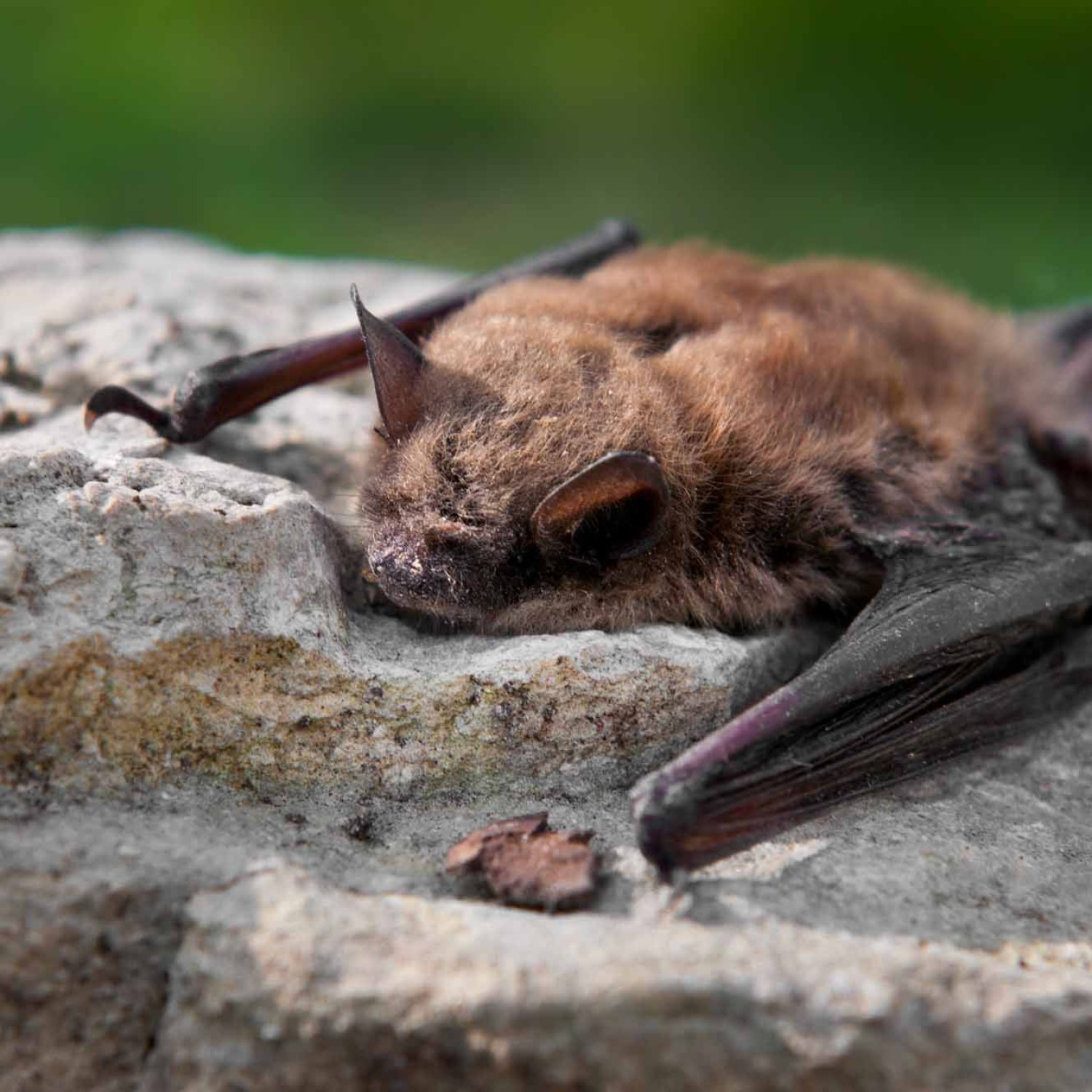
Little Brown Bat
3.1-3.9 inches
The Little Brown Bat is one of the most common bats in North America, with a small and compact body shape. It belongs to the Vespertilionidae family and can range from 3.1-3.9 inches in length. Despite its name, it is not actually brown but varies in color. They are important for insect control and can eat up to their body weight in insects each night. Keep an eye out for these beneficial creatures in your local area! #LittleBrownBat #NorthAmericanBats #Vespertilionidae #InsectControl
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Little Brown Bat
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Forests, fields, and urban areas
The Fascinating World of the Little Brown Bat
The animal kingdom is home to some of the most diverse and intriguing creatures, each with their own unique qualities and adaptations. One such animal is the Little Brown Bat, scientifically known as Myotis lucifugus. Despite its small size, this tiny mammal has captured the imagination of researchers and animal lovers alike, with its adaptive abilities and mysterious nature.An Introduction to the Little Brown Bat
The Little Brown Bat belongs to the order Chiroptera, which means hand-winged in Greek, as the animal's wings are formed from stretched skin between its long fingers Little Brown Bat. It is also a member of the Vespertilionidae family, commonly known as the evening bats.This species is native to North America, with the United States being its country of origin. It can be found throughout the continent, from the forests of Canada to the southern United States. Their preferred habitat includes forests, fields, and urban areas, making them a truly adaptable species.
The Physical Characteristics of the Little Brown Bat
The Little Brown Bat is, as the name suggests, small and compact, with a body shape that allows it to navigate through the air with precision and speed. It measures between 3.1 to 3.9 inches in length, making it one of the smallest bat species in North America.One of its most distinctive features is its brown coloration, which helps it blend in with its surroundings Lace Monitor. However, some individuals may also have a reddish or grayish tinge to their fur. They also have small, beady eyes and large ears, which aid in their echolocation abilities.
The Feeding Habits of the Little Brown Bat
The Little Brown Bat is an insectivore, meaning it feeds primarily on insects. This species has evolved to have an incredibly sophisticated echolocation system, which helps them navigate and hunt in the dark. They emit ultrasonic sounds, which bounce off their prey, giving them a precise location.Their diet consists mainly of moths, beetles, flies, and mosquitoes, making them an essential insect control species. In fact, a single bat can consume thousands of insects in just one night, making them an invaluable part of the ecosystem.
The Geographical Distribution of the Little Brown Bat
As mentioned earlier, the Little Brown Bat is native to North America, with its range spanning across the entire continent. They can be found in almost every state in the United States, from Alaska to Florida, and as far north as Canada and as far south as Mexico.They are also found in a variety of habitats, from urban cities to rural forests, showcasing their remarkable adaptability. In fact, they even roost in man-made structures, such as attics, barns, and abandoned buildings.
The Role of the Little Brown Bat in the Ecosystem
The Little Brown Bat plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems, particularly in insect control. As mentioned before, their diet consists of a wide range of insects, making them valuable in controlling pest populations that could damage crops or spread diseases.Additionally, their guano (feces) is rich in nutrients and used as a natural fertilizer. Several plant species depend on bat guano for their growth, further emphasizing the importance of these animals in maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
The Conservation Status of the Little Brown Bat
With its vital role in the ecosystem, it is no surprise that the Little Brown Bat has been facing threats to its population. The primary factors that have contributed to its decline are habitat loss and white-nose syndrome, a disease caused by a fungus that affects hibernating bats.To address these threats, several conservation efforts have been put in place, including monitoring and protecting bat colonies, promoting bat-friendly habitats, and educating the public about its importance.
Final Thoughts
The Little Brown Bat may be small, but its impact on the ecosystem is immeasurable. Its adaptability, unique characteristics, and important role in insect control make it a fascinating and essential species in the animal kingdom.As we continue to learn more about these creatures, it is crucial to also do our part in preserving and protecting their habitats, ensuring that future generations can also experience the wonder of the Little Brown Bat.
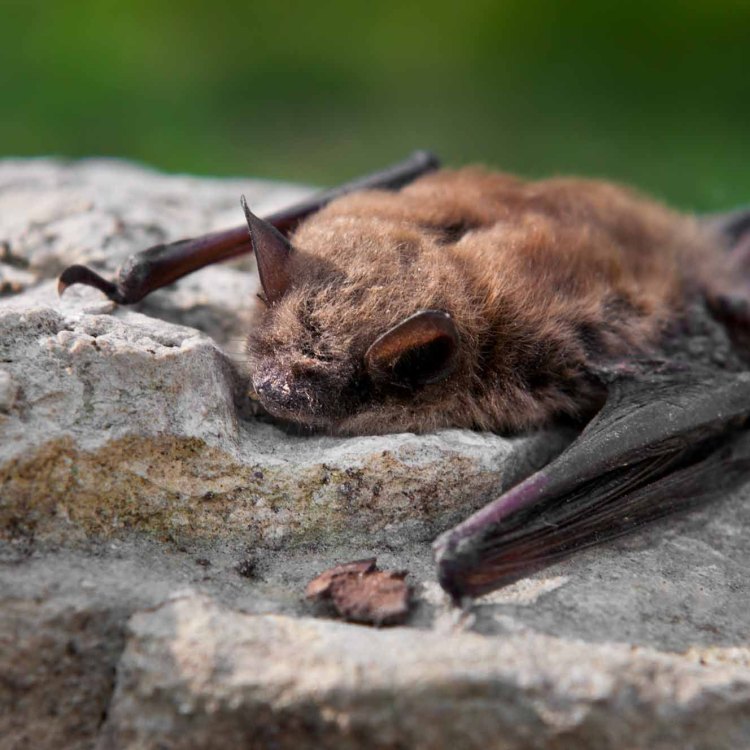

Little Brown Bat
Animal Details Little Brown Bat - Scientific Name: Myotis lucifugus
- Category: Animals L
- Scientific Name: Myotis lucifugus
- Common Name: Little Brown Bat
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Chiroptera
- Family: Vespertilionidae
- Habitat: Forests, fields, and urban areas
- Feeding Method: Insectivorous
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Throughout North America
- Animal Coloration: Brown
- Body Shape: Small and compact
- Length: 3.1-3.9 inches
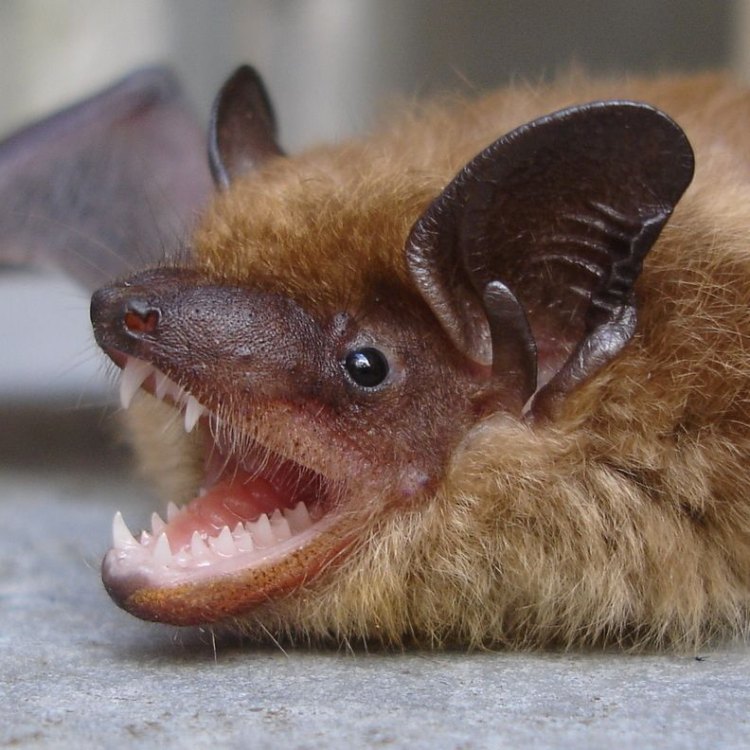

Little Brown Bat
- Adult Size: 9-10 grams
- Average Lifespan: 10-20 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs during late summer or fall
- Sound or Call: Echolocation calls
- Migration Pattern: Migrate to warmer regions
- Social Groups: Colonial
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Threats: Habitat loss, disturbance, and white-nose syndrome
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important pollinators and insect population control
- Human Use: Pest control and research
- Distinctive Features: Large ears and wings, and a small body size
- Interesting Facts: They can eat up to 1,200 mosquitoes in an hour
- Predator: Owls, hawks, and snakes
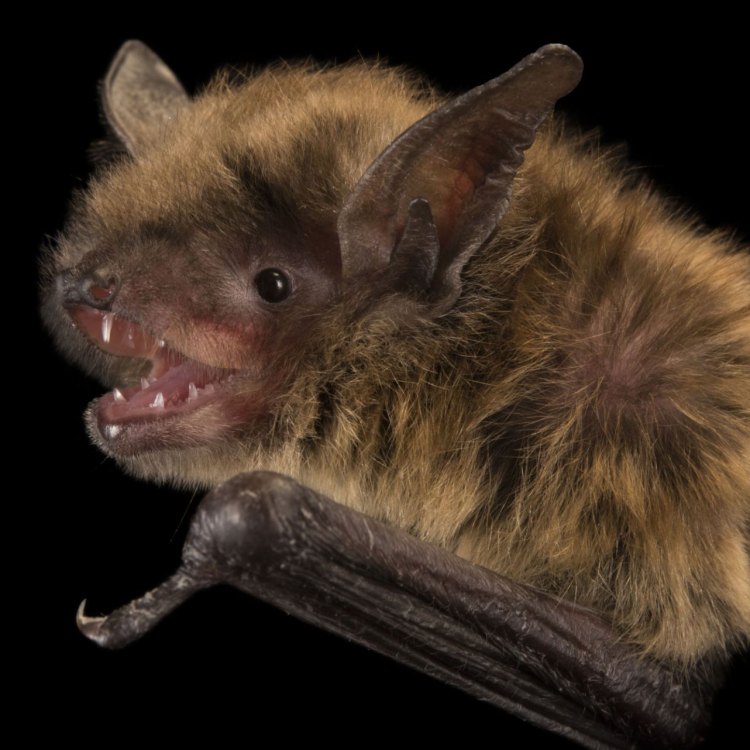

Myotis lucifugus
The Fascinating World of the Little Brown Bat
In the world of night creatures, one tiny mammal stands out for its unique characteristics and important role in maintaining a healthy ecosystem - the little brown bat. These fascinating creatures may seem small and ordinary, but they have remarkable abilities and play a significant part in keeping our environment balanced. In this article, we will delve into the world of the little brown bat, exploring its size, habits, and impact on the world around us.The Size and Lifespan of a Little Brown Bat
The little brown bat, scientifically known as Myotis lucifugus, is one of the smallest bat species in the world PeaceOfAnimals.Com. As adults, they typically weigh only 9-10 grams, which is equivalent to just a few teaspoons of sugar. They have a body length of 2.5-4.5 inches and a wingspan of 6-8 inches. Despite their diminutive size, these bats can live for up to 10-20 years, which is quite impressive for such a tiny creature.The Reproductive Behavior of Little Brown Bats
Like other mammalian species, little brown bats reproduce sexually. However, their mating habits are quite unique. Mating occurs during late summer or fall, which coincides with their migration to warmer regions. During this time, the bats form large mating groups, with males competing for females by engaging in aerial acrobatics and vocal displays Labraheeler.After mating, females store the sperm in their bodies for several months while they hibernate. This sperm then fertilizes their eggs in the spring when the bats are active again. Little brown bats have a slow reproductive rate, with females giving birth to only one offspring per year. This low reproductive rate makes them vulnerable to population decline and impacts their conservation status.
The Sound of Little Brown Bats
One of the most fascinating features of the little brown bat is its echolocation calls. These bats use high-frequency sounds, inaudible to human ears, to navigate and find their prey. They emit these sounds through their mouths or nostrils and then listen for the echoes bouncing back from objects in their surroundings. This ability allows them to fly and hunt in the dark with impressive accuracy.Interestingly, each bat species has a unique echolocation call, making it easier for them to recognize and avoid collisions with other bat species while flying in groups. The little brown bat's calls are usually short, low-frequency chirps, making them distinct from other bat species.
The Migration Pattern of Little Brown Bats
As temperatures start to drop in the late fall, little brown bats migrate to warmer regions for hibernation. They travel in large groups, often covering hundreds of miles, to reach their hibernation sites. During this migration, they face many threats, such as harsh weather conditions, predators, and human disturbances. Sadly, many bats do not survive the journey.The Social Groups and Behavior of Little Brown Bats
Little brown bats are colonial creatures, preferring to roost and hibernate in large groups of up to several thousand individuals. These colonies, also known as maternity colonies, are usually found in dark, humid caves or abandoned buildings. The bats huddle closely together in these colonies to conserve body heat, especially during hibernation when their body temperature drops significantly.As nocturnal animals, little brown bats are active at night, hunting for insects like mosquitoes, moths, and beetles. They can consume up to 1,200 mosquitoes in just one hour, making them a valuable natural pest control agent.
The Threats Facing Little Brown Bats
The little brown bat is facing various threats, primarily caused by human activities. Habitat loss is a significant concern for these bats, as their natural roosting and hibernation sites are continuously destroyed or disturbed. The disturbance can come from human developments, such as cave exploration or the demolition of buildings where bats roost.The introduction of white-nose syndrome, a fungal disease that affects bats while they hibernate, has also had a devastating impact on the little brown bat population. Millions of bats have succumbed to this disease since its discovery in 2006, resulting in a significant decline in their numbers.
The Conservation Status of Little Brown Bats
Despite the threats they face, the little brown bat is currently listed as "Least Concern" on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. This status is due to their wide distribution and large population size. However, this does not mean that we should ignore the threats facing these bats. It is crucial to protect their habitats and reduce factors that contribute to their decline to maintain a healthy population.The Impact of Little Brown Bats on the Ecosystem
The importance of little brown bats in our ecosystem cannot be overstated. As mentioned earlier, they are essential natural pest control agents, regularly consuming insects that can become pests for humans and crops. In addition to that, they are also vital pollinators, helping to pollinate numerous plants that rely on bats for pollination.Without bats, our ecosystem would suffer from imbalances, as insects would multiply and plants would not receive proper pollination. This would have a negative impact on our agricultural sector, leading to lower crop yields and potential food shortages.
The Role of Little Brown Bats in Human Use
Humans have utilized little brown bats for centuries in various ways. In the past, bats were used for their guano (droppings), which were collected and used as fertilizer. Today, they are still used for pest control, as farmers establish bat houses on their properties to attract the bats and control insect populations naturally.Furthermore, researchers continue to study these fascinating creatures, hoping to understand more about their echolocation abilities and how they can be used for technological advancements.
The Unique Features and Predators of Little Brown Bats
The little brown bat has several distinctive features that make it stand out from other bat species. One of its most notable features is its large ears and wings, which are proportionally larger than its small body size. These features help the bat with its echolocation abilities and allow it to fly quickly and efficiently.In addition to owls, hawks, and snakes, little brown bats also face threats from domestic cats and humans. Domestic cats, who often hunt for sport, can significantly reduce bat populations in certain areas. Humans also contribute to their decline through the various threats mentioned earlier.
Interesting Facts About Little Brown Bats
To wrap up our exploration of the little brown bat, here are a few interesting facts that highlight the unique characteristics and abilities of these tiny mammals:- Little brown bats can live up to 10-20 years, which is equivalent to 3-4 times their body size.
- They can fly at speeds of up to 40 kilometers per hour, with their wings beating over 10 times per second.
- These bats can consume insects that make up to half of their body weight in just one night.
- The hibernation period of little brown bats can last up to six months, with their body temperature dropping to as low as 3 degrees Celsius.
- The high-pitched calls of little brown bats are so loud that they can damage human hearing if heard up close.
In Conclusion
The little brown bat may seem like just another creature of the night, but it is a fascinating and essential part of our ecosystem. Their size, abilities, and impact on the environment make them a vital species to protect. As responsible citizens, it is our duty to take measures to conserve these bats and ensure their survival for future generations. Through education, awareness, and conservation efforts, we can help maintain a healthy balance in our ecosystem and continue to marvel at the wonders of the little brown bat.
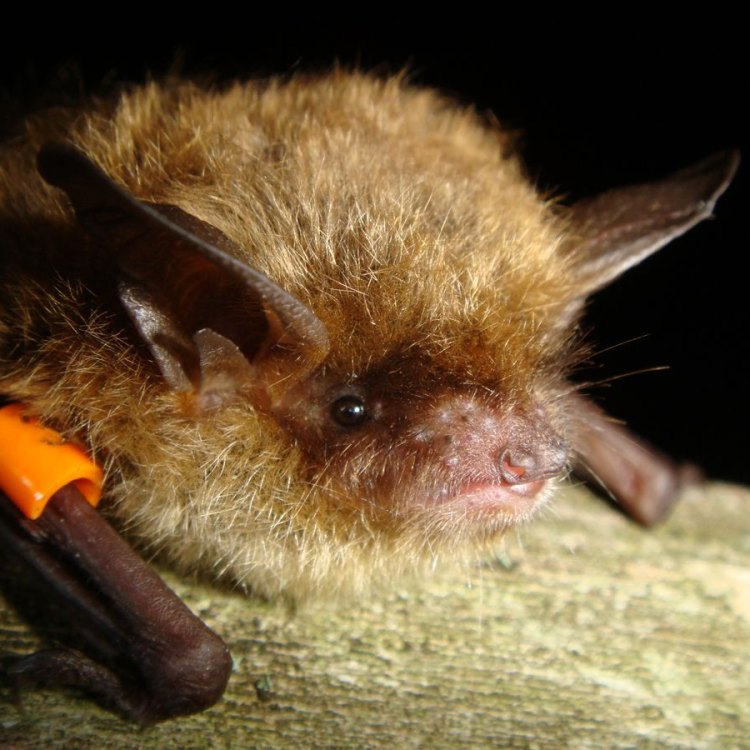

The Fascinating World of the Little Brown Bat
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.