it comes to reproduction, leopard sharks follow a different pattern. They are oviparous, meaning they lay eggs instead of giving birth to live young. Female leopard sharks produce egg cases called mermaid's purses, which are typically around 7 inches long and 2 inches wide. These egg cases are often found washed up on beaches and have a unique design that helps leopard shark embryos develop.
The female leopard sharks will lay these egg cases in shallow waters, and after a gestation period of 10 to 12 months, the eggs will hatch, and the baby sharks will emerge. This is a crucial part of the leopard sharks' life cycle, ensuring the survival of the species.
But despite their impressive abilities and unique behaviors, leopard sharks are facing numerous threats that put their survival at risk. Habitat degradation, pollution, and overfishing are among the biggest threats to this species.
Leopard sharks are bottom-dwelling creatures, which makes them vulnerable to habitat degradation. Human activities such as coastal development and dredging can destroy their preferred habitats, making it difficult for them to find food and shelter.
Pollution is also a significant issue for leopard sharks. As they live close to the ocean floor, they often come in contact with pollutants that have been dumped into the ocean. These pollutants can be harmful to the sharks and can also impact their food sources, leading to health issues and a decrease in population.
But perhaps the biggest threat to leopard sharks is overfishing. They are often caught as bycatch in commercial fishing nets, but they are also targeted by humans for food. Their meat is considered a delicacy in some parts of the world, and their fins are used in shark fin soup. This overfishing has led to a decline in leopard shark populations, putting them in the "Near Threatened" category on the IUCN Red List.
This decline in leopard shark populations has a significant impact on the ecosystem. As bottom-dwelling predators, leopard sharks play a crucial role in regulating prey populations and maintaining balance in the ecosystem. Without them, prey populations can increase rapidly, leading to a ripple effect on the entire food chain.
In addition to their important role in the ecosystem, leopard sharks also have a significant impact on humans. While they are not normally targeted for their meat, they are sometimes fished for food. Their docile nature and distinct markings make them a popular species in aquariums and for public display. This allows people to observe and learn about these magnificent creatures up close.
But even with these human interactions, there is still much to learn about leopard sharks. Due to their mostly solitary nature and preference for shallow coastal waters, studying them can be challenging. However, researchers and marine biologists are working to gather more information about these sharks to help protect them and ensure their survival.
Despite their vulnerable status, there is hope for the future of leopard sharks. Conservation efforts such as protected marine areas and regulations on fishing practices have shown some success in increasing their populations. But there is still much work to be done to ensure the preservation of these incredible creatures.
In conclusion, the leopard shark is a fascinating and crucial species in our oceans. From their unique physical characteristics and behaviors to their importance in the ecosystem and their interaction with humans, there is no denying their significant impact on the marine world. As we continue to explore and learn more about these creatures, we must also take action to protect them and preserve their rightful place in the ocean.

The Unique and Beautiful Leopard Shark: A Fascinating Member of the Animal Kingdom
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.