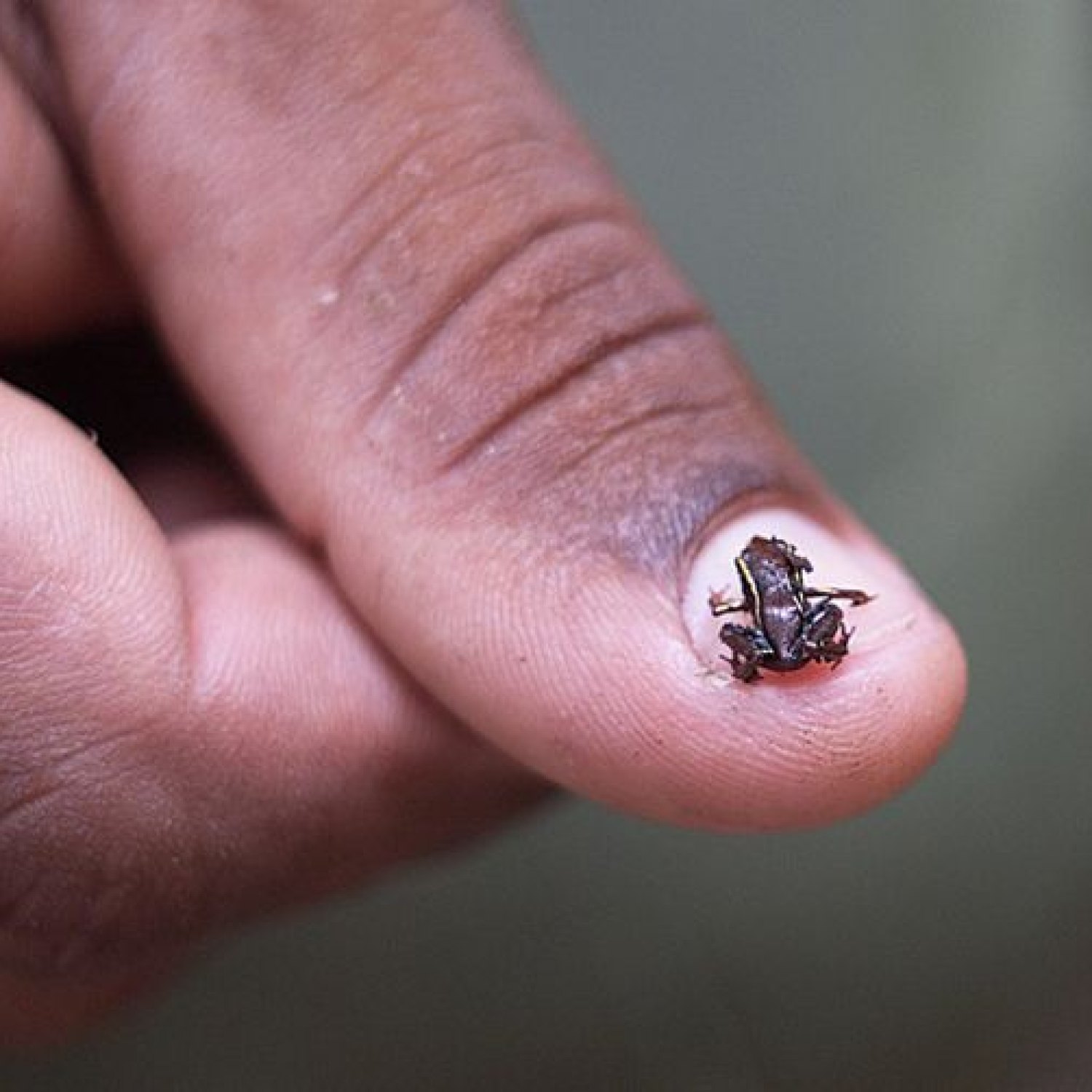
Monte Iberia Eleuth
1.3-2.4 cm (0.5-0.9 in)
The Monte Iberia Eleuth, also known as the Monte Iberia Robber Frog, is a tiny frog found in the Sierra Maestra mountain range in Cuba. At only 1.3-2.4 cm in length, this small and stocky frog is the smallest in its family, Eleutherodactylidae. Its size may be small, but its loud and distinctive call makes it a unique and fascinating species to spot in the wild.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Monte Iberia Eleuth
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Moist montane forests
The Elusive Monte Iberia Eleuth
Nestled within the lush and verdant montane forests of Cuba lies a small, but mighty creature - the Monte Iberia Eleuth. With a scientific name of Eleutherodactylus iberia, this tiny anuran species may not immediately capture the attention of the average person. However, this elusive creature boasts numerous unique features and characteristics that make it a truly fascinating amphibian.When exploring the animal kingdom, one may come across popular and well-known species such as lions, elephants, or dolphins Monte Iberia Eleuth. However, it is these lesser-known creatures, such as the Monte Iberia Eleuth, that capture our imagination and reveal the incredible diversity of life on our planet. So, let us take a closer look at this remarkable amphibian and uncover the features that make it a true marvel of nature.
Origin and Distribution
The Monte Iberia Eleuth, as its name suggests, calls the Monte Iberia region in Cuba its home. This small island nation, situated in the Caribbean Sea, is home to an array of unique flora and fauna, including this elusive amphibian. The Eleutherodactylus iberia is endemic to Cuba and can only be found in the Monte Iberia region, specifically in the Sierra Maestra mountain range.This species' restricted geographic distribution makes it incredibly special and endearing to both the scientific community and local communities. Unfortunately, due to habitat destruction, its already limited range is further dwindling, making conservation efforts incredibly crucial to safeguard its future.
Habitat
The Monte Iberia Eleuth is primarily found in the moist montane forests of the Sierra Maestra mountain range. This type of habitat is characterized by high humidity levels, ranging from 70-90%, and abundant rainfall throughout the year Morkie. These environments are vital for the Eleutherodactylus iberia's survival, as they offer a constant supply of moisture that they require to thrive.Within this habitat, the Monte Iberia Eleuth makes its home among the leaf litter and debris on the forest floor. This is an essential feature to note as it makes them incredibly challenging to detect and study, adding to their mystique and elusiveness.
Appearance
The Monte Iberia Eleuth may not catch one's eye with its coloration, but it is still a striking creature in its own right. This tiny anuran species is typically brown or black in color, with darker spots covering its body. Its dark coloration provides excellent camouflage in the leaf litter of its habitat, helping it evade predators.Apart from its color, the Monte Iberia Eleuth has a small and stocky body shape, with a length of 1.3-2.4 cm (0.5-0.9 in). This may seem small, but it is a vital adaptation to its environment. Being tiny and compact allows it to navigate through the dense forest floor with ease, as well as conserve energy while hunting and evading predators.
Carnivorous Diet
As a small and agile species, the Monte Iberia Eleuth's primary feeding method is carnivorous. Despite its tiny size, it is a predator that preys on smaller insects such as beetles, flies, and spiders. It is believed that this species employs a sit-and-wait strategy when hunting, ambushing its prey from its leaf litter hideouts.Their carnivorous diet allows them to obtain essential nutrients and energy, contributing to their survival and success in their challenging habitat. It also plays a crucial role in shaping the delicate balance of their ecosystem, as they help control insect populations.
Unique Adaptations
Apart from its small size and dark coloration, the Monte Iberia Eleuth boasts several unique adaptations that make it stand out in the animal kingdom. These features and behaviors demonstrate the incredible resilience and adaptability of this species, which has allowed it to thrive in its limited and challenging environment.One of its most remarkable adaptations is its ability to survive extreme climatic conditions, particularly droughts. During extended dry periods, the Eleutherodactylus iberia enters a state of dormancy, slowing its metabolism and conserving energy until water becomes available. This incredible feat allows them to survive in a habitat that is prone to erratic climatic conditions.
Another adaptation that sets this species apart is its high-pitched vocalization. Despite its small size, the Monte Iberia Eleuth produces loud trilling sounds that can be heard throughout the forest. This serves both as a means to attract mates and to communicate with other individuals. It is a crucial survival mechanism, as it allows them to locate and identify potential competitors and mates in their dense and leafy habitat.
Threats to Survival
Despite its incredible adaptability and resilience, the Monte Iberia Eleuth faces many challenges that endanger its survival. The primary threat to this species is habitat destruction, resulting from human activities such as deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization. With its already limited range and specific habitat requirements, any disturbance or destruction can have a severe impact on this species.Furthermore, as an endemic species, the Monte Iberia Eleuth is highly vulnerable to changes in its small and isolated population. Disease outbreaks, climate change, and natural disasters can have devastating effects on their numbers, making it imperative to implement conservation measures to protect their future.
The Role of Conservation
The elusive nature of the Monte Iberia Eleuth has contributed to its low profile and limited knowledge about its biology and behavior. However, with increased conservation efforts and scientific research, more is being uncovered about this tiny amphibian. We now understand its importance in its ecosystem and the need to protect its natural habitat.Several organizations and institutions in Cuba are actively involved in monitoring and protecting this species. They employ measures such as habitat restoration, education and awareness programs, and captive breeding programs to ensure the preservation of the Monte Iberia Eleuth for future generations to admire and appreciate.
In Conclusion, the Monte Iberia Eleuth may not be the most well-known or popular species, but it is a remarkable and unique creature in its own right. Its restricted range and habitat, as well as its elusive nature, make it a true gem within the animal kingdom. With continued conservation efforts, we can help secure its future and ensure that this tiny and mighty creature continues to thrive in its natural habitat.
Monte Iberia Eleuth
Animal Details Monte Iberia Eleuth - Scientific Name: Eleutherodactylus iberia
- Category: Animals M
- Scientific Name: Eleutherodactylus iberia
- Common Name: Monte Iberia Eleuth
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Amphibia
- Order: Anura
- Family: Eleutherodactylidae
- Habitat: Moist montane forests
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Monte Iberia, Cuba
- Country of Origin: Cuba
- Location: Monte Iberia, Sierra Maestra mountain range
- Animal Coloration: Brown or black with darker spots
- Body Shape: Small and stocky
- Length: 1.3-2.4 cm (0.5-0.9 in)
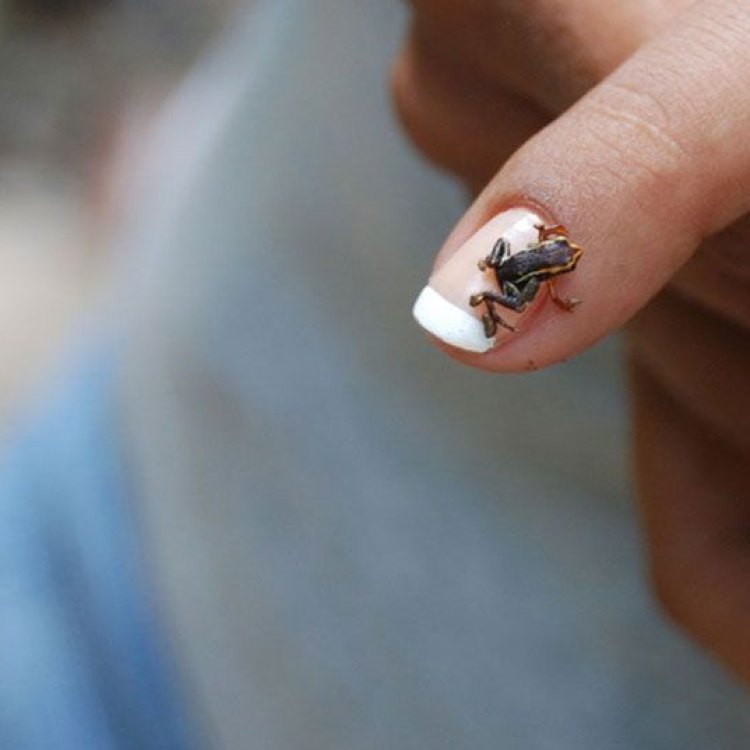

Monte Iberia Eleuth
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 2-5 years
- Reproduction: Egg-laying
- Reproductive Behavior: Males call to attract females
- Sound or Call: Distinctive call that sounds like a high-pitched whistle
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, climate change
- Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
- Impact on Ecosystem: Helps control insect populations
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Small size, dark coloration, distinctive call
- Interesting Facts: It is considered the smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Predator: Unknown
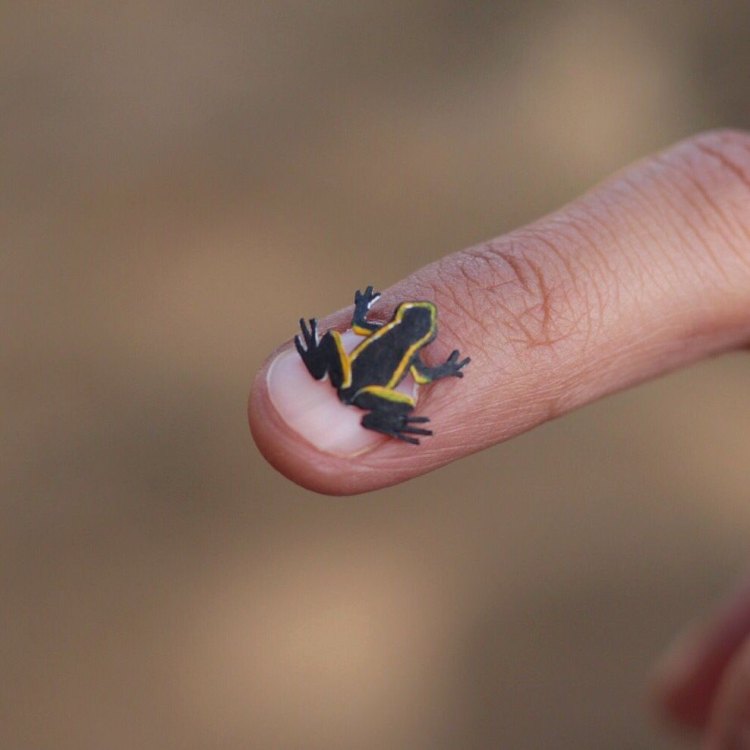
Eleutherodactylus iberia
The Tiny and Endangered Monte Iberia Eleuth
In the depths of the rainforests of Cuba lies a tiny and elusive creature, the Monte Iberia Eleuth. This minuscule frog, measuring only 10 to 12 millimeters in length, is not only the smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere but also one of the most critically endangered species in the world. Its unique features and behaviors make it a fascinating creature, but its declining population and threats to its survival make it a cause for concern.Physical Characteristics
The Monte Iberia Eleuth, known scientifically as Eleutherodactylus iberia or "Iberian Eleuth," is a member of the Leptodactylidae family PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They have dark-colored skin with a light stripe running down their back. Their small size and dark coloration help them blend in with their environment, making them tricky to spot. They have four toes on their front feet and five toes on their back feet, each with tiny adhesive pads that help them cling onto leaves and trees as they search for food.
Life Span and Reproductive Behavior
On average, Monte Iberia Eleuths have a lifespan of 2 to 5 years, with some individuals living up to 10 years. They reach sexual maturity at two years of age and reproduce through egg-laying. But what makes their reproductive behavior particularly interesting is the role of the males in attracting females.
Males have a distinctive, high-pitched whistle-like call that can be heard throughout the forests at night. They call from high perches near the ground to attract potential mates. This behavior is believed to be essential for finding a mate in the dense and dark rainforest environment Mollusk.
Social Behavior and Migration Patterns
Monte Iberia Eleuths are solitary creatures, with little information about their social interaction or group dynamics. They are primarily found hiding under logs, rocks, or in leaf litter during the day. As nocturnal creatures, they become active at night, hopping around in search of food such as insects, spiders, and other small invertebrates.
One unique feature of this species is its non-migratory behavior. Unlike many other amphibian species, they do not undertake seasonal migrations. Instead, they remain in their small home range, usually less than one square meter, for their entire lives.
Threats to Survival
Sadly, the Monte Iberia Eleuth population is declining, with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) listing them as critically endangered. There are fewer than 300 individuals left in the wild, and their population is decreasing due to various threats.
A major threat to the Iberian Eleuth is habitat loss. Cuba's rainforests have been significantly reduced due to deforestation for agriculture, urban development, and logging. As a result, the tiny amphibians are squeezed into smaller and more vulnerable habitats, making them more susceptible to extinction.
Furthermore, pollution, particularly from agriculture and mining, is another significant threat. Chemicals and runoff from these activities can contaminate the water, killing the amphibians and their prey.
Climate change is also a concern as it can affect the availability of water sources and alter the temperature and humidity of the rainforest, impacting the Eleuth's survival and reproduction.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts are being made to protect the Monte Iberia Eleuth and prevent its extinction. The ongoing research on the species' behavior and biology provides valuable information for conservation efforts. Moreover, the Cuban government has set aside protected areas, such as the Alejandro de Humboldt National Park, to preserve the Eleuth's habitat.
Several conservation organizations, such as Amphibian Ark, focus on raising awareness about the significance of conservation and the need to protect the Monte Iberia Eleuth. They work closely with local communities to promote sustainable practices and preserve the rainforest ecosystem.
Impact on Ecosystem
Despite their small size, the Monte Iberia Eleuth plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem. As insectivores, they help control insect populations, reducing the risk of insect-borne diseases and maintaining the health of the forest. Furthermore, as prey for larger predators, they contribute to the food web of the rainforest.
Lack of Human Use
The Monte Iberia Eleuth has no known use for humans. They are not used for food, medicine, or any other purpose. However, their existence contributes to the biodiversity of our planet, making them valuable in their own right.
Interesting Facts
Besides being the smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere, the Monte Iberia Eleuth has some other interesting facts:
- It is found only in Cuba, making it an endemic species.
- It is believed to be one of the 52 species that were living in Cuba before it became an island.
- Its small size is an adaptation to its limited habitat, allowing it to navigate and survive in the dense rainforest.
- The species was first identified and described in 1996, making it relatively new to the scientific world.
Predators and Protection Mechanisms
As elusive creatures, not much is known about their predators. However, their small size and dark coloration help them camouflage in their surroundings, providing some protection against predators. Additionally, their sticky toe pads and ability to jump long distances help them escape from danger.
Conclusion
The Monte Iberia Eleuth, the world's smallest frog in the Northern Hemisphere, is a fascinating creature. Its size, behavior, and distinctive features make it unique, but its declining population and threats to survival make it a cause for concern. It serves as a reminder of the fragility of our ecosystems and the need for sustainable practices to protect and preserve our planet's biodiversity. As we continue to learn more about this tiny frog and its importance, it is our responsibility to take action and ensure its survival for future generations to come.
The Elusive Monte Iberia Eleuth
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












