Triggerfish
9 to 30 inches
Triggerfish are fascinating creatures found in the ocean. They can grow up to 30 inches in length and have an oval and compressed body shape. They belong to the Balistidae family and are known for their unique ability to 'trigger' their dorsal fin as a defense mechanism. Keep an eye out for these colorful and curious fish on your next ocean adventure! #Triggerfish #OceanLife #Balistidae
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Triggerfish
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Coral reefs, rocky reefs, kelp forests
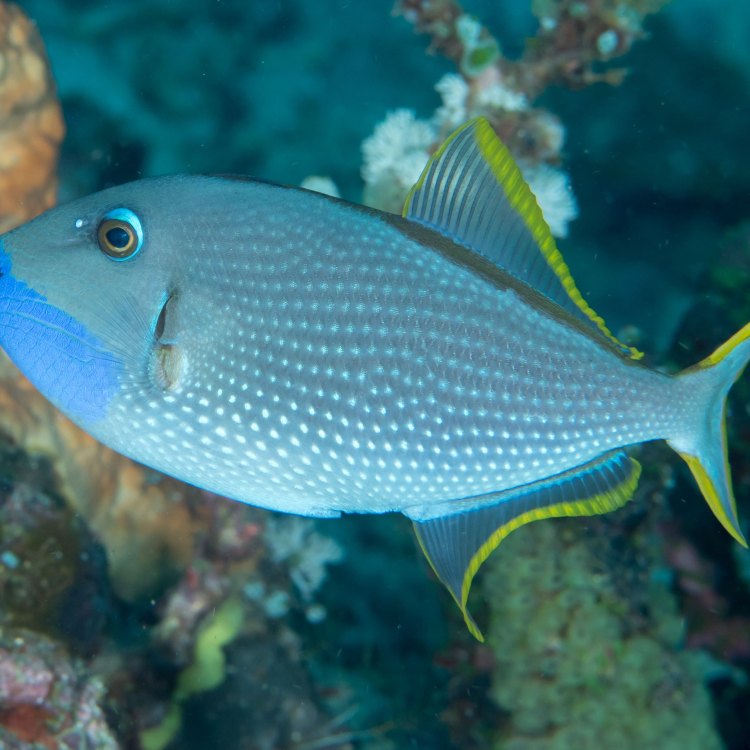
The Fascinating World of Triggerfish: A Colorful Wonder of the Ocean
As we explore the depths of the ocean, one animal that truly stands out with its vibrant colors and bold patterns is the triggerfish. These tropical and subtropical marine creatures have captured the attention of divers and ocean enthusiasts for centuries with their unique appearance and behavior. In this article, we will delve into the world of triggerfish, learning about their scientific classification, habitat, feeding habits, geographical distribution, and more.Scientific Classification of Triggerfish
Let us begin by understanding the scientific classification of the triggerfish Triggerfish. These intriguing creatures belong to the family Balistidae, which is a part of the kingdom Animalia. They are classified under the phylum Chordata, which includes all vertebrate animals. The class Actinopterygii, which means "ray-finned fish," includes triggerfish, along with many other familiar fish species. Triggerfish fall under the order Tetraodontiformes, which also includes pufferfish, filefish, and boxfish. Overall, the scientific name for triggerfish is Balistidae.
Habitat and Feeding Habits of Triggerfish
Triggerfish are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide, and they can be found in various habitats such as coral reefs, rocky reefs, and kelp forests. These intriguing fish are omnivorous, meaning they consume both plant and animal matter as part of their diet. Their feeding habits vary depending on the species and their location. Some triggerfish like to feed on small invertebrates hiding in the sand, while others prefer to feed on algae and smaller fish Texas Coral Snake. Their unique teeth structure, with sharp front teeth for crushing shells and flat back teeth for grinding, allows them to handle a diverse range of food.
Their Stunning Geographical Distribution
One of the most fascinating aspects of triggerfish is their geographical distribution. They can be found in various countries across the world, including the Philippines, Indonesia, Tanzania, Maldives, Australia, and more. One species that stands out is the Picasso triggerfish (Rhinecanthus aculeatus), found in the Indo-Pacific Ocean, from the Red Sea and the coast of Africa to the Hawaiian Islands. Another interesting species is the clown triggerfish (Balistoides conspicillum), found in tropical regions of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Their Habitat in the Ocean
As mentioned earlier, triggerfish are usually found in coral reefs, rocky reefs, and kelp forests. These habitats provide them with ample food sources and shelter from predators. Triggerfish are also known to be territorial creatures, and they defend their chosen areas with gusto. They often use their sharp teeth to fend off any potential threats to their territory. As they move through the water, their unique body shape helps them navigate through coral crevices and rocky areas with ease.
Their Vibrant Colors and Body Shape
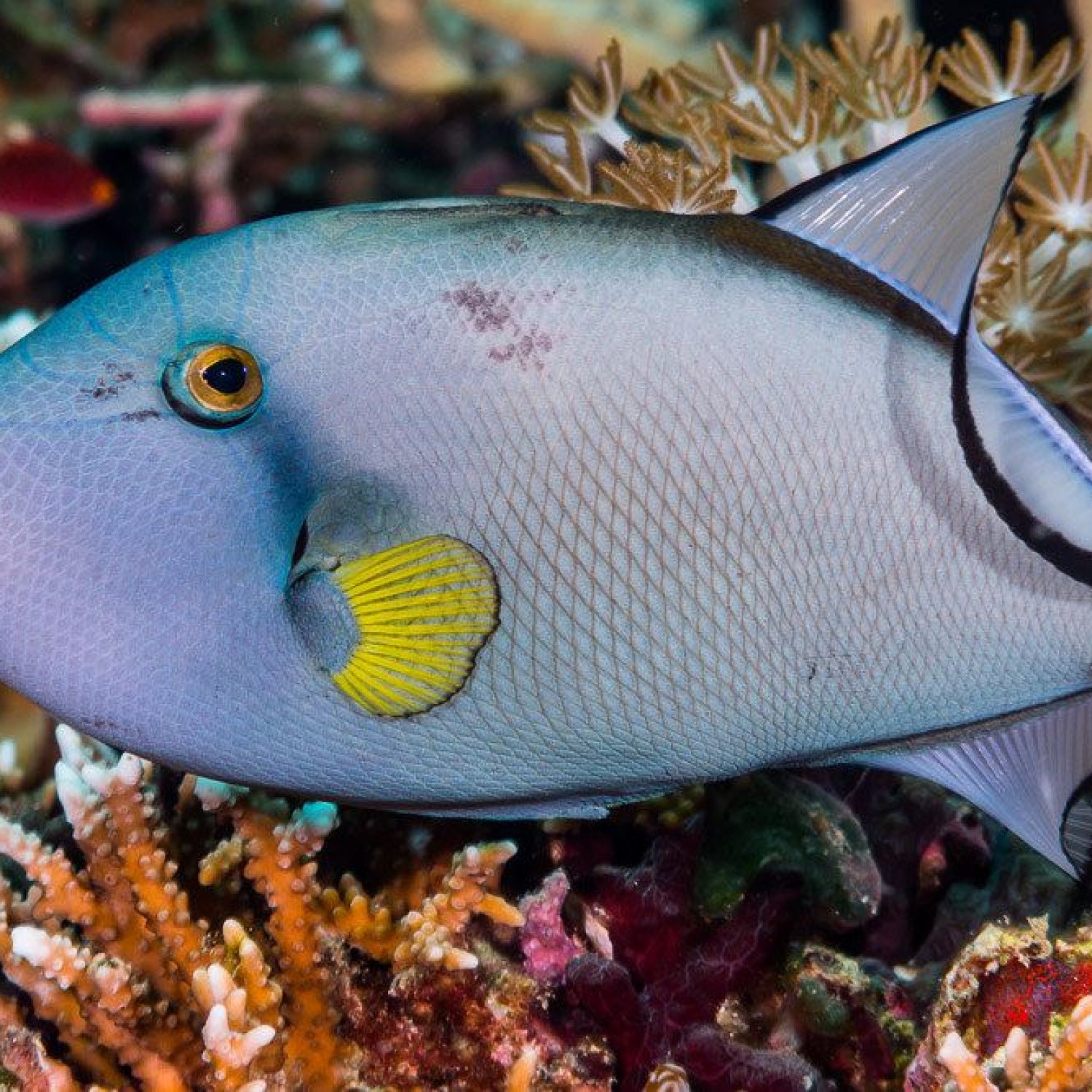
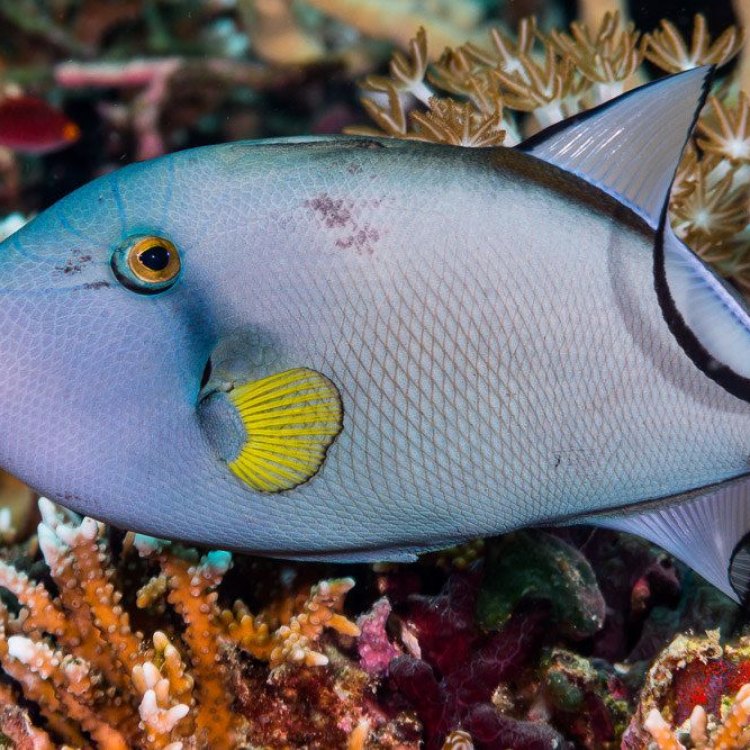
One look at a triggerfish, and it's easy to understand why they have captivated the hearts of ocean enthusiasts. These creatures are famous for their vibrant colors, ranging from blues, greens, reds, yellows, and more. They also have bold patterns on their bodies, making them stand out even more in the ocean. But their striking appearance is not just for show. These colors serve as a form of camouflage, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings and avoid potential predators.
In terms of their body shape, triggerfish have an oval and laterally compressed body, meaning that it is flattened from side to side. This body shape helps them navigate through tight spaces and avoid being caught in the many crevices and holes present in their habitat.
Interesting Facts about Triggerfish
- Triggerfish have a unique way of sleeping. They create a sleeping burrow on the ocean floor, where they rest on their side and use their dorsal spine to lock themselves in.
- These fish also have a distinct way of swimming, using their dorsal and anal fins in a way that resembles bird flapping its wings.
- The triggerfish's dorsal spine is sharp and can be locked in place, making it difficult for predators to grab onto them.
- Female triggerfish can lay up to 150 eggs at a time, and the male is responsible for guarding the eggs until they hatch.
- Triggerfish are known to form monogamous pairs during their mating season, which can last up to one month.
In Conclusion
Triggerfish may be a small species in the vast ocean, but they have a unique and captivating presence that cannot be ignored. From their vibrant colors to their territorial nature, these fish have many interesting features that make them stand out in the ocean. With their diverse geographical distribution, it is no wonder that these intriguing creatures have captured the hearts of ocean enthusiasts around the world. The next time you dive into the ocean or snorkel on a coral reef, keep an eye out for triggerfish. Who knows what fascinating behavior you may witness from these colorful wonders of the ocean.

Triggerfish
Animal Details Triggerfish - Scientific Name: Balistidae
- Category: Animals T
- Scientific Name: Balistidae
- Common Name: Triggerfish
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Tetraodontiformes
- Family: Balistidae
- Habitat: Coral reefs, rocky reefs, kelp forests
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide
- Country of Origin: Various countries
- Location: Ocean
- Animal Coloration: Vibrant colors, often with bold patterns
- Body Shape: Oval and laterally compressed
- Length: 9 to 30 inches

Triggerfish
- Adult Size: Varies depending on species
- Average Lifespan: 10 to 15 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Egg-laying
- Sound or Call: Triggerfish do not produce sounds or calls
- Migration Pattern: Some species may undertake seasonal migrations
- Social Groups: Solitary or small groups
- Behavior: Aggressive and territorial
- Threats: Habitat degradation, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Varies depending on species (some are of least concern, while others are vulnerable or near threatened)
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important role in controlling populations of invertebrates and algae on coral reefs
- Human Use: Commercial and recreational fishing, aquarium trade
- Distinctive Features: Powerful jaw and teeth, trigger-like dorsal fin
- Interesting Facts: 1. Some species of triggerfish are known to construct nests or burrows in the sand for breeding. 2. Triggerfish are highly adapted to feeding on hard-shelled prey such as crabs and sea urchins, using their strong jaws. 3. The dorsal fin of the triggerfish can be locked into place by a spine, giving it its name.
- Predator: Sharks, large predatory fish

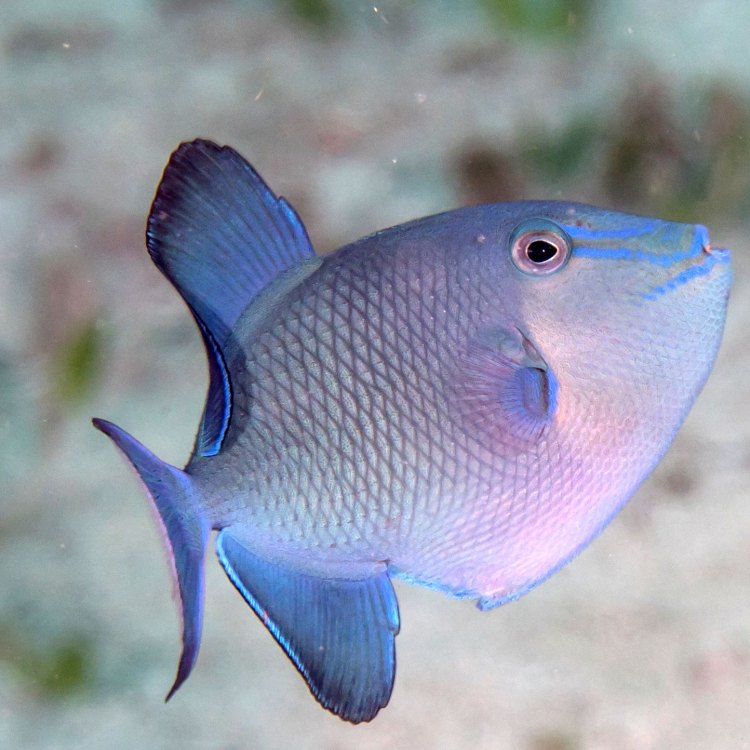
Balistidae
The Fascinating World of Triggerfish: From Aggressive Behavior to Important Ecosystem Role
The ocean is home to a diverse array of creatures, each with their own unique set of characteristics and behaviors. Among them is the fascinating triggerfish, known for its distinctive features and intriguing behavior. In this article, we will explore the world of triggerfish, from their aggressive nature to their important role in the ecosystem.Triggerfish, scientifically known as the family Balistidae, are a group of reef-dwelling fish found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They are known for their powerful jaws and teeth, which are designed for crushing hard-shelled prey such as crabs and sea urchins. They also have a trigger-like dorsal fin, which can be locked into place by a spine, giving them their name.
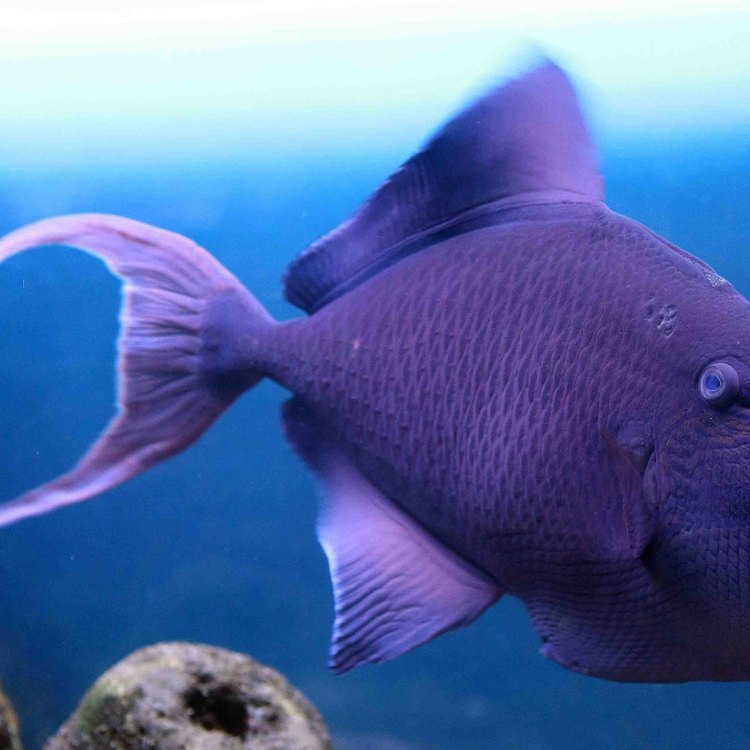
Triggerfish come in a variety of sizes and colors, with their adult size depending on the species. They range from small, less than a foot in length, to larger species that can reach up to 3.3 feet. Some species, like the grey triggerfish, have a stunning array of colors and patterns, making them a popular choice for aquariums.
On average, triggerfish can live up to 10 to 15 years in the wild. However, their lifespan can vary depending on their environment and species. Some species of triggerfish, like the humuhumunukunukuapua'a, have been observed living up to 20 years in captivity Thylacosmilus.
When it comes to reproduction, triggerfish are sexual, with males and females coming together to mate. The reproductive behavior of triggerfish involves the female laying eggs, which are then fertilized by the males. The eggs are carefully guarded and protected by the male until they hatch, with some species of triggerfish constructing nests or burrows in the sand for breeding.
One of the most distinctive features of triggerfish is their aggressive and territorial behavior. They are solitary or found in small groups, with each individual fiercely defending their territory from other fish. Triggerfish are known for their aggression towards other fish, which can be quite intimidating to witness. They are also fiercely protective of their nests and will not hesitate to attack any perceived threats, including humans.
Although they may seem ruthless, triggerfish play an important role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystems they inhabit. They control the population of invertebrates and algae on coral reefs, preventing them from overgrowing and damaging the reef. Their powerful jaws and teeth are perfectly adapted to feeding on hard-shelled prey, making them vital for maintaining the health of the reef.
Unfortunately, like many other species, triggerfish are facing threats to their survival. Habitat degradation, caused by human activities such as pollution and climate change, is a major threat to their population. Overfishing is also a concern, with triggerfish being targeted for their meat and as part of the aquarium trade. As a result, the conservation status of triggerfish varies depending on the species, with some being of least concern while others are vulnerable or near threatened.
Despite their aggressive behavior, triggerfish are also preyed upon by larger predators, such as sharks and other large predatory fish. They have developed some clever defense mechanisms, including their trigger-like dorsal fin, to escape from predators. Some species are also capable of changing their skin color to blend in with their surroundings, making them less visible to their predators.
Humans have also long been fascinated by triggerfish, using them for both commercial and recreational fishing. Their strong and flavorful meat makes them a popular choice in many countries, and their unique appearance makes them a sought-after catch for recreational fishing. They are also commonly kept as pets in aquariums, especially smaller species that are more suitable for home aquariums.
In addition to their importance in the ecosystem and human use, triggerfish have some interesting facts that make them even more fascinating. For instance, some species of triggerfish, like the titan triggerfish, are known to produce sounds by grinding their teeth, but for the most part, they do not produce sounds or calls. They also have a tendency to hide in crevices when they sleep, making them a difficult catch for their predators.
In conclusion, triggerfish may seem like just another fish in the sea, but they are truly a unique and fascinating species. From their aggressive and territorial behavior to their important role in the ecosystem, they are essential for the health of coral reefs. As we continue to strive for the conservation of our oceans, it is crucial to understand and appreciate the diversity of creatures like the triggerfish and the ecosystem they call home.

The Fascinating World of Triggerfish: A Colorful Wonder of the Ocean
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.