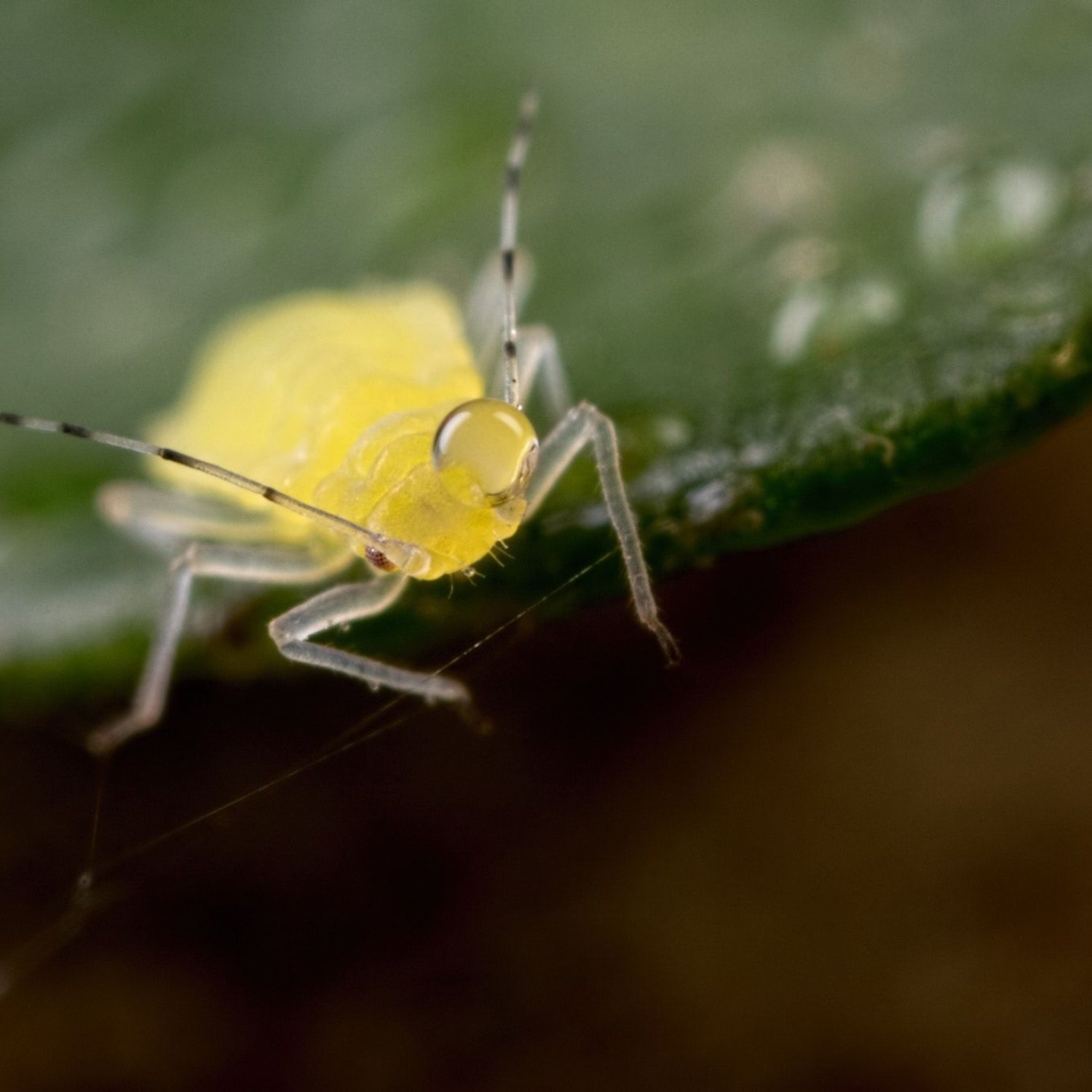
Yellow Aphids
1-4 mm
Yellow aphids are tiny insects that are commonly found in many regions around the world. These small, soft-bodied creatures belong to the family Aphididae and can measure anywhere between 1 to 4 mm in length. Despite their small size, they can cause serious damage to plants by sucking out their sap. Taking preventive measures such as regular gardening practices can help control and prevent infestations. Always be on the lookout for these pesky pests when tending to your garden! #YellowAphids #GardeningTips #PestControl
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Yellow Aphids
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Grasslands, gardens, crops
Get to Know the Mighty Yellow Aphids: Tiny Insects with a Big Impact
In the vast world of insects, there is a creature that may seem insignificant at first glance but actually plays a crucial role in our ecosystem. Meet the yellow aphids, scientifically known as Aphis fabae. These small, soft-bodied insects belong to the Hemiptera order, commonly known as the "true bugs," and are part of the Aphididae family.Despite their small size, yellow aphids have a significant impact on the environment and play a vital role in agriculture Yellow Aphids. Let's dive into the world of these mighty yellow insects and uncover their fascinating features and characteristics.
Habitat and Distribution
Yellow aphids are found worldwide, with a preference for temperate regions. They can be spotted in diverse habitats such as grasslands, gardens, and agricultural fields. However, they are not limited to these areas and can thrive in diverse environments.The exact country of origin of yellow aphids is unknown, but they have been observed in different locations worldwide, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. This widespread distribution has allowed them to adapt to different climates and environments, making them a resilient species.
Physical Characteristics
As the name suggests, yellow aphids have a distinct yellow coloration, which ranges from light yellow to bright lemon yellow. This unique color makes them stand out in green environments, making them easy to spot.Yellow aphids have a small, soft-bodied shape, measuring only 1-4 mm in length Yellowtail Snapper. Their oval-shaped body has a pair of long antennae and six legs, allowing them to move quickly on plants and crops.
Feeding and Reproduction
Yellow aphids are classified as sap-sucking insects, meaning they use their specialized mouthparts to pierce plant tissues and feed on the sap. This feeding method can cause significant damage to host plants and crops, making yellow aphids a notorious pest for farmers.In addition to feeding, yellow aphids also play a role in plant pollination. During their feeding, they may transfer pollen grains from one plant to another, aiding in pollination.
These insects reproduce rapidly, with a single female being capable of producing up to 20 offspring in just one day. This fast reproduction rate allows yellow aphids to quickly multiply and colonize plants, making it challenging to control their population.
The Impact of Yellow Aphids
Although yellow aphids are considered pests due to their feeding behavior, they also have a vital role in the ecosystem. These insects serve as a food source for many predators such as ladybugs, lacewings, and small birds. Their ability to transfer pollen also aids in plant growth and diversity.However, when their population becomes too high, yellow aphids can cause significant damage to crops and plants. The yellow stains they leave on leaves and their excessive sap-sucking can weaken plants, making them vulnerable to other diseases and pests.
The Relationship with Ants
One of the most unique features of yellow aphids is their relationship with ants. These insects have a symbiotic relationship with ants, where the ants provide protection and shelter for the aphids in exchange for honeydew, a sugary substance produced by aphids.Ants have been observed "farming" yellow aphids, moving them to different plants and protecting them from predators. In return, the ants collect the honeydew, which serves as a food source for the ants.
Controlling Yellow Aphids
Due to their rapid reproduction rate and resilience to various environments, controlling yellow aphids can be challenging. However, there are some methods that can help reduce their population and minimize their impact on crops.Introducing natural predators such as ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on aphids, can help keep their population in check. Using insecticidal soaps and oils can also be effective in controlling their numbers, as well as regularly pruning and keeping plants healthy.
In Conclusion
The yellow aphid may be small, but its impact on the environment is significant. These tiny insects play a vital role in pollination while also serving as a food source for many predators. However, when their population becomes too high, they can pose a threat to crops and plants.Through their unique coloration and symbiotic relationship with ants, yellow aphids have captured the fascination of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Their adaptability and resilience make them a critical species to monitor and study, as their population can fluctuate depending on the environment.
Despite being classified as pests, it is essential to understand the role that yellow aphids play in our ecosystem and the delicate balance required to maintain a healthy environment for all species. And the next time you spot a tiny yellow insect on a plant, take a closer look and appreciate the mighty yellow aphid.
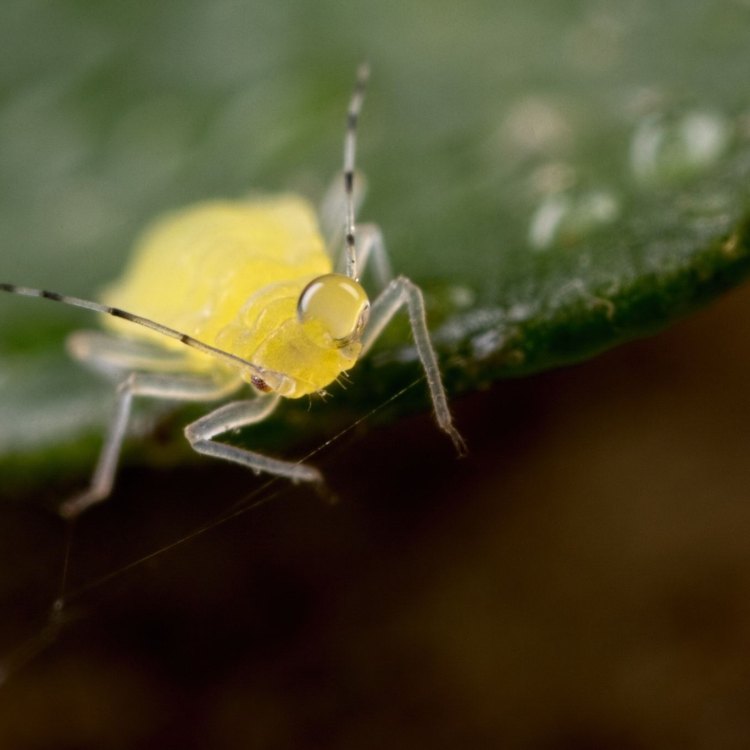

Yellow Aphids
Animal Details Yellow Aphids - Scientific Name: Aphis fabae
- Category: Animals Y
- Scientific Name: Aphis fabae
- Common Name: Yellow Aphids
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Family: Aphididae
- Habitat: Grasslands, gardens, crops
- Feeding Method: Sap-sucking
- Geographical Distribution: Worldwide
- Country of Origin: Unknown
- Location: Found in different regions around the world
- Animal Coloration: Yellow
- Body Shape: Small, soft-bodied
- Length: 1-4 mm
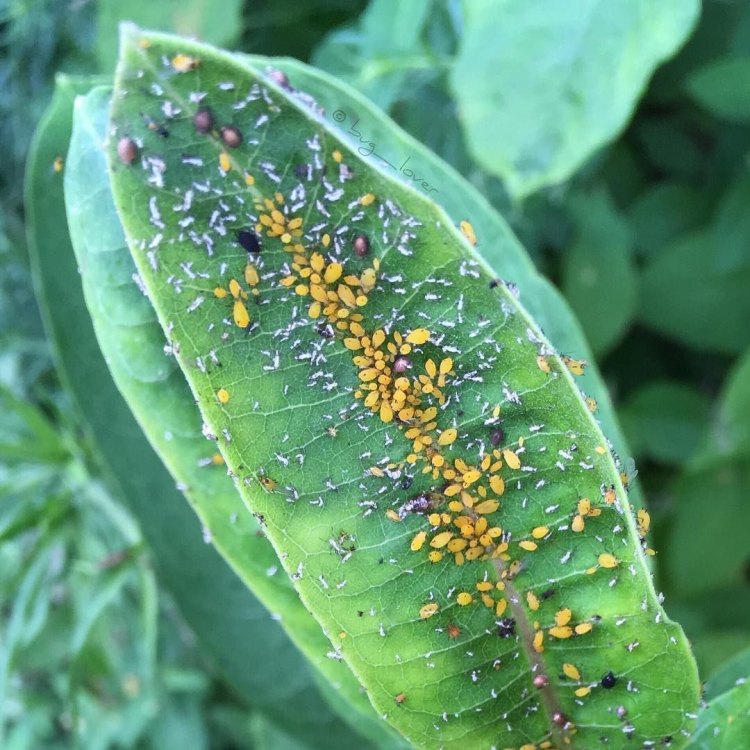

Yellow Aphids
- Adult Size: Small
- Average Lifespan: 1-2 weeks
- Reproduction: Asexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Reproduce rapidly in favorable conditions
- Sound or Call: No sound or call
- Migration Pattern: No migration pattern
- Social Groups: Large groups
- Behavior: Cluster together on plants
- Threats: Predation, adverse weather conditions, pesticides
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Can cause damage to crops
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Distinct yellow coloration
- Interesting Facts: Yellow aphids are a common pest in gardens and agricultural crops.
- Predator: Ladybugs, lacewings, parasitic wasps
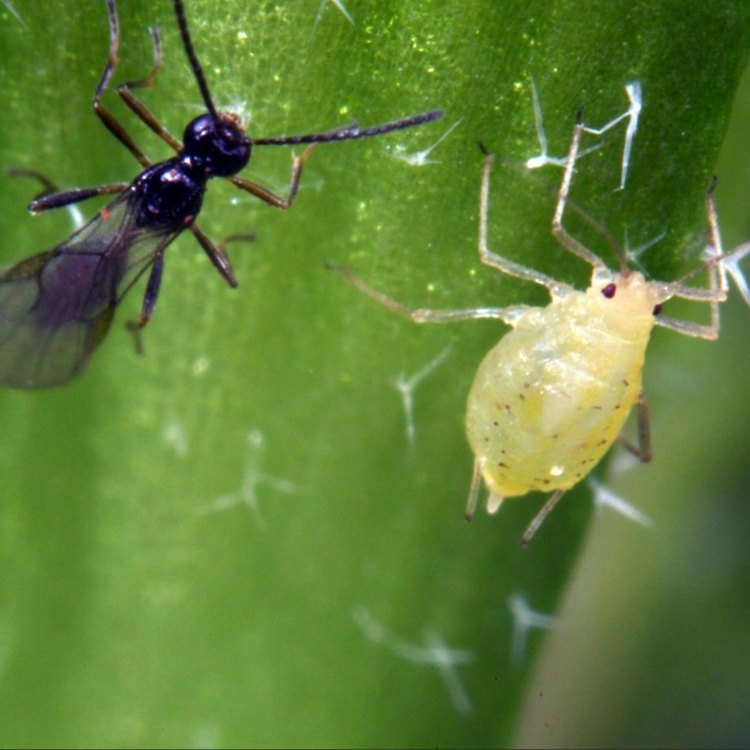

Aphis fabae
The Prolific Yellow Aphids: A Tiny Yet Mighty Pest
The world of insects can often be overlooked, as they are small and unassuming creatures, but their presence is vital for the balance of our ecosystem. However, among these tiny creatures, some have gained quite a notorious reputation for their ability to cause damage to crops and plants. One such insect is the yellow aphid, a tiny yet mighty pest that can wreak havoc on gardens and agricultural crops. In this article, we will delve into the world of yellow aphids, exploring their unique features, behavior, and impact on the ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com.The Yellow Aphid, scientifically known as Aphis fabae, is a species of small insects belonging to the Aphididae family. They are commonly found in temperate regions, especially in North America and Europe. These tiny insects may seem harmless, but their rapid reproduction and feeding habits make them a menace to plants and crops.
The Size and Lifecycle of Yellow Aphids
Yellow aphids are small in size, ranging from 1 to 3 millimeters in length. They have a unique teardrop-shaped body, with six long and delicate legs. These pests are usually a bright yellow color, with variations of green, red, or black in some species.Their average lifespan is only 1-2 weeks, making them one of the shortest-lived insects. However, this short lifespan does not hinder their ability to reproduce rapidly and cause widespread damage. Female aphids can produce up to 100 offspring during their lifespan, and they also have the ability to give birth asexually through a process called parthenogenesis Yellow Tanager. This means that they do not require a male to reproduce, making their population growth even more rapid.
Rapid Reproduction and Clustering Behavior
Speaking of reproduction, yellow aphids have a unique characteristic that sets them apart from other insects – their ability to reproduce rapidly in favorable conditions. When the conditions are right, female aphids can give birth to live offspring every day, making their population boom in a short period. This rapid reproduction is a survival strategy for the species, enabling them to quickly increase their numbers before their food supply runs out.Another interesting behavior of yellow aphids is their tendency to cluster together on plants. You may have seen them on your garden plants, gathered in large groups, especially on the underside of leaves. This behavior is advantageous for them as it provides protection from predators and also helps them to conserve moisture in dry conditions.
The Lack of Sound or Call, and Migration Pattern
Yellow aphids are not known for making any sounds or calls. They do not possess the necessary organs for producing sounds like some other insects, such as crickets and grasshoppers. This characteristic also contributes to their survival, as it prevents them from drawing attention to themselves and making themselves vulnerable to predators.Moreover, yellow aphids do not have a significant migration pattern. They tend to stay in one area as long as their food supply is readily available. This is why they are commonly found in gardens and crops, as they do not migrate to other locations in search of food.
Social Groups and Threats to Yellow Aphids
Despite their small size, yellow aphids are social insects and tend to live in large groups. This is especially evident when you see them clustered together on a plant. This social behavior is also crucial for their survival, as they can communicate with each other and increase their chances of finding food and protection from predators.Speaking of predators, yellow aphids face several threats in their natural habitats. They are a primary food source for many insects, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps. These predators are essential for maintaining balance in the ecosystem, as they keep the aphid population in check.
Furthermore, yellow aphids also face threats from adverse weather conditions and pesticides. Heavy rain or wind can displace large groups of aphids, leaving them vulnerable to predators. Pesticides, although used to control their population, can also harm other beneficial insects and disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem.
The Impact of Yellow Aphids on the Ecosystem
As mentioned earlier, yellow aphids may seem harmless due to their size, but in reality, they can cause significant damage to plants and crops. They feed on the sap of plants, which can weaken and stunt the growth of the plants. In large numbers, they can completely destroy a plant and even spread viruses that can potentially kill the plant.Their damage is not limited to individual plants; they can also cause harm to entire crops, leading to financial losses for farmers and a decrease in food production. This is why controlling their population is crucial, and farmers often use natural predators or organic methods to keep their numbers in check.
The Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts about Yellow Aphids
One of the most distinctive features of yellow aphids is, of course, their bright yellow coloration. This color serves as a warning to potential predators that they are bad-tasting and can release a sticky, bitter substance when threatened. This substance can also serve as protection as it can trap predators and deter them from attacking.Furthermore, yellow aphids have a unique reproductive ability, as mentioned earlier, but they also have another interesting fact - they can form wings when the conditions become unfavorable. The presence of wings allows them to migrate and find a new location with better food sources.
The Lack of Human Use and Conservation Status
Unfortunately, yellow aphids have no known human uses. Their role in the ecosystem is primarily to serve as food for other insects, and their rapid reproduction and destructive behavior make them a nuisance for humans. Due to this, their conservation status has not been evaluated. However, it is essential to note that they are essential for maintaining the balance in the ecosystem and controlling their population should be done in an eco-friendly manner.The Natural Predator of Yellow Aphids
As mentioned earlier, yellow aphids have several natural predators that keep their population in check. One of the most effective and commonly used predators is the ladybug. These colorful and harmless-looking insects are, in fact, voracious predators of aphids. A single ladybug can consume up to 50 aphids in a day, making them an efficient and eco-friendly natural pesticide.Lacewings and parasitic wasps are also common predators of aphids. They lay their eggs inside the aphids, and when the eggs hatch, the larvae feed on the aphids from the inside, eventually killing them. This method of controlling aphids is effective and has minimal impact on other insects and the environment.
The Harmful Effects of Pesticides
While chemical pesticides can be useful in controlling the population of yellow aphids, they can also have harmful effects on the environment and other beneficial insects. Pesticides not only kill yellow aphids, but they also kill other insects, including natural predators of aphids. This leads to an imbalance in the ecosystem and can further harm crops. Moreover, the use of pesticides can also contaminate the soil and water, affecting other plants and animals in the ecosystem.Conclusion
In conclusion, yellow aphids may seem small and unassuming, but their impact on the ecosystem is significant. Their distinctive yellow color, rapid reproduction, and clustering behavior make them a unique species, but their destructive feeding habits can cause harm to plants and crops. However, they are an essential part of the ecosystem and play a crucial role in keeping it in balance. Therefore, it is vital to find natural and eco-friendly ways to control their population instead of resorting to harmful pesticides. So the next time you spot these tiny yet mighty pests in your garden, remember their role in the ecosystem and find ways to coexist with them.

Get to Know the Mighty Yellow Aphids: Tiny Insects with a Big Impact
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.