Blue Death Feigning Beetle
8 to 20 millimeters
Did you know that the Blue Death Feigning Beetle can be found in Southern California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Nevada? These small oval-shaped beetles, belonging to the Tenebrionidae family, range in size from 8 to 20 millimeters. Despite their name, they don't actually play dead but instead tuck their legs in and remain motionless when threatened. How fascinating is that? #BlueDeathFeigningBeetle #Tenebrionidae #SouthernCalifornia #Arizona #NewMexico #Nevada
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Blue Death Feigning Beetle
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Desert regions
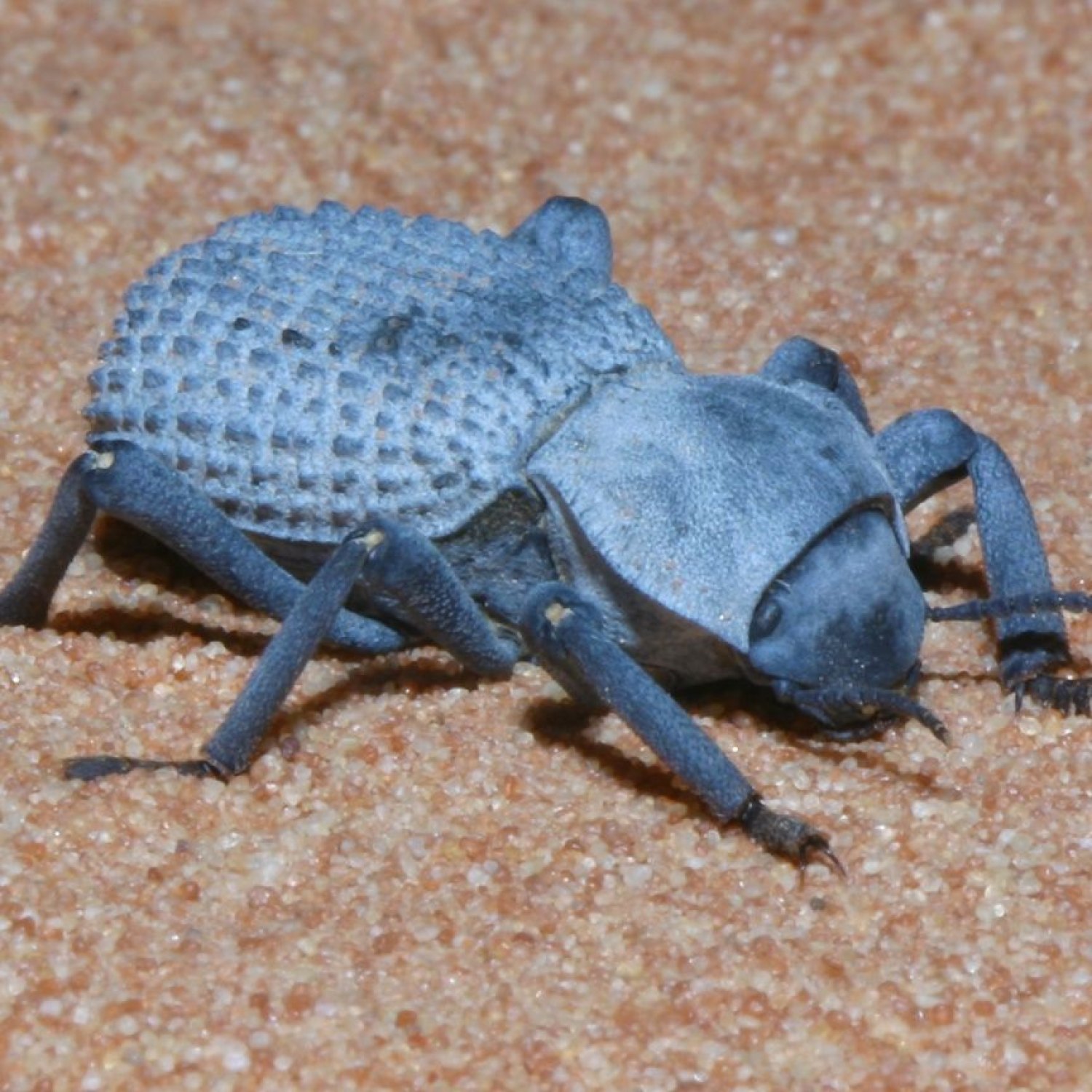
Blue Death Feigning Beetle: The Mysterious Insect of the Desert
It's a warm summer evening in the desert, and the sun is beginning to set. Most animals are seeking shelter from the harsh rays, but there is one creature that thrives in this arid environment – the Blue Death Feigning Beetle. This small, blue-black insect has captured the attention of many nature enthusiasts with its unique features and behaviors. In this article, we will delve into the world of the Blue Death Feigning Beetle, exploring its scientific classification, habitat and distribution, physical characteristics, and fascinating survival tactics Blue Death Feigning Beetle.Scientific Classification
The scientific name of the Blue Death Feigning Beetle is Asbolus verrucosus. It belongs to the Animalia kingdom, which includes all living organisms classified as animals. From there, it is further classified into the Arthropoda phylum, which includes all animals with exoskeletons and jointed appendages. It is then classified as an insect under the class Insecta, which includes familiar insects like butterflies, bees, and ants. The Blue Death Feigning Beetle is part of the order Coleoptera, which includes beetles, and the family Tenebrionidae, which comprises darkling beetles. From its scientific classification alone, we can see that this little insect is part of a diverse and extensive group of animals.
Habitat and Distribution
The Blue Death Feigning Beetle is primarily found in desert regions in North and Central America. Its main country of origin is the United States, specifically in the states of Southern California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Nevada. These states have a hot and dry climate, making it the ideal habitat for this particular species of beetle Boggle. They can also be found in some parts of Mexico. Within their desert habitat, Blue Death Feigning Beetles can be found in sandy or rocky areas, often burrowing in the ground during the hottest parts of the day.
Physical Characteristics
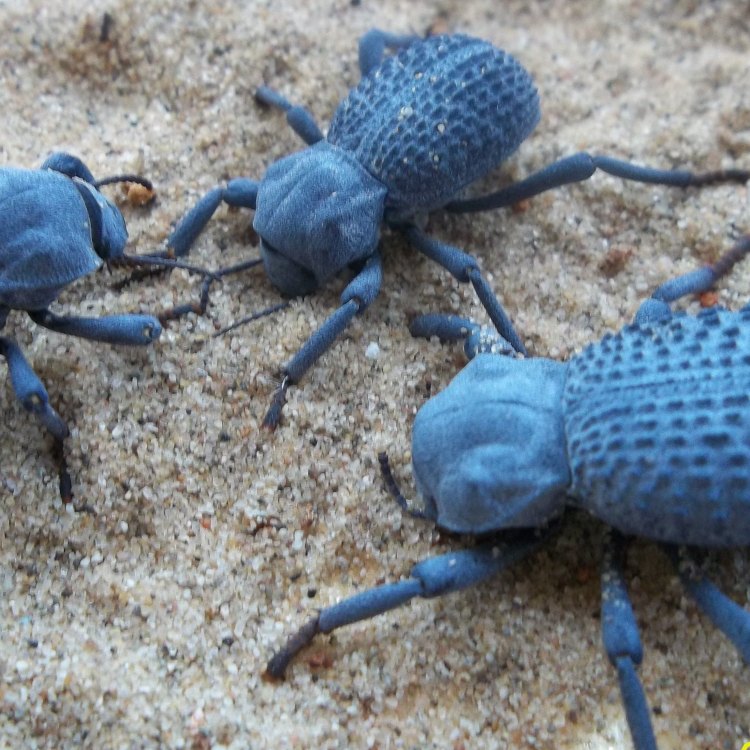
The Blue Death Feigning Beetle is undoubtedly a unique-looking insect. It is dark blue-black, with a metallic sheen that gives it a striking appearance. Its body shape is oval, with a hard and thick exoskeleton that protects its internal organs from predators and harsh environments. On average, these beetles can grow to be anywhere between 8 to 20 millimeters in length.
Apart from its distinct coloration and body shape, the Blue Death Feigning Beetle also has two prominent antennae, a head, a thorax, and an abdomen. Its compound eyes, located on the sides of its head, allow it to have a 360-degree view of its surroundings. These beetles also have six legs, which they use for movement and digging burrows. The female Blue Death Feigning Beetle is slightly larger than the male, but both sexes possess similar physical characteristics.
Survival Tactics
The Blue Death Feigning Beetle's most impressive feature is its unique defense mechanism – playing dead. When threatened, these beetles will pretend to be dead, hoping that the predator will lose interest and walk away. To achieve this, the beetle will lie on its back, with its legs and antennae curled up close to its body. It will also release a foul-smelling odor to make itself seem unappetizing. The Blue Death Feigning Beetle can play dead for several minutes, giving it enough time for the predator to leave, or the coast to clear.
This defense mechanism is known as thanatosis, also known as death-feigning. It is a common tactic among many insects, but the Blue Death Feigning Beetle takes it to a whole new level. They have been observed to remain completely motionless, even when being poked or prodded, and are only known to come back to life when the threat has passed.
Feeding Method
The Blue Death Feigning Beetle is a scavenging insect, which means it feeds on decaying matter. They are often found near carrion, dead plants, or animal droppings, which they will consume for sustenance. This feeding method helps to keep the ecosystem balanced by recycling organic matter and enriching the soil.
Interestingly, Blue Death Feigning Beetles do not require water to survive as they can extract enough moisture from their food. This is a useful adaptation in their dry desert habitat, where water is scarce.
Conservation Status and Threats
The Blue Death Feigning Beetle is not currently classified as a threatened or endangered species. However, like many other insects, its population may be declining due to habitat loss and human interference. The introduction of non-native plants or animals in their habitat could also pose a threat to their survival.
Furthermore, these beetles are often collected and sold as exotic pets, which can impact their population in the wild. It is essential to remember that all animals, including insects, play a vital role in the ecosystem, and it is our responsibility to ensure their survival.
In Conclusion
The Blue Death Feigning Beetle may seem like a simple and unremarkable insect at first glance, but upon closer inspection, it reveals intriguing features and behaviors that have captivated researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Its unique coloration, oval shape, and impressive defense mechanism make it an exciting species to study and observe.
As we continue to explore and learn more about the natural world, it is crucial to remember that every living creature, no matter how big or small, plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our planet. The Blue Death Feigning Beetle is a prime example of how even the smallest of creatures can have a significant impact on their environment. Let us continue to appreciate and protect these incredible insects, ensuring that they thrive for generations to come.
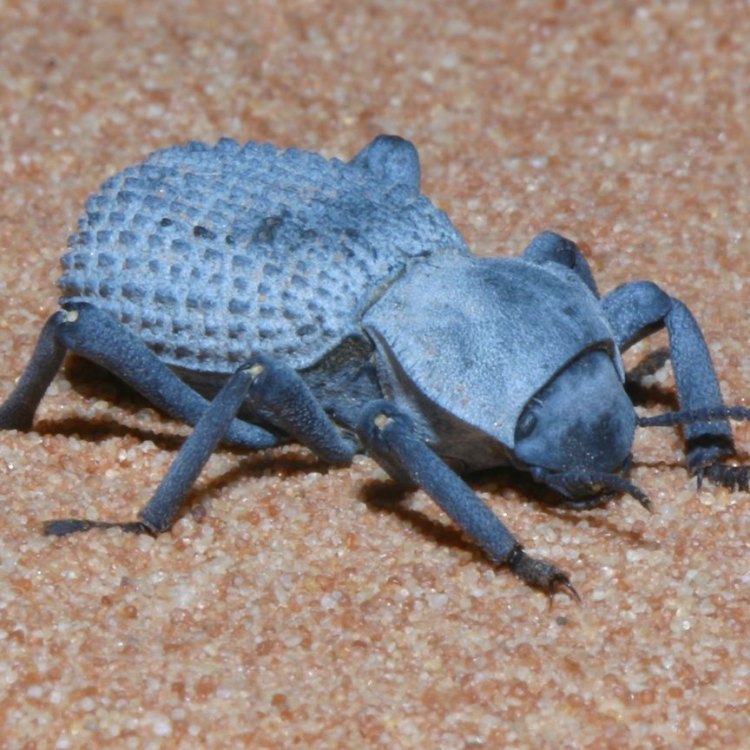

Blue Death Feigning Beetle
Animal Details Blue Death Feigning Beetle - Scientific Name: Asbolus verrucosus
- Category: Animals B
- Scientific Name: Asbolus verrucosus
- Common Name: Blue Death Feigning Beetle
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Family: Tenebrionidae
- Habitat: Desert regions
- Feeding Method: Scavenger
- Geographical Distribution: North and Central America
- Country of Origin: United States
- Location: Southern California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Nevada
- Animal Coloration: Dark blue-black
- Body Shape: Oval-shaped
- Length: 8 to 20 millimeters
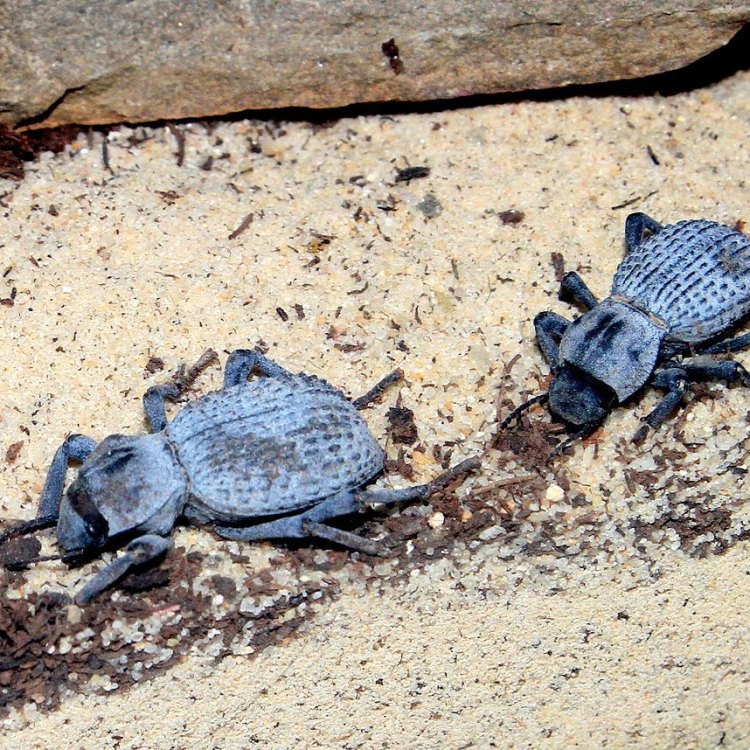

Blue Death Feigning Beetle
- Adult Size: Medium-sized
- Average Lifespan: 1 to 3 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males use pheromones to attract females
- Sound or Call: No sound production
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Feigns death when threatened
- Threats: Predators, habitat loss
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Scavenges on dead plants and insects, contributing to nutrient recycling
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Hard exoskeleton, ability to curl up and play dead
- Interesting Facts: Can survive in extremely dry conditions by entering a state of torpor
- Predator: Birds, lizards, spiders

Asbolus verrucosus
The Resilient Blue Death Feigning Beetle: A Master of Survival
The animal kingdom is full of intriguing and fascinating creatures, each with its own unique set of skills and traits. One such creature is the Blue Death Feigning Beetle, a seemingly unassuming insect with remarkable survival abilities. From its ability to play dead to its resilient nature, this beetle has caught the attention of researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. In this article, we will dive into the world of the Blue Death Feigning Beetle and explore its distinctive features, behavior, and impact on the ecosystem PeaceOfAnimals.Com.The Blue Death Feigning Beetle (Asbolus verrucosus) is a medium-sized beetle, reaching an adult size of about 0.5 to 1 inch. Found in the deserts of the Southwestern United States and Mexico, this species is a member of the darkling beetle family (Tenebrionidae). Its name may sound ominous, but do not be deceived, these beetles are harmless to humans and do not pose any known threats.
Despite its name, the Blue Death Feigning Beetle has a relatively long lifespan, living up to 1 to 3 years in the wild. This is quite impressive for an insect, as most of their counterparts have much shorter lifespans. The exact reason for their longer lifespan is still unknown, but it may be due to their resilient nature and ability to survive in harsh environments.
One interesting fact about the Blue Death Feigning Beetle is its reproductive behavior. As with most insects, these beetles reproduce sexually, but what sets them apart is the unique way in which males attract females Blue Andalusian. Males use pheromones, chemical compounds secreted by the body, to communicate and attract potential mates. These pheromones are released into the air, and female beetles use them to locate males. It is a fascinating process that highlights the complex communication systems in the animal kingdom.
Another distinctive feature of the Blue Death Feigning Beetle is its hard exoskeleton. Like most beetles, they have a tough and rigid outer covering that protects their delicate bodies. This exoskeleton is made of chitin, a sturdy material that allows these beetles to withstand harsh conditions and predators.
However, the most remarkable feature of the Blue Death Feigning Beetle is its ability to feign death when threatened. This behavior is known as thanatosis, and it involves the beetle curling up its legs, remaining motionless, and dropping to the ground. To an unsuspecting predator, it appears as if the beetle has died, hence the name "death feigning." This clever survival tactic allows the beetle to trick its enemies and increase its chances of survival.
But what happens when the beetle plays dead? To understand this, we must first look at the environmental conditions in which the Blue Death Feigning Beetle lives. These beetles are primarily found in arid, desert-like environments, where they are exposed to extreme temperatures and low humidity. In such conditions, water is scarce, and dehydration is a significant threat.
When a Blue Death Feigning Beetle feels threatened, it will enter a state of torpor, a period of minimal activity similar to hibernation. During this time, all bodily functions slow down, and the beetle goes into a state of suspended animation. By doing so, the beetle conserves energy and reduces the need for water, increasing its chances of survival in extreme dry conditions.
Predators of the Blue Death Feigning Beetle include birds, lizards, and spiders. These predators may have a harder time recognizing the beetle's feigning behavior, making it a successful survival strategy. The beetles also have a few tricks up their sleeves to deter predators. They can produce a noxious odor from their abdomen, which is repulsive to predators. Additionally, their hard exoskeleton makes it difficult for predators to crush them, further increasing their chances of survival.
However, despite their incredible survival abilities, Blue Death Feigning Beetles are still facing some threats in their natural habitat. Habitat loss due to human activities and climate change is a significant concern for these beetles. As their natural habitat becomes increasingly fragmented, their survival becomes more challenging. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural development all contribute to the decline in the Blue Death Feigning Beetle's population.
Furthermore, the impact of these beetles on the ecosystem should not be underestimated. While they may not seem like significant players in the food chain, these beetles play a vital role in nutrient recycling. They feed on decaying plants and insects, aiding in the decomposition process and contributing to the ecosystem's overall health. They are also a source of food for various predators, further illustrating their importance in the food web.
Despite their resilience and unique features, the Blue Death Feigning Beetle's conservation status is classified as "not evaluated" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that there is not enough data available to determine their population status and the level of threat they face. However, as their habitats continue to shrink, it is essential to monitor the beetle's population and take steps to protect their natural habitats.
When it comes to human use, the Blue Death Feigning Beetle does not have any significant impact. They are not used for any medicinal or commercial purposes, nor are they considered a pest. They are simply fascinating creatures that have captured the attention of researchers and nature enthusiasts.
In conclusion, the Blue Death Feigning Beetle may not be the most striking or well-known creature, but it has a unique set of features that make it a master of survival. From its ability to feign death to its resilient nature, this beetle has earned its place in the animal kingdom. However, as their habitats continue to decline, it is crucial to raise awareness about their importance and take necessary steps to protect them. These resilient insects deserve to thrive and continue to play a vital role in their ecosystems.

Blue Death Feigning Beetle: The Mysterious Insect of the Desert
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.