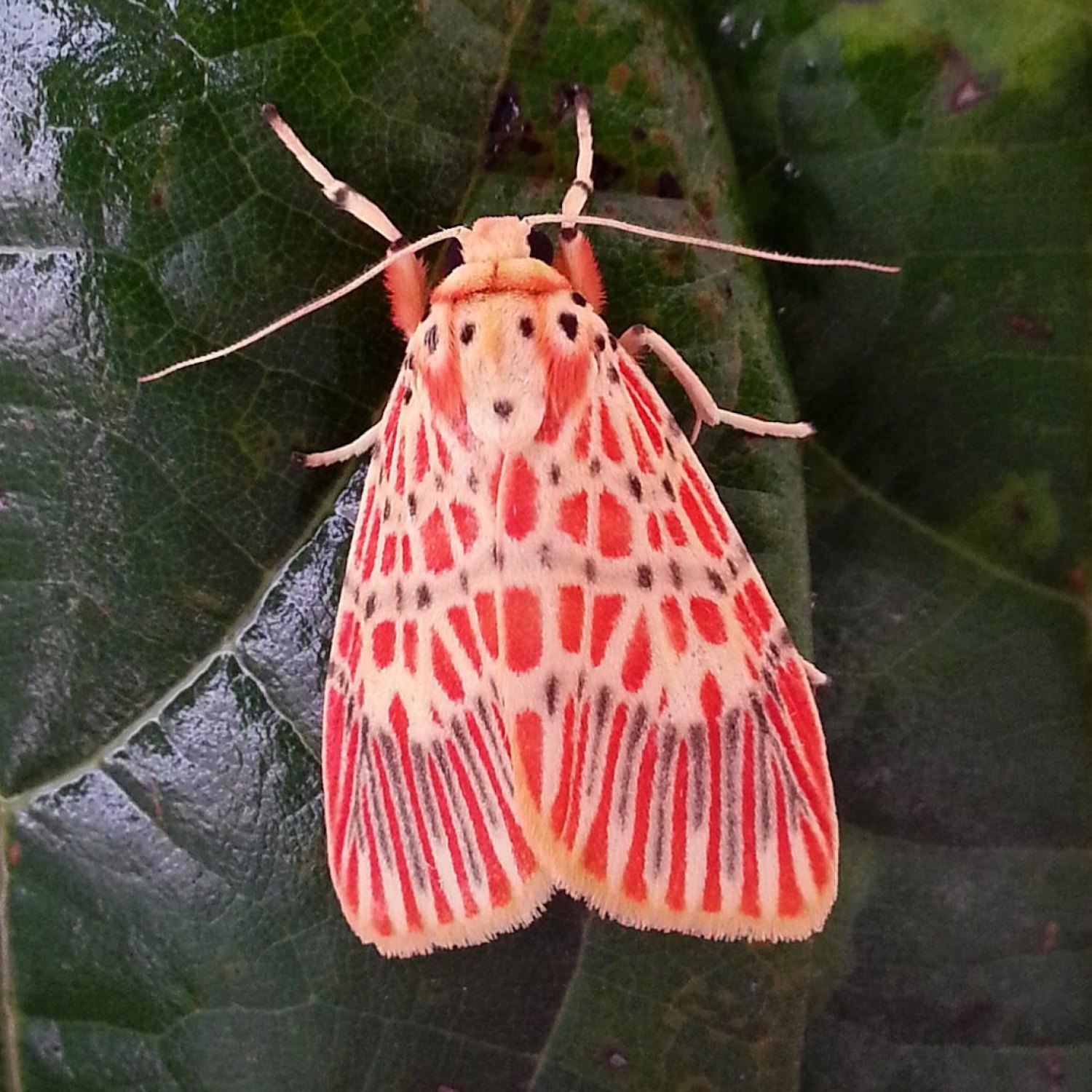
Spongy Moth
Up to 9 cm (3.5 inches)
The Spongy Moth is a beautiful insect found in eastern and southern Africa. With a maximum length of 9 cm and a cylindrical body shape, it is a sight to behold. It belongs to the Saturniidae family and has a fluffy, spongy appearance. Keep an eye out for this gentle creature on your next trip to Africa! #SpongyMoth #AfricanWildlife #Saturniidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Spongy Moth
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Grasslands and savannas
The Secret Life of the Spongy Moth: Exploring the Enigmatic World of Gonimbrasia belina
In the vast, grassy plains of Africa, a unique and mysterious creature flutters its way into existence. This is the spongy moth, scientifically known as Gonimbrasia belina. Despite its seemingly nondescript name, this insect possesses a range of extraordinary characteristics that make it truly one of a kind.Found in Eastern and Southern Africa, the spongy moth is a member of the Lepidoptera order, topped by its gloriously exotic and fuzzy appearance Spongy Moth. Clothed in a range of colors from green to brown, the spongy moth stands out from its surroundings with its distinctive camouflage. But there is more to this creature than meets the eye.
A Brief Overview of the Spongy Moth's Taxonomic Classification
To truly understand the spongy moth, we must first dig deeper into its scientific classification. As with all living organisms, the spongy moth is categorized based on its physical and behavioral characteristics. According to the taxonomic hierarchy, the spongy moth's classification is as follows:Kingdom: Animalia
The spongy moth, like all animals, falls under the kingdom Animalia. This kingdom encompasses all living organisms that are multicellular, heterotrophic, and possess the ability to move.
Phylum: Arthropoda
In the phylum Arthropoda, the spongy moth is grouped with other insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and myriapods. This phylum's defining characteristics include a segmented body, jointed appendages, and an exoskeleton.
Class: Insecta
As a member of the class Insecta, the spongy moth is one of the most diverse groups of animals, with an estimated 5 Scotch Collie.5 million different species. Insects are further characterized by their six legs, three body segments, and a pair of antennae.
Order: Lepidoptera
As mentioned earlier, the spongy moth belongs to the order Lepidoptera, meaning "scaled wings." This order includes butterflies and moths, known for their distinctive wing scales and feeding habits.
Family: Saturniidae
Within the Lepidoptera order, the spongy moth belongs to the family Saturniidae, also known as the "giant silk moths". This family is known for its large, colorful, and often fuzzy wings.
Now that we have a better understanding of the spongy moth's classification, let's dive deeper into its fascinating world.
Habitat and Range
The spongy moth is a creature of the grasslands and savannas, predominantly found in Eastern and Southern Africa. Within these regions, they can be spotted in countries like Zimbabwe, South Africa, and Botswana.Grasslands and savannas provide the perfect habitat for the spongy moth, where they can thrive on the abundant vegetation. These areas also offer shelter from potential predators, making it an ideal home for these delicate creatures.
Feeding Habits
As herbivores, the spongy moth's diet consists mainly of plants, leaves, and grasses. The caterpillars, in particular, are voracious eaters, constantly consuming large amounts of food to fuel their growth. During the caterpillar stage, they can grow up to 9 cm in length, making them one of the largest in the Lepidoptera order.Coloration and Body Structure
One of the most intriguing aspects of the spongy moth is its vibrant and ever-changing colors. As caterpillars, they are typically green, blending in with the foliage around them. As they enter the pupal stage, they transform into a brownish color, mimicking tree bark and providing the perfect camouflage.In terms of body structure, the spongy moth's caterpillar stage is characterized by a cylindrical body, with six small, jointed legs propping them up. This body shape is integral to their survival, allowing them to move quickly and efficiently as they search for food.
Behavior and Life Cycle
The spongy moth is a nocturnal creature, preferring to come out under the cover of darkness. During the day, they rest in the safety of tall grasses and vegetation, avoiding potential predators.Their life cycle begins as eggs, laid on various plant materials, which hatch into larvae or caterpillars. As mentioned earlier, this stage is marked by rapid growth, as they feed on vegetation and prepare for their next transformation. Once fully grown, the caterpillars enter the pupal stage, where they encase themselves in a cocoon and undergo a metamorphosis. Finally, as adults, they emerge as full-grown moths, ready to continue the cycle by laying eggs and starting the process all over again.
The Secret Lives of Spongy Moths
The spongy moth may seem like a plain, unassuming creature, but it holds many secrets and unique characteristics, making it truly one of a kind.One of the most notable features of the spongy moth is its ability to produce silk thread, used to create their cocoons. Unlike other silk moths, who produce their silk from salivary glands, the spongy moth creates its silk from a specialized organ in its abdomen. This silk is valuable and is often used to create textiles and fabrics, providing an additional source of income for communities living in the spongy moth's native habitat.
Another interesting aspect of the spongy moth's behavior is its tendency to gather in large numbers during its migration season. These swarms of moths, known as "mopane worms," travel in search of new feeding grounds, causing quite a stir in the communities where they pass through.
The spongy moth is also culturally significant to the African communities where it is found. In many cultures, the moth's annual migration is considered a delicacy and a valuable source of protein, with countless recipes and dishes featuring the spongy moth as the main ingredient.
Threats and Conservation Efforts
Despite its abundance and resilience, the spongy moth is facing several threats that put its survival at risk. One of the biggest threats to the spongy moth is deforestation and habitat loss. As grasslands and savannas are cleared for agriculture and urban development, this reduces the spongy moth's natural habitat and food sources.Another concern is overharvesting for their silk and as a food source. With the increasing demand for their silk and the traditional consumption of the mopane worms, there are fears that the spongy moth's population may decline in the future.
Fortunately, several conservation efforts are currently underway to protect and preserve the spongy moth. One such initiative is the sustainable farming of the moth, where communities are taught how to rear the spongy moth and harvest their cocoons without harming their population.
Another effort is establishing protected areas and reserves for the preservation of the spongy moth's natural habitat. By designating these areas, authorities can regulate activities and protect the spongy moth's food sources and breeding grounds.
In Conclusion
The spongy moth, with its varied colors, unique physiological characteristics, and enigmatic behavior, is a truly fascinating creature. Despite facing threats to its survival, the spongy moth continues to amaze and intrigue scientists and the general public alike.As we learn more about the spongy moth and its role in the African ecosystem, it becomes even more vital to protect and preserve this extraordinary insect. By taking swift and sustainable action, we can ensure that the spongy moth continues to flutter its way through Africa's grasslands and savannas for generations to come.
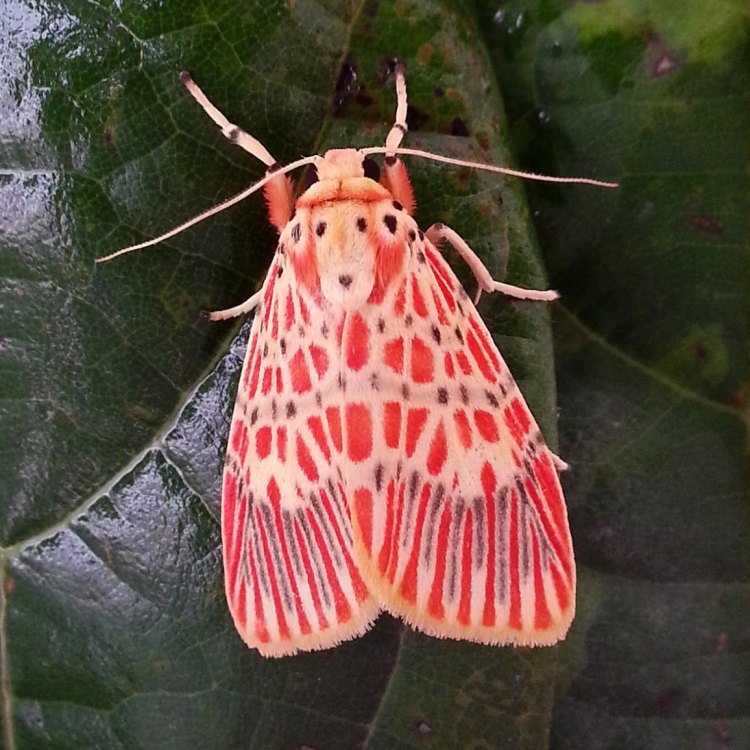

Spongy Moth
Animal Details Spongy Moth - Scientific Name: Gonimbrasia belina
- Category: Animals S
- Scientific Name: Gonimbrasia belina
- Common Name: Spongy Moth
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Lepidoptera
- Family: Saturniidae
- Habitat: Grasslands and savannas
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Africa
- Country of Origin: Zimbabwe
- Location: Eastern and southern Africa
- Animal Coloration: Variable, from green to brown
- Body Shape: Caterpillar has a cylindrical body
- Length: Up to 9 cm (3.5 inches)

Spongy Moth
- Adult Size: Wingspan up to 10 cm (4 inches)
- Average Lifespan: 2 to 4 weeks
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males attract females with pheromones
- Sound or Call: None
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Pollinators
- Human Use: Edible, considered a delicacy in some African countries
- Distinctive Features: Large, fluffy caterpillar
- Interesting Facts: The caterpillar is commonly known as the mopane worm.
- Predator: Birds, small mammals
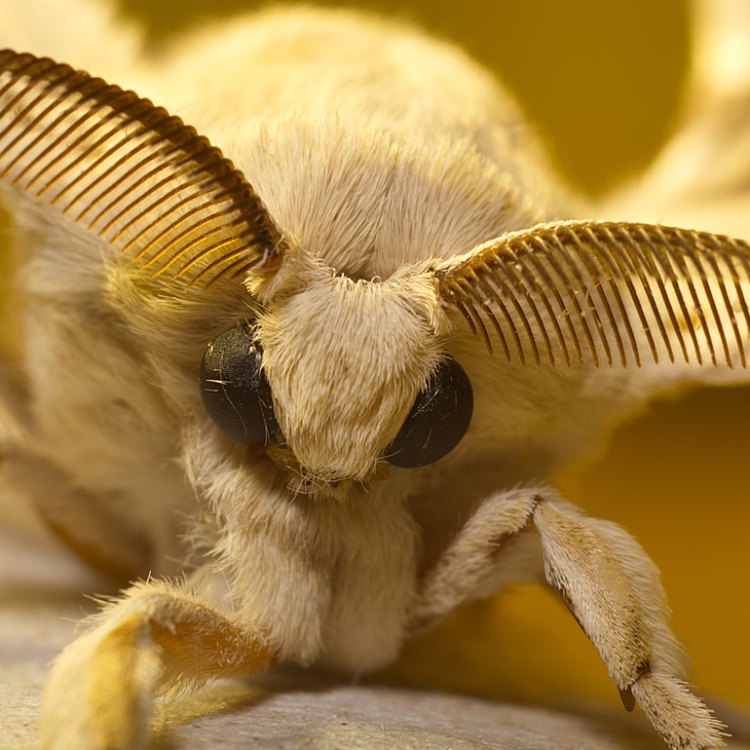

Gonimbrasia belina
The Fascinating World of the Spongy Moth
In the vast, diverse and ever-changing world of insects, there are many fascinating creatures that often go unnoticed. One such creature is the Spongy Moth, a species that is both mesmerizing and mysteriously unique in its own way. With a wingspan of up to 10 cm (4 inches), the Spongy Moth is a remarkable insect that brings a touch of wonder and beauty to the world of entomology.From its lifecycle to its behaviors and impacts, there is much to discover about this seemingly simple moth PeaceOfAnimals.Com. So, let's dive into the fascinating world of the Spongy Moth and uncover its mysterious characteristics.
The Adult Size and Average Lifespan of the Spongy Moth
The Spongy Moth, scientifically known as Trabala vishnou, is a species of moth that belongs to the family Lasiocampidae. It is mostly found in the tropical regions of Asia and Africa and is also commonly known as the Indian Lappet Moth or Vishnu Moth.One of the most distinctive features of the Spongy Moth is its size. With a wingspan of up to 10 cm (4 inches), it is one of the largest species of moth in the world. The vibrant colors and intricate patterns on its wings make it a sight to behold. The vibrant colors and intricate patterns on its wings make it a sight to behold. The bright orange and black patterns are believed to serve as a warning to potential predators of its toxic nature.
The Spongy Moth's lifespan is relatively short, lasting only 2 to 4 weeks on average Smooth Hammerhead Shark. This short lifespan is due to its reproductive behavior, which we'll explore in the next section.
Reproductive Behavior and Attracting Mates with Pheromones
Like most insects, the Spongy Moth reproduces sexually. This means that the moth has two distinct genders, male and female, and the females lay eggs that hatch into larvae.But what makes the Spongy Moth's reproductive behavior even more fascinating is the way males attract females. Unlike other moths that use pheromones as a means of communication, the male Spongy Moth produces a special type of pheromone that not only attracts females but also confuses and repels other competing males.
The intricate balance of pheromones and the moth's ability to produce them in just the right amounts is a miraculous feat of evolution. The male Spongy Moth puts great effort into attracting a mate, ensuring the best chances for their offspring's survival.
The Silence of the Spongy Moth
One unique characteristic of the Spongy Moth is that it does not make any sounds or calls. Unlike other moths and insects that use sounds to communicate, the Spongy Moth relies solely on its pheromones and visual cues for reproduction and survival.This silence may seem like a disadvantage for the Spongy Moth, but it also serves as a form of defense against predators. By not making any noise, the moth can avoid attracting the attention of its predators, increasing its chances of survival.
Non-Migratory and Solitary Creatures
While some species of moths and butterflies migrate over long distances, the Spongy Moth is a non-migratory species. This means that it stays in its habitat throughout its entire lifespan.The Spongy Moth is also a solitary creature. It does not form social groups or colonies like some other species of moths. Instead, it prefers to live and thrive on its own, relying on its own instincts and skills for survival.
A Nocturnal Beauty
The Spongy Moth is a nocturnal insect, meaning that it is most active at night. It spends its days resting and feeding, then comes to life as the sun sets. This behavior can be attributed to its large and bright wings, which are highly noticeable to predators during the day. By being active at night, the Spongy Moth can effectively avoid potential threats and survive in its natural habitat.Threats to the Spongy Moth's Survival
Like many other species of insects, the Spongy Moth faces threats to its survival. Habitat loss and climate change are two of the most significant threats to the Spongy Moth's existence. As human populations continue to expand and encroach upon natural habitats, the population of the moth's preferred host plant, the mopane tree, is declining.Mopane trees are also sensitive to changes in temperature and precipitation, making them vulnerable to the effects of climate change. As these trees decline, so does the population of the Spongy Moth, leading to a decline in its overall numbers.
The Importance of the Spongy Moth as a Pollinator
Despite its short lifespan, the Spongy Moth plays a vital role in the ecosystem as a pollinator. As it moves from flower to flower in search of nectar, it collects and transfers pollen, aiding in the pollination process.Without the Spongy Moth, many plants would not be able to reproduce, resulting in a significant impact on the ecosystem. Pollinators like the Spongy Moth are essential for maintaining a healthy and diverse environment.
The Human Use of the Spongy Moth
Interestingly, the Spongy Moth is not only found in nature but also plays a role in human use. In many African countries, the moth's larvae, commonly known as the mopane worm, is considered a delicacy and is a significant source of food for many communities.The mopane worm is highly nutritious and is rich in proteins, making it an essential part of the local diet. It is prepared in a variety of ways, including frying, drying, and boiling, and is a popular snack and ingredient in traditional dishes.
The Mysterious Caterpillar Behind the Spongy Moth
While the adult Spongy Moth is a sight to behold, its larval form, the caterpillar, also has unique features worth mentioning. The caterpillar of the Spongy Moth is commonly known as the mopane worm and is often seen as a pest by farmers.However, this caterpillar is anything but ordinary. It is large and fluffy, with vibrant colors that serve as a warning to potential predators of its toxicity. The caterpillar feeds on the leaves of the mopane tree and is a vital part of its ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Spongy Moth is a fascinating and mysterious insect that deserves more attention and recognition in the world of entomology. Its size, reproductive behavior, and unique features make it a remarkable species that plays an essential role in the ecosystem.However, the threats of habitat loss and climate change are putting the Spongy Moth's survival at risk. As responsible inhabitants of this planet, it is our responsibility to ensure the conservation of this species and its natural habitat.
So, the next time you see a Spongy Moth in the wild, take a moment to appreciate its beauty and importance in the ecosystem. And for those brave enough, don't be afraid to try the mopane worm, a delicacy that has been a part of African cuisine for centuries.
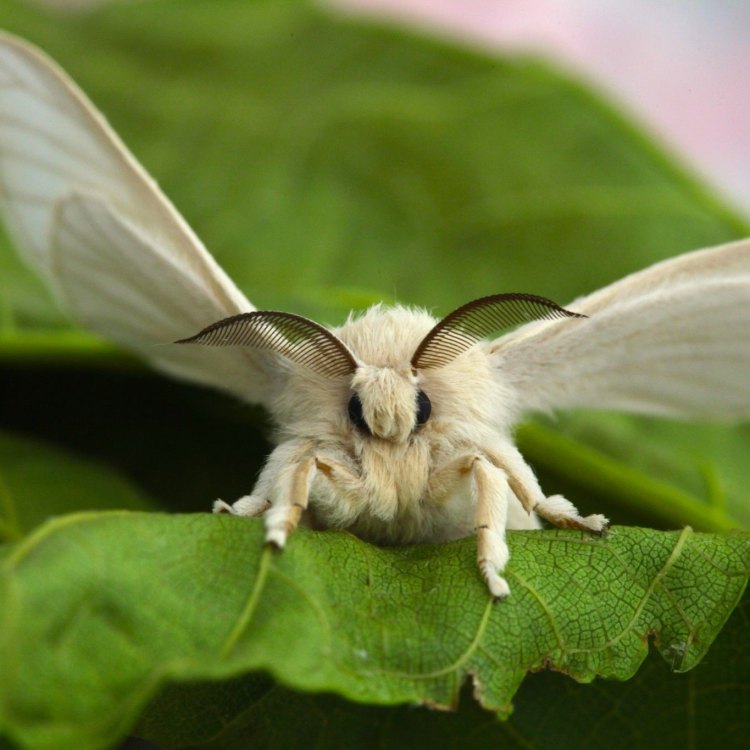

The Secret Life of the Spongy Moth: Exploring the Enigmatic World of Gonimbrasia belina
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.