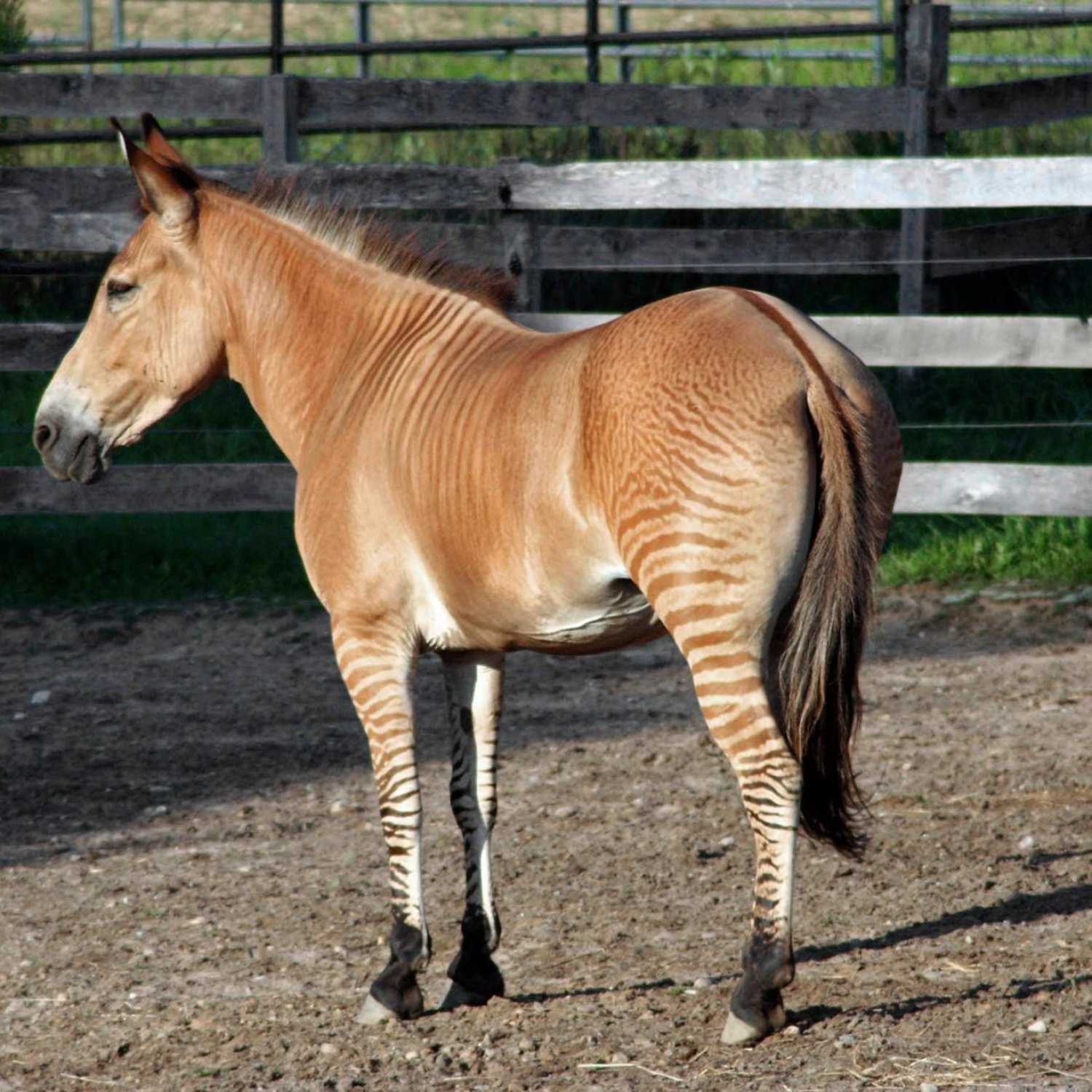
Zorse
Varies depending on parentage
The Zorse is an intriguing hybrid of a zebra and a horse, with unique features and a passionate fan base. While their length varies based on their parents, their captivating appearance and friendly demeanor can be found worldwide. As a member of the Equidae family, they share similar body shapes to their horse ancestors. Fascinated by the Zorse? Visit a zoo or animal park near you to see one in person!
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Zorse
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Varies depending on location
The Intriguing World of Zorses: A Fascinating Hybrid of Nature and Nurture
In the vast and diverse world of animals, there are those that captivate us with their unique appearances and behaviors. From majestic lions to graceful dolphins, each species has its own fascinating characteristics. However, one animal that often goes unnoticed is the zorse – a hybrid of two iconic animals, the zebra and the horse.The zorse, also known as equus zebra x E Zorse. caballus, is a remarkable creature that has caught the attention of animal lovers and scientists alike. It is a testament to the power of nature and nurture, as it combines the distinct features of its wild and domesticated parents. Let's delve deeper into the world of zorses and uncover the captivating facts about this fascinating animal.
A Brief Introduction to the Zorse
The zorse, as its name suggests, is a hybrid of a zebra and a horse. It typically has the body and head of a horse, with the distinctive stripes of a zebra adorning its body. The exact origins of the zorse are unknown, as it is a result of captivity breeding. However, it is believed to have originated in the last two centuries, with the earliest known instances of zorses being bred in South Africa and India. Today, zorses can be found worldwide, as they are bred in captivity by various zoos, farms, and private owners.The Science Behind the Zorse
The zorse belongs to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, and class Mammalia Zebra Shark. It is part of the order Perissodactyla, which includes animals with hooves and an odd number of toes, such as horses, zebras, and rhinoceroses. The zorse is a member of the family Equidae, which includes horses, donkeys, and zebras. This genetic makeup is what allows the zorse to possess traits from both its wild zebra parent and its domesticated horse parent.The unique combination of zebra and horse in the zorse is made possible through the process of hybridization. This occurs when two different species within the same genus (in this case, zebra and horse belong to the genus Equus) mate and produce offspring. While most hybrids are usually infertile, zorses have been known to produce viable offspring with both zebras and horses.
The Evolution of the Zorse
The evolutionary history of the zorse is a fascinating one. While zebras and horses share a common ancestor, they diverged around 4-5 million years ago. This divergence has resulted in significant differences between the two species, from their physical appearance to their behavior.Zebras are known for their social and aggressive nature, while horses are known for their docile and domesticated behavior. The zebra's stripes are also a vital defense mechanism in the wild, as they confuse predators and make it challenging to isolate and attack one individual. On the other hand, horses have been selectively bred for domestication and have lost some of their natural defense mechanisms.
The zorse, therefore, inherits a mixture of physical and behavioral traits from its parents, making it a truly unique species.
The Features of the Zorse
The zorse's physical appearance can vary greatly, depending on the parentage of each individual. Some zorses may have more zebra-like stripes, while others may have fewer stripes and resemble horses more closely. Additionally, the coat color of a zorse can also vary, depending on the types of zebra and horse that were bred to create it.In terms of body shape, zorses typically have a horse-like appearance, with long legs, a muscular body, and a thick mane. However, some zorses may have a slightly shorter back and larger head, which are more characteristic of zebras.
The average length and weight of a zorse also vary, depending on the parentage. Most zorses can grow to be about 12-14 hands (or 48-56 inches) at the shoulder and weigh around 500-700 pounds. However, there have been instances of zorses growing taller and heavier than their parents, making them truly unique in their size and appearance.
The Unique Habits of Zorses
As a hybrid of two species with distinct behaviors, zorses can exhibit a variety of habits. Like horses, they are herbivorous, feeding on grass, leaves, and other plants. Their diet consists mainly of grains and hay, similar to domesticated horses.Behaviorally, zorses are known to exhibit both the social and aggressive qualities of their parents. In captivity, they can be trained and ridden like horses, but they may also display some of the more wild behaviors of zebras, such as vocalizing and nibbling on their handlers. Zorses are also energetic and highly active animals, making them suitable for activities like trail riding and endurance competitions.
In terms of their habitat, zorses can adapt to various environments, depending on their location. In the wild, zebras are found in open grasslands and savannas, while horses can thrive in a variety of climates and terrains. As such, zorses have been bred in captivity in various locations worldwide and can adapt to their surroundings with ease.
Conservation and Protection of Zorses
While zorses are not considered a separate species, they are still a valuable part of the animal kingdom. As a hybrid, they also face threats and challenges unique to their genetic makeup. One of the biggest challenges for zorses is the risk of inbreeding, which can occur if they are bred with close relatives. To combat this, it is important to carefully manage breeding programs and ensure that zorse populations remain healthy and diverse.Additionally, as with any animal in captivity, it is also essential to provide zorses with proper care and living conditions. Those who own or breed zorses should have a thorough understanding of their needs and behavior to ensure they live happy and fulfilling lives.
The Fascinating World of Zorses: A Hybrid of Nature and Nurture
The zorse is undoubtedly a remarkable creature, with its unique appearance and behavior. It's a testament to the power of nature and nurture, and the incredible potential of hybridization. While still a rare sight in the wild, zorses have captured the attention and hearts of many, and their popularity continues to grow.Whether you're an animal lover, a scientist, or anyone who appreciates the wonders of nature, the zorse is a fascinating creature that is worth learning more about. From its evolution to its physical features and habits, there is always something new and interesting to discover about the zorse. So, the next time you hear about this incredible hybrid, remember the fascinating story of its origins and how it came to be a unique combination of its wild and domesticated parents.
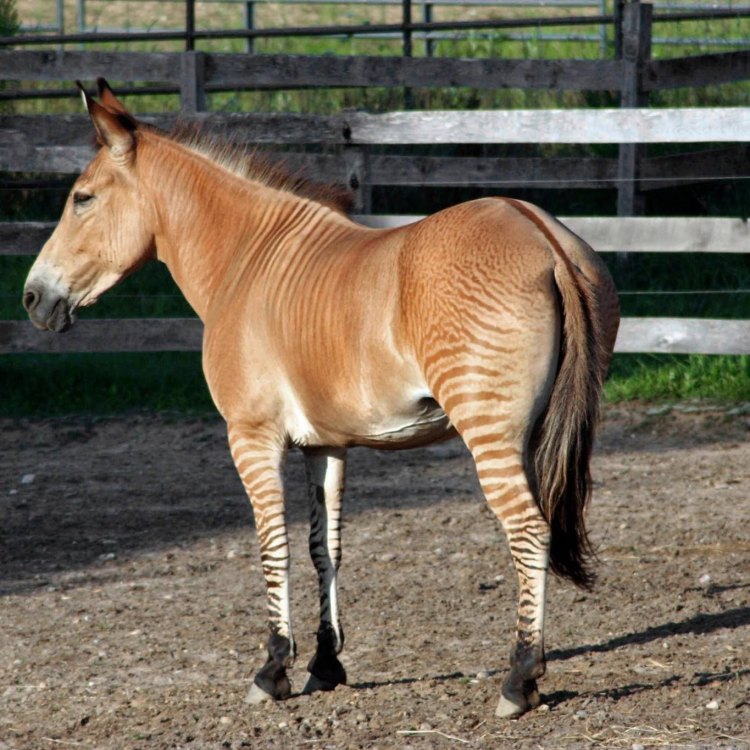

Zorse
Animal Details Zorse - Scientific Name: Equus zebra x E. caballus
- Category: Animals Z
- Scientific Name: Equus zebra x E. caballus
- Common Name: Zorse
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Perissodactyla
- Family: Equidae
- Habitat: Varies depending on location
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Varies depending on location
- Country of Origin: Unknown (resulted from captivity breeding)
- Location: Worldwide (as a result of captivity breeding)
- Animal Coloration: Varies depending on parentage
- Body Shape: Horse-like
- Length: Varies depending on parentage
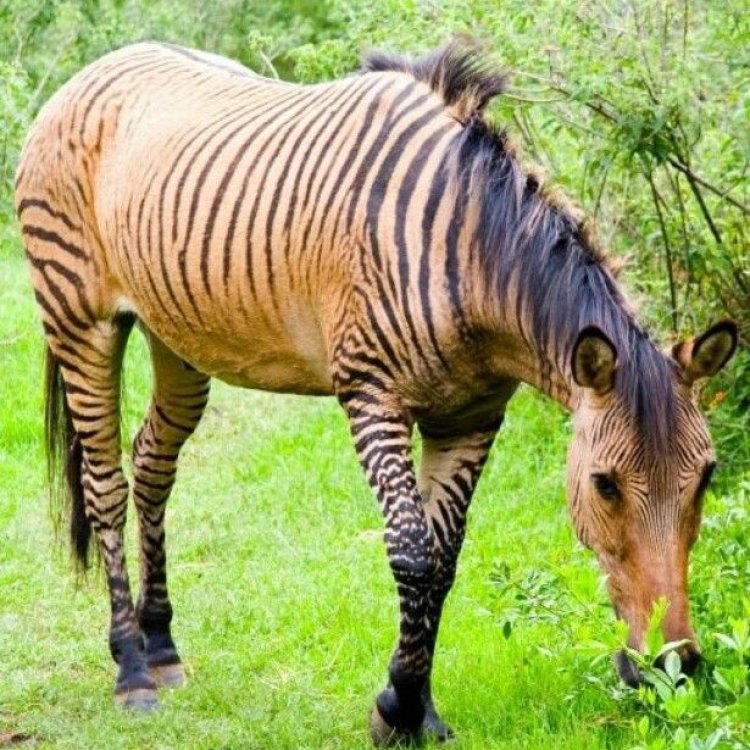

Zorse
- Adult Size: Varies depending on parentage
- Average Lifespan: 20-25 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Polygynous
- Sound or Call: Varies depending on parentage
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Varies depending on parentage
- Behavior: Varies depending on parentage
- Threats: Unknown
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated (as a hybrid species)
- Impact on Ecosystem: Unknown
- Human Use: Zoos and as riding animals
- Distinctive Features: Striped or partly striped body
- Interesting Facts: Zorses are sterile and cannot reproduce
- Predator: Predators may vary depending on location
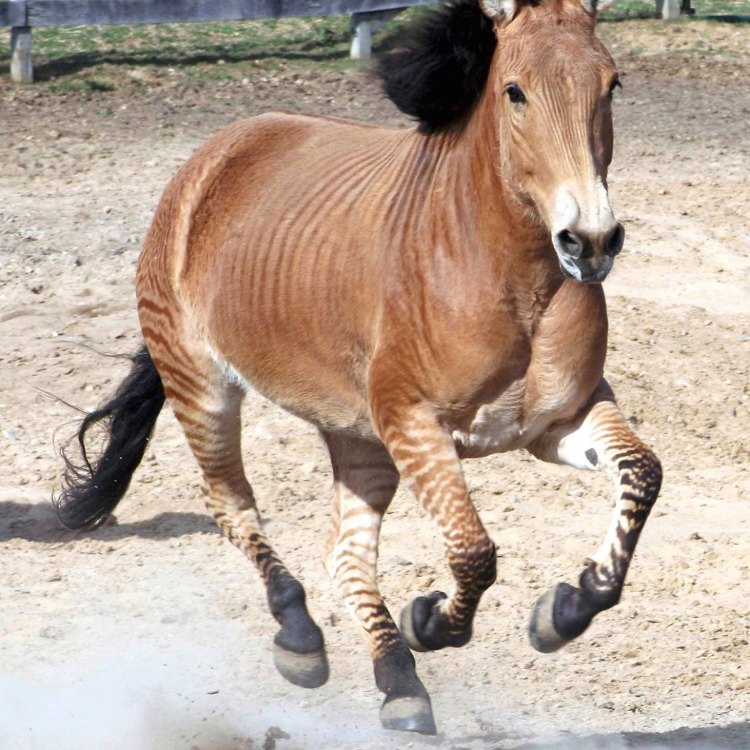

Equus zebra x E. caballus
The Fascinating World of Zorses: The Unique Hybrid Species
People have always been intrigued by the unknown and the rare, especially when it comes to animals. From mythical creatures to exotic species, we are constantly fascinated by the diversity of life on our planet. And one such unique animal that has captured our attention for centuries is the zorse.The zorse, also known as a zebroid or the zebra horse, is a hybrid species that is a cross between a zebra and a horse PeaceOfAnimals.Com. Their distinctive striped or partly striped bodies make them stand out in a crowd, but there is so much more to these magnificent creatures. Let's dive into the fascinating world of zorses and discover why they are so special.
The Origins and Appearance of Zorses
Zorses are a relatively new species, believed to have first appeared in the mid-19th century in the United States. They were first bred in captivity, and their existence is purely due to human intervention. When zebras were brought to Europe during the colonial era, they were often kept in captivity near horses, which led to their crossbreeding.Adult Zorses can vary in size, and their appearance depends on their parentage. Their average size is similar to that of a horse, standing at an average height of 14-16 hands (56-64 inches) at the shoulder. They can weigh anywhere between 700-1,000 pounds, making them the perfect size for riding animals.
One of the most distinctive features of zorses is their striped or partly striped body Zebra. However, the degree and pattern of stripes can vary greatly depending on their parentage. Some may have bold black and white stripes like a typical zebra, while others may just have a few faint stripes on their legs or hindquarters. This variation only adds to their charm and uniqueness.
The Life and Reproduction of Zorses
Like their appearance, the lifespan of zorses can also vary depending on their parentage. On average, zorses can live for 20-25 years, which is similar to the lifespan of a horse. However, there have been cases of zorses living up to 30 years, surpassing the lifespan of their parent species.Being hybrids, zorses are sterile and cannot reproduce. This means that they are a one-of-a-kind species that cannot be bred in the wild. They can only be created through human intervention, making them a rare and exclusive species.
When it comes to reproductive behavior, zorses can exhibit polygynous behavior, meaning a male zorse can have multiple female partners. This is similar to the behavior of zebras and gives them a social structure similar to their zebra parent.
The Behavior and Social Patterns of Zorses
As with their appearance, the behavior of zorses can vary depending on their parentage. They can inherit behavioral traits from both horses and zebras, giving them a unique blend of characteristics. Zorses are generally docile and sociable animals, making them easy to train and interact with.In terms of social groups, zorses can vary greatly depending on their parentage. Some may exhibit the herd mentality of horses, while others may have a more solitary nature like zebras. Due to their sterile nature, zorses do not have a natural wild habitat and are often found in captivity.
In captivity, they can be kept in groups, but like horses, they can also be trained and used for solo riding. This versatility makes them a popular choice for zoos and as riding animals for recreational purposes.
Unknown Threats and Conservation Status of Zorses
As a hybrid species, zorses are not recognized as a distinct species by conservation organizations. This means that their conservation status is not evaluated, leaving their threats largely unknown.In captivity, zorses are susceptible to the same threats as horses, such as illnesses and injuries. However, in the wild, various predators may pose a threat to zorses, depending on their location. For example, in Africa, lions and hyenas may prey on zorses, while in the Americas, cougars and wolves may pose a threat.
The Impact and Use of Zorses in Human Society
Zorses have an interesting history with humans, starting with their creation due to human intervention. Today, they are mainly used in zoos for educational and entertainment purposes. However, they have also been used as riding animals, particularly in circuses.Their distinctive appearance and docile nature make them a popular attraction, especially for children. In some cultures, zorses are also considered symbols of wealth and are kept as exotic pets.
The Uniqueness of Zorses: Fun Facts and Predators
Apart from their distinctive stripes and hybrid nature, there are a few more fascinating facts about zorses that make them stand out from other species. As mentioned before, zorses are sterile and cannot reproduce, making them a completely unique and rare species.Another interesting fact is that zorses do not have a specific sound or call like their parent species. Instead, their vocalizations can vary depending on their parentage, making them even more fascinating.
As for their predators, it can vary depending on their location. In areas where zebras and horses coexist, zorses may not have any natural predators. However, in some cases, zorses may fall prey to large predators such as lions, hyenas, or wolves, just like their parent species.
In Conclusion
The world of zorses is a fascinating and relatively unknown one. As a hybrid species, they possess a unique blend of traits from their parent species, making them a one-of-a-kind animal. Their striped bodies, sociable nature, and docile behavior make them a popular attraction in zoos and as riding animals.However, with their conservation status not evaluated, we are yet to understand the full extent of threats and impact zorses may have on our ecosystem. As we continue to explore and learn about these unique creatures, let us appreciate their rarity and the beauty of nature's creations.
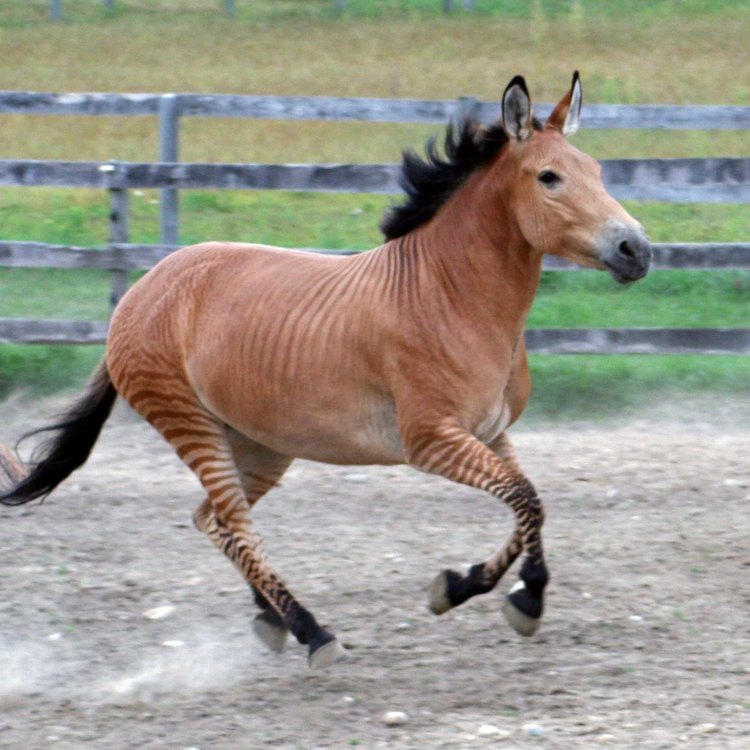

The Intriguing World of Zorses: A Fascinating Hybrid of Nature and Nurture
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.