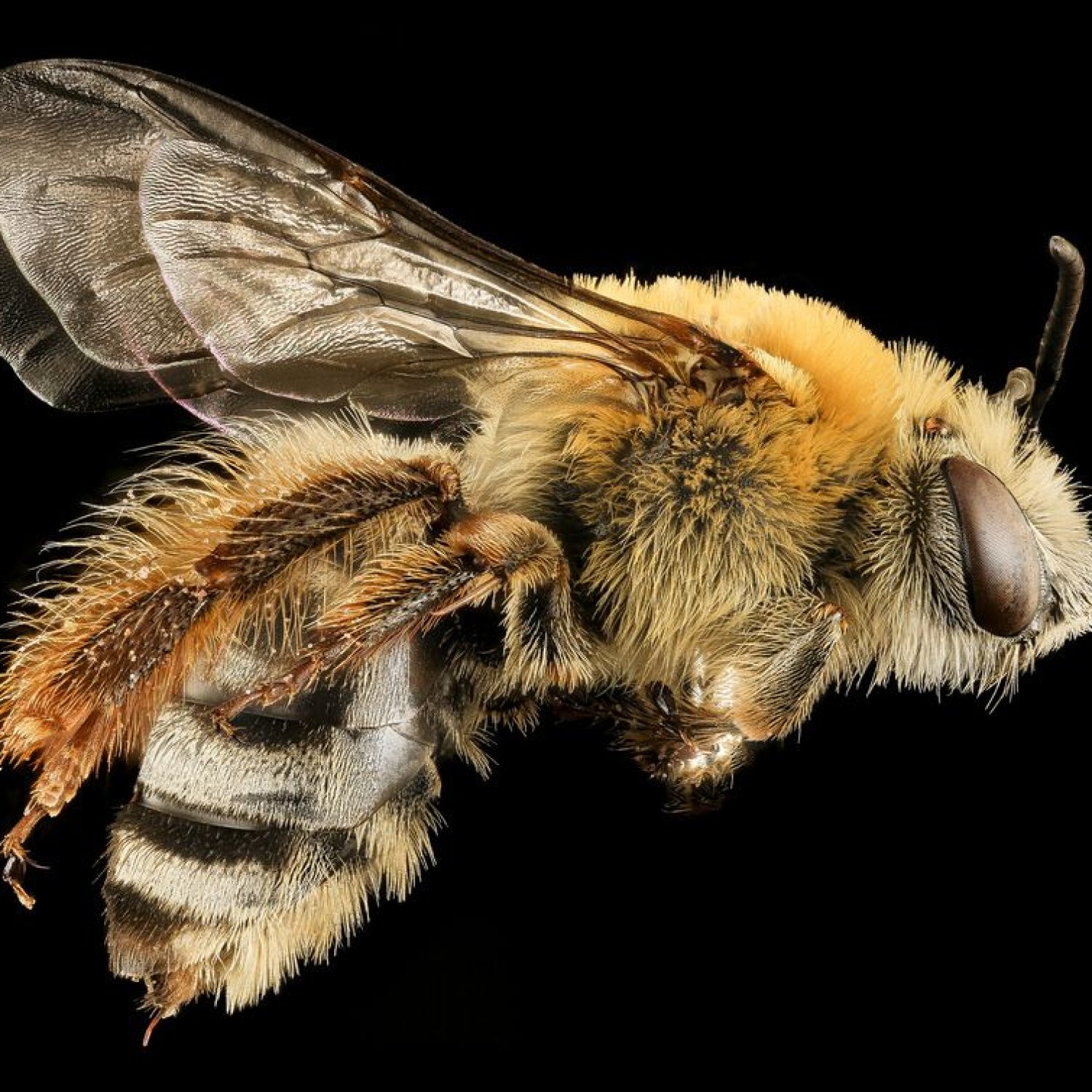
Squash Bee
7-12 mm
If you live in eastern or central North America, you may have spotted a Squash Bee buzzing around your garden. These small and compact bees, measuring 7-12 mm in length, are important pollinators for crops like squash, pumpkins, and gourds. Belonging to the Apidae family, they are solitary bees that live in underground nests and are crucial for a robust harvest. Keep an eye out for these hard-working bees during the warmer months! #SquashBee #Pollinators #GardenFriends
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Squash Bee
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Prairies, meadows, farmland
The Amazing Squash Bee: Natural Pollinators of North America
Nature is full of incredible creatures, each with their unique characteristics and abilities. Among them is the small but mighty squash bee, also known as Peponapis pruinosa. This little insect is not your average bee – it has some incredible features that make it stand out from other members of the animal kingdom.Let's delve into the world of this amazing pollinator and discover what makes it so special Squash Bee.
The Kingdom of Squash Bees
As with all living organisms, the squash bee belongs to a particular kingdom – in this case, the kingdom of Animalia. This kingdom includes all animals, from the tiniest insects to the largest mammals. It is a vast and diverse category, with over 1.5 million known species.The Phylum of Arthropods
Within the Animalia kingdom, the squash bee falls into the phylum of Arthropoda. This phylum is home to a whopping 85% of all animal species, including insects, spiders, crustaceans, and more. Arthropoda comes from the Greek words "arthro" meaning joint and "poda" meaning foot, which accurately describes the segmented limbs that these creatures have.The Insect Class
Next in line in the classification of the squash bee is the class Insecta. This class is incredibly diverse, making up almost three-quarters of all known animal species Sumatran Tiger. Insects have three body segments, six jointed legs, and often have wings. They play a vital role in various ecosystems, including pollination, decomposition, and pest control.The Order of Hymenoptera
The squash bee belongs to the order of Hymenoptera, which includes insects such as bees, wasps, and ants. This order is known for its remarkable social structure, with many species living and working together in organized colonies.The Fascinating Family of Apidae
The Hymenoptera order is further divided into families, and the squash bee belongs to the Apidae family. Bees of this family are known for being excellent pollinators, and many species are also critical for the production of honey. The squash bee is a solitary bee, meaning they do not live in colonies like other bees. However, they still play a crucial role in pollination, making them essential to the ecosystem of their habitat.
Around the World: the Amazing Habitat of Squash Bees
Squash bees were first discovered in the 1800s on the east coast of the United States. Today, they can be found in prairies, meadows, and farmland throughout eastern and central North America. These bees prefer sunny, open areas with well-drained soil, making them common in cultivated fields and gardens.The Herbivorous Feeding Method
One of the most critical roles of the squash bee is pollination. As herbivores, they play an essential part in the life cycle of many plant species. These bees are particularly drawn to squash and pumpkin plants, which is how they earned their common name. Without pollinators like the squash bee, these plants would struggle to reproduce and produce the fruits we love to eat.Size and Color: the Striking Body of Squash Bees
The squash bee may be small, but they are incredibly striking in their appearance. They have a compact body shape, measuring between 7-12 mm in length. Their black coloration is a stark contrast to the vibrant and colorful flowers they pollinate, making them easy to spot in a sea of petals.The Secret to Efficient Pollination
So, what makes the squash bee such efficient pollinators? Unlike other bee species, squash bees are early risers, often emerging before the sun rises. This habit allows them to take advantage of the cooler morning temperatures when plants' pollen is most abundant. They also have specialized structures on their legs that enable them to collect and transport pollen efficiently. All of these factors contribute to their essential role in pollinating crops like squash and pumpkin, benefiting both farmers and the environment.Threats and Conservation Efforts
Like many other bee species, squash bees face threats such as habitat loss and pesticide use. These bees are excellent at adapting to new environments, but they still rely on specific plants for food and shelter. With continued urbanization and agricultural expansion, their habitats are becoming increasingly fragmented, making it challenging for them to survive.Fortunately, conservation efforts are underway to protect these vital pollinators. By planting pollinator-friendly gardens and reducing the use of harmful pesticides, we can help squash bees thrive and continue to play their essential role in the ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the squash bee may be small, but it is a mighty and vital creature in the animal kingdom. From its classification in the phylum of Arthropoda to its unique role in pollination, everything about this insect is fascinating. As we continue to learn more about this incredible species, it is crucial to protect their habitats and support conservation efforts. After all, the tiny squash bee plays a significant role in maintaining the beauty and balance of the natural world.
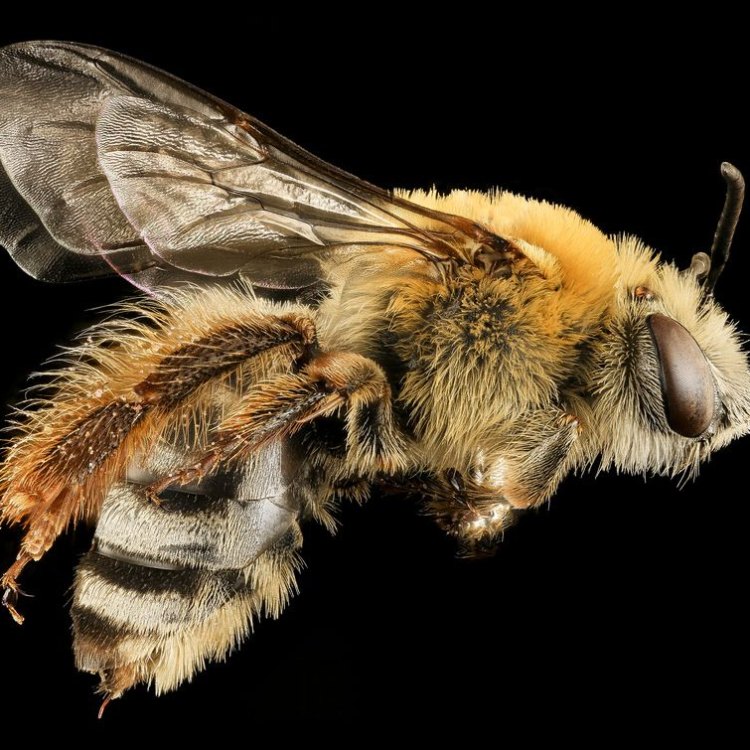

Squash Bee
Animal Details Squash Bee - Scientific Name: Peponapis pruinosa
- Category: Animals S
- Scientific Name: Peponapis pruinosa
- Common Name: Squash Bee
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hymenoptera
- Family: Apidae
- Habitat: Prairies, meadows, farmland
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Eastern and central North America
- Animal Coloration: Black
- Body Shape: Small and compact
- Length: 7-12 mm
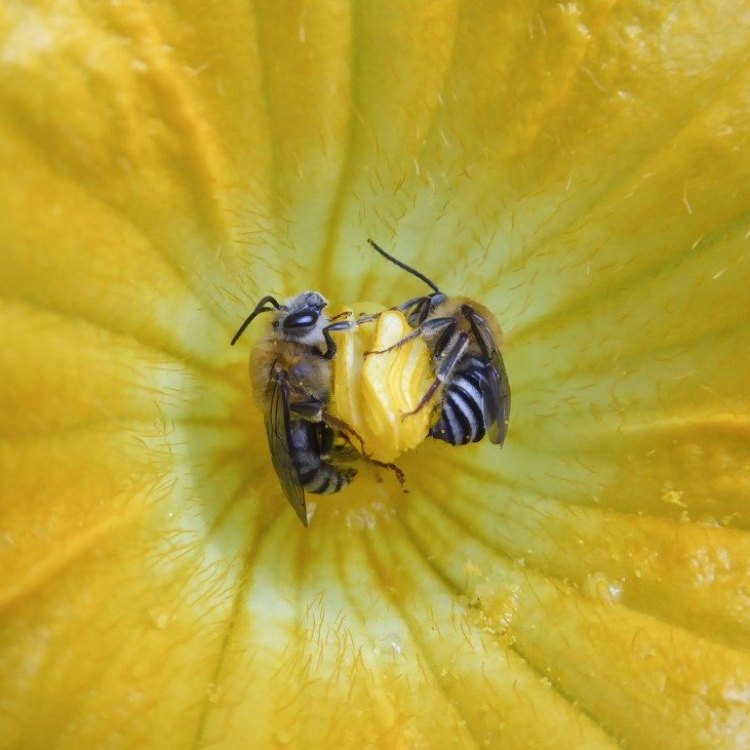

Squash Bee
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 1 year
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Solitary
- Sound or Call: No specific sound or call
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Active during the day, especially in the morning
- Threats: Habitat loss, pesticide exposure
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important pollinators for squash and pumpkin plants
- Human Use: Used for crop pollination
- Distinctive Features: Covered in dense hairs
- Interesting Facts: Squash bees are specialists, pollinating only plants in the Cucurbita genus
- Predator: Birds, spiders, mantises
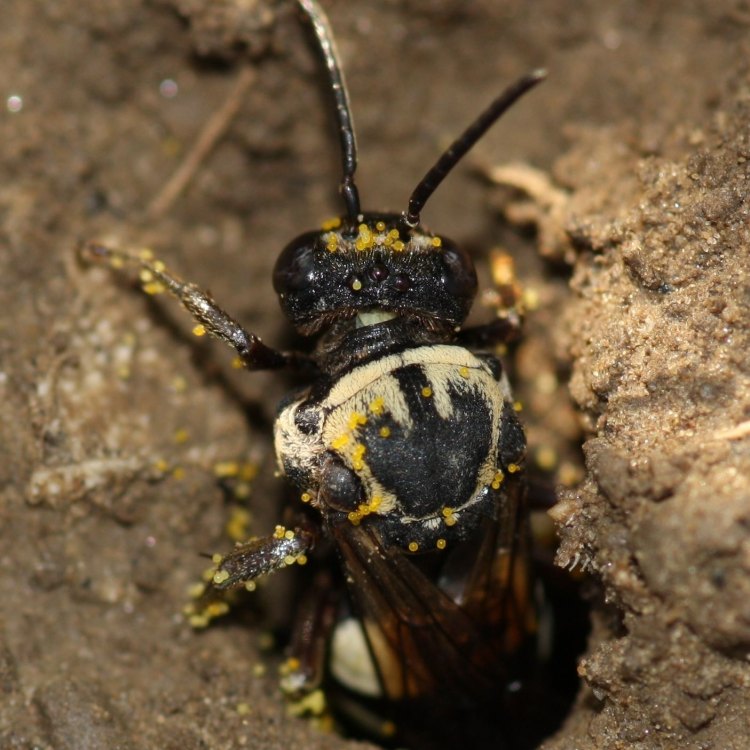

Peponapis pruinosa
The Amazing Life of the Squash Bee: A Unique Pollinator
When we think of bees, we often envision the familiar honeybee buzzing around flowers in search of nectar. However, there is a lesser-known bee species that is just as important – the squash bee. This tiny, solitary bee plays a crucial role in the ecosystem, particularly for the pollination of squash and pumpkin plants. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the squash bee and uncover the unique features that make it such a vital pollinator PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Size and Reproduction
The squash bee, also known by its scientific name Peponapis pruinosa, is a small bee, with adult females measuring about half an inch in length. They are typically smaller than honeybees and bumblebees, making them easy to overlook. Despite their size, squash bees are strong and hardy creatures, capable of flying long distances to forage for food.
Like most bees, the squash bee has a relatively short lifespan, averaging only about a year. However, in this short time, they play a crucial role in plant pollination, making them an essential part of the ecosystem.
Reproductive Behavior and Social Groups
Unlike honeybees, which live in large colonies, squash bees are solitary creatures, with each female building and tending to her own nest. They are known to be sexually reproductive, meaning that they require a male and female bee to reproduce. The males, much like other bee species, do not have a stinger and are mainly responsible for mating with the females.
Squash bees are not known for making specific sounds or calls, unlike other bees that use buzzing and dancing to communicate and navigate Southern House Spider. Instead, they rely on their keen sense of smell and sight to locate flowers and communicate with other bees.
Migratory Patterns and Behavior
Squash bees are non-migratory creatures, meaning that they do not travel long distances in search of food or shelter. Instead, they tend to remain in the same area for their entire lifespan. This behavior is essential as it helps ensure that they pollinate plants in their immediate environment, making them vital contributors to the local ecosystem.
In terms of behavior, squash bees are active during the day, with their highest activity levels being in the morning. They can be seen foraging for food, collecting pollen and nectar from flowers, and building their nests. Their solitary nature means that they do not interact with other bees in the same way that honeybees do, making them quite peaceful and non-aggressive.
Threats and Conservation Status
Like many other bee species, the squash bee faces various threats, primarily due to human activities. Habitat loss, caused by urbanization and agricultural development, is one of the biggest threats that these bees face. As their natural habitat disappears, it becomes harder for them to find adequate shelter and sources of food.
Additionally, the widespread use of pesticides in agriculture has had a devastating impact on squash bees and other pollinators. These chemicals are known to harm not only the bees themselves but also the plants they pollinate, leading to a decline in their numbers.
Despite these threats, the conservation status of the squash bee has yet to be evaluated. This is mainly due to the fact that these bees are not as well-studied or recognized as other bee species. However, it is clear that they play a vital role in the ecosystem and should not be overlooked or taken for granted.
Impact on Ecosystem and Human Use
As mentioned earlier, squash bees are specialists, only pollinating plants in the Cucurbita genus, which includes squash, pumpkins, and gourds. This unique trait makes them essential for the reproduction of these plants, which are valuable food sources for both humans and animals. Without the squash bee, these plants would struggle to reproduce, leading to a significant impact on the ecosystem.
Moreover, the importance of squash bees in crop pollination is not limited to the wild. Farmers and gardeners also rely on these busy bees to help pollinate their squash and pumpkin crops, ensuring a bountiful harvest. This reliance on squash bees shows just how crucial they are for human use and highlights the need for their conservation.
Distinctive Features and Predators
One of the most distinctive features of the squash bee is its dense covering of hairs. Unlike other bees that have visible stripes and patterns, squash bees are almost entirely covered in dense, yellow-black hairs. This hairiness is thought to help protect the bee from the hot sun as they search for food.
Unfortunately, despite their hairiness, squash bees are not immune to natural predators. Birds, spiders, and praying mantises are some of the common predators of these bees. However, their solitary nature also serves as a form of protection, as it reduces the chances of attracting predators with large colonies.
Interesting Facts
Apart from their unique reproductive behavior and solitary nature, squash bees have various other interesting traits that make them stand out. One of the most intriguing is their specialized diet. As mentioned earlier, they primarily feed on pollen and nectar from plants in the Cucurbita genus. This makes them different from other bee species that tend to feed on a diverse range of flowers.
Furthermore, squash bees are also known as "squash bees" because of their close relationship with these plants. Scientists have discovered that squash bees and squash plants have co-evolved, meaning that they have adapted and evolved together. This close relationship is what makes squash bees specialists in pollinating these specific plants.
In Conclusion
The squash bee may be small and often overlooked, but it plays a critical role in the ecosystem. Their specialized diet and solitary behavior make them unique and essential for the pollination of squash and pumpkin plants. As their habitat and populations continue to face threats, it is vital that we recognize the value of these busy bees and take steps to protect them. By doing so, we can ensure a thriving ecosystem and a bountiful harvest of delicious squash and pumpkins for years to come.
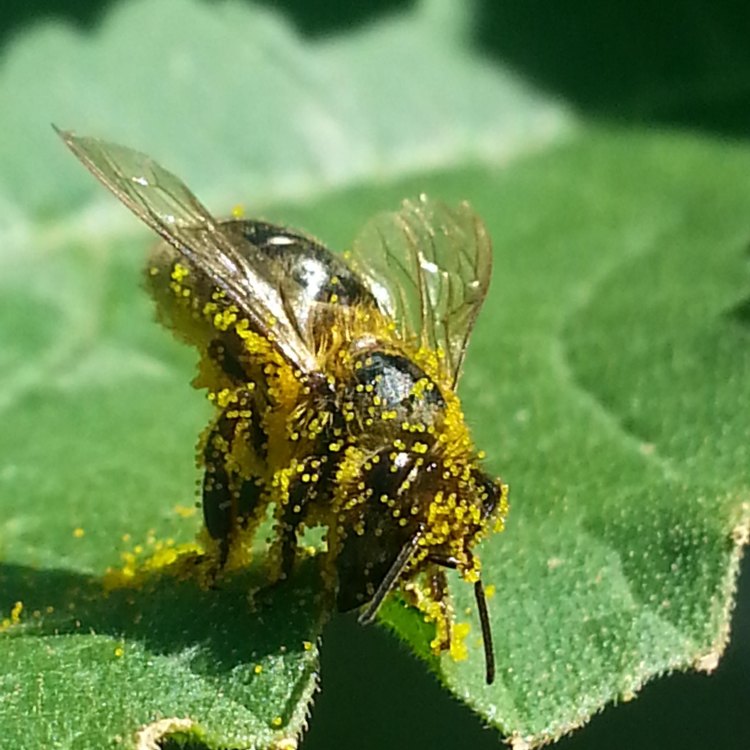

The Amazing Squash Bee: Natural Pollinators of North America
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.