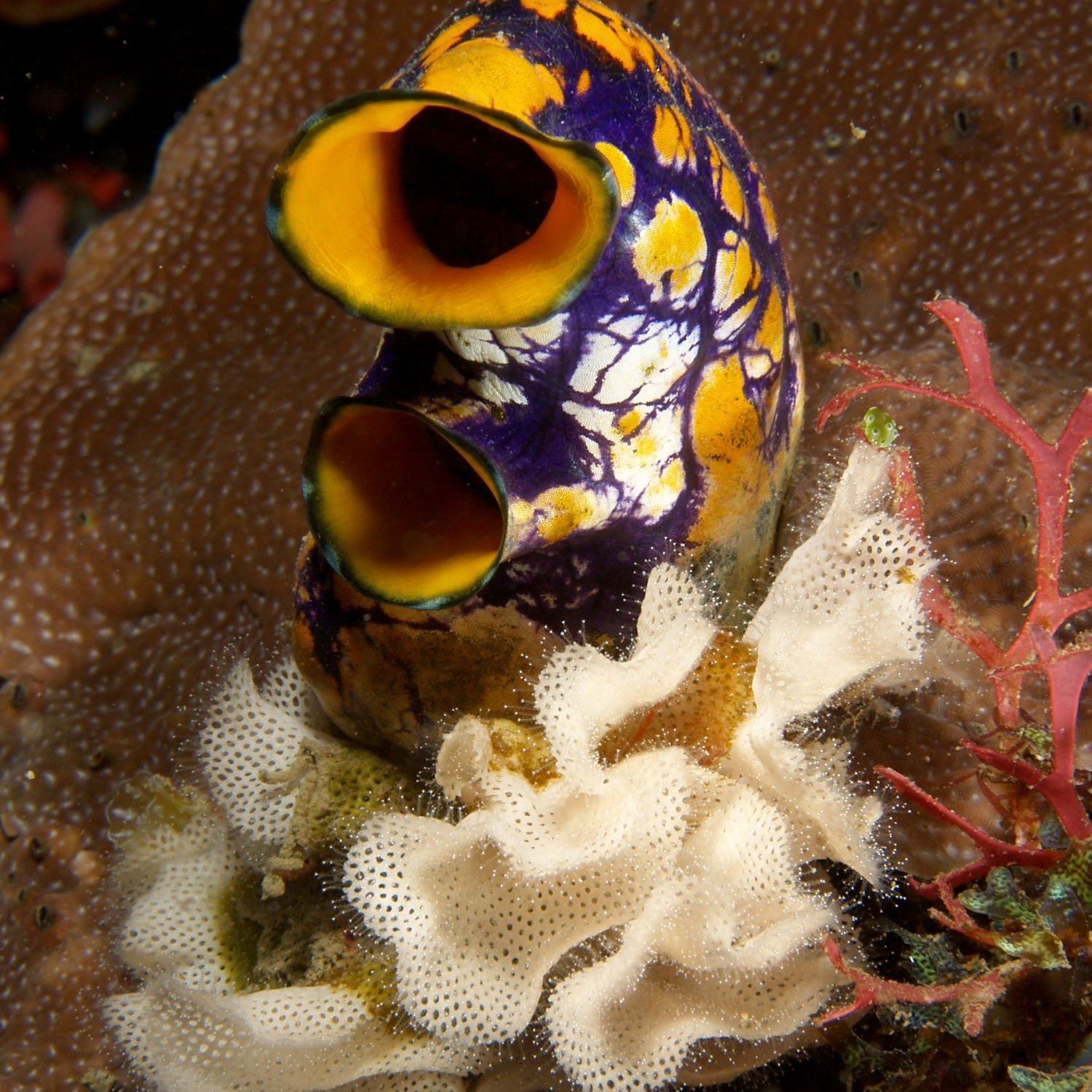

Sea Squirt
0.5 inches to 5.9 feet
Sea Squirts, also known as Tunicates, are fascinating and diverse creatures found in the ocean. Ranging in size from 0.5 inches to 5.9 feet, these tube-shaped or asymmetrical animals come in a variety of colors and belong to various families. Spot one on your next dip in the ocean and marvel at their unique features. #SeaSquirts #OceanLife #Tunicates
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Sea Squirt
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Marine
The Fascinating Creature of the Ocean: Sea Squirt
The vast expanse of the ocean hides many secrets and mysteries, home to millions of species that are yet to be discovered. Among these creatures is the intriguing sea squirt, a filter-feeding marine animal that belongs to the class Ascidiacea. The sea squirt may not be as famous as other marine animals like dolphins or sharks, but it is no less fascinating. In this article, we will explore the remarkable characteristics and habits of the sea squirt, delving into its scientific name, classification, behavior, and more Sea Squirt. So, let's dive deep and discover the amazing world of the sea squirt.The Scientific Name and Classification of Sea Squirt
The sea squirt may have a somewhat amusing name, but its scientific name is just as impressive - "ascidiacea." This name comes from the Greek word "askos," which means "bag" or "sac," and "dia," which means "through." The name is fitting as the sea squirt has a soft and squishy body, and water flows in and out of it through two siphons.The sea squirt belongs to the Kingdom Animalia, which includes all animals, from microscopic organisms to large mammals. Within the animal kingdom, the sea squirt belongs to the Phylum Chordata, which includes all animals with a notochord (a flexible rod-like structure found in embryonic stages). The sea squirt then falls under the class Ascidiacea, which includes about 2,300 known species. This class is divided into two orders - the Aplousobranchia and the Enterogona.
The Habitat and Geographical Distribution of Sea Squirts
Just like their scientific name suggests, sea squirts are commonly found in marine environments, although some species can also be found in brackish waters Shastasaurus. They are sessile animals, meaning they attach themselves to hard surfaces such as rocks, corals, or other marine animals. Their preferred habitats range from coastal areas to the open sea, and they can be found from the tidal zone to depths of up to 33,000 feet.The sea squirt is a cosmopolitan animal, meaning it can be found worldwide. These creatures are abundant in tropical and temperate waters, and they can be found in all the oceans of the world. However, some species have a limited geographical distribution, such as the Pyura chilensis, which is only found in the rocky coasts of Chile and Peru.
Appearance and Physical Characteristics of Sea Squirts
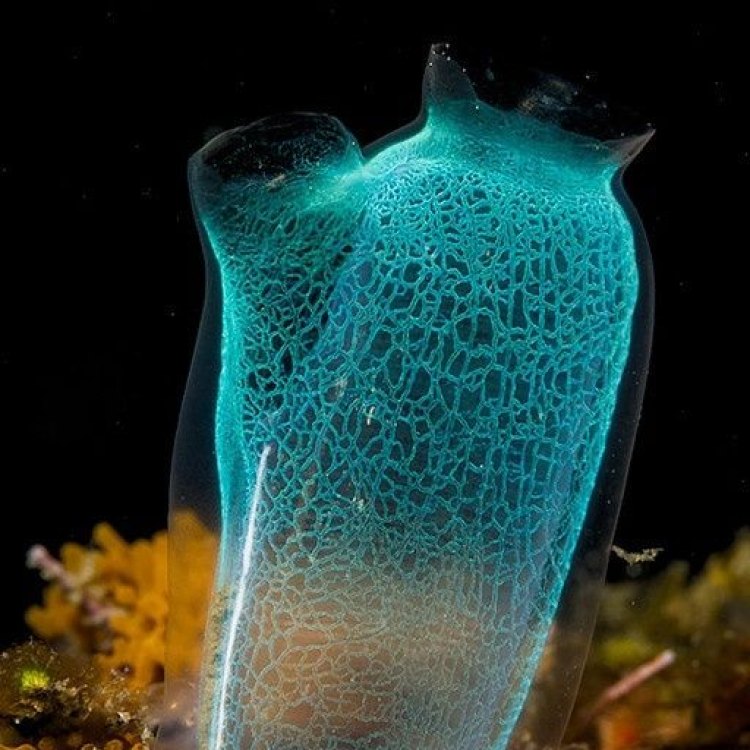
The sea squirt may not be the most colorful creature in the ocean, but its appearance is still fascinating. These animals can come in a variety of shapes and colors, with the most common ones being tubular or asymmetrical. Some species may also have a more complex structure, with branching tentacles or elongated bodies.One surprising characteristic of the sea squirt is its ability to self-destruct. When threatened or disturbed, some species of sea squirt can expel a jet of water to propel themselves away from danger. In doing so, they also release a burst of chemicals that can repel predators or even kill them. This remarkable defense mechanism earned the sea squirt the nickname "the animal that fights back."
The Feeding Method of Sea Squirts: Filter Feeders
Sea squirts get their nutrition through a process known as filter-feeding. They use their siphons to draw in water, filtering out tiny particles such as plankton, detritus, and other organic matter. They then trap the food particles using a sticky mucus layer, which is then transported to their stomachs for digestion.The sea squirt's filter-feeding method not only provides them with nutrition, but it also has an important ecological role in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. By consuming large quantities of small particles, they help regulate the nutrient cycle and, in turn, provide food for other marine animals.
The Family and Country of Origin of Sea Squirts
Sea squirts have varied and diverse families, with some species forming colonies, while others are solitary. Some commonly known families include Ascidiidae, Cionidae, and Molgulidae, but there are many more that still need to be discovered and classified.As for their country of origin, sea squirts are considered cosmopolitan animals, so they don't have a specific country of origin. They can be found in all oceans, and their exact origins remain a mystery.
Threats and Conservation Efforts for Sea Squirts
Like many other marine animals, sea squirts face various threats. These include pollution, overfishing, and destruction of their habitats. The rise in ocean temperatures due to climate change is also a significant threat, as it can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems and cause coral bleaching, which has a direct impact on sea squirt populations.To address these threats, conservation efforts are in place to protect sea squirts. Some initiatives include creating marine sanctuaries, implementing sustainable fishing practices, and reducing pollutants in our oceans. However, there is still much to be done to ensure the long-term survival of sea squirts and other marine creatures.
The Importance of Studying Sea Squirts
The study of sea squirts is not only important for understanding the diversity of marine life, but it also has practical applications. For instance, some researchers are investigating the chemicals produced by sea squirts as a potential source for new drugs. These chemicals have shown promise in treating cancer, Alzheimer's, and other diseases, which highlights the importance of preserving these animals and studying their biology.Furthermore, sea squirts are used as bioindicators, which means they can provide valuable information about the health of marine ecosystems. By studying their populations and behavior, scientists can gain insights into the impact of environmental changes on the ocean and its inhabitants.
In Conclusion
The sea squirt may not be the most well-known marine animal, but it is undoubtedly an intriguing and unique creature. From its scientific name to its feeding habits and defense mechanisms, there is no shortage of fascinating details about this animal. As we continue to explore and understand our oceans, let's not forget to appreciate and protect the sea squirt and the many other incredible species yet to be discovered. After all, the ocean is a vast and wondrous place, full of surprises waiting to be unraveled.
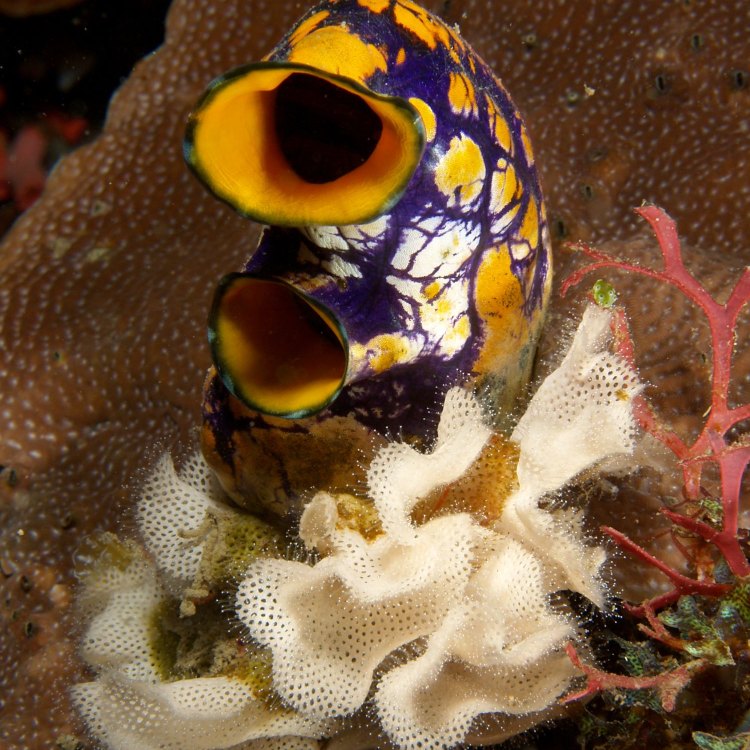

Sea Squirt
Animal Details Sea Squirt - Scientific Name: ascidiacea
- Category: Animals S
- Scientific Name: ascidiacea
- Common Name: Sea Squirt
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Ascidiacea
- Order: Enterogona
- Family: Various
- Habitat: Marine
- Feeding Method: Filter Feeder
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: N/A
- Location: Ocean
- Animal Coloration: Varies
- Body Shape: Tubular or Asymmetrical
- Length: 0.5 inches to 5.9 feet
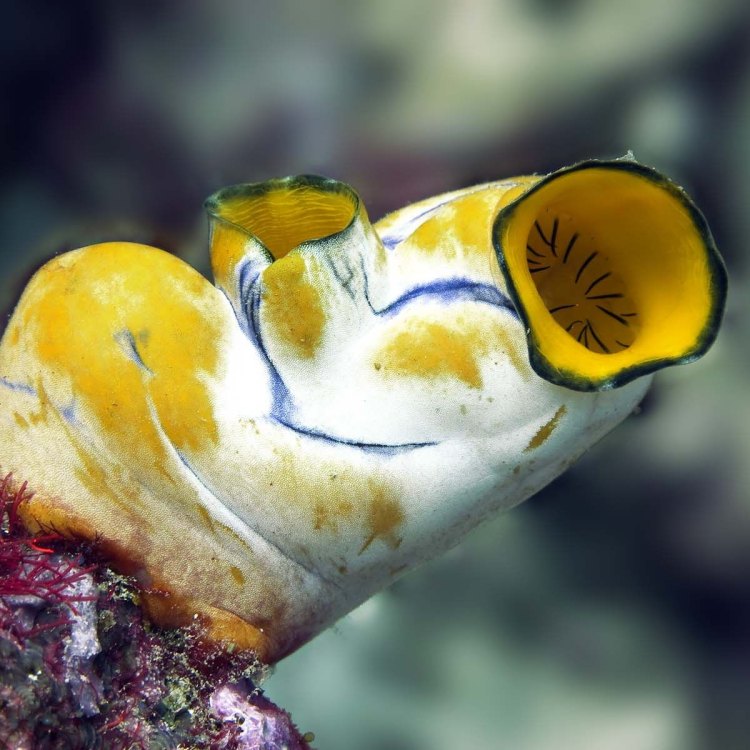

Sea Squirt
- Adult Size: Varies
- Average Lifespan: Few months to a few years
- Reproduction: Sexual or Asexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Various
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary or Colonial
- Behavior: Sessile
- Threats: Predators, pollution, habitat loss
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Biofouling, water filtration
- Human Use: Research, food
- Distinctive Features: Siphons, tunic, incurrent and excurrent siphons
- Interesting Facts: The sea squirt is an invertebrate chordate, which means it is related to vertebrates like fish and mammals. It got its name due to its habit of squirting water when touched. Sea squirts are filter feeders, pumping and filtering seawater to obtain food particles. They are important in marine ecosystems as they help purify the water and provide habitat for other organisms. Some species of sea squirts are invasive and can cause harm to local ecosystems. Sea squirts are often used in scientific research due to their unique biology and ability to regenerate body parts.
- Predator: Various marine animals
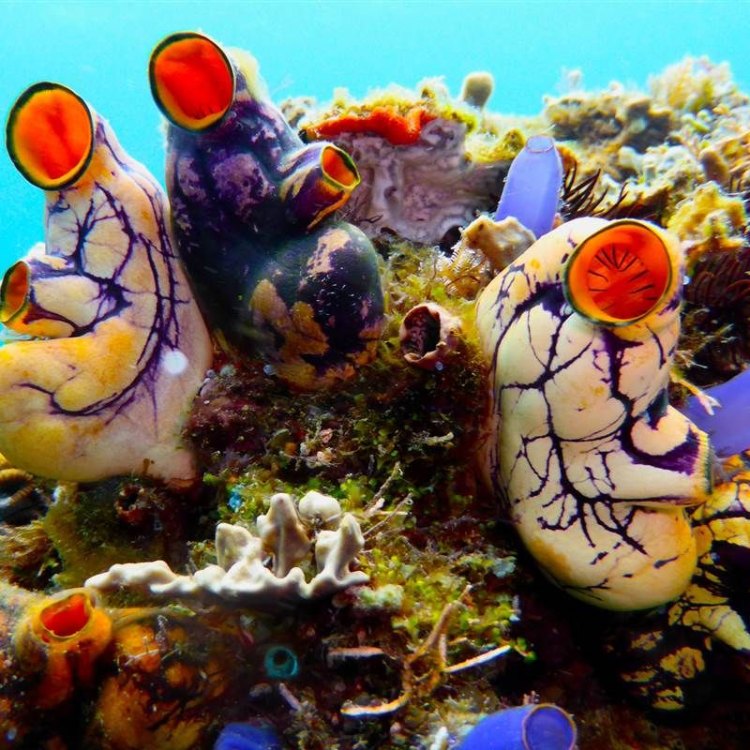

ascidiacea
The Sea Squirt: A Marvelous and Mysterious Invertebrate
The vast and mysterious ocean is home to countless creatures, each with their own unique features and behaviors. Among them, the sea squirt stands out as a truly fascinating creature. From its intriguing reproductive behavior to its important role in marine ecosystems, there is much to discover about this invertebrate.Sea squirts, or ascidians, are a group of marine animals that belong to the phylum Chordata PeaceOfAnimals.Com. This means they are related to vertebrates like fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. However, unlike their vertebrate relatives, sea squirts lack a backbone and a brain.
Adult sea squirts come in a variety of sizes, with some species growing as small as a few millimeters and others reaching up to a meter in length. They have a lifespan that varies from just a few months to a few years, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
One of the most fascinating aspects of sea squirts is their reproductive behavior. They can reproduce either sexually or asexually, depending on the species and environmental conditions. Some species have separate sexes, while others are hermaphroditic and can produce both eggs and sperm. Asexual reproduction occurs through a process called budding, where a small part of the adult sea squirt breaks off and develops into a new individual.
When it comes to courtship and mating, sea squirts exhibit various behaviors Sika Deer. Some species release sperm and eggs into the water column, where fertilization takes place. Others have internal fertilization, and the larvae develop inside the adult's body before being released into the ocean.
Despite their diverse reproductive behavior, sea squirts do not produce any sound or call. Instead, they communicate through chemical signals, allowing them to coordinate their activities and interactions with other members of their species.
Sea squirts are primarily sessile, meaning they are attached to a surface and cannot move freely. As filter feeders, they rely on the constant flow of water to bring in food particles. To achieve this, sea squirts have a unique structure called the tunic, which is a protective outer covering that surrounds their soft bodies. It is made of a gelatinous substance and can range in colors from vibrant reds and oranges to more subdued greens and browns.
The most distinctive feature of sea squirts is their siphons, which are used for feeding and waste removal. These siphons are divided into two openings: the incurrent siphon, which brings in water and food particles, and the excurrent siphon, which expels waste and water. The siphons also play a vital role in the sea squirt's defense mechanism. When touched or disturbed, they can rapidly expel water, earning them the name "sea squirt."
Sea squirts can be found in both solitary and colonial forms. Solitary species live alone, while colonial species form groups or clusters. These colonies can vary in size, with some species forming elaborate structures that can resemble underwater forests.
As sessile creatures, sea squirts face a range of threats in their environment. They are often preyed upon by various marine animals, including fish, crabs, and sea stars. Habitat loss and pollution also pose a significant threat, as they can disrupt the sea squirt's food supply and affect the quality of their surrounding water.
Despite these threats, sea squirts are not currently evaluated for conservation status. However, they play a vital role in marine ecosystems as filter feeders, helping to purify the water and provide shelter and habitat for other organisms.
Their role as filter feeders also has a significant impact on human use. Sea squirts are used in scientific research as model organisms due to their unique biology and ability to regenerate lost body parts. They have contributed to advancements in fields such as bioengineering, regenerative medicine, and developmental biology.
In some parts of the world, sea squirts are also used as a food source, particularly in Asian cultures. They are considered a delicacy and are typically served boiled, fried, or pickled.
Unfortunately, some species of sea squirts have become problematic invaders in non-native habitats. These invasive species can outcompete native species for resources and disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems. One notable example is the most invasive sea squirt species, Didemnum vexillum, which has caused significant damage to shellfish farms in New Zealand and Japan.
In conclusion, the sea squirt is indeed a marvelous and mysterious invertebrate that continues to fascinate scientists and marine enthusiasts. From its unique reproductive behavior to its vital role in marine ecosystems and human use, there is still much to uncover about this peculiar creature. As we continue to explore and understand the ocean, we can only hope to gain a greater appreciation for these fascinating and essential creatures.
The Fascinating Creature of the Ocean: Sea Squirt
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












