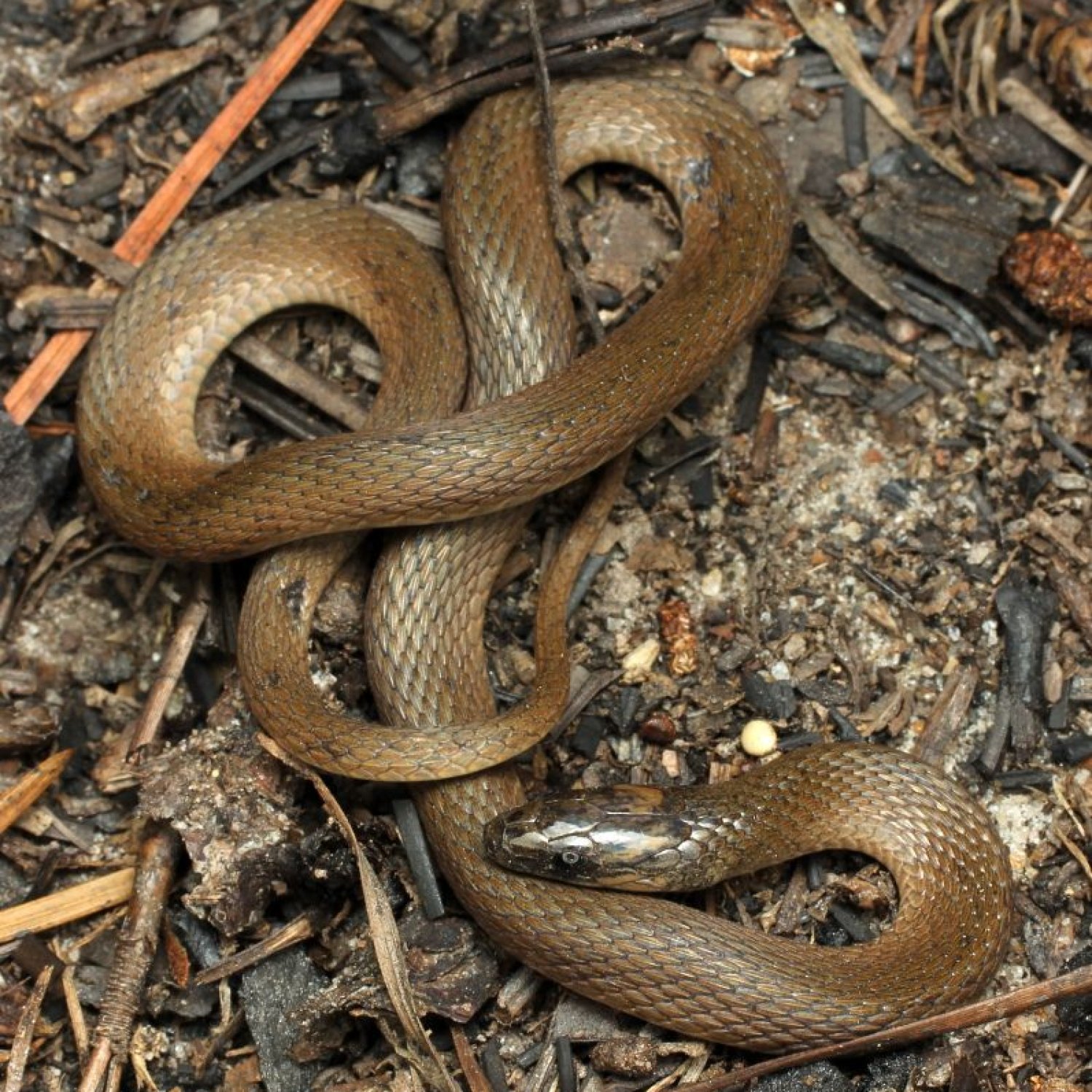
Rough Earth Snake
10-15 inches
Meet the Rough Earth Snake, a slender and elusive species found in the Eastern United States. With a length of 10-15 inches and belonging to the Colubridae family, these harmless snakes are masters of camouflage and are an important part of their ecosystem. Keep an eye out for this cryptic creature on your next nature walk! #RoughEarthSnake #USWildlife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Rough Earth Snake
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Woodlands, forests, grasslands, and marshes
The Slender and Elusive Rough Earth Snake of Eastern United States
Hidden within the dense woodlands, forests, grasslands, and marshes of the Eastern United States, there lies a unique and fascinating animal – the rough earth snake. With the scientific name Virginia striatula, this slender reptile belongs to the class Reptilia and the order Squamata. Known for its cryptic nature and elusive behavior, the rough earth snake is a small but mighty creature that has captured the attention and curiosity of many naturalists and wildlife enthusiasts.The Appearance of Rough Earth Snake
The rough earth snake, also known as "brown snake" or "brown earth snake," is a small snake that typically ranges from 10 to 15 inches in length Rough Earth Snake. Its slender body is covered with smooth and shiny scales, with a brown or gray coloration. This coloration is often accompanied by darker blotches or stripes that run from the head to the tail. The rough earth snake's scales are typically uniform in size, which makes its skin appear smooth instead of rough, contradicting its name. However, the texture of its scales can feel rough to the touch, which led to its common name.A Carnivorous Predator
Despite its small size, the rough earth snake is a carnivorous predator, feeding on a variety of insects and small vertebrates such as earthworms, small frogs, and slugs. Its diet mainly consists of earthworms, hence its name. The rough earth snake has a unique feeding method, where it uses its sharp and recurved teeth to grab its prey and then swallows it whole. Its jaw is specially designed to stretch to accommodate relatively large prey, making it a formidable predator in its habitat.The Habitat and Distribution of Rough Earth Snake
The rough earth snake is native to the Eastern United States, with a distribution that spans from New York to Florida and as far west as Texas and Kansas Rainbow Boa. It prefers habitats with moist soils and abundant ground cover, such as woodlands, forests, grasslands, and marshes. The rough earth snake is often found hiding under logs, rocks, and other debris, making it challenging to spot in the wild. It also spends most of its time underground, digging burrows and tunnels for shelter and protection from predators.The Life Cycle of Rough Earth Snake
The rough earth snake is a live-bearing species, meaning that it gives birth to live young rather than laying eggs. Its breeding season typically starts in the spring, with females giving birth to 6-14 offspring after a gestation period of about 2-3 months. The young snakes are born fully developed and are independent from birth, often measuring around 4 inches in length. The rough earth snake's reproductive age ranges from 2-4 years, and it can live up to 5 years in the wild.The Role of Rough Earth Snake in Its Ecosystem
Despite its small size and elusive nature, the rough earth snake plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a predator of insects and small vertebrates, it helps to control their populations, preventing overpopulation and maintaining balance in the food chain. It also serves as a food source for larger snakes and birds of prey, contributing to the diverse and complex web of life in its habitat.The Threats and Conservation Status of Rough Earth Snake
Like many other species, the rough earth snake faces various threats that jeopardize its survival. Habitat destruction and fragmentation, caused by urbanization, agriculture, and other human activities, are amongst the main threats to this species. Pollution and pesticide use also pose a risk, as they can harm the rough earth snake directly or indirectly by reducing its prey populations. Furthermore, illegal collection for the pet trade and road accidents are also significant threats to this elusive species.Due to these threats, the rough earth snake's population has declined in some areas, leading to its classification as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List. However, its secretive nature makes it challenging to determine its current population size accurately. Therefore, conservation efforts for this species mainly focus on habitat protection and restoration. Raising awareness about the rough earth snake's importance in its ecosystem is also crucial in ensuring its continued survival.
Tips for Observing Rough Earth Snake in the Wild
If you happen to come across a rough earth snake in the wild, consider yourself lucky, as it is not easy to spot them due to their elusive nature. To increase your chances of spotting one, here are some tips to keep in mind:- Visit areas with suitable habitats, such as woodlands or wetlands.
- Carefully overturn logs, rocks, and other debris to look for hidden rough earth snakes.
- Go out on warm and sunny days, as the rough earth snake is more active during these conditions.
- Be patient and move slowly, as the rough earth snake is easily spooked and might hide quickly.
- Carry a camera with you to capture the beauty of this elusive creature without disturbing its natural habitat.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, the rough earth snake, with its slender body and elusive nature, is a fascinating species that plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. Found in the woodlands, forests, grasslands, and marshes of the Eastern United States, this small but mighty reptile feeds on insects and small vertebrates and serves as prey for larger species. However, like many other animals, the rough earth snake faces threats to its survival, making conservation efforts essential to ensure its continued existence. So, if you ever come across a rough earth snake, remember to admire its beauty and appreciate its role in the delicate balance of its habitat.
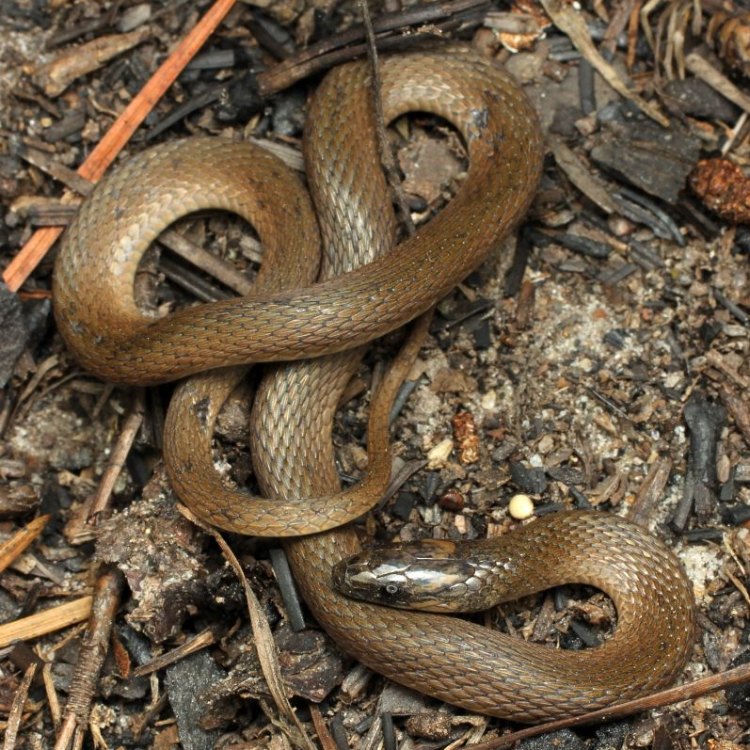

Rough Earth Snake
Animal Details Rough Earth Snake - Scientific Name: Virginia striatula
- Category: Animals R
- Scientific Name: Virginia striatula
- Common Name: Rough Earth Snake
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Family: Colubridae
- Habitat: Woodlands, forests, grasslands, and marshes
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Eastern United States
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Eastern United States
- Animal Coloration: Brown or gray with darker blotches
- Body Shape: Slender
- Length: 10-15 inches

Rough Earth Snake
- Adult Size: 10-15 inches
- Average Lifespan: 3-5 years
- Reproduction: Oviparous
- Reproductive Behavior: Mating occurs in the spring
- Sound or Call: Does not produce any sound or call
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Burrows underground and is primarily active during the night
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Feeds on small invertebrates and helps control their populations
- Human Use: Not used significantly by humans
- Distinctive Features: Smooth scales, small eyes, and pointed snout
- Interesting Facts: Rough Earth Snakes are harmless and often mistaken for venomous snakes
- Predator: Birds of prey, larger snakes, and mammals
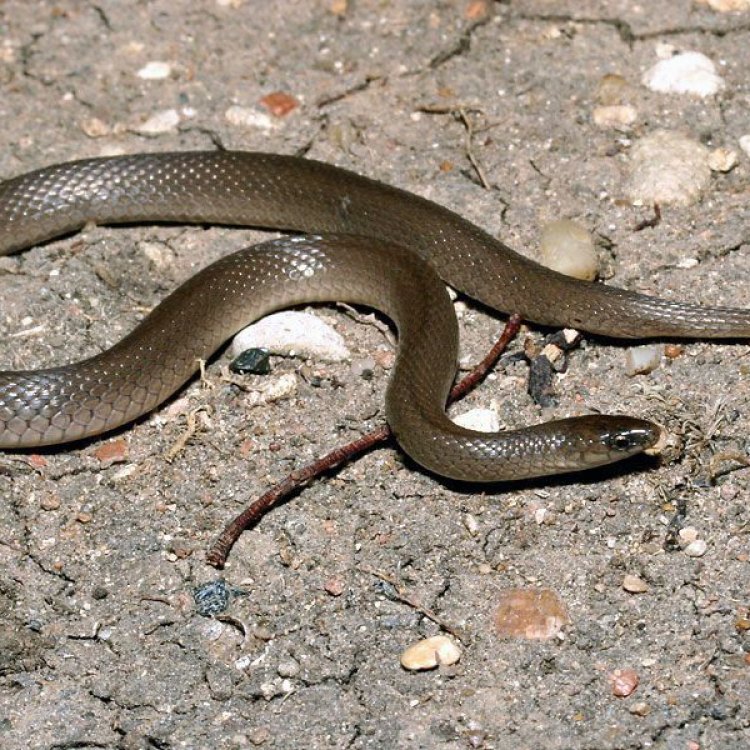

Virginia striatula
The Fascinating World of the Rough Earth Snake
The earth is home to a vast array of snake species, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. While some are well-known and feared, others tend to fly under the radar, often overlooked and misunderstood. One such creature is the Rough Earth Snake, a small and inconspicuous species that holds many secrets waiting to be uncovered.Found across North America, this unassuming snake may not be the star of the show, but it plays a crucial role in the delicate balance of our ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com. In this article, we will dive deeper into the intriguing world of the Rough Earth Snake, learning about its distinctive features, behavior, and impact on the environment.
An Adult Size of 10-15 Inches
At first glance, the Rough Earth Snake may appear to be a mere earthworm due to its small size. Adult Rough Earth Snakes typically reach a length of 10-15 inches, making them one of the smallest snake species in North America.Their slender bodies are covered in smooth scales, which gives them a sleek and shiny appearance. The coloration of this species is variable, ranging from light brown to gray, with some individuals having a reddish hue. They also have a distinctive dark line running down the center of their back, adding to their unique appearance.
Average Lifespan of 3-5 Years
Like most reptiles, the Rough Earth Snake has a relatively short lifespan, averaging between 3-5 years. However, wild individuals are known to live longer, with some reaching up to 8 years of age.Their short lifespan is due to various factors, including predation, disease, and environmental changes Rockhopper Penguin. Despite their brief life, Rough Earth Snakes play a vital role in their habitat, as we will discover later in this article.
Oviparous Reproduction
Unlike some snake species that give birth to live young, the Rough Earth Snake is oviparous, which means it lays eggs. Females typically lay 4-12 eggs in a secluded and protected spot, such as a rotting log or under leaf litter.The female Rough Earth Snake will stay with her eggs, coiling around them to keep them warm and protect them from predators. After an incubation period of 6-8 weeks, the eggs will hatch, and the tiny hatchlings will make their way into the world.
Mating Occurs in the Spring
The reproductive behavior of the Rough Earth Snake is closely linked to the changing seasons. Mating typically occurs in the spring when the weather starts to warm up, and males actively seek out females.During this time, male Rough Earth Snakes emit pheromones, which attract females. The male will then perform a unique courtship dance, intertwining his body with the female and rubbing his chin on her neck to stimulate her to mate.
No Sound or Call Produced
While many snake species produce hissing or rattling sounds as a defense mechanism, the Rough Earth Snake does not possess this ability. This species does not produce any sound or call, relying instead on its small size and camouflage to avoid predators.Non-Migratory Migration Pattern
Rough Earth Snakes are non-migratory, meaning they do not undertake regular, long-distance movements. Instead, they tend to stay within a relatively small area, typically less than an acre.However, they may occasionally relocate to find suitable habitat or to mate during the spring. But these movements are not considered a migration pattern as they are short and not seasonal in nature.
Solitary Social Groups
Due to their solitary nature, Rough Earth Snakes do not form social groups like other species. They are primarily active at night and spend much of their time burrowing underground, making them challenging to spot in the wild.However, during the mating season, male and female Rough Earth Snakes will come together to breed before going back to their solitary ways.
Burrowers and Nocturnal Behavior
Rough Earth Snakes are secretive and elusive creatures, primarily active during the night. During the day, they burrow underground, using their sharp snouts and small eyes to navigate and hunt for food.These snakes are not exclusively nocturnal, and they have been observed basking in the sun during the cooler parts of the day. But, their nocturnal behavior helps them avoid the heat and potential predators, making it their preferred time of activity.
Threats to Rough Earth Snakes
Despite not being venomous, Rough Earth Snakes still face many threats in the wild. The most significant threat to their survival is habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities. As urbanization and agriculture continue to expand, natural habitats are being destroyed, leaving these snakes with limited places to live.Roadkill is also a significant cause of mortality for Rough Earth Snakes, as they often travel across roads in search of suitable habitat or mates. They are also vulnerable to predation by birds of prey, larger snakes, and mammals, highlighting the importance of their elusive nature.
Least Concern Conservation Status
Despite these threats, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists the Rough Earth Snake as a species of Least Concern. This means they are not currently at risk of extinction, but efforts must still be made to ensure their survival.Conservation efforts for Rough Earth Snakes include protecting and preserving their habitats, educating the public about their importance, and encouraging responsible development practices that consider the needs of wildlife.
Impact on the Ecosystem
Although small in size, Rough Earth Snakes have a significant impact on their ecosystem. As they primarily feed on small invertebrates such as earthworms, snails, and insects, they play a crucial role in balancing their populations.These small creatures are essential in maintaining the health of soils, which, in turn, affects plant growth. By controlling the populations of these invertebrates, Rough Earth Snakes help to maintain a healthy ecosystem, making them a valuable species in our environment.
Not Significant for Human Use
Rough Earth Snakes are not used significantly by humans. They are not venomous, which means they do not pose a threat to human health. Additionally, they do not have any economic value, making them generally overlooked by humans.As a result, they often fall victim to human activities such as habitat destruction or accidental death from cars. But, it's essential to recognize the vital role they play in their environment and take measures to protect them.
Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts
The Rough Earth Snake has many distinctive features that make it stand out from other snake species. Its smooth scales, small eyes, and pointed snout are some of the most notable physical characteristics that set it apart. But there is more to this species than just its appearance.Despite their similarities, Rough Earth Snakes are often mistaken for venomous snakes like the Copperhead due to their coloration and pattern. However, they are entirely harmless to humans, and their docile nature makes them an ideal pet for reptile enthusiasts.
Rough Earth Snakes are also unique in that they are one of the few snake species that will not bite when handled, preferring to coil up and play dead instead. Their small size and non-aggressive behavior make them a popular choice for reptile pets.
In addition to these interesting facts, Rough Earth Snakes are also vital players in the food chain. They are a food source for many predators, and their survival is essential to maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
In Conclusion
The Rough Earth Snake may not be the most eye-catching or well-known snake species, but its role in the ecosystem is crucial. Despite facing threats from human activities, this elusive and often misunderstood creature continues to survive and thrive in its natural habitat.By understanding and appreciating the unique characteristics and behaviors of the Rough Earth Snake, we can ensure its conservation and contribution to the delicate balance of our environment. Let us protect and preserve these fascinating creatures for future generations to admire and learn from.

The Slender and Elusive Rough Earth Snake of Eastern United States
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.