Purple Tarantula
Up to 6 inches (15 cm)
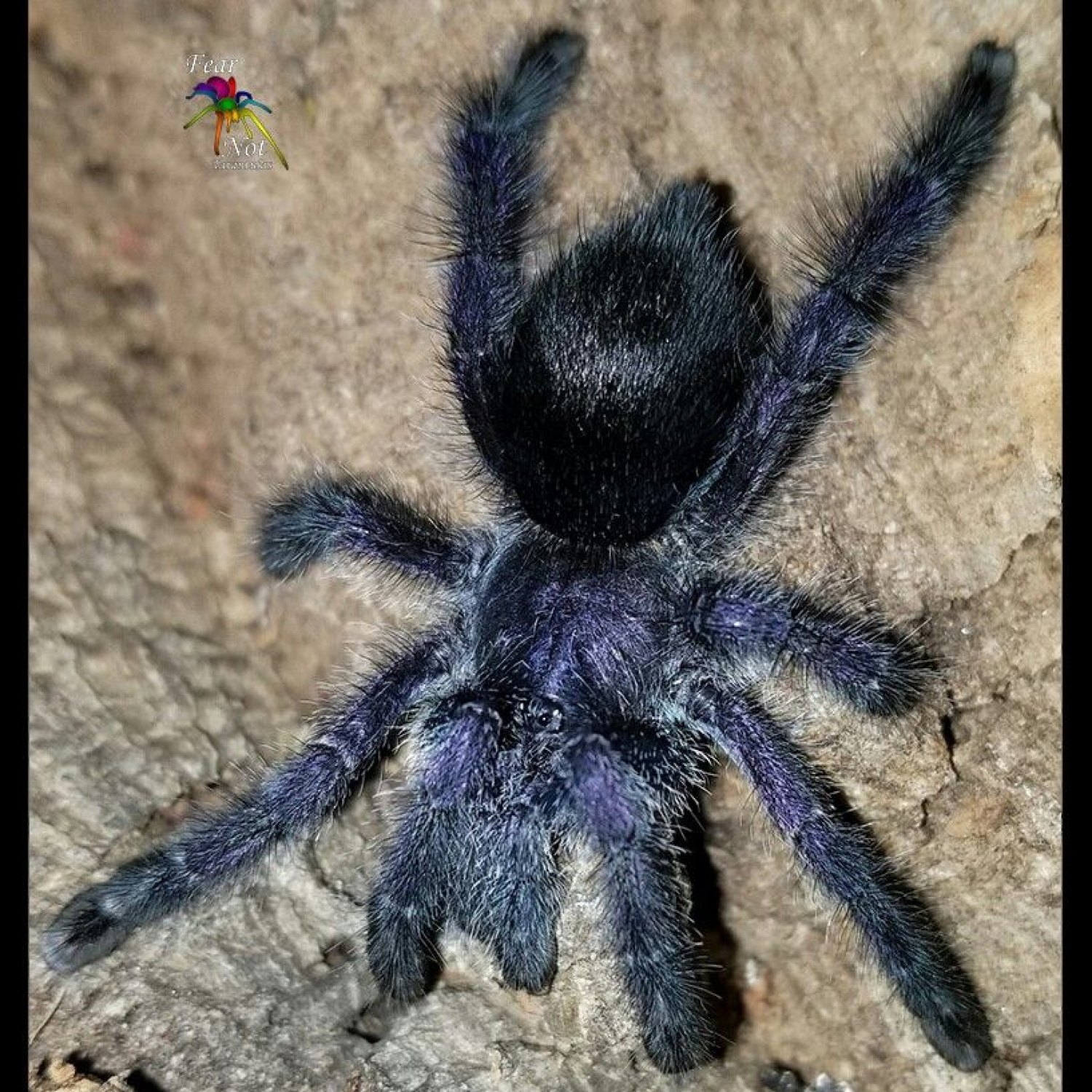
The Purple Tarantula, a member of the family Theraphosidae, can grow up to 6 inches in length. They can be found in tree trunks or burrows, and have a large and hairy body. Despite their intimidating appearance, these spiders are relatively harmless to humans and play an important role in their ecosystem. #PurpleTarantula #Theraphosidae #spiders #ecosystem #biodiversity
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Purple Tarantula
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Rainforests, tropical areas
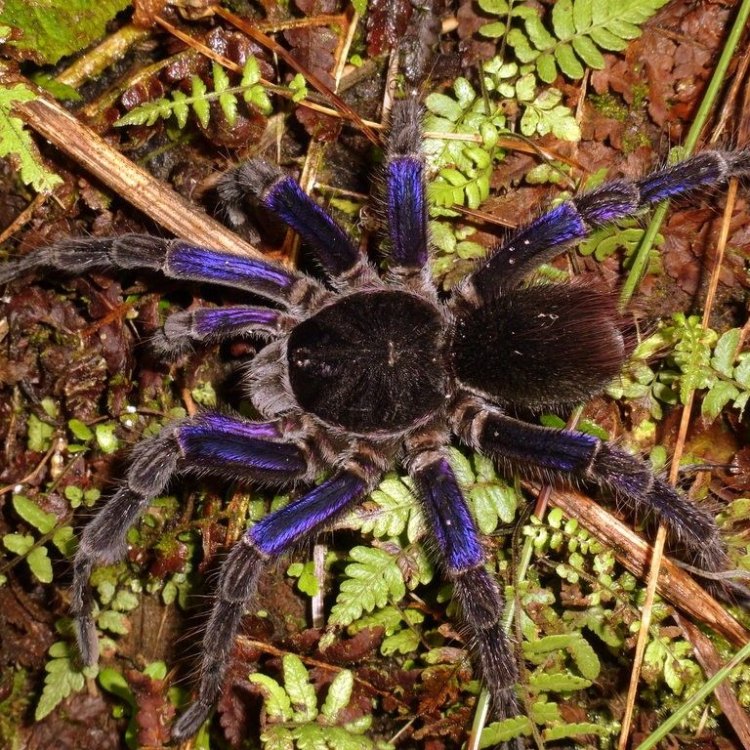
The World of the Purple Tarantula: A Closer Look at These Giant Spiders
Tarantulas have a reputation for being scary and dangerous creatures, with their large size and venomous bites. However, not all tarantulas fit into this stereotype. In fact, the Purple Tarantula, also known as Avicularia purpurea, is a perfect example of a gentle giant. With its stunning coloration and unique characteristics, the Purple Tarantula is a fascinating creature that deserves more attention and admiration Purple Tarantula.The Basics: What is a Purple Tarantula?
Scientifically known as Avicularia purpurea, the Purple Tarantula is a species of tarantula that belongs to the Arthropoda phylum and Arachnida class. They are part of the Theraphosidae family, which includes over 900 species of spiders. These spiders are found in South America, specifically in countries like Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. They are also commonly found in rainforests and tropical areas.The Purple Tarantula was first described in 1989 by Brazilian arachnologist and tarantula expert, Dr. Sylvia Márix. It is one of the newer species of tarantula discovered and has gained popularity among arachnid enthusiasts for its unique appearance.
Appearance: What Makes the Purple Tarantula Stand Out?
One look at the Purple Tarantula is enough to make anyone stop and admire its beauty. As its name suggests, this tarantula is known for its dark purple coloration, ranging from a deep, almost black, hue to a reddish-brown shade Pygmy Rattlesnake. This unique color is due to specialized pigment cells in their exoskeleton called chromatophores, which allow them to change their color depending on their mood and environment.Aside from their distinct color, the Purple Tarantula also has a large and hairy body with a leg span of up to 6 inches (15 cm). This, coupled with their slow and deliberate movements, gives them a majestic appearance as they crawl or rest on tree trunks or in their burrows.
Habitat and Distribution: Where Can You Find the Purple Tarantula?
The Purple Tarantula is native to South America, specifically in the countries of Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. They are found in rainforests and tropical areas, where they can thrive in the humid and warm climate. They are ground-dwelling spiders, but they are also commonly found in tree trunks and burrows.One of the interesting facts about the Purple Tarantula's habitat is that they are often found in close proximity to each other. It is not uncommon to find several individuals living in the same area, which can sometimes lead to cannibalism when resources are scarce.
Feeding Behavior: How Does the Purple Tarantula Hunt and Eat?
Like most tarantulas, the Purple Tarantula is a carnivorous predator. Their main source of food is insects, but they are also known to eat small reptiles and mammals if given the chance. They are nocturnal creatures, and they use their excellent night vision and sensitive hairs on their legs to locate prey.Once their prey is within reach, the Purple Tarantula will use its fangs to inject venom and paralyze its victim. They then use their strong and sharp pedipalps (appendages near their mouth) to crush and tear apart their food. They also have specialized mouthparts called chelicerae, which are used to suck and liquefy their meal.
Interestingly, female Purple Tarantulas have been observed to share their food with their young, which is not common among most spider species.
Behavior and Defense Mechanisms: What is the Purple Tarantula's Temperament?
Despite their intimidating appearance, Purple Tarantulas are generally docile and shy creatures. They are not aggressive and will only attack if they feel threatened or disturbed, such as when their burrows are disturbed or during mating.When confronted, the Purple Tarantula will use various defense mechanisms to protect itself. One of these is their urticating hairs, which they can release from their abdomen. These tiny, barbed hairs can cause irritation and even allergic reactions in predators or humans. They can also use their fangs and venom if necessary.
Another interesting behavior of the Purple Tarantula is their ability to "kick" their urticating hairs towards a potential threat. This is done by rubbing their hind legs against their abdomen, releasing a cloud of hairs towards the offender.
The Purple Tarantula and Humans: Should We Be Afraid of Them?
It is a common misconception that all spiders, especially tarantulas, are dangerous and should be feared. The truth is, most tarantulas, including the Purple Tarantula, are harmless to humans. Their venom is not fatal, and they would only bite as a last resort.In fact, the Purple Tarantula has become a popular choice among tarantula enthusiasts as pets. They are low maintenance, relatively docile, and fascinating to observe. However, it is essential to note that they should not be handled regularly, as they can still bite and release their urticating hairs when agitated.
Conservation Status: Are Purple Tarantulas Endangered?
At the moment, the Purple Tarantula is not listed as an endangered species. However, habitat destruction, illegal pet trade, and collection for the exotic pet market have threatened their population in the wild. Responsible pet ownership and conservation efforts are crucial in ensuring the survival of these beautiful creatures.Final Thoughts: Let's Appreciate and Protect the Purple Tarantula
In the world of arachnids, the Purple Tarantula stands out for its stunning coloration, unique behaviors, and gentle demeanor. As we continue to learn more about these creatures, it is important to appreciate and protect their existence in their natural habitat.With responsible pet ownership and conservation efforts, we can ensure that future generations can also have the opportunity to admire and study these fascinating creatures. The Purple Tarantula may seem like a scary spider at first glance, but a closer look reveals an incredible and essential member of our ecosystem.
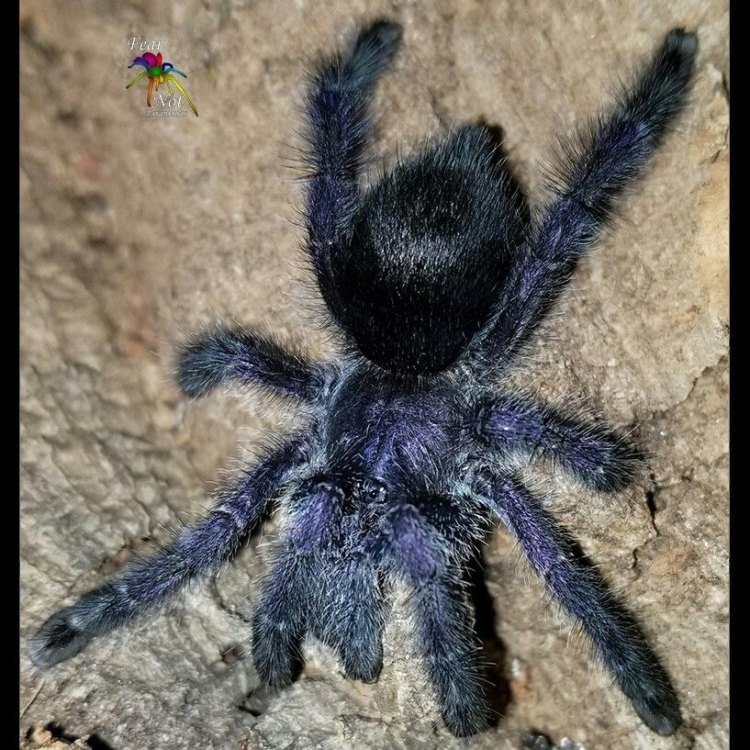

Purple Tarantula
Animal Details Purple Tarantula - Scientific Name: Avicularia purpurea
- Category: Animals P
- Scientific Name: Avicularia purpurea
- Common Name: Purple Tarantula
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Arachnida
- Order: Araneae
- Family: Theraphosidae
- Habitat: Rainforests, tropical areas
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: South America
- Country of Origin: Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana
- Location: Tree trunks, burrows
- Animal Coloration: Dark purple to reddish-brown
- Body Shape: Large and hairy
- Length: Up to 6 inches (15 cm)
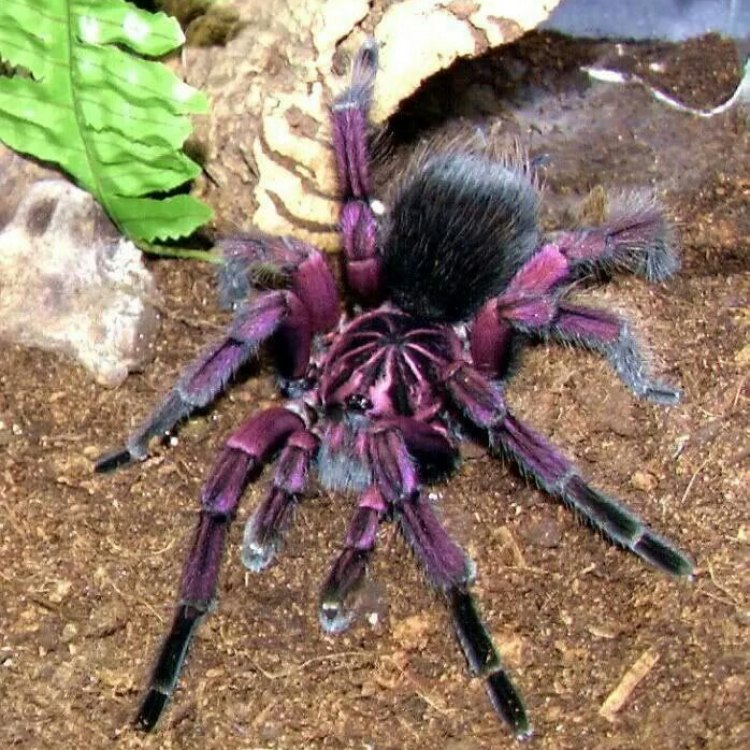

Purple Tarantula
- Adult Size: Medium-sized
- Average Lifespan: 10-15 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males perform courtship rituals
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal and secretive
- Threats: Habitat loss and collection for pet trade
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated (IUCN)
- Impact on Ecosystem: Predator
- Human Use: Popular in the pet trade
- Distinctive Features: Vibrant purple coloration, hairy body
- Interesting Facts: Purple tarantulas are arboreal spiders that spend most of their time in trees. They use their silk to create elaborate nests and climb from one tree to another. Despite their name, they are not completely purple and can vary in color from dark purple to reddish-brown.
- Predator: Birds, snakes, mammals
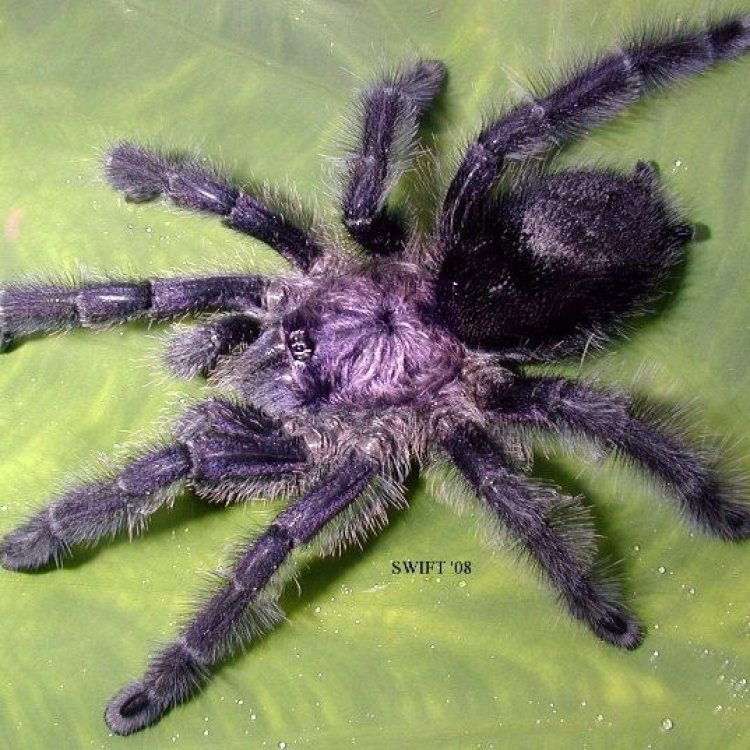

Avicularia purpurea
The Mysterious Purple Tarantula: A Vibrant Spider in the Shadows
In the world of spiders, there's one creature that captures the attention of both arachnophiles and arachnophobes alike - the purple tarantula. With its vibrant purple color, hairy body, and mysterious behavior, it's no surprise that this spider has become a popular species in the pet trade. But beyond its striking appearance, there's much more to discover about this elusive and fascinating creature.The purple tarantula, scientifically known as Avicularia purpurea, is a medium-sized tarantula native to the forests of South America PeaceOfAnimals.Com. Its average lifespan is 10-15 years, making it a long-lived species in the tarantula world. They are known to be sexually reproducing creatures, with males performing intricate courtship rituals to attract females. Like most spiders, they lay eggs in egg sacs and take care of their offspring until they hatch.
But what sets the purple tarantula apart from other species is its unique reproductive behavior. Males are known to perform elaborate courtship dances, where they use their colorful front legs to create a visual display to attract females. They also produce a special pheromone to further entice the female spider. Once they have successfully mated, the female will lay eggs and protect them until they hatch.
When it comes to communication, the purple tarantula does not produce any sounds or calls. They rely on body language and pheromones to communicate with other spiders and potential mates Pine Beetle. As solitary creatures, they do not form social groups and prefer to live alone. This is why they are often found in isolated areas of the rainforests and are not known to migrate from one place to another.
One of the most interesting behaviors of the purple tarantula is its nocturnal and secretive nature. They are most active during the night and spend most of their time hiding in their silk-lined nests or burrows. This behavior makes them difficult to spot in their natural habitat, adding to their mysterious reputation. It's also one of the reasons why they make great pets, as they require minimal care and thrive in a low-stress, solitary environment.
Despite their elusive nature, the purple tarantula is not immune to threats. Habitat loss due to deforestation and urban development is one of the major threats to their survival. As arboreal spiders, they spend most of their time in trees, and when their habitat is destroyed, they struggle to survive and reproduce. Another threat to their existence is the collection for the pet trade, as their beautiful color and interesting behavior make them popular among tarantula enthusiasts.
Currently, the purple tarantula is not evaluated by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means there is not enough information on their population size and conservation status. However, their role in the ecosystem as predators is crucial. As they feed on insects and other small creatures, they help maintain the balance in their habitat. Additionally, they also serve as prey for other animals, such as birds, snakes, and mammals.
In terms of human use, the purple tarantula has become a sought-after species in the pet trade, especially among arachnid enthusiasts. However, it's important to note that keeping any wild animal as a pet requires proper research and responsibility in caring for them. These spiders have specific needs and may not be suitable for everyone, so it's essential to consult with a professional before deciding to bring one home.
Aside from their behavior and impact on the ecosystem, one cannot overlook the distinctive features of the purple tarantula. As the name suggests, they have a vibrant purple coloration, which sets them apart from other tarantula species. However, it's worth noting that not all individuals of this species are entirely purple. Some may have a mix of purple, blue, or reddish-brown colors, making each spider unique and adding to their beauty.
Despite their striking appearance and popularity, there's still much to learn about the elusive purple tarantula. Scientists are continually studying these spiders to uncover more information about their behavior, reproduction, and ecology. With their mysterious and solitary nature, it's not surprising that they have captured the imagination of many and continue to intrigue and fascinate us.
In conclusion, the purple tarantula is a unique and enigmatic species that calls the rainforests of South America home. With their vivid coloration, solitary behavior, and intricate reproduction rituals, they have captured the attention of the scientific community and the general public. However, as with any wild animal, it's essential to understand and respect their needs and role in the ecosystem. So the next time you come across a purple tarantula, remember to admire its beauty and appreciate the mystery behind this vibrant spider in the shadows.

The World of the Purple Tarantula: A Closer Look at These Giant Spiders
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.