Orange Baboon Tarantula
Approximately 15 cm (6 inches)
The Orange Baboon Tarantula, found in the savannah regions of Africa, is a fascinating and slightly intimidating creature. With a length of approximately 15 cm (6 inches), this large and robust spider belongs to the family Theraphosidae. Despite its name, it is not actually orange in color, but rather has a reddish-brown hue. Its impressive size and unique appearance make it a popular choice among exotic pet owners.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Orange Baboon Tarantula
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Terrestrial
The Colorful and Fierce Orange Baboon Tarantula
When you hear the word tarantula, what comes to mind? Perhaps an image of a large and creepy spider with dark and hairy features. Most people do not associate tarantulas with bright colors and fierce behaviors. But in the case of the Orange Baboon Tarantula, its name is a perfect description of its characteristics. These arachnids are famous for their stunning orange coloration and their aggressiveness, making them a unique and interesting addition to the world of spiders Orange Baboon Tarantula.The scientific name for the Orange Baboon Tarantula is Pterinochilus murinus, but they are more commonly known as Orange Baboon Tarantulas or Orange Baboon Spiders. They belong to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Arthropoda, and class Arachnida, which includes spiders, scorpions, and ticks. This species belongs to the order Araneae and the family Theraphosidae, which are also known as tarantulas. These impressive creatures can be found in the Savannah regions of Africa and have a wide distribution throughout the continent.
Fun fact: There are over 45,000 known species of spiders in the world, and tarantulas make up about a quarter of those species.
Baboon-like Appearance and Unique Behavior
One of the most striking features of the Orange Baboon Tarantula is its bright orange coloration, which gives them their name. This unique color is not often seen in tarantulas, making the Orange Baboon Spider stand out from other species. The vibrant orange color covers their entire body, including their legs, abdomen, and cephalothorax. These tarantulas also have a unique body shape, which is described as large and robust Osprey. The average size of an adult Orange Baboon Tarantula is approximately 15 cm, which is about 6 inches in length.But don't let their colorful appearance deceive you. These spiders are also known for their fierce and aggressive behavior. They have a defensive posture that resembles a baboon, with their front legs raised and their fangs exposed. This stance can be intimidating, and they are not afraid to use their venom to defend themselves if needed.
Fun fact: Tarantulas do not have a centralized nervous system. Instead, they have several ganglia, or nerve clusters, spread throughout their body, making them more decentralized and in control of their movements.
The Ideal Habitat and Feeding Habits
Orange Baboon Tarantulas are a terrestrial species, meaning they live on land. They prefer areas that are dry and warm, such as savannahs, shrublands, and grasslands. These arachnids can also be found in burrows or crevices, where they create their nests. They are nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active at night, and will spend their days hiding in their burrows.As carnivorous creatures, the Orange Baboon Tarantulas have a diet of insects, small reptiles, and small mammals. Their hunting technique involves ambushing their prey by using their well-developed eyesight and powerful fangs to inject venom. They are also known to have strong front legs that are used to quickly grab their prey. Once caught, the prey is killed by the tarantula's venom, and then they are consumed.
Fun fact: Tarantulas have a unique way of digesting their food. They use enzymes to liquefy their prey's insides, and then they use their fangs to suck out the liquid.
Multiple Countries in Africa as Their Origins
As mentioned earlier, the Orange Baboon Tarantula can be found in various countries across Africa. Some of the countries where they are known to originate from include Ghana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Botswana, and Namibia. These spiders have also been introduced to other countries, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, through the pet trade.Interesting fact: Tarantulas are popular as pets, especially in the United States. They are relatively low maintenance and can live up to 20 years in captivity.
Threats and Conservation Status
While the Orange Baboon Tarantula is not currently listed as an endangered species, they face some threats that could endanger their population in the future. These threats include habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization. They are also hunted for their venom, which is used in traditional medicines. In some areas, they are also considered a delicacy and are consumed by humans.To protect this species, it is essential to implement conservation measures that focus on preserving their natural habitats. It is also important to educate the public about these spiders and their essential role in the ecosystem. By doing so, we can ensure that future generations can continue to admire these fascinating creatures in their natural environment.
The Amazing World of Spiders
The Orange Baboon Tarantula is just one of the many fascinating species of spiders in the world. These arachnids are diverse, with over 45,000 known species, each with unique characteristics and behaviors. While some may find them scary or creepy, they are vital to the balance of our ecosystem and deserve our respect and understanding.As we continue to explore and learn more about the animal kingdom, it is crucial to remember that every creature has its purpose and place in this world. So, the next time you come across a spider, take a moment to appreciate its beauty and the incredible things it can do. And if you ever encounter an Orange Baboon Tarantula, remember to admire its stunning orange color, but also keep your distance and respect its aggressive nature.
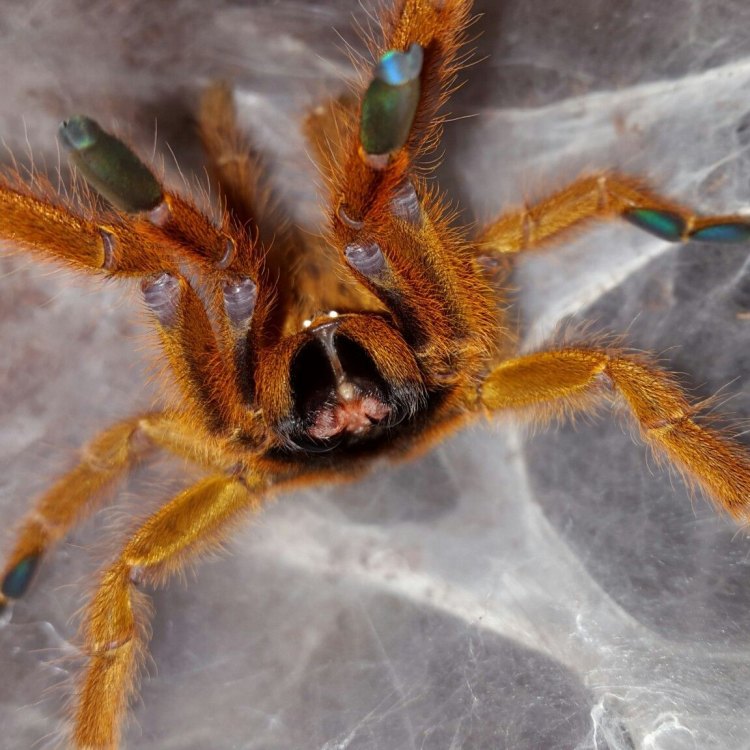

Orange Baboon Tarantula
Animal Details Orange Baboon Tarantula - Scientific Name: Pterinochilus murinus
- Category: Animals O
- Scientific Name: Pterinochilus murinus
- Common Name: Orange Baboon Tarantula
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Arachnida
- Order: Araneae
- Family: Theraphosidae
- Habitat: Terrestrial
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Africa
- Country of Origin: Multiple countries in Africa
- Location: Savannah regions of Africa
- Animal Coloration: Orange
- Body Shape: Large and robust
- Length: Approximately 15 cm (6 inches)
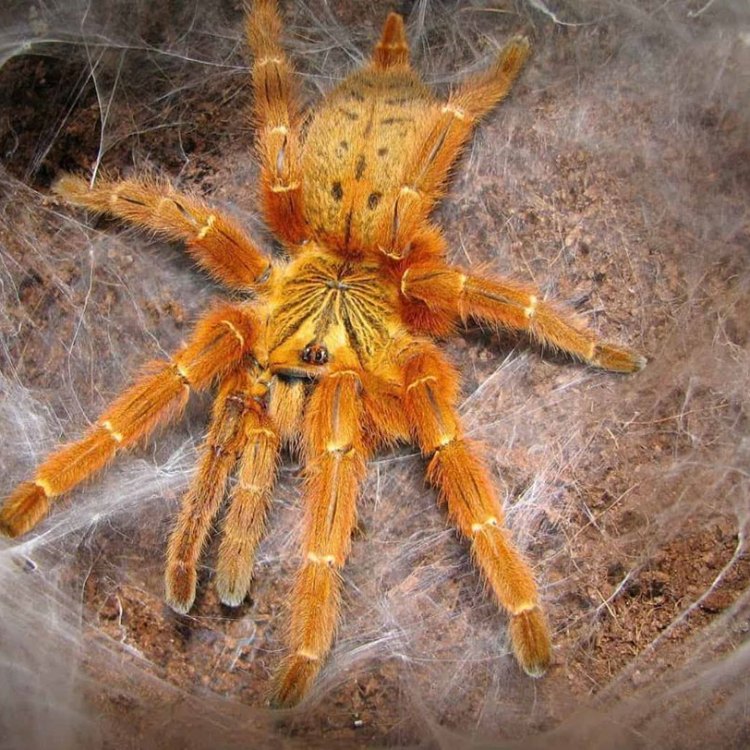

Orange Baboon Tarantula
- Adult Size: Males: 4-6 inches, Females: 6-7 inches
- Average Lifespan: 10-15 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males perform elaborate courtship rituals
- Sound or Call: No notable sounds or calls
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Aggressive and defensive
- Threats: Habitat destruction, collection for pet trade
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated (NE)
- Impact on Ecosystem: As predators, they help maintain balance in their ecosystems
- Human Use: Popular species among tarantula enthusiasts as pets
- Distinctive Features: Bright orange coloration, dense setae on legs
- Interesting Facts: Orange Baboon Tarantulas are known for their aggressive nature and potent venom
- Predator: Various bird species, small mammals
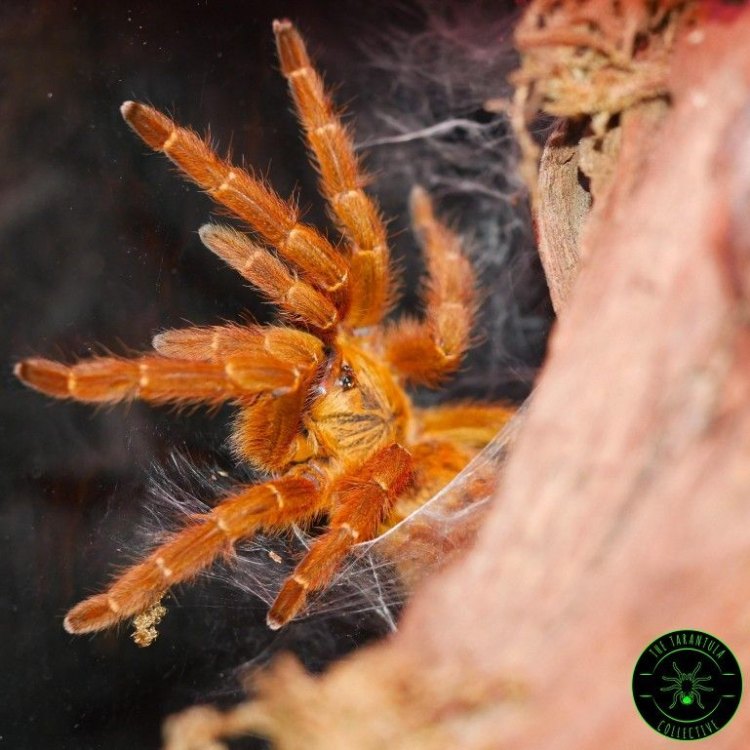

Pterinochilus murinus
The Fascinating World of the Orange Baboon Tarantula
In the arid regions of Africa, a bold and striking creature roams the land - the Orange Baboon Tarantula. With its bright orange coloration and fierce demeanor, this tarantula has captured the fascination of tarantula enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. In this article, we will take a closer look at the unique features and behaviors of this magnificent spider.Size and Lifespan
The Orange Baboon Tarantula is a relatively large species of tarantula, with males reaching an adult size of 4-6 inches and females growing up to 6-7 inches PeaceOfAnimals.Com. This makes them one of the larger and more intimidating species of tarantula, adding to their allure. They have a lifespan of 10-15 years, which is longer than many other tarantula species.
Reproduction and Courtship
Like most tarantulas, the Orange Baboon Tarantula reproduces through sexual means. However, what sets them apart is the elaborate courtship rituals performed by males to attract females. These rituals can include drumming their front legs on the ground and waving their pedipalps (a pair of leg-like appendages near the mouth) to display their fitness as a potential mate. This display of courtship is not only fascinating to watch but also highlights the complexity of tarantula behaviors.
No Notable Sounds or Calls
While many animals use sounds or calls to communicate, the Orange Baboon Tarantula is not known to make any notable sounds or calls. They rely mainly on visual and chemical cues, such as pheromones, to communicate with other spiders.
Non-Migratory and Solitary
Unlike other species of tarantulas, the Orange Baboon Tarantula is non-migratory, meaning they do not move to other locations Ocean Perch. They are also solitary creatures, preferring to live alone rather than in social groups. This behavior is not uncommon among tarantulas, as they are generally non-social animals.
Aggressive and Defensive Behaviors
One of the most distinctive traits of the Orange Baboon Tarantula is its aggression and defensive nature. When threatened, they will raise their front legs and show their fangs, warning any potential predator to stay away. They may also release their urticating hairs, which are small bristles on their abdomen that can cause irritation or even injury to predators. This behavior is common among tarantulas as a defense mechanism, and the Orange Baboon Tarantula is no exception.
Threats
Sadly, the Orange Baboon Tarantula, like many other species of tarantula, is facing threats in its natural habitat. Habitat destruction, mainly caused by human activities such as mining and agriculture, poses a significant threat to the survival of these spiders. Additionally, they are often collected for the pet trade, which can also have negative impacts on their populations in the wild.
Conservation Status
Despite facing threats in the wild, the Orange Baboon Tarantula has not been evaluated for its conservation status by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that there is not enough data available to determine the level of threat to their populations. However, it is essential to monitor their populations and work towards protecting their natural habitats.
Impact on Ecosystem
As predators, the Orange Baboon Tarantula plays a vital role in their ecosystem. They help maintain the balance by controlling the populations of their prey, which can include insects and small vertebrates. Without these crucial predators, an overabundance of prey species can potentially lead to negative effects on the ecosystem.
Human Use
While many may fear or avoid tarantulas, the Orange Baboon Tarantula is a popular species among tarantula enthusiasts as a pet. Their striking appearance and unique behaviors make them a sought-after species for those interested in keeping tarantulas. However, it is essential to note that caring for any pet requires knowledge and responsibility. Tarantulas, in particular, have specific needs and should never be taken from the wild as pets. Instead, those interested in owning an Orange Baboon Tarantula should opt for ethically sourced and captive-bred individuals.
Distinctive Features
The most striking feature of the Orange Baboon Tarantula is undoubtedly its bright orange coloration. This unique color is what gives this species its name and sets it apart from other tarantulas. They also have dense setae or bristles on their legs, giving them a fuzzy appearance. This feature not only adds to their aesthetic appeal but also aids in sensing their environment and their prey.
Interesting Facts
Aside from their distinctive features and behaviors, the Orange Baboon Tarantula has many interesting facts that make them a fascinating species. For one, they are known for their potent venom, which is a defense mechanism against predators and aids in subduing their prey. However, their venom is not considered medically significant to humans, and their bites are rarely fatal. Another interesting fact is that their bright orange coloration serves as a warning sign to predators, indicating their potentially dangerous venom.
Predators
While tarantulas may seem like the ultimate predator, they too have their enemies in the wild. The Orange Baboon Tarantula's main predators include various bird species, such as snakes, and small mammals such as rodents. However, their aggressive and defensive behaviors serve as their first line of defense against these predators.
In Conclusion
The Orange Baboon Tarantula is a remarkable and unique species, with its striking appearance and bold behaviors. As with any animal, it is essential to respect and appreciate them in their natural habitat and to not disrupt or harm their populations for human use. With proper conservation efforts, we can ensure the survival of these fascinating spiders and continue to marvel at their remarkable features and behaviors.
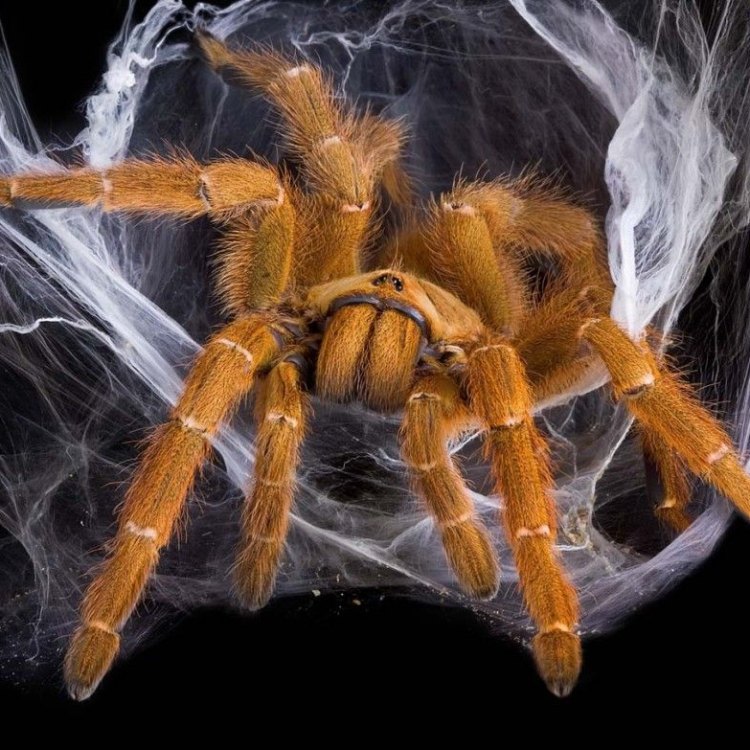

The Colorful and Fierce Orange Baboon Tarantula
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.