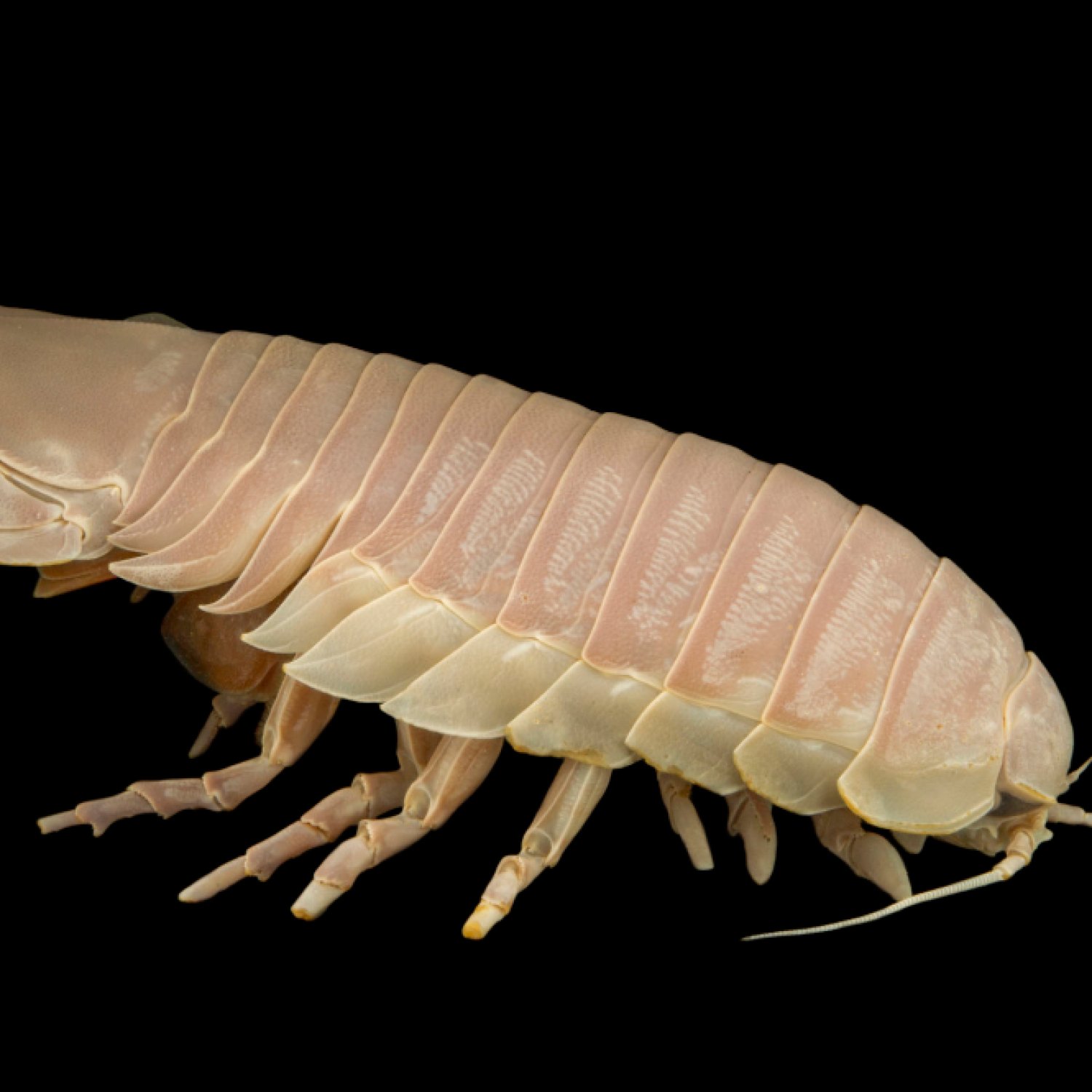

Sea Roach
Up to 3 cm
The Sea Roach, also known as the Sand Hopper, is a tiny aquatic creature found in coastal regions. With a length of up to 3 cm, this oval and flattened animal belongs to the Ligiidae family. It may seem unassuming, but the Sea Roach plays a crucial role in coastal ecosystems as a decomposer and a food source for larger sea creatures. Keep an eye out for this fascinating creature next time you're at the beach! #SeaRoach #SandHopper #CoastalAnimals #MarineLife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Sea Roach
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Rocky shores, coral reefs, intertidal zones
The Fascinating World of Sea Roach: An Unconventional Creature of the Sea
When you think of marine animals, you may envision majestic creatures like dolphins, sharks and colorful fish. But there is one creature that often goes unnoticed due to its small size and unappealing appearance – the Sea Roach. Despite its unimpressive name, the Sea Roach, scientifically known as Ligia oceanica, is a fascinating animal that deserves our attention and admiration.A Member of the Animal Kingdom
The Sea Roach belongs to the Animalia kingdom, which comprises all living organisms that have cells with a nucleus and can move voluntarily Sea Roach. Within this kingdom, the Sea Roach belongs to the phylum Arthropoda, which encompasses animals with segmented bodies and jointed limbs. This phylum is also the largest in the animal kingdom, with over one million identified species.An Unconventional Class and Order
What sets the Sea Roach apart from other sea creatures is its class and order. Belonging to the class Malacostraca, the Sea Roach is considered a "superclass" as it has a wide range of species with a variety of characteristics. The Order Isopoda, on the other hand, consists of small crustaceans with flattened bodies. While most Isopods live in the ocean, the Sea Roach prefers to live near the coast.A Unique Family
The Sea Roach belongs to the family Ligiidae, which is composed of small, elongated marine isopods. These isopods are commonly found in coastal areas, feeding on decaying matter and plants. This family also comprises around 50 species, with the Sea Roach being one of the most well-known Siamese.Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Sea Roaches can be found in rocky shores, coral reefs, and intertidal zones. They prefer living in areas where there are crevices and caves, giving them a place to hide from predators and harsh weather. The Sea Roach is also commonly found in coastal regions of the Atlantic Ocean, including countries like Portugal, France, and the UK.Coloration and Body Shape
Sea Roaches are known for their distinctive dark brown or black coloration, which allows them to blend in with their surroundings. This makes them less likely to be noticed by predators. Their oval and flattened body shape also allows them to easily maneuver through small crevices and cracks, making them highly adaptable to their rocky habitats.Feeding Habits
As detritivores, Sea Roaches play an essential role in the marine ecosystem by feeding on decaying matter and helping to break it down. They mainly feed on dead plant material and algae, contributing to the recycling of nutrients in their environment. This makes them an essential part of the food chain, providing food for larger predators and maintaining a balance in the marine ecosystem.A Tiny but Hardy Creature
Despite their small size, Sea Roaches are incredibly hardy creatures. They have a thick exoskeleton that protects them from predators and rough waves. This shell is also essential for maintaining moisture in their body, allowing them to survive in various conditions. They are also capable of surviving for long periods out of the water, making them highly adaptable to changes in their environment.The Fascinating Adaptations of Sea Roaches
One of the most interesting features of Sea Roaches is their ability to breathe through their gills and their skin. These gills are located on their underside and are constantly moist, allowing them to absorb oxygen from the water. However, when Sea Roaches are out of the water, they can also absorb oxygen through their skin, thanks to their thin membrane.Another noteworthy adaptation of the Sea Roach is its ability to withstand high levels of salinity in their environment. This allows them to inhabit a wide range of coastal areas, including tidal pools and estuaries, where the water can have varying levels of salt content.
The Importance of Studying Sea Roaches
While Sea Roaches may seem like insignificant creatures, they play a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. Studying these animals can also provide us with insights into the mechanisms of adaptation and evolution. Due to their hardy nature and ability to thrive in various conditions, Sea Roaches are also being studied for their potential medical benefits, such as their antibacterial properties.In Conclusion
In the vast and diverse world of marine animals, the Sea Roach may seem like a tiny and unappealing creature. However, upon closer inspection, it becomes clear that they are unique and fascinating creatures that contribute to the stability of coastal environments. From their hardy adaptations to their crucial role in the marine food chain, Sea Roaches are a testament to the wonders of nature and deserve to be appreciated and studied further.
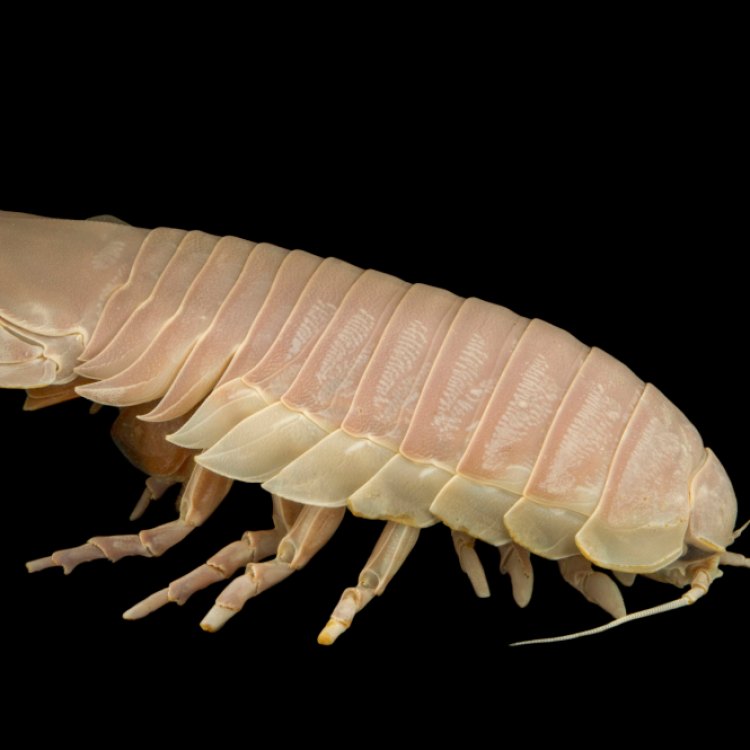

Sea Roach
Animal Details Sea Roach - Scientific Name: Ligia oceanica
- Category: Animals S
- Scientific Name: Ligia oceanica
- Common Name: Sea Roach
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Malacostraca
- Order: Isopoda
- Family: Ligiidae
- Habitat: Rocky shores, coral reefs, intertidal zones
- Feeding Method: Detritivore
- Geographical Distribution: Coastal areas of the Atlantic Ocean
- Country of Origin: Multiple countries including Portugal, France, UK
- Location: Coastal regions
- Animal Coloration: Dark brown or black
- Body Shape: Oval and flattened
- Length: Up to 3 cm
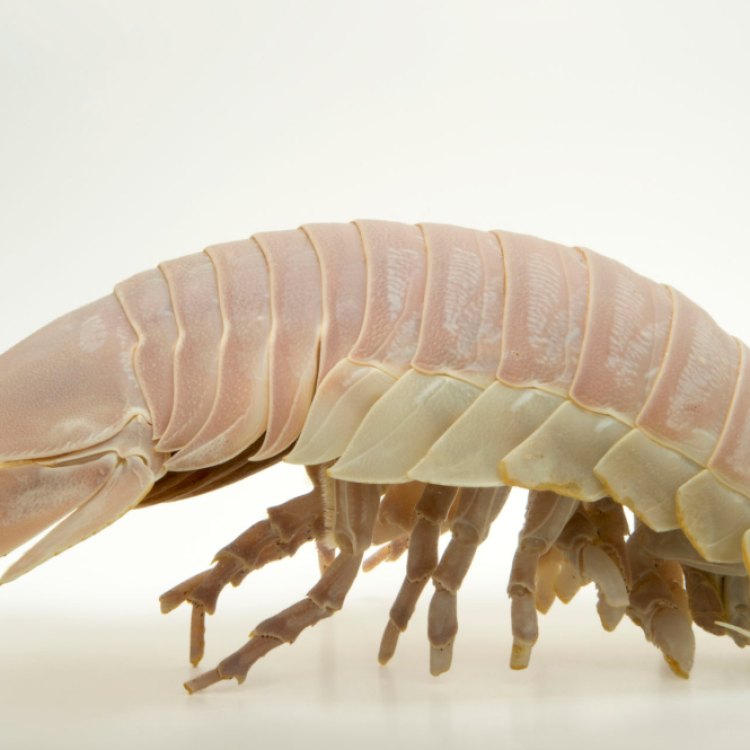

Sea Roach
- Adult Size: Up to 3 cm
- Average Lifespan: 1-2 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Internal fertilization
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal, hides in cracks and crevices during the day
- Threats: Predation, habitat loss, pollution
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important role in nutrient cycling
- Human Use: Not used by humans
- Distinctive Features: Numerous legs, gills for respiration
- Interesting Facts: Not a true roach, but a type of marine isopod
- Predator: Birds, fish, crabs
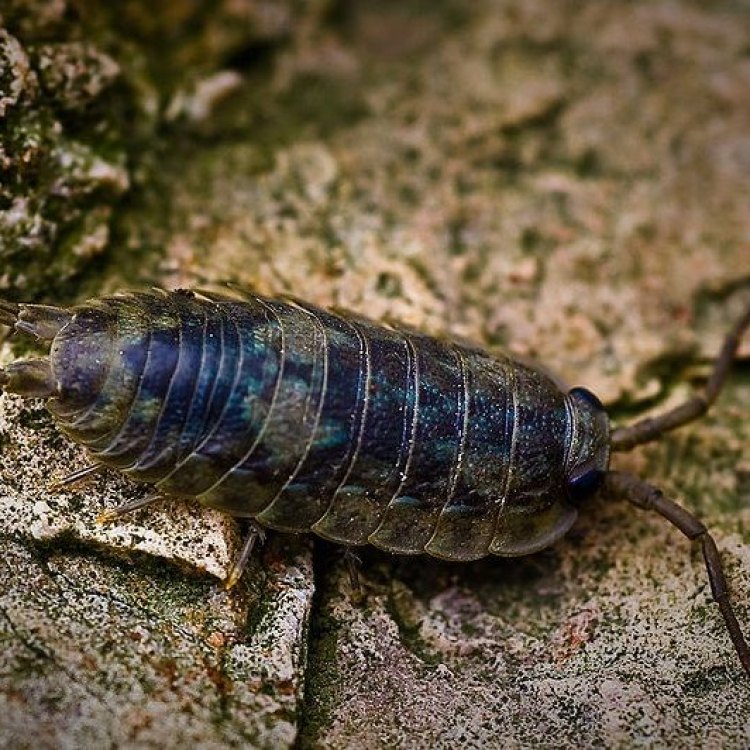

Ligia oceanica
The Sea Roach: A Small but Mighty Mystery of the Ocean
The vastness of the ocean holds many mysteries, and among them is the sea roach. Although often overlooked and misunderstood, this tiny creature plays a vital role in the ocean's ecosystem. With its distinctive features and interesting behavior, the sea roach is a fascinating creature worthy of our attention and appreciation.The sea roach, also known as Limnoria quadripunctata, is a marine crustacean that belongs to the isopod family PeaceOfAnimals.Com. It is not a true roach, as its name suggests, but rather a distant relative of the terrestrial woodlouse. Despite its small size, reaching only up to 3 cm in length, this little creature has a lot to offer.
Appearance and Behavior
The sea roach has a cylindrical body with a grayish-brown color. It has an elongated head with two pairs of antennae and numerous legs that it uses for swimming and crawling. These legs also help the sea roach to hold onto rocks and other surfaces in its habitat. Unlike other crustaceans, the sea roach does not have a hard exoskeleton but rather a soft, flexible covering that allows it to wiggle through tight spaces.
As a nocturnal creature, the sea roach prefers to stay hidden during the day to avoid predators. It typically hides in cracks and crevices, making it challenging to spot in its natural habitat. Its solitary nature and nocturnal behavior make it challenging to study, contributing to its mystery Sheep.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
The sea roach has a unique reproductive behavior in that it practices internal fertilization. This means that the female stores the male's sperm and can use it to fertilize her eggs when conditions are favorable. The female sea roach can lay up to 100 eggs and attaches them to rocks or other surfaces in the ocean. After a few weeks, the eggs hatch into tiny larvae that eventually develop into adult sea roaches.
The sea roach has a relatively short lifespan, with the average adult living for only 1-2 years. However, researchers believe that some individuals may live for longer periods, but more studies need to be done to confirm this theory fully.
The Sea Roach's Role in the Ecosystem
As a small and often overlooked creature, one may wonder what role the sea roach plays in the ocean's vast ecosystem. But, in reality, it has a significant impact on the environment. The sea roach is a detritivore, meaning it feeds on decaying organic matter such as dead plants and animals. In doing so, it plays a crucial role in the ocean's nutrient cycling, breaking down and recycling essential nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Moreover, the sea roach also serves as a food source for many predators, including birds, fish, and crabs. Its small size and ability to hide make it a challenging prey, but it still contributes to the marine food web. With its crucial role in the ecosystem, the sea roach is an integral part of maintaining a healthy ocean.
Threats and Conservation Status
Despite its important role in the ecosystem, the sea roach faces several threats that put its population at risk. Habitat loss, pollution, and predation are among the main threats that this creature faces. Coastal development and human activities, such as marine pollution and overfishing, can have a significant impact on the sea roach's population. Furthermore, the rise in sea temperatures due to climate change can harm the sea roach and its habitat, affecting its survival.
However, despite these threats, the sea roach's conservation status is currently listed as "not evaluated" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). More research and studies are needed to fully assess the sea roach's population and the potential impact of these threats. It is essential to gather more information about this creature to ensure its protection and conservation in the future.
How Humans Interact with the Sea Roach
The sea roach is not used by humans in any significant way, and its role is primarily limited to the ocean's ecosystem. However, it can sometimes cause damage to wooden structures, earning its name "sea roach" as it resembles the terrestrial woodlouse that feeds on wood. Researchers are currently studying ways to prevent such damage without harming the sea roach.
Fascinating Facts about the Sea Roach
One of the most interesting facts about the sea roach is that it is not a true roach at all. Its name comes from its resemblance to its terrestrial relative, the woodlouse, even though their behaviors and habitats are vastly different. Moreover, the sea roach's gills, which it uses for respiration, are quite a unique feature. These gills are located on the sides of its body, allowing it to absorb oxygen from the water.
Another interesting fact is that the sea roach is a prevalent species in areas with wooden structures, such as piers. It is estimated that there can be hundreds of thousands of individuals within a small area, making it a crucial part of the marine ecosystem in these areas.
The Mystery Continues
The sea roach may be a small and often overlooked creature, but it holds many mysteries that are yet to be unraveled. Its unique features, behavior, and role in the ecosystem make it a fascinating subject for further research. Understanding more about this creature can help us protect it and appreciate its vital role in maintaining a healthy marine ecosystem.
In conclusion, the sea roach may not be a well-known or commonly seen creature, but it has a significant impact on the ocean's ecosystem. Its distinctive features, interesting behavior, and crucial role in the environment make it a worthy subject of study and conservation efforts. As we continue to explore and discover the mysteries of the ocean, let us not forget the small but mighty sea roach.
The Fascinating World of Sea Roach: An Unconventional Creature of the Sea
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












