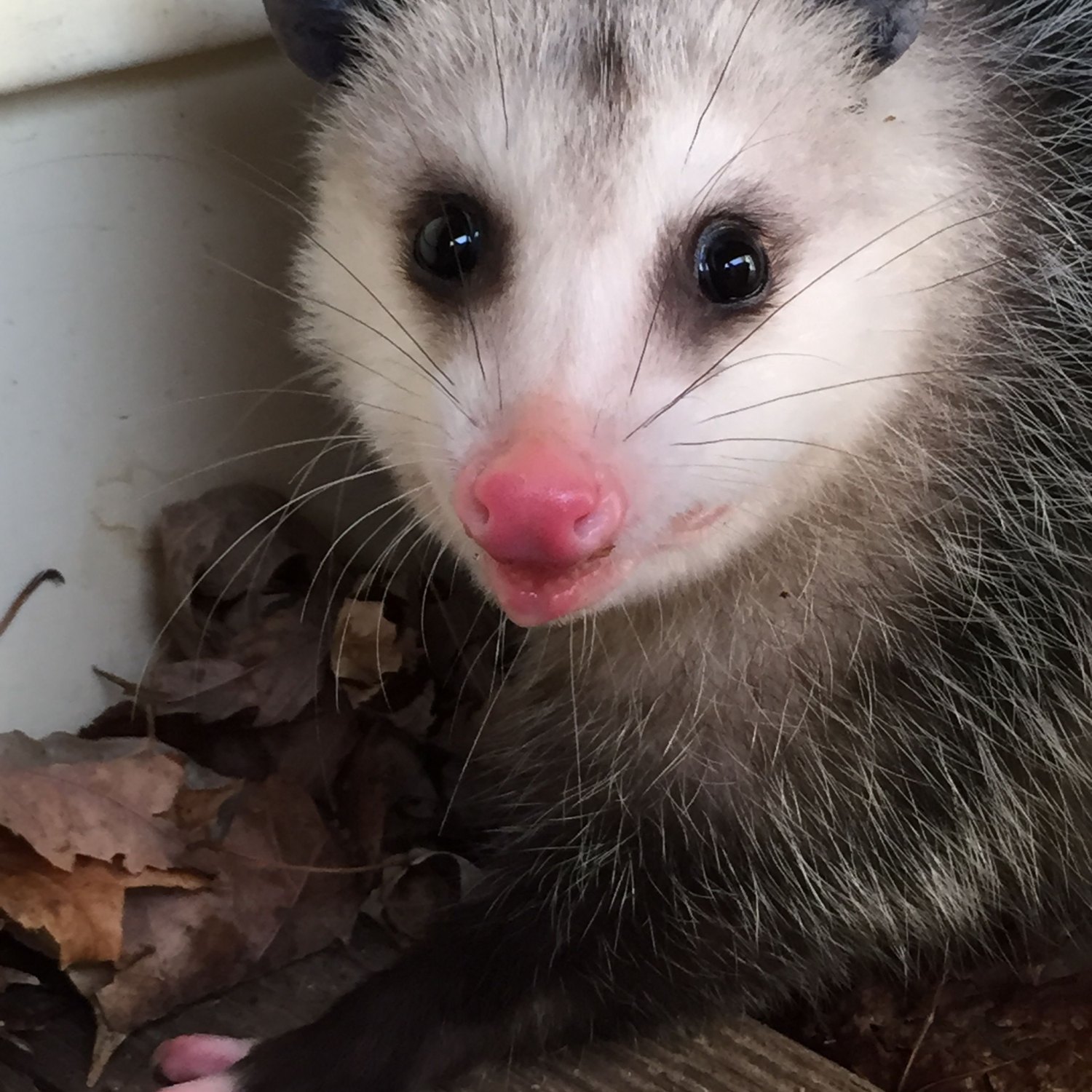
Possum
6 to 20 inches
Did you know possums are found in North America, Central America, South America, and Australia? These small to medium-sized animals belong to the Didelphidae family and can grow up to 6 to 20 inches in length. Their distinctive long tail helps them climb and balance. #possum #animals #wildlife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Possum
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and semi-arid environments
The Amazing World of Possums: Nature's Hidden Gems
Have you ever heard of a possum? This small, furry creature often goes unnoticed in the wild, despite its fascinating features and unique behaviors. But, don't let its unassuming appearance fool you – the possum is a complex and intriguing animal with a rich history and a vital role in our ecosystem.Let's dive deeper into the world of possums and discover what makes them one of nature's hidden gems.
The Scientific Classification of Possums
Firstly, let's start with the basics – the scientific classification of possums Possum. The scientific name for the possum is Didelphimorphia, which translates to "having two-wombs" in Greek. This refers to the female possums' unique reproductive system, where they have two uteri and can give birth to large litters of up to 20 babies.Possums belong to the Kingdom Animalia, Phylum Chordata, and Class Mammalia. Within the class, they are classified under the Order Didelphimorphia, and the Family Didelphidae. The classification "Didelphidae" comes from the Greek word "didelphys," meaning "double-wombed." This playful name is a nod to the possum's reproductive system, which is a defining characteristic of the species.
These small, furry creatures have a unique place in the animal kingdom, belonging to a group that is distinct from other mammals. Unlike other mammals, possums have a primitive brain structure that makes them more closely related to birds and reptiles than other mammals. This makes them an intriguing study for scientists, continuously discovering new information about their behavior and evolution Pond Skater.
The Habitat and Distribution of Possums
Possums can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, woodlands, and semi-arid environments. They are native to the Americas, Australia, and Papua New Guinea, with Australia being the country of origin.In North America, possums are commonly found in the Southeastern United States, Mexico, and Central America. In South America, they can be found as far south as Argentina. In Australia, they are widespread throughout the continent, with a concentration in the northeastern and southeastern regions.
Despite their varying habitats, possums are incredibly adaptable animals, and their distribution has expanded over time due to human intervention. They have even been introduced to countries such as New Zealand, where they were not originally found.
The Physical Characteristics of Possums
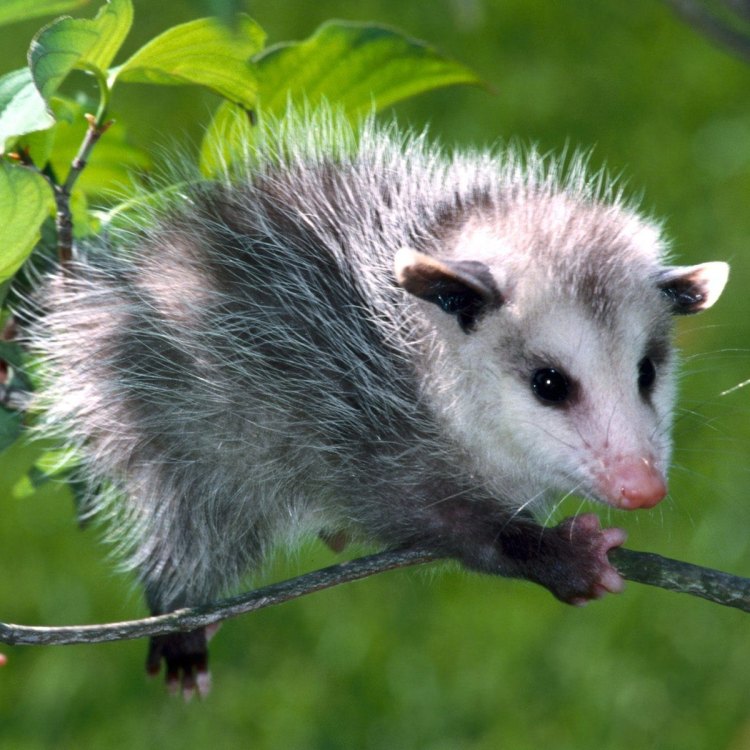
Possums come in a variety of species, with varying physical characteristics. However, there are some defining features that most possums share. They are small to medium-sized animals, with a body shape that is typically described as "boxy." They have a squat body, short legs, and a small head with a pointy snout.One of the most notable features of a possum is its long, hairless tail. This tail serves many purposes, including balancing while climbing, grasping objects, and even acting as a fifth limb. The length of a possum's tail can range anywhere from 6 to 20 inches, depending on the species.
Possums can also vary in size, with the smallest species, the Dwarf or Virginia Opossum, measuring only about 6 inches in length, while the largest species, the Woolly Possum, can reach up to 20 inches. Their weight can range from 11 ounces to 14 pounds, depending on the species and their age.
The Diversity in Coloration of Possums
As mentioned earlier, possums come in various species, each with its own unique coloration. However, most possums are gray, brown, or black, with a coarse and thick coat of fur. Their fur is designed to help them adapt to their surroundings, providing camouflage and insulation.Some species may have stripes or spots on their fur, while others have distinct patterns and colors. For example, the Virginia opossum has a white face and a black stripe running down its back, while the Brush-tailed Possum in Australia is usually gray with a bushy black tail.
Possums also have a unique defense mechanism called "playing possum," where they play dead to avoid predators. During this act, their coloration may change, and they may release a foul-smelling odor to appear unappealing to predators.
Omnivorous Feeding Habits of Possums
One of the most fascinating aspects of possums is their diet. These creatures are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plants and animals. They are opportunistic feeders, which means they will eat whatever is available in their environment.Possums primarily feed on fruits, insects, small mammals, eggs, and even carrion. They have a particular fondness for fruits, and their strong, sharp teeth allow them to consume hard-shelled foods such as nuts and seeds. They also have a remarkable ability to adapt to human settlements and may often be seen scavenging for food in trash cans and compost bins.
This omnivorous diet is essential for possums' survival and also plays a vital role in our ecosystem. As scavengers, they help keep our environment clean by consuming carrion and preventing diseases from spreading.
The Importance of Possums in Our Ecosystem
While they may not be as popular as other animals, possums play a crucial role in our ecosystem. As scavengers, they help clean up the environment by consuming carrion that may harbor harmful bacteria and diseases. They also play a vital role in controlling insect populations, preventing them from becoming pests and affecting our crops.Additionally, possums are an important food source for many predators, including birds of prey, foxes, and wildcats. Their presence in an ecosystem helps maintain a balance in the food chain, ensuring the survival of various species.
Moreover, possums are essential for seed dispersal. As they travel and forage for food, they eat fruits and spread seeds throughout their environment, aiding in the growth and diversity of plant life.
The Threats and Conservation Efforts for Possums
Unfortunately, the possum population is facing several threats that have resulted in a decline in their numbers. One of the primary threats is habitat loss due to human development and deforestation. As their natural habitats are destroyed, possums have to adapt to new environments, often leading to conflicts with humans.Possums are also at risk of being hunted and killed for their fur. Their soft fur is prized for use in coats and other clothing items, leading to illegal hunting and trading of possums.
In response to these threats, various conservation efforts have been put in place to protect and preserve the possum population. In countries like Australia, where possums are native, there are stringent laws in place to protect them from exploitation and hunting. These laws have helped in maintaining the possum population and conserving their natural habitats.
Additionally, educating the public about the importance of possums and the role they play in our ecosystem is crucial in promoting their conservation. By raising awareness and understanding of these creatures, we can take steps to coexist with them and protect their well-being.
The Fascinating Behaviors of Possums
Apart from their unique physical features and diet, possums also exhibit fascinating behaviors that make them intriguing creatures to observe. Here are a few of their most notable behaviors:- Playing possum: As mentioned earlier, possums have a unique defense mechanism of playing dead when faced with a threat. Their body goes limp, and they remain still for several minutes, tricking predators into thinking they are dead.
- Grinning: Possums have a habit of opening their mouth and baring their teeth, sometimes giving the impression that they are grinning. This behavior is an attempt to appear more significant and more intimidating to predators.
- Walking backwards: Possums have the ability to walk backward on all four feet, which allows them to escape predators that may be chasing them.
- Tail curling: When climbing, possums often use their prehensile tails to wrap around branches for balance and support. However, they also use their tails to curl up and create a cozy nest for themselves.
In Conclusion
In the vast world of animals, possums may not be the first creatures that come to mind, but they are undoubtedly one of nature's hidden gems. From their unique physical features to their omnivorous diet and fascinating behaviors, possums are a fascinating species that deserve our attention and respect.Despite facing threats and challenges, possums continue to thrive in their diverse habitats, playing an essential role in our ecosystem. As humans, it is our responsibility to preserve and protect these creatures, and by raising awareness and understanding of their value, we can ensure that they continue to be a part of our natural world for years to come.
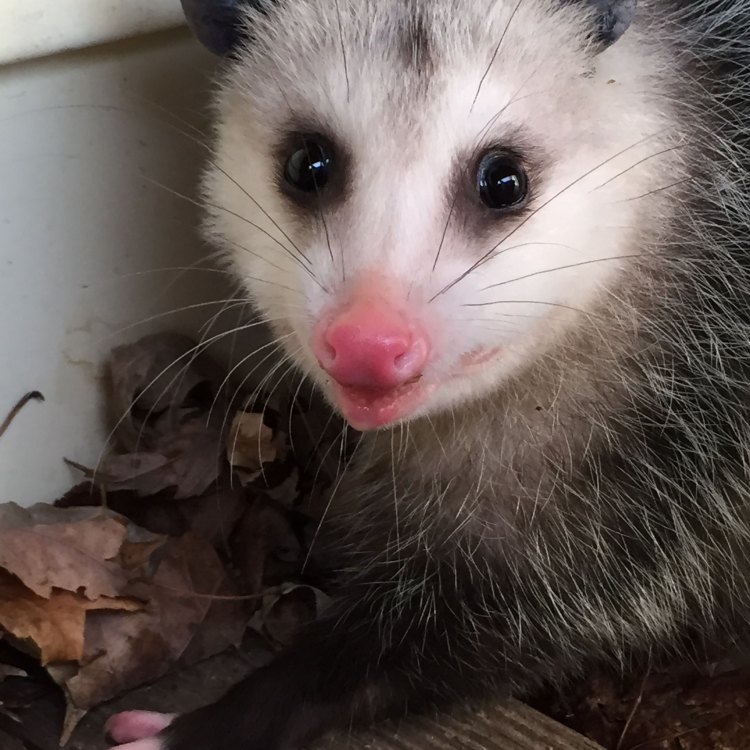

Possum
Animal Details Possum - Scientific Name: Didelphimorphia
- Category: Animals P
- Scientific Name: Didelphimorphia
- Common Name: Possum
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Didelphimorphia
- Family: Didelphidae
- Habitat: Forests, woodlands, and semi-arid environments
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Americas, Australia, and Papua New Guinea
- Country of Origin: Australia
- Location: North America, Central America, South America, Australia
- Animal Coloration: Varies depending on the species, but generally gray, brown, or black
- Body Shape: Small to medium-sized with a long tail
- Length: 6 to 20 inches
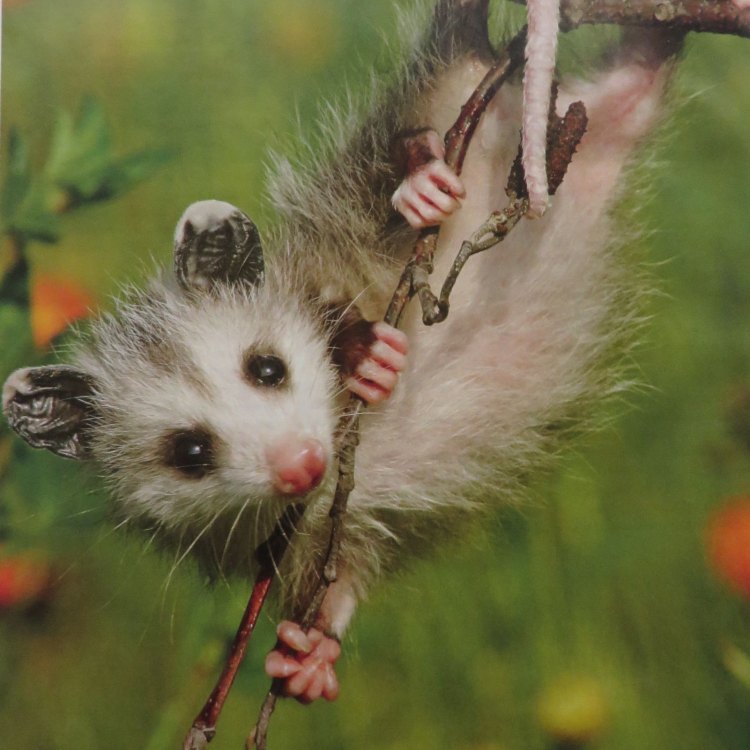

Possum
- Adult Size: 6 to 20 inches
- Average Lifespan: 2 to 4 years in the wild
- Reproduction: Marsupial
- Reproductive Behavior: Females have a pouch where the babies develop after birth
- Sound or Call: Squeaking, screeching, and hissing sounds
- Migration Pattern: Not typically migratory
- Social Groups: Generally solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal and arboreal
- Threats: Habitat loss, road mortality, predation by domestic pets
- Conservation Status: Varies depending on the species; some are listed as least concern, while others are listed as endangered
- Impact on Ecosystem: Help control populations of small animals and insects
- Human Use: Sometimes kept as pets or used for research
- Distinctive Features: Prehensile tail, opposable thumbs on their hind feet
- Interesting Facts: Possums are the only marsupials found in the Americas
- Predator: Coyotes, foxes, dogs, owls, and large birds of prey

Didelphimorphia
A Not So Ordinary Marsupial - The Unique Features of Possums
Possums, also known as opossums, are a group of approximately 103 species of medium-sized marsupials native to the Americas. They are known for their distinctive prehensile tails, opposable thumbs on their hind feet, and unique reproductive behavior. These creatures may seem familiar to us, but there is much more to them than meets the eye. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of possums and uncover their unique features that make them stand out from other animals PeaceOfAnimals.Com.The Basics of Possums
Before we delve into the distinctive features of possums, let's first understand the basics of these nocturnal creatures. Possums are found in various sizes, ranging from 6 to 20 inches in length, with an average lifespan of 2 to 4 years in the wild. They are generally solitary animals, with no specific social groups or hierarchies. Possums are known for their adaptation skills, as they can thrive in different habitats, ranging from forests to urban areas.
Moreover, possums are not migratory animals. They tend to stay in one area, as long as it provides enough food and shelter. Oftentimes, they use abandoned burrows or tree hollows as their dens. However, they are efficient climbers and are commonly found in trees, hence their classification as arboreal animals.
Reproduction and Parenting
One of the most unique features of possums is their reproductive behavior Peacock Bass. As marsupials, females have a pouch where the babies, called joeys, develop after birth. Unlike other marsupials, possum mothers have two uteruses and produce two separate litters per year. They typically give birth to 6 to 8 young, weighing only 0.13 grams each. The newborn joeys are blind, hairless, and the size of a grain of rice, but they quickly make their way into their mother's pouch.
The pouch serves as a protective nursery for the joeys, where they will continue to grow and nurse for about 70 days. After they outgrow the pouch, they will ride on their mother's back, holding onto her fur with their little toes. This unique method of attachment is a defining feature of possums and allows the mother to carry her young while foraging for food.
The Vocal Abilities of Possums
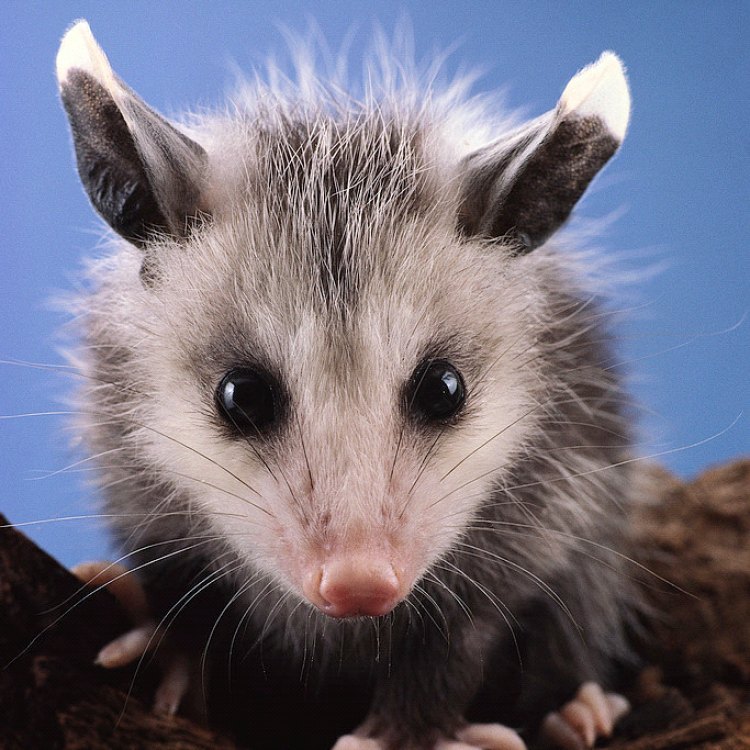
Possums are not particularly known for their vocalizations, but they do have a variety of sounds and calls. Their most common ones are squeaking, screeching, and hissing sounds. They use these vocalizations to communicate with each other and warn of potential threats. Possums are primarily nocturnal animals, so these sounds are usually heard at night when they are most active.
In addition to their vocal abilities, possums also have a keen sense of smell and hearing. These senses, combined with their silent movements and nocturnal habits, make them elusive and effective in avoiding predators.
Adaptations and Survival Techniques
As nocturnal animals, possums have developed unique adaptations to help them survive in the dark. Their eyes have a tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer at the back of the eye that allows them to see better in low light conditions. This adaptation also gives their eyes a characteristic creepy glow at night, making them easily distinguishable from other animals.
Another survival technique of possums is their ability to play dead. When they feel threatened, possums will enter an involuntary state of coma, resembling death. This defense mechanism is called "playing possum" and can last for several minutes up to a few hours. During this time, their body becomes stiff, they excrete a foul-smelling odor, and their tongue may hang out, giving the illusion of death. This behavior acts as a deterrent for potential predators, giving the possum a chance to escape.
Threats and Conservation Status
Despite their adaptability and survival techniques, possums are facing numerous threats in the wild. Habitat loss is one of the biggest contributors to their declining populations. As human development expands, possums lose their natural habitats, including tree hollows and burrows. This loss of shelter and foraging grounds can lead to malnutrition, disease, and reduced breeding success.
Road mortality is also a significant threat to possums. Their slow movement and habit of playing dead puts them at risk of being hit by cars while crossing roads. Furthermore, predation by domestic pets, such as cats and dogs, is also a major factor in their decline.
The conservation status of possums varies depending on the species. Some are listed as least concern, while others are listed as endangered. The Virginia opossum, for instance, has a stable population and is not of concern, but other species, like the black-vented shearwater, are endangered due to habitat destruction and predation.
The Importance of Possums in Ecosystems
Despite the threats they face, possums play an essential role in maintaining the balance in ecosystems. They help control populations of small animals and insects, such as snails, slugs, and ticks. These creatures are often considered pests, and without natural predators, their populations can quickly get out of control. Therefore, possums act as the "cleanup crew" of the ecosystem, ensuring the health and balance of other animal populations.
Moreover, possums also serve as indicators of ecosystem health. Since they are adaptable to different habitats, their presence or absence can be a sign of the state of the environment. By monitoring possum populations, scientists can gauge the health and vitality of an ecosystem and take necessary conservation actions.
Possums and Human Interactions
Due to their unique features and interesting behaviors, possums have been the subject of human fascination for centuries. Some cultures, like the indigenous peoples of the Americas, see them as a source of food and use their fur for warmth. However, in modern times, possums are more commonly seen as pests or roadkill rather than a source of food. They are sometimes kept as pets or used for research purposes, but their impact on human lives is mostly indirect.
In Conclusion
Possums may seem like ordinary, unremarkable creatures, but a closer look reveals their truly unique features and behaviors. As the only marsupials found in the Americas, they have adapted to a wide range of habitats and developed intricate survival techniques. Unfortunately, possums are facing multiple threats in the wild, but their importance in maintaining a healthy ecosystem cannot be overlooked. As we continue to share our environment with these fascinating marsupials, it is crucial to raise awareness and take necessary conservation measures to ensure their survival.

The Amazing World of Possums: Nature's Hidden Gems
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.