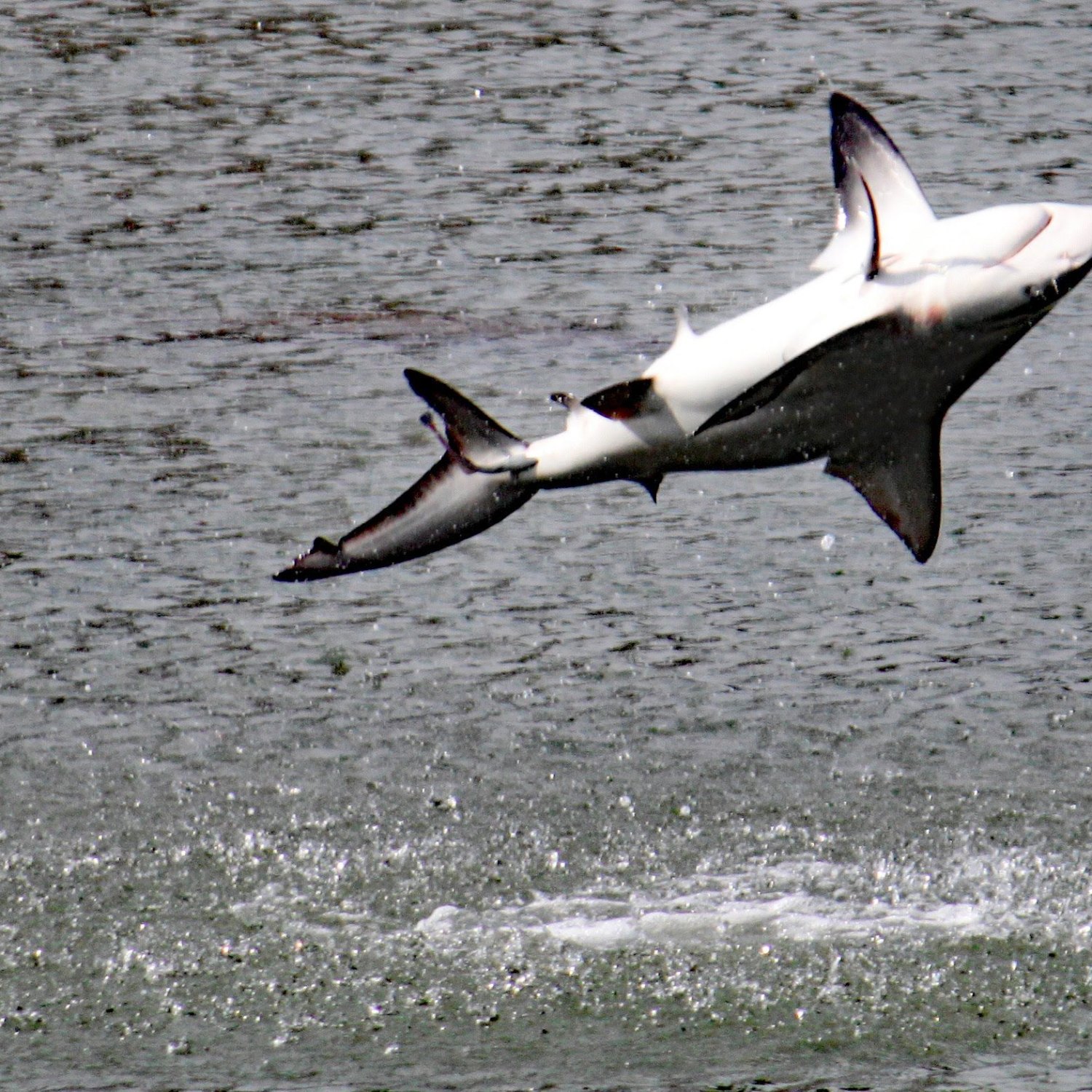
Spinner Shark
6.6 to 9.8 feet (2 to 3 meters)
The Spinner Shark, found in the oceans, belongs to the Carcharhinidae family. Known for their slender and streamlined body shape, they can grow up to 6.6 to 9.8 feet (2 to 3 meters) in length. Their distinctive spinning jumps are a sight to behold. Keep an eye out for this beautiful creature on your next beach trip! #SpinnerShark #OceanLife #Carcharhinidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Spinner Shark
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Coastal and offshore waters
The Marvelous World of the Spinner Shark
The ocean is a vast and wondrous place, filled with many mysteries and creatures. From the tiniest plankton to the largest whale, the ocean holds a vast array of species that continue to amaze and fascinate us. But there is one particular creature that stands out in the vastness of the ocean – the spinner shark.Known scientifically as Carcharhinus brevipinna, the spinner shark is a member of the Carcharhinidae family, which is a part of the larger class of Chondrichthyes, or cartilaginous fish Spinner Shark. These include sharks, rays, and skates. The spinner shark can be found in coastal and offshore waters, making its home in the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world.
With its distinctive appearance and unique behaviors, the spinner shark is a fascinating creature that deserves much attention and admiration. Let's dive deeper into the marvelous world of the spinner shark and uncover its incredible features.
Appearance and Anatomy
The spinner shark has a streamlined and slender body, allowing it to move swiftly through the water. Its body shape is perfect for sneaking up on its prey and making sharp turns to catch them. The body is covered in small, overlapping scales, which are known as placoid scales. These scales are rough to touch, similar to sandpaper, and help protect the shark's skin from any rough surfaces in its environment.In terms of coloration, the spinner shark has a grayish-brown upper body and a whitish underside Sambar. This coloration acts as camouflage, helping the shark to blend in with its surroundings and avoid predators. This kind of coloration is known as countershading and is a common characteristic of many oceanic animals.
The head of the spinner shark is distinctive, with large, round eyes and small nostrils. The mouth, located on the underside of the head, contains several rows of sharp, triangular teeth. These teeth are essential for the shark's predatory feeding method.
Feeding and Hunting
The spinner shark is a predatory species, meaning it feeds on other animals in its ecosystem. Its diet primarily consists of small fish, such as mackerel and herring, but it is known to also eat squid and crustaceans. The spinner shark has a powerful bite, thanks to its sharp teeth, which it uses to stun and immobilize its prey.What sets the spinner shark apart from other sharks is its unique hunting technique – spinning. As the name suggests, the spinner shark is known for its incredible ability to leap out of the water and spin while catching its prey. This magnificent acrobatic display allows the shark to catch fish at the surface of the water, where they are most abundant. This behavior is fascinating to observe and is what gives the shark its name.
Habitat and Distribution
As mentioned earlier, the spinner shark can be found in both coastal and offshore waters. It prefers tropical and warm temperate regions, and its distribution is widespread, including areas such as the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. However, the specific country of origin of the spinner shark is unknown.The shark's preferred habitat is in the open ocean, but it can also be found in shallower waters, making it a versatile species. It is mostly found in the upper layers of the water column, where it can easily spot its prey and make its hunting maneuvers.
Threats and Conservation
Like many other shark species, the spinner shark faces various threats that put its survival at risk. The biggest threat is overfishing, where large numbers of sharks are caught for their meat and fins. Shark finning, a cruel practice where a shark's fins are harvested, is still prevalent, and it is estimated that tens of millions of sharks are killed in this way every year.Another significant threat to the spinner shark is bycatch – unintentional capture by fishermen targeting other species. The spinner shark's reproductive rate is relatively slow, making it susceptible to population declines caused by these threats.
To protect the spinner shark and many other shark species, conservation efforts are in place. Through initiatives such as marine protected areas and strict fishing regulations, authorities aim to preserve their populations. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed the spinner shark as a vulnerable species, and it is essential to continue to raise awareness about its plight to ensure its survival.
Interesting Facts
As if the spinner shark's unique hunting technique wasn't impressive enough, here are a few more interesting facts that make this species truly extraordinary:- The spinner shark is known to migrate long distances, covering thousands of miles in search of food and breeding grounds.
- Its lifespan is estimated to be between 15 to 20 years, but due to environmental pressures, their average lifespan may be lower.
- The spinner shark is a viviparous species, meaning the female gives birth to live young. The gestation period is about 12 months, and the female can give birth to up to 15 pups at a time.
- The spinner shark is not considered dangerous to humans and is not known to attack people, making it a relatively safe shark species to swim with.
Final Thoughts
The spinner shark is a magnificent creature that continues to amaze us with its unique appearance and behaviors. From its distinct hunting technique to its incredible ability to adapt to different environments, this shark species is a remarkable addition to the diverse ecosystem of the ocean.However, like many other marine creatures, the spinner shark faces multiple threats that put its survival at risk. It is our responsibility to raise awareness about these threats and to take action to protect not only the spinner shark but also all the beautiful creatures that call the ocean their home. Let us work together to ensure the spinner shark continues to spin and thrive in the vast, marvelous world of the ocean.
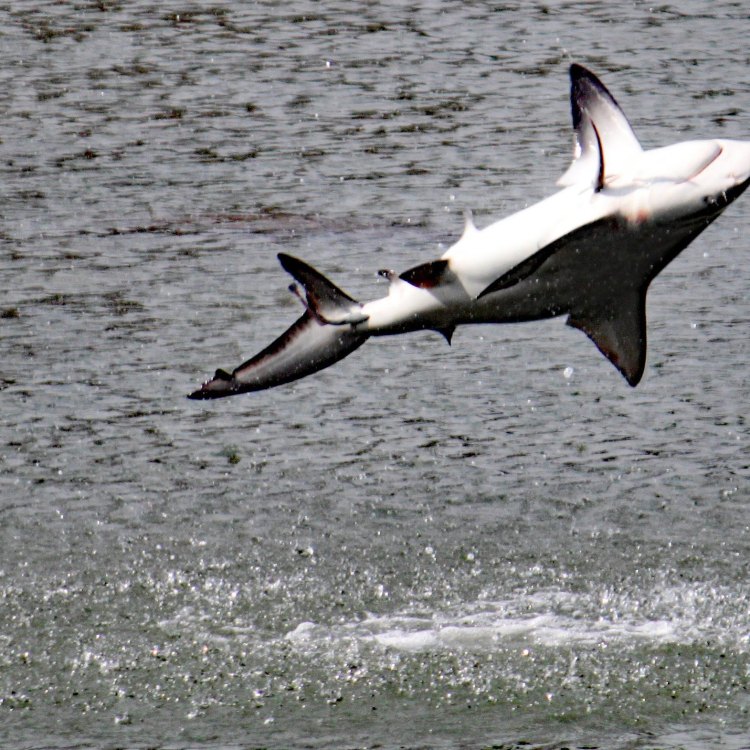

Spinner Shark
Animal Details Spinner Shark - Scientific Name: Carcharhinus brevipinna
- Category: Animals S
- Scientific Name: Carcharhinus brevipinna
- Common Name: Spinner Shark
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Carcharhinidae
- Habitat: Coastal and offshore waters
- Feeding Method: Predatory
- Geographical Distribution: Tropical and warm temperate waters worldwide
- Country of Origin: Unknown
- Location: Ocean
- Animal Coloration: Grayish-brown on the upper body, white on the underside
- Body Shape: Streamlined and slender
- Length: 6.6 to 9.8 feet (2 to 3 meters)
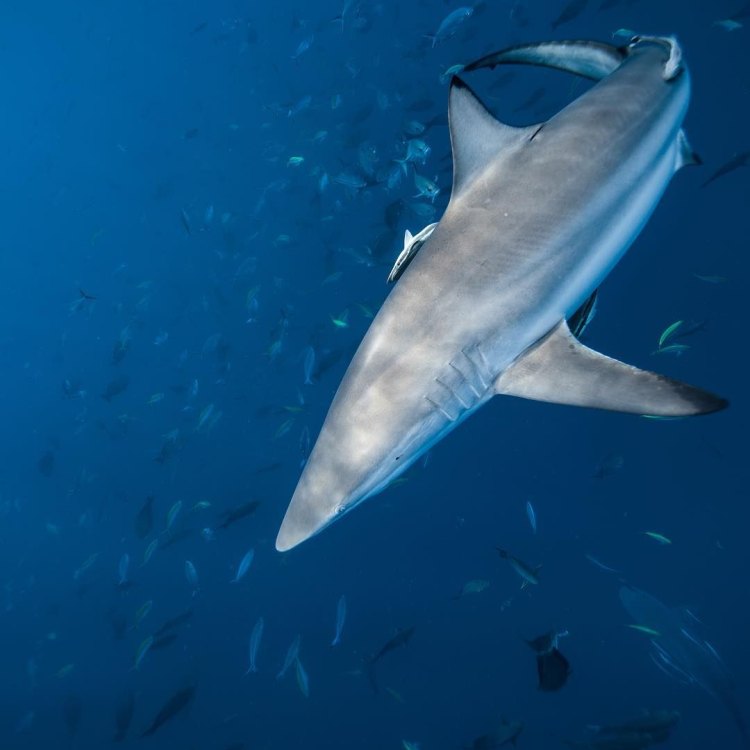

Spinner Shark
- Adult Size: Up to 9.8 feet (3 meters)
- Average Lifespan: Up to 15 years
- Reproduction: Viviparous (live-bearing)
- Reproductive Behavior: Unknown
- Sound or Call: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Seasonal migration
- Social Groups: Unknown
- Behavior: Spinner sharks are known for their acrobatic spinning leaps out of the water. They are fast and agile swimmers and often hunt in groups. They feed on small fish and cephalopods.
- Threats: Overfishing, habitat degradation, fishing bycatch
- Conservation Status: Near Threatened
- Impact on Ecosystem: As top predators, spinner sharks help regulate the population of prey species and maintain the balance of the marine ecosystem.
- Human Use: Commercial and recreational fishing
- Distinctive Features: Long, slender body shape, black tips on the pectoral fins, and the ability to leap out of the water
- Interesting Facts: 1. Spinner sharks get their name from their spinning leaps out of the water. 2. They are capable of spinning multiple times in the air before landing back in the water. 3. Spinner sharks are highly migratory and often form large schools. 4. They are known to perform breathtaking aerial displays during feeding frenzies. 5. Spinner sharks are popular targets for sport fishing due to their agility and acrobatics.
- Predator: Larger sharks and marine mammals
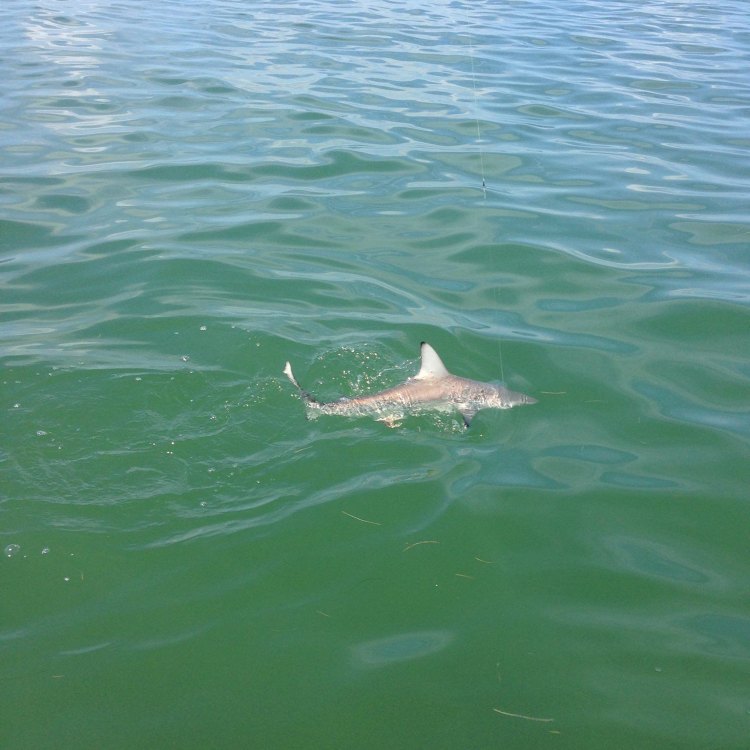

Carcharhinus brevipinna
The Majestic Spinner Shark: A Master of Acrobatics in the Ocean
The ocean is home to a vast array of fascinating creatures, each with their own unique characteristics and behaviors. Among these creatures is the spinner shark, a sleek and agile predator known for its acrobatic spinning leaps out of the water. Found in tropical and warm-temperate waters all over the world, these sharks are a sight to behold and are a critical part of the marine ecosystem.Spinner sharks, also known by their scientific name Carcharhinus brevipinna, are named for their impressive and entertaining ability to spin out of the water PeaceOfAnimals.Com. These sharks can reach an adult size of up to 9.8 feet (3 meters) and have an average lifespan of up to 15 years. They are classified as near threatened on the IUCN Red List, mainly due to overfishing, habitat degradation, and fishing bycatch.
However, before we dive deeper into the threats facing these majestic creatures, let's first understand more about their reproductive behavior, social interactions, and unique features.
Like most sharks, little is known about the reproductive behavior of spinner sharks. They are viviparous, which means they give birth to live young. However, their specific mating behaviors and breeding grounds remain a mystery. Researchers believe that they may reproduce year-round, although their peak season is still unknown.
Spinner sharks are solitary creatures, and their social groups are not well studied Song Thrush. Despite this, they are known to form large schools during seasonal migrations, suggesting some form of social interaction. These migrations can be hundreds of miles long, and the purpose of these journeys is still a topic of study. It is believed that these migrations may be related to finding food sources or avoiding unfavorable environmental conditions.
The distinctive feature that sets spinner sharks apart from other species is their ability to leap out of the water and spin. This behavior gives them their name, and it is truly a sight to behold. These agile creatures can spin multiple times in the air before returning to the water, making it a breathtaking display for any lucky onlookers.
Their long, slender body shape allows them to be fast and agile swimmers, crucial for hunting and evading predators. They also have black tips on their pectoral fins, which is a unique feature among sharks and serves as a camouflage against the bright ocean surface when seen from below.
Now, let's explore more interesting facts about the spinner shark that make it a truly remarkable creature.
Firstly, as mentioned earlier, spinner sharks get their name from their spinning leaps out of the water. This behavior is not only for entertainment purposes; it also helps them catch prey by surprising and disorienting them. This is a crucial tactic for these sharks, given that they primarily feed on fast and elusive prey such as small fish and cephalopods.
Secondly, spinner sharks are capable of spinning multiple times in the air before landing back in the water. This acrobatic ability is possible because of their lightweight and flexible bodies. They use their powerful and elongated caudal fin, also known as a crescent-shaped tail fin, to thrust themselves out of the water and rotate in the air. This ability also helps them evade larger predators, which struggle to keep up with their spinning moves.
Thirdly, these sharks are highly migratory and often form large schools. They are found in tropical and warm-temperate waters all over the world, including the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans. These schools also provide protection from larger predators and increase their chances of finding food during migrations.
Fourthly, spinner sharks are known to perform breathtaking aerial displays during feeding frenzies. When hunting small fish in large groups, they create a spectacle by leaping out of the water in unison, spinning, and splashing down into the water with incredible precision. This behavior is not only impressive to watch but also helps them catch a large number of prey in a short amount of time.
Lastly, because of their agility and acrobatics, spinner sharks are a popular target for sport fishing. When caught, they put up a fierce fight, making them an exciting catch for recreational anglers. However, overfishing and bycatch from commercial fishing pose a significant threat to this species, contributing to their near-threatened status on the IUCN Red List.
Speaking of threats, let's take a closer look at the challenges facing these magnificent predators.
The primary threat to spinner sharks is overfishing, mainly driven by the demand for their meat, fins, and liver oil. These sharks are often caught as bycatch in gillnets, longlines, and purse seines used to catch other species. This unsustainable fishing practice poses a significant risk to the survival of spinner sharks, as it hinders their ability to reproduce and maintain healthy population levels.
Habitat degradation is another major threat to spinners sharks. As with many marine creatures, they rely on healthy and diverse ocean ecosystems to survive and thrive. However, activities such as pollution, coastal development, and climate change can significantly impact their habitats, making it difficult for them to survive.
Fishing bycatch, where spinner sharks are caught unintentionally in fishing gear, is also a significant cause of their declining numbers. This is especially problematic given the lack of knowledge about their reproductive and population dynamics. As a result, conservation measures and management strategies are challenging to implement, making it difficult to protect spinner sharks effectively.
Despite these threats, there is still hope for the survival of these beautiful creatures. Several organizations and governments have implemented conservation measures, such as fishing restrictions, to protect spinner sharks. These actions aim to reduce fishing pressure and promote sustainable fishing practices, such as the use of circle hooks to minimize bycatch.
But, why should we care about saving these sharks?
As top predators, spinner sharks play a vital role in regulating the population of their prey species and maintaining a healthy balance in the marine ecosystem. By keeping the population of small fish and cephalopods in check, they help prevent overgrazing of algae and seagrass beds, which are vital habitats and sources of oxygen for many marine species. Without these sharks, the marine food chain and ecosystem would be significantly disrupted, altering the ocean's delicate balance.
Furthermore, spinner sharks are also important for ecotourism. Their acrobatic displays and large migratory schools make them a popular attraction for divers and tourists, boosting economies in coastal communities. Saving these sharks, therefore, has not only ecological but also economic benefits.
In conclusion, the spinner shark is a truly remarkable and fascinating creature, with its unique acrobatic abilities and crucial role in maintaining a healthy marine ecosystem. Despite facing numerous threats, efforts are being made to protect and conserve this near-threatened species. As individuals, we can also contribute to their protection by making sustainable seafood choices and supporting organizations working to save these majestic creatures. Let's work together to ensure that the spinner shark continues to spin and thrive in our oceans for generations to come.
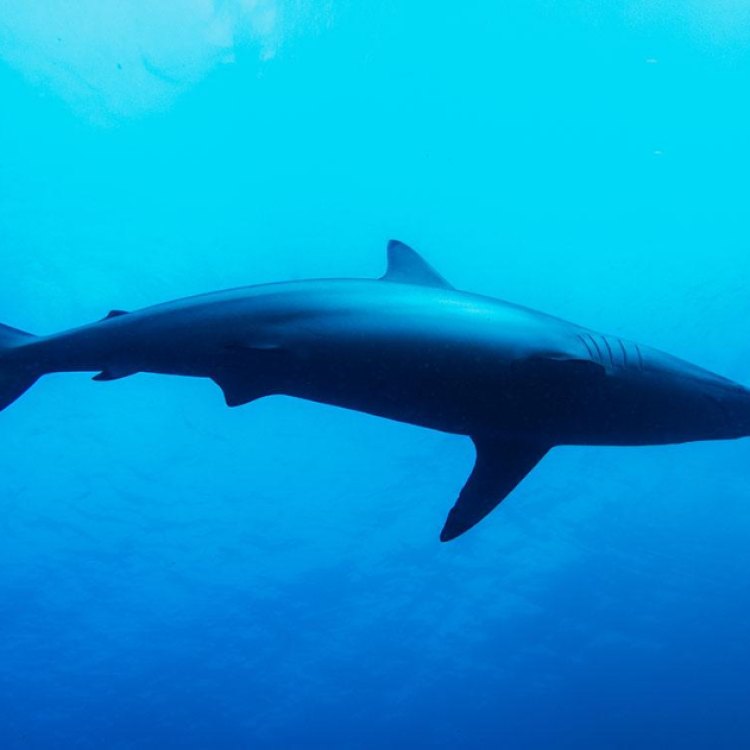

The Marvelous World of the Spinner Shark
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.