Naegleria
10-35 micrometers
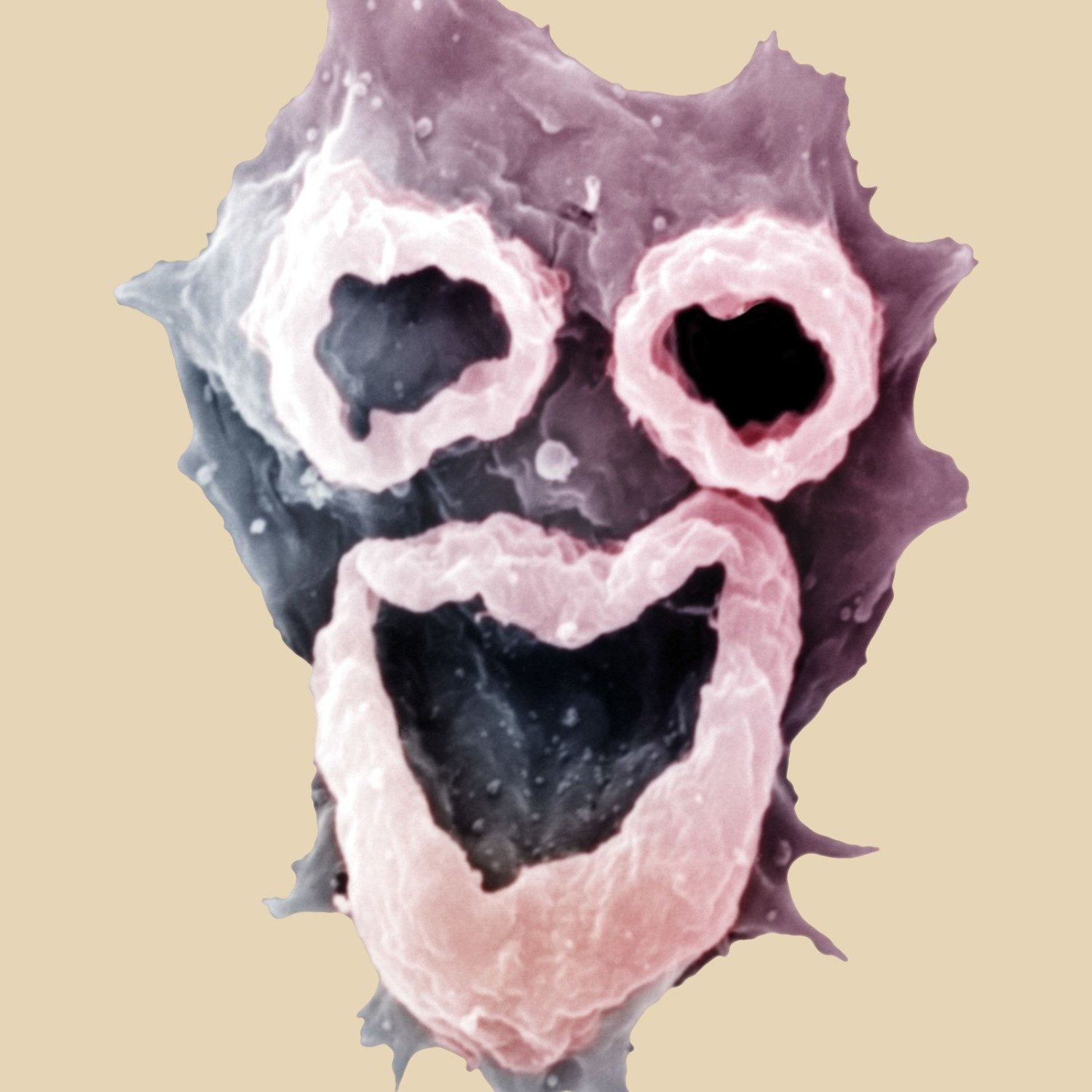
Naegleria is a tiny amoeboid found in lakes, rivers, and hot springs. Measuring 10-35 micrometers in length, it belongs to the Naegleriidae family and goes by the common name of brain-eating amoeba. Although rare, infection can occur when water containing Naegleria enters the body through the nose, causing a fatal brain infection. Avoid submerging your head in warm freshwater to lower the risk of exposure. Stay safe and enjoy the outdoors responsibly. #Naegleria #Amoeba #WaterSafety
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Naegleria
Kingdom: Protista
Habitat: Freshwater environments
Navigating the Mysteries of Naegleria: A Tiny yet Mighty Creature
Hidden deep within the freshwater environments of the world lies a tiny yet mighty creature known as Naegleria. With its scientific name bearing the same moniker, this elusive and enigmatic protista has piqued the interest of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. While its country of origin remains unknown, its presence can be found in lakes, rivers, and hot springs all around the globe. In this article, we will delve into the peculiar characteristics of Naegleria, from its unique habitat to its feeding method, and discover why this creature is truly one of a kind Naegleria.Unraveling the Mysteries of Naegleria's Taxonomy
At first glance, Naegleria seems like any other microscopic organism, but a closer look reveals a complex taxonomy that sets it apart from other creatures. Belonging to the kingdom Protista, Naegleria falls under the phylum Amoebozoa, highlighting its amoeba-like body shape. However, its class is what truly sets it apart, as it belongs to the Heterolobosea group. This class is characterized by the presence of a flagellum, a whip-like structure used for movement. Within this class, Naegleria belongs to the order Schizopyrenida, and its family name, Naegleriidae, is derived from the same. While these scientific terms may seem like a mouthful, understanding Naegleria's taxonomy is crucial in comprehending its unique characteristics.A Habitat Like No Other
One of the most intriguing aspects of Naegleria is its habitat - freshwater environments. Unlike most protists, which are found in a variety of habitats, Naegleria thrives specifically in freshwater, making it a highly specialized organism. From lakes to rivers to hot springs, this tiny creature can be found everywhere, even in tap water! However, its preference for warm temperatures makes hot springs the ideal environment for Naegleria to thrive Naked Mole Rat.The Art of Feeding - Heterotrophic Style
One of the most critical functions of any organism is its feeding method, and in the case of Naegleria, it is classified as heterotrophic. This means that it obtains its nutrients by consuming other organisms, making it a crucial part of the food chain in freshwater environments. Unlike other protists that rely on photosynthesis for energy, Naegleria uses its flagellum to capture food particles, such as bacteria and algae, through phagocytosis. This unique feeding mechanism allows Naegleria to survive and thrive in its specialized environment.From Lakes to Hot Springs - Globetrotting Naegleria
While the country of origin for Naegleria remains unknown, its presence has been confirmed worldwide. This small but mighty organism can be found in various countries and different continents, making it a true globetrotter. However, it is believed that Naegleria originates from a warm, tropical climate, given its preference for warm temperatures. Research has suggested that Naegleria may have migrated through water bodies and spread to different continents, making its presence known globally.The Basics of Naegleria's Appearance
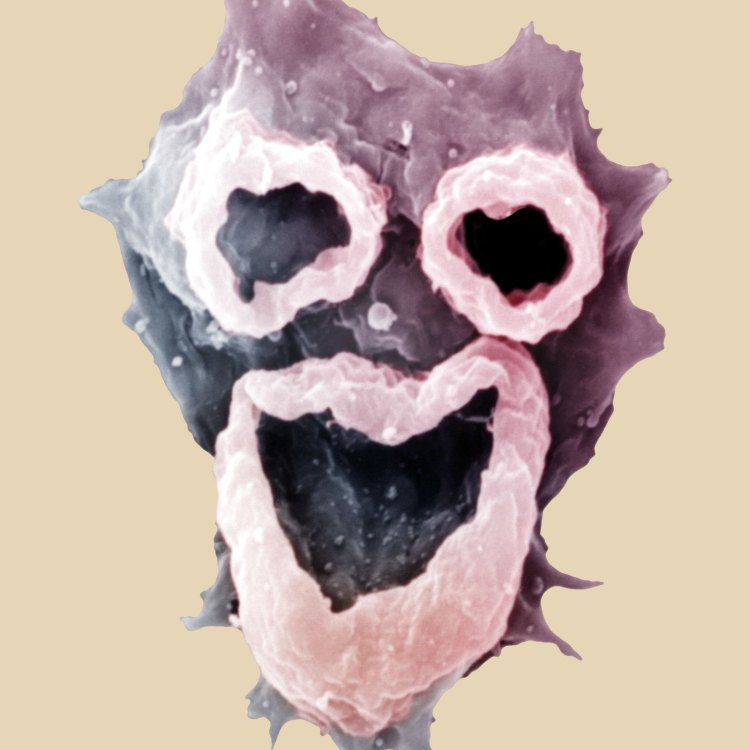
One of the distinguishing features of Naegleria is its colorless body, making it almost invisible to the naked eye. This characteristic means that it is difficult to spot in its natural habitat, adding to its mysterious nature. Its small size, measuring only 10-35 micrometers, also plays a significant role in its elusive appearance. However, what is most striking about Naegleria is its shape - amoeboid. This means that it has the ability to change its shape and form, much like a typical amoeba, making it a truly fascinating creature.The Might within the Miniature
While Naegleria's appearance and size may lead some to underestimate its capabilities, the truth is quite the opposite. This tiny organism possesses several unique traits that make it a formidable creature. Its ability to self-propel through water using its flagellum allows it to move at a fast pace, making it highly mobile. Additionally, its shape-shifting abilities make it challenging to capture and study, adding to its mysterious aura. Naegleria also has the ability to form cysts, which are protective shells that allow it to survive in harsh environmental conditions. This feature not only helps it survive but also makes it challenging to eradicate, making it a resilient protist.In Conclusion
Powerful, elusive, and enigmatic - these are just some of the words used to describe Naegleria, the tiny yet mighty protist. Its unique taxonomy, specialized habitat, and distinct feeding method make it a fascinating creature to study. While its diminutive size and colorless appearance may lead some to believe otherwise, Naegleria possesses several remarkable traits that make it a force to be reckoned with. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this tiny protist, one thing is for sure - Naegleria will continue to captivate and intrigue us.
Naegleria
Animal Details Naegleria - Scientific Name: Naegleria
- Category: Animals N
- Scientific Name: Naegleria
- Common Name: Naegleria
- Kingdom: Protista
- Phylum: Amoebozoa
- Class: Heterolobosea
- Order: Schizopyrenida
- Family: Naegleriidae
- Habitat: Freshwater environments
- Feeding Method: Heterotrophic
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: Unknown
- Location: Lakes, rivers, and hot springs
- Animal Coloration: Colorless
- Body Shape: Amoeboid
- Length: 10-35 micrometers
Naegleria
- Adult Size: Microscopic
- Average Lifespan: Unknown
- Reproduction: Asexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Unknown
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: None
- Behavior: Motile, can form cysts
- Threats: None
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Unknown
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Presence of pseudopodia
- Interesting Facts: Naegleria fowleri is a species of Naegleria that can cause a rare and severe brain infection in humans
- Predator: Unknown
Naegleria
The Unseen Microscopic World of Naegleria
When we think of the natural world, we often imagine vast landscapes, towering trees, and majestic animals roaming the earth. However, there is a whole other world around us that is invisible to the naked eye. The world of microscopic organisms is teeming with life and plays a crucial role in maintaining our ecosystems. One such organism is the Naegleria PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Naegleria is a genus of free-living amoebae that are commonly found in soil and freshwater habitats. They are so small that they cannot be seen with the human eye, measuring only about 15-45 micrometers in size. These single-celled organisms may be tiny, but they have an immense impact on the environment. In this article, we will explore the unique features of Naegleria and shed light on its role in the natural world.
Life in a Drop of Water
Naegleria is a genus of amoeboid protists, meaning they have a shapeless form and move by extending their pseudopodia (false feet). They are found all over the world, from the warm waters of the tropics to the cold waters of the poles. These microscopic organisms thrive in a wide range of environments, including lakes, rivers, and even hot springs. They can also survive in moist soils and can even be found in our tap water.With such a diverse distribution, it's no wonder that there are over 50 species of Naegleria Nigerian Goat. Most of these species are harmless and play a vital role in nutrient recycling and decomposition. However, one species, Naegleria fowleri, has gained significant attention in the media for its ability to cause a rare and deadly brain infection in humans.
A Deadly Amoeba
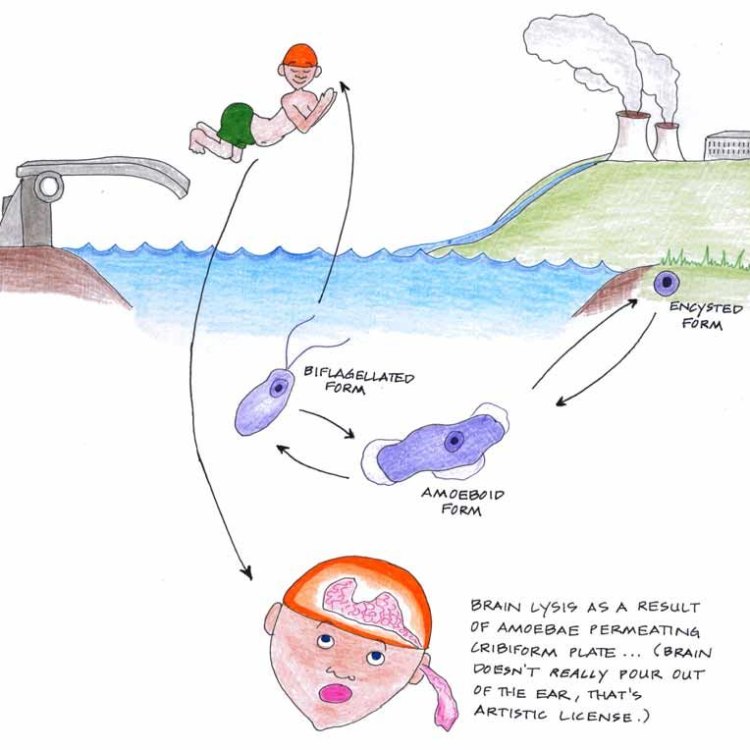
Naegleria fowleri, also known as the "brain-eating amoeba," is a species of Naegleria that is responsible for a rare and severe brain infection called primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). This infection occurs when the amoeba enters the body through the nose and travels to the brain, causing inflammation and destruction of brain tissue.The first case of PAM was reported in Australia in 1965, and since then, there have been about 143 cases reported in the United States. While this may seem like a small number, PAM has an extremely high mortality rate, with only four known survivors to date. It is most commonly found in warm freshwater bodies, especially during the summer months when water temperatures are high.
Asexual Reproduction and Unknown Behaviors
Naegleria has a unique reproductive strategy as they reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission. This means that a single cell divides into two new daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This type of reproduction allows for rapid and efficient reproduction, contributing to the widespread presence of Naegleria in various habitats.As for their behavioral patterns, not much is known about Naegleria's social behaviors or migration patterns. They are non-migratory, meaning they do not travel from one habitat to another, and they do not form social groups. In fact, Naegleria is generally considered solitary and motile. However, they do have the ability to form cysts, which allows them to survive in harsh environmental conditions.
The Role of Naegleria in the Ecosystem
Despite their small size, Naegleria plays an essential role in the ecosystem. As mentioned earlier, most species of Naegleria are decomposers and help break down organic matter, contributing to the nutrient cycle. They also serve as a food source for other organisms, such as bacteria and algae, in the aquatic food chain. Therefore, their presence is crucial for maintaining a healthy ecosystem.However, Naegleria may also have negative impacts on certain ecosystems. In some cases, Naegleria can outcompete other organisms, leading to a decrease in biodiversity. Additionally, the introduction of invasive Naegleria species to new habitats can disrupt the balance of the ecosystem, leading to unforeseen consequences.
The Distinctive Features of Naegleria
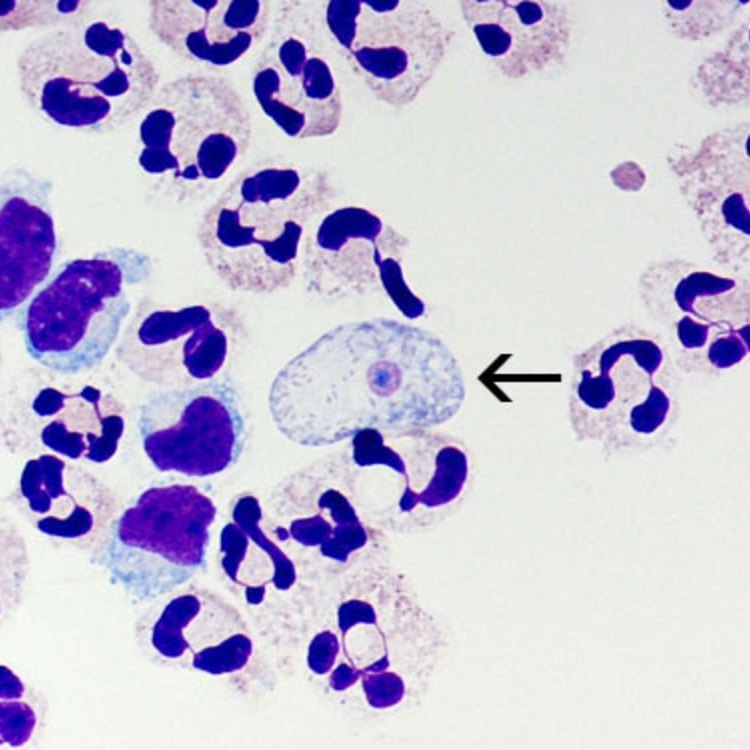
One of the most unique features of Naegleria is the presence of pseudopodia, which are extensions of their cytoplasm used for movement and food capture. These pseudopodia are constantly changing, allowing Naegleria to move in different directions and engulf food particles. They also have a round, ovoid-shaped nucleus, which contains their genetic material.Other than their distinctive pseudopodia, Naegleria does not have any notable physical features. They are translucent, making them virtually invisible to the naked eye, and they do not possess any appendages like other microscopic organisms, such as cilia or flagella.
The Unknown Lifespan of Naegleria
Due to their size and complexity, it is challenging to determine the exact lifespan of Naegleria. However, studies have shown that under optimal conditions, Naegleria can reproduce and survive indefinitely, as long as they have access to food and suitable environments. This is made possible by their ability to form cysts, allowing them to enter a dormant state until conditions become favorable again.The Conservation Status of Naegleria
Currently, there is no conservation status for Naegleria as a whole as they are not evaluated by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is due to their widespread distribution and lack of significant threats to their population. However, it is essential to protect their habitats and maintain a balance in their ecosystems to ensure their continued survival.Exploring the Unseen
Naegleria may be microscopic and mostly unseen, but they have a significant impact on our environment and our health. They serve as a reminder that there is an entire world out there that we cannot see with our own eyes. With the advancement of technology, we have been able to explore this unseen world and gain a better understanding of its inhabitants.Studies on Naegleria have also led to important medical advancements, such as treatments for PAM and the development of novel drug delivery systems. So, while they may be a small part of the natural world, Naegleria has made a big impact on our lives.
The Unknown Future of Naegleria
As our world continues to change and evolve, it is unknown how Naegleria will adapt and survive in the face of climate change and human activities. So far, there have been no significant threats to their population, but with increasing pollution and habitat destruction, their survival may be at risk.It is essential to continue studying Naegleria and other microscopic organisms to understand their role in the ecosystem and the potential impacts they may have on our health and the environment. Only then can we take the necessary steps to protect and preserve these unseen but vital organisms.
Invisible but Vital
Naegleria, a genus of microscopic amoebae, may go unnoticed by most of us, but they play a vital role in the natural world. They are constantly moving and reproducing, maintaining the balance of our ecosystems and serving as a food source for other organisms. However, their presence can also pose a threat to humans, as seen with the deadly Naegleria fowleri.As we continue to explore and learn about the unseen world, we must also consider the impacts of our actions on these microscopic organisms. With their unique features and unknown behaviors, Naegleria remains a fascinating and mysterious part of nature, reminding us that there is still so much to discover in our own backyards.

Navigating the Mysteries of Naegleria: A Tiny yet Mighty Creature
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












