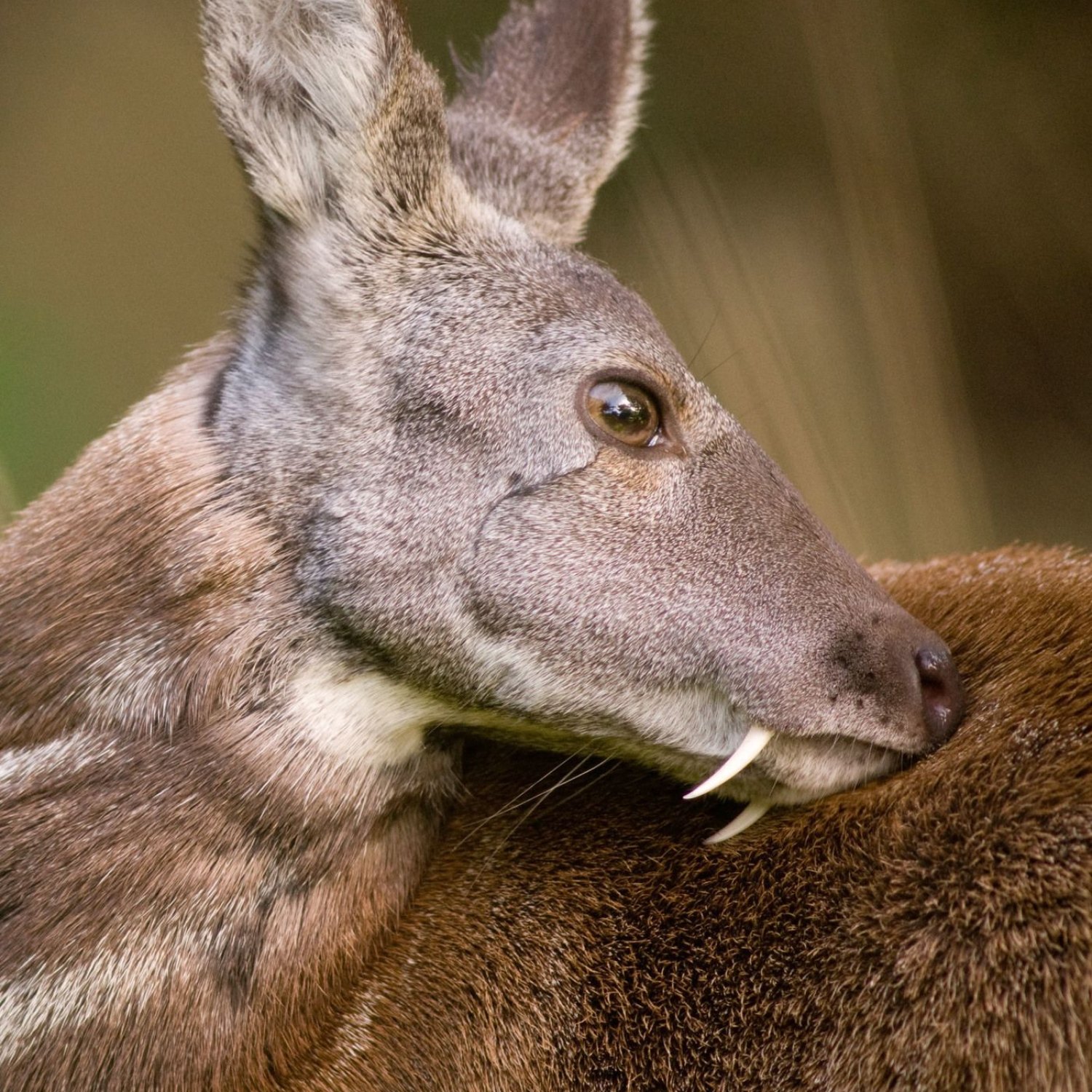
Musk Deer
80-100 cm
The Musk Deer is a unique animal found in mountainous regions. It belongs to the family Moschidae and has a body shape that is medium-sized and stocky. They are known for their musk, a valuable substance used in perfumes and traditional Chinese medicine. These beautiful creatures measure 80-100 cm in length and are a must-see for nature enthusiasts. #MuskDeer #MountainAnimals #NatureLovers
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Musk Deer
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Mountain forests
The Fascinating World of Musk Deer
Majestic and elusive, the musk deer has captivated humans for centuries with its unique features and mysterious nature. These animals belong to the genus Moschus, and are commonly known as musk deer. They are found in mountain forests across Central and East Asia, and have been an important part of Asian culture and medicine for centuries.But what makes musk deer so special? Let us dive deeper into the world of these beautiful creatures to uncover their fascinating features and behavior Musk Deer.
The Classification of Musk Deer
The scientific name of musk deer is Moschus, which belongs to the Animalia kingdom. They are classified under the chordata phylum and mammalia class. Within the mammalia class, musk deer belong to the order Artiodactyla, which means "even-toed" animals. This order includes other species such as deer, antelopes, and giraffes.Musk deer are the only members of the family Moschidae, making them a unique and distinct group of animals. They have evolved to adapt to their mountainous habitat and have developed some fascinating features over time.
Habitat and Distribution
Musk deer are primarily found in mountain forests, where they can blend in with their surroundings and hide from predators. They are mainly found in the mountainous regions of China, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Myanmar, although they have also been spotted in Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Russia.One of the reasons musk deer are found in such a wide geographical distribution is their ability to survive in different habitats Mountain Feist. They can adapt to living in areas with rocky terrain, dense forests, and extreme weather conditions.
Herbivorous Diet
As herbivores, musk deer primarily feed on a variety of plants and fruits. Their diet mainly consists of leaves, twigs, bark, grass, and herbs. In the harsh mountainous terrain, where food can be scarce, musk deer are able to survive on a variety of vegetation and can go without water for long periods.Interestingly, musk deer have a unique way of feeding. They do not have upper front teeth but instead have a pair of hardened canines, which they use to grind and crush their food. This adaptation has also been observed in other herbivorous animals living in mountainous regions.
Elusive Behavior
Musk deer are solitary creatures, and they prefer to live and wander alone. They have highly developed senses, and their keen eyesight and hearing help them detect predators from a distance. When they sense danger, they will remain still, relying on their camouflage and staying out of sight until the threat has passed.Due to their solitary nature, it is challenging to spot musk deer in the wild. They are also active mostly at dawn and dusk, making it even harder for humans to catch a glimpse of them.
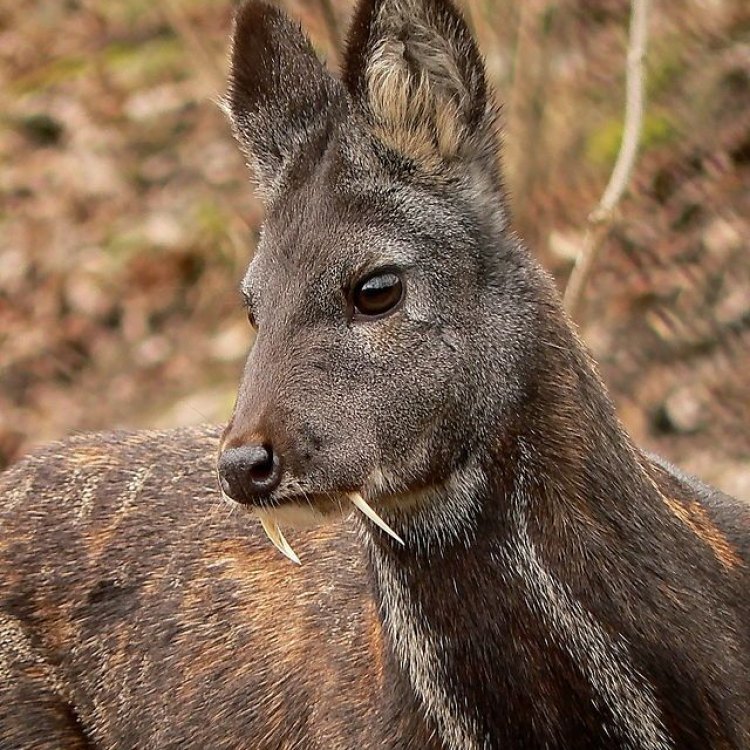
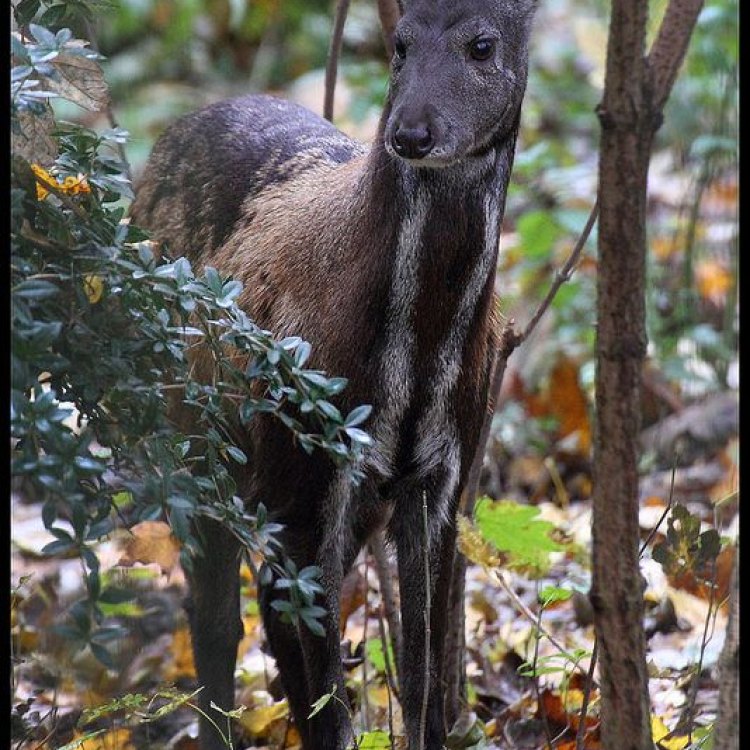
The Intriguing Body of a Musk Deer
Musk deer have a medium-sized, stocky body, which is well adapted to their mountainous habitat. They have short legs but are agile and can climb steep slopes effortlessly.One of the most striking features of musk deer is their coloration. They have a dark brown or reddish-brown coat with lighter underparts to help them blend in with their surroundings. Their fur is also thick and soft, providing insulation in the cold, mountainous climate.
Their body shape is also unique, with a distinctive hump on their shoulders. This hump is a fatty deposit that serves as an energy reserve during harsh winters when food is scarce.
Reproductive Cycle
Musk deer have a breeding season that lasts from November to December, during which males compete for the attention of females. They use their sharp canines to fight with other males, and the winners get to mate with multiple females.After a gestation period of around 6 months, female musk deer give birth to a single offspring. The young are born with a spotted coat, which helps them blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators. The mother takes care of the offspring for about a year, after which the young musk deer will venture out on their own.
The Significance of Musk Deer in Asian Culture
Musk deer have a special place in Asian culture, particularly in Chinese medicine. The musk gland, located in the deer's abdomen, has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. It is believed to have therapeutic properties and is used in treating various ailments, including skin diseases, headaches, and even epilepsy.The musk gland of a musk deer is precious and has led to its hunting and poaching, resulting in the decline in the population of musk deer in the wild. Efforts are being made to conserve the species and protect them from illegal poaching.
Conclusion
Musk deer have captivated humans for centuries with their unique features and elusive nature. Their ability to survive in harsh mountainous regions, coupled with their intriguing adaptations, make them a fascinating animal to study.But with their population declining due to human exploitation, it is crucial to raise awareness and take measures to conserve these beautiful creatures. Let us appreciate and admire musk deer from a distance, and work towards preserving their existence for generations to come.
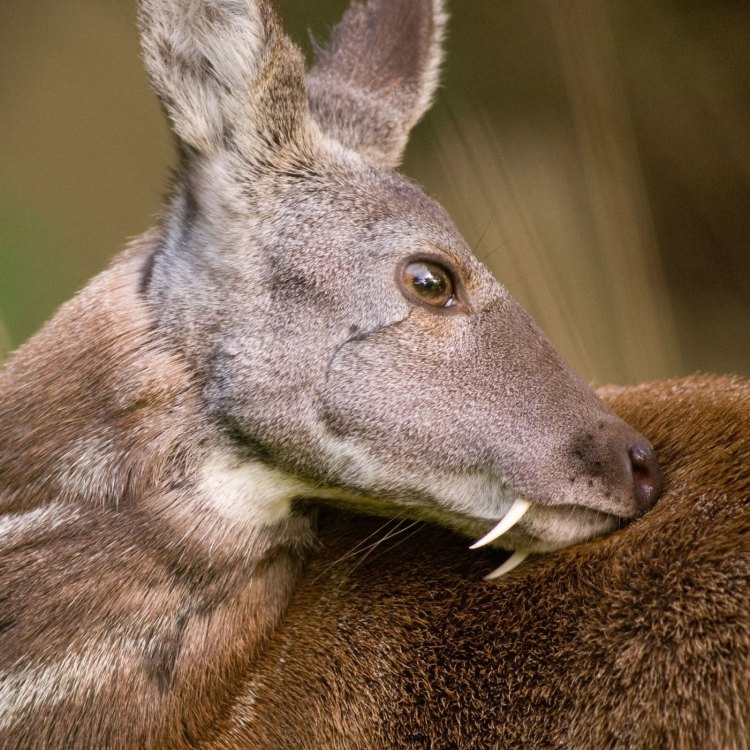

Musk Deer
Animal Details Musk Deer - Scientific Name: Moschus
- Category: Animals M
- Scientific Name: Moschus
- Common Name: Musk Deer
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Artiodactyla
- Family: Moschidae
- Habitat: Mountain forests
- Feeding Method: Herbivore
- Geographical Distribution: Central and East Asia
- Country of Origin: China, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar
- Location: Mountainous regions
- Animal Coloration: Dark brown or reddish-brown
- Body Shape: Medium-sized, stocky
- Length: 80-100 cm
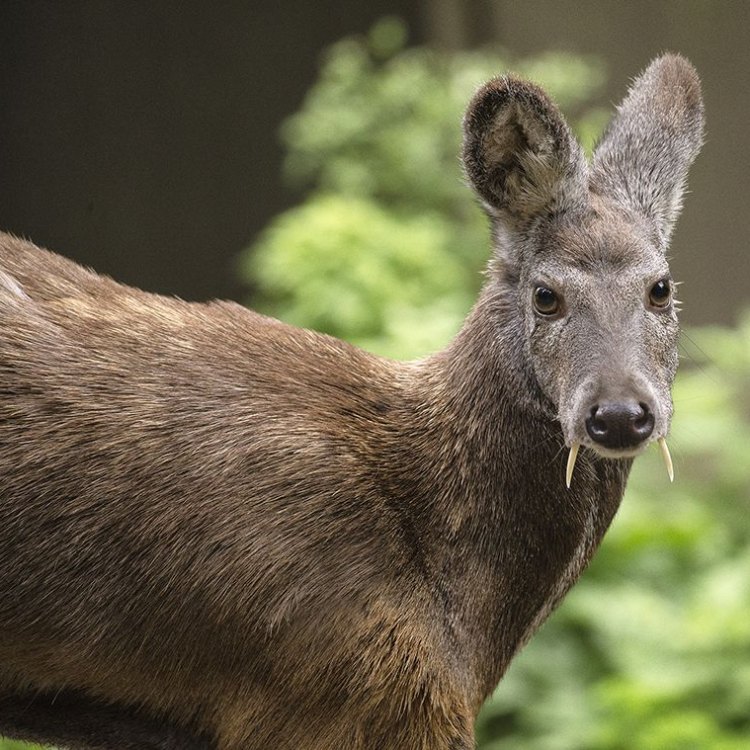

Musk Deer
- Adult Size: 15-35 kg
- Average Lifespan: 10-15 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males fight for females, mating season in late fall
- Sound or Call: Males produce a musky odor and use vocalizations
- Migration Pattern: No regular migration pattern
- Social Groups: Solitary or small groups
- Behavior: Nocturnal, shy and elusive
- Threats: Hunting for musk gland, habitat loss, illegal trade
- Conservation Status: Vulnerable
- Impact on Ecosystem: Seed dispersers, maintain forest ecosystems
- Human Use: Hunted for musk gland, used in traditional medicine and perfume industry
- Distinctive Features: Fang-like tusks, scent glands
- Interesting Facts: Musk deer are the only deer species that have tusks
- Predator: Snow leopards, wolves, lynxes

Moschus
The Elusive and Endangered Musk Deer: A Unique and Important Species
The musk deer, also known as the "Kasturi Mriga" or "Moschus" in scientific terms, is a species of deer that is found in the mountainous regions of Asia. These solitary creatures are known for their unique features and habits, making them a fascinating species to study. However, despite their elusive nature, they are facing numerous threats, landing them on the list of vulnerable species.As we delve into the world of the musk deer, we will explore its distinct features, behaviors, and the vital role it plays in the ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com.
The Size and Lifespan of a Musk Deer
The musk deer is a relatively small-sized deer, with adult males weighing between 15 to 35 kilograms and females weighing around 10 to 18 kilograms. Their fur is usually dark brown, gray, or yellowish-brown, with a lighter underbelly and white spots on their back. Their coats also thicken during the winter months to protect them from the harsh cold climate of their habitat.On average, a musk deer lives for 10 to 15 years in the wild. However, their lifespan can vary depending on their living conditions and threats they face.
Reproduction and Mating Behavior
Like most mammals, musk deer reproduce sexually, with a distinct mating season that occurs in late fall. During this time, males compete for the attention of females by fighting with each other. Their primary goal is to establish dominance and secure breeding rights with the females.Interestingly, these fights are not physical but are rather vocal and olfactory-based Marabou Stork. The males produce a powerful musky odor from their scent glands located near their genitals. This musky smell can attract females and also serve as a means of communication between males.
Nocturnal and Elusive Behavior
Musk deer are known for being nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active at night. They have a shy and elusive nature, making them challenging to spot in the wild. They prefer to live in dense, remote forests, away from humans and other predators.Their elusive behavior is also due to their solitary or small group social structure. They do not live in large herds like other deer species, which makes it easier for them to hide and avoid detection.
No Regular Migration Pattern and Human Use
Unlike many other deer species, musk deer do not have a regular migration pattern. They tend to stay within their defined home range, which can vary from a few square kilometers to larger areas.In the past, musk deer were primarily hunted for their musk gland, located on their abdomen. This scent gland is highly sought after for its use in traditional medicine and the perfume industry. However, due to strict regulations and conservation efforts, the hunting of musk deer is now illegal in most countries.
Distinct Features that Set Them Apart
Musk deer have several unique features that set them apart from other deer species. The most distinctive feature is their fang-like tusks, also known as sabers, that protrude from their mouths. These tusks are present in both males and females and are used for self-defense and display during the mating season.Their musky odor and vocalizations also make them stand out. The males use these features to attract females and establish dominance, while the females use their olfactory and auditory senses to select the most suitable mate.
The Importance of Musk Deer in the Ecosystem
Despite their small size and elusive nature, musk deer play a vital role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem. They are one of the few herbivores in their habitat, making them important seed dispersers. As they feed on various plants and shrubs, they help in the regeneration of the forest by spreading seeds to new areas.The presence of musk deer also helps in controlling the growth of vegetation, preventing overgrazing and creating a diverse landscape for other animals to thrive in. Their role as seed dispersers also benefits humans, as it helps in maintaining healthy forests that provide us with essential resources.
Threats to Musk Deer and their Conservation Status
Despite their important role in the ecosystem, musk deer are facing multiple threats that have resulted in their vulnerable status. The most significant threat is the demand for their musk gland, which has led to illegal hunting and trade. Even though hunting is now illegal, there is still a significant market for musk, making it challenging to eliminate this threat entirely.Habitat loss is another significant threat faced by musk deer. As human populations continue to grow and expand, forests are being cleared for agriculture, development, and other purposes. This destruction of their natural habitat leaves musk deer with limited space, affecting their survival and reproduction.
Predators of Musk Deer
Musk deer have several predators in their natural habitat, including snow leopards, wolves, and lynxes. Their elusive behavior and sharp senses help them evade these predators, but they are not entirely safe. Climate change is also affecting their predators' habitats, leading to potential imbalances in their ecosystem.Preserving the Future of Musk Deer
The conservation efforts for musk deer have primarily focused on reducing hunting and improving their living conditions. Strict regulations and penalties for hunting and trading musk deer have been put in place to deter illegal activities. However, there is still a long way to go in protecting and preserving this unique species.Education and awareness also play a crucial role in the conservation of musk deer. As more people learn about the importance of these animals and the threats they are facing, there can be a collective effort to protect them and their habitat. Ecotourism, when properly managed, can also provide a sustainable form of income for local communities, promoting the protection of musk deer and their environment.
Conclusion
The musk deer may be small in size, but it is a species with distinct features and behaviors that make it stand out in the animal kingdom. From their fang-like tusks to their musky scent and elusive nature, these creatures are truly fascinating.However, the continued demand for their musk gland and habitat loss poses a significant threat to their survival. With conservation efforts and awareness, we can protect and preserve these unique animals, ensuring their place in the ecosystem and our world. Let us continue to marvel at the beauty and importance of the elusive and endangered musk deer.

The Fascinating World of Musk Deer
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.