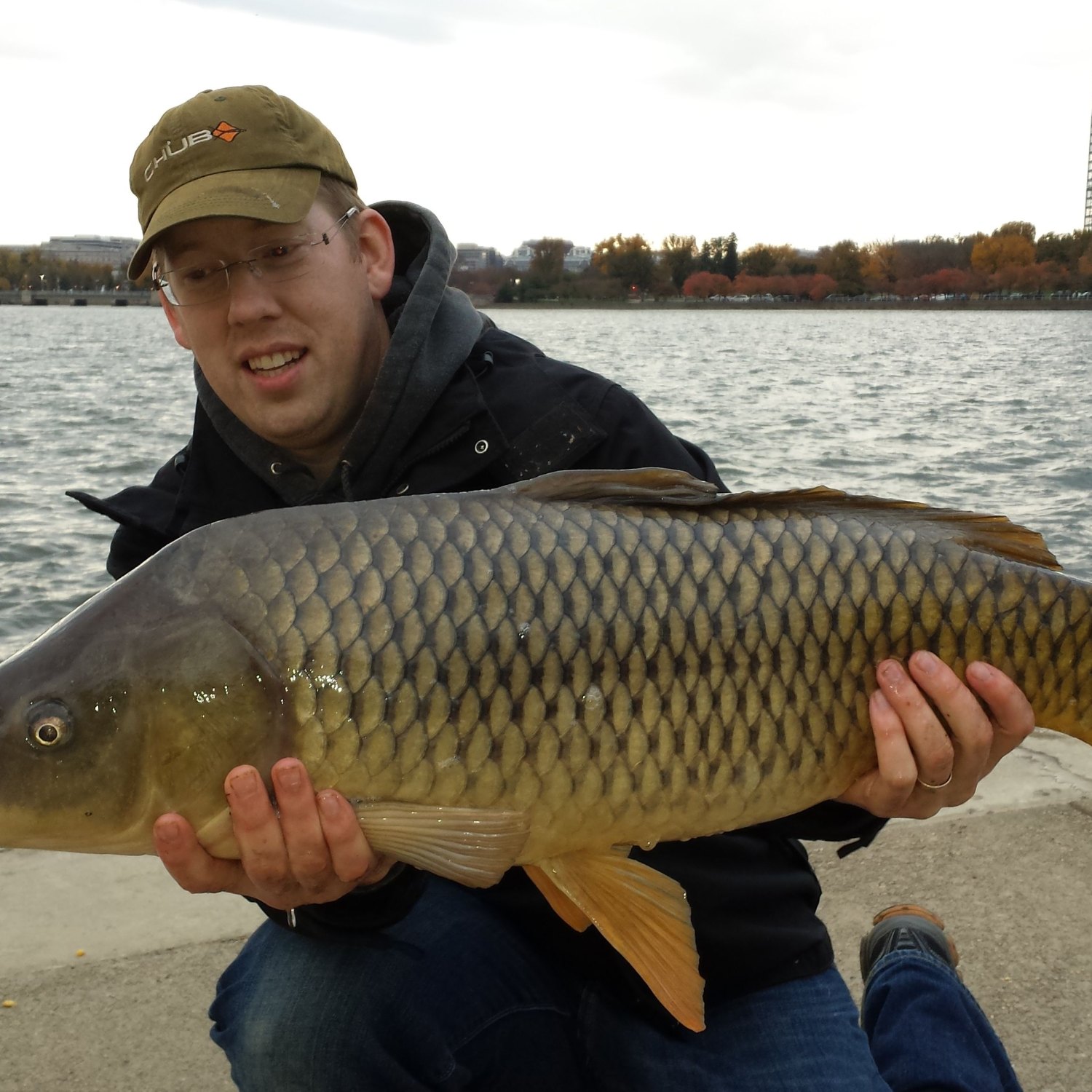
Common Carp
40-80 cm
The common carp (Cyprinus carpio) is a popular freshwater fish known for its elongated and cylindrical body shape. They can grow up to 40-80 cm in length and belong to the Cyprinidae family, commonly found in ponds, lakes, and rivers. With their peaceful nature and adaptive behavior, they make great additions to any aquatic ecosystem.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Common Carp
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Freshwater
The Mighty Fish: Discovering the Wonders of the Common Carp
Do you enjoy fishing or spending time by the water? Have you ever come across a large, golden brown fish with an elongated body while out on a fishing trip or a walk by the pond? If so, you may have encountered the mighty common carp.Known for its impressive size and strength, the common carp (Cyprinus carpio) is a freshwater fish found primarily in Europe and Asia. This remarkable fish, despite its popularity in some regions, remains a mystery to many. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the remarkable features and characteristics of the common carp Common Carp.
The Classification of the Common Carp
Before we delve into its features and behavior, let's first understand the taxonomy of the common carp. Scientific classification is essential in understanding the relationships, characteristics, and evolution of different species.The common carp belongs to the kingdom Animalia, which includes all animals on Earth. It falls under the phylum Chordata, which comprises all animals with a notochord (a flexible rod that serves as the central support of the body). Within the phylum, the common carp belongs to the class Actinopterygii, also known as ray-finned fish. This class contains over 30,000 species of fish, making it the largest class of vertebrates (animals with backbones).
Next, the common carp belongs to the order Cypriniformes, which includes carps, minnows, and loaches. Within this order, the common carp belongs to the family Cyprinidae, commonly known as the carps or minnows. This family is known for its large and diverse number of species, with over 3,000 known species Chamois.
Habitat and Distribution
The common carp is a freshwater species, meaning it can only survive in bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, and rivers. It inhabits a variety of freshwater habitats, including stagnant ponds, slow-moving rivers, and fast-flowing streams. This adaptable fish can also thrive in a wide range of water temperatures and qualities, making it a common species in different regions.While the common carp is native to China, it has successfully been introduced to various regions worldwide, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It is a popular sport fish in many countries, with some regions actively breeding and stocking them in freshwater systems for recreational fishing.
Feeding Method
The common carp is an omnivorous species, meaning it feeds on both plant and animal matter. While its diet may vary depending on its habitat and availability of food, the common carp generally consumes a diet of small insects, crustaceans, and small fish. It also feeds on a variety of plant matter, including aquatic plants, algae, and seeds.This feeding behavior makes the common carp a vital species in maintaining the balance of freshwater ecosystems by controlling the population of small organisms and helping to redistribute nutrients.
Distinct Physical Features
The common carp has several unique physical features that make it easily distinguishable from other fish species. One of its most notable characteristics is its golden brown coloration, which gives it a majestic and eye-catching appearance.The body shape of the common carp is also quite distinctive. It has an elongated, cylindrical body, with a high, arched back and a broad head. It has a relatively large mouth with firm, thick lips, and four barbels (whisker-like sensory organs) near its mouth. These barbels are believed to help the common carp locate food in murky water.
Another unique feature of the common carp is its scale-less head and a partially scaled body. The scales that cover its body range in color from golden brown to dark brown, with a shiny, almost metallic appearance. The color of the scales can vary depending on its habitat and the type of water it resides in.
Size and Growth
The common carp is a large fish, with an average length of 40-80 cm, with some specimens reaching up to 120 cm. It usually weighs between 2-14 kg, although some may weigh as much as 25-30 kg. The size and weight of common carp can vary depending on feeding habits, environmental conditions, and genetics.In terms of growth, the common carp grows at a rate of approximately 4 cm per year until it reaches sexual maturity at around 4-5 years of age. However, with the right conditions and proper management, some specimens can grow up to 5-10 cm per year.
Breeding and Reproduction
The common carp reaches sexual maturity between 2-5 years of age, depending on its conditions and location. Breeding can occur throughout the year, but it typically happens between April and June in temperate climates. During this time, males will develop small, white tubercles (small white bumps) on their head and pectoral fins.Common carp reproduce by spawning, where the female lays eggs while the male releases sperm to fertilize them. Females can lay up to 3 million eggs in a single spawning event, with some females spawning up to five times in a season.
The eggs are adhesive, allowing them to attach to aquatic plants or objects, and the male then fertilizes them. Common carp eggs typically hatch within 3-5 days, and the fry (baby fish) begin to swim freely after a week.
Behavior and Adaptability
The common carp is a highly adaptable species, able to thrive in a wide range of water conditions. This adaptability is one of the reasons why this fish has successfully been introduced to different regions worldwide, making it one of the most widespread freshwater species.While it is usually known as a bottom-feeding fish, the common carp also has a unique feeding behavior called "drifting." This behavior involves the carp swimming in open water while keeping its mouth open, feeding on plankton and other small organisms.
In addition to its feeding behavior, the common carp is also known for its potential to jump out of the water when hooked or startled. This jumping behavior is especially common during the breeding season, as males compete for females.
Conservation Status and Threats
While the common carp is a widespread and adaptable species, it is facing several threats to its survival. One of the most significant threats is invasive species introduction. Human activity, such as stocking non-native fish for sport fishing, has introduced non-native carp species such as the silver carp and grass carp. These species can harm the native ecosystem and outcompete the common carp for resources.Pollution and habitat destruction are also major threats to the common carp's existence. As human populations and industries continue to grow, freshwater ecosystems are becoming increasingly threatened, leading to a decline in the common carp population.
However, the common carp is not currently classified as an endangered species. Its adaptability and successful breeding and stocking programs have helped to maintain its population, although conservation efforts are necessary to ensure its long-term survival.
The Versatile Common Carp
The common carp may not be the most well-known fish species, but it is undoubtedly one of the most remarkable. From its unique physical features and behavior to its adaptability and importance in freshwater ecosystems, this fish is truly versatile.If you ever come across a common carp on your next fishing trip or walk by the pond, take a moment to appreciate its beauty and significance. With this newfound knowledge, you can now appreciate the mighty fish even more and spread the word about the wonders of the common carp.
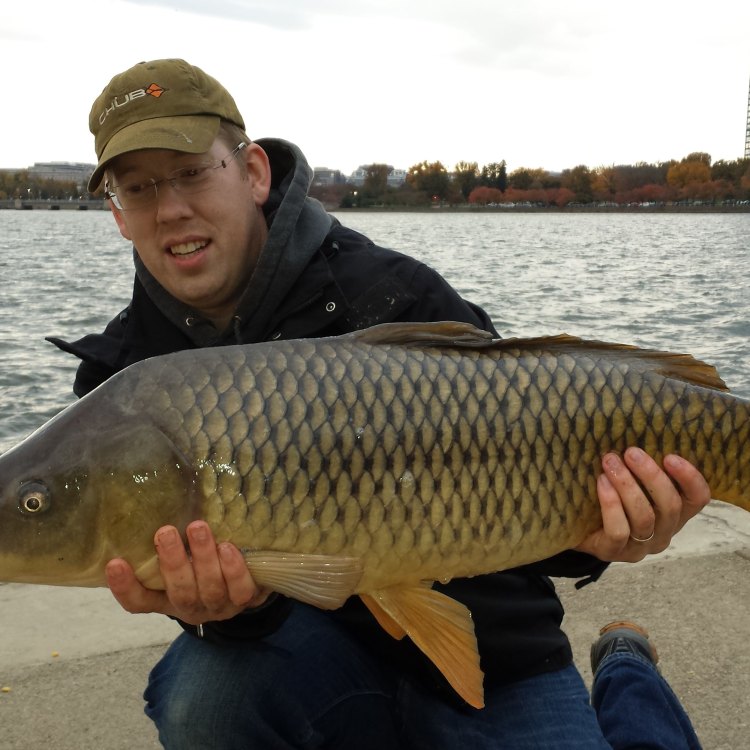

Common Carp
Animal Details Common Carp - Scientific Name: Cyprinus carpio
- Category: Animals C
- Scientific Name: Cyprinus carpio
- Common Name: Common Carp
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Cypriniformes
- Family: Cyprinidae
- Habitat: Freshwater
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Europe, Asia
- Country of Origin: China
- Location: Ponds, lakes, rivers
- Animal Coloration: Golden brown
- Body Shape: Elongated and cylindrical
- Length: 40-80 cm
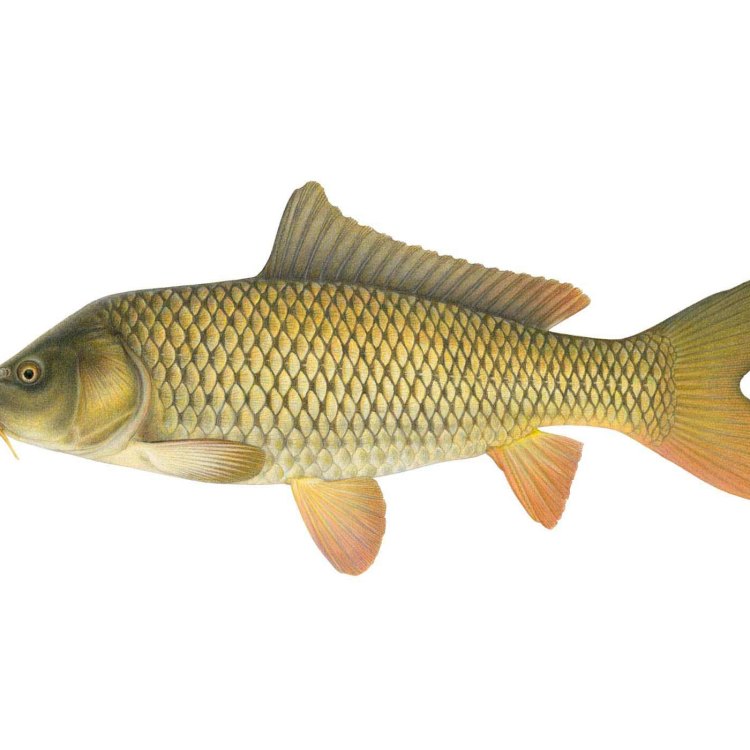

Common Carp
- Adult Size: Up to 120 cm
- Average Lifespan: up to 20 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Spawning
- Sound or Call: No sound production
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Schools
- Behavior: Active during the day, bottom-dwelling
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Can damage aquatic ecosystems
- Human Use: Commercial and recreational fishing
- Distinctive Features: Large scales, two pairs of barbels
- Interesting Facts: Can grow to impressive sizes, introduced to many countries worldwide
- Predator: Large fish, birds
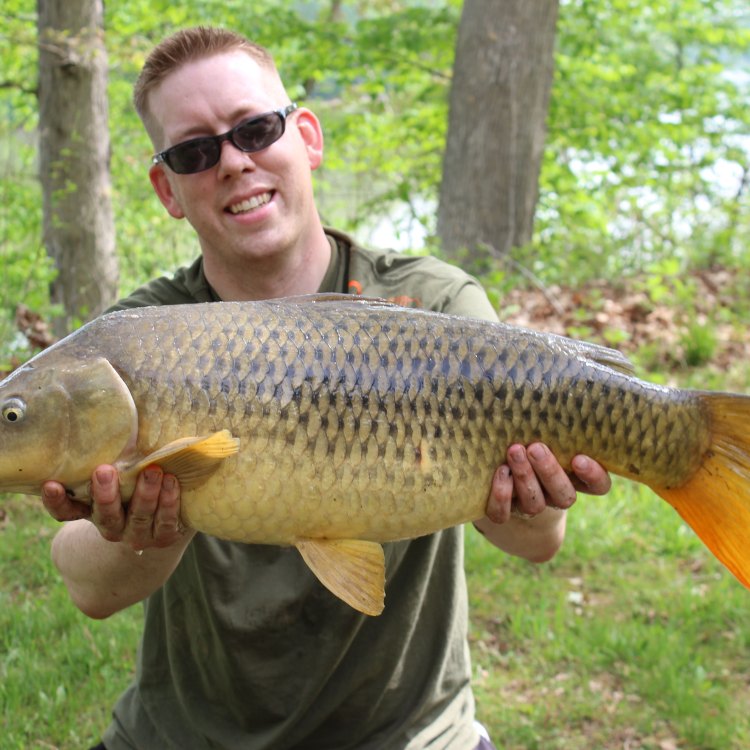

Cyprinus carpio
The Majestic Common Carp: An Impressive, Yet Controversial Species
When you hear the word “carp”, you may think of the small, peaceful fish that often inhabit calm lakes and ponds. However, there is one species of carp that stands out among the rest – the Common Carp. From its massive size to its distinctive features, this fish has captured the fascination of both scientists and fishermen alike. However, its presence in various environments and human use has also sparked controversy and concern PeaceOfAnimals.Com. In this article, we will explore the unique characteristics of the Common Carp and its impact on the ecosystem and human society.At first glance, the Common Carp may not seem very different from other carp species. It has a long, streamlined body and is typically brown or grey in color. However, what sets it apart are its impressive size and distinctive features. As an adult, the Common Carp can reach lengths of up to 120 cm, making it one of the largest freshwater fish in the world. Its average lifespan can also range up to 20 years, with some individuals living even longer.
Reproduction in the Common Carp is sexual, with males using their barbels (small sensory organs near their mouths) to attract females during spawning season. Spawning behavior is another unique feature of this species. Unlike many other fish, the Common Carp do not just lay their eggs randomly in the water Comb Jellyfish. Instead, they perform a synchronized dance, swimming in circles and releasing their eggs and sperm simultaneously. This highly coordinated behavior ensures a higher chance of successful fertilization and survival of their offspring.
Interestingly, the Common Carp do not produce any sound or calls. They communicate through their movements and visual cues, such as flashing their scales or darting in a specific direction. This behavior is rooted in their non-migratory pattern – they do not travel long distances but instead reside in the same location for most of their lives.
In terms of social groups, Common Carp typically form schools, swimming together and sharing resources. This behavior allows for protection against predators and increases the chances of finding food. However, the fact that they are bottom-dwelling fish also means that they can be quite destructive to aquatic ecosystems.
Speaking of predators, the Common Carp has few natural threats due to its large size. However, larger fish and birds can prey on young or smaller individuals. As for human use, Common Carp have been highly valued in both commercial and recreational fishing. Their large size and abundance make them a popular target for fisherman, especially in Europe and Asia. In fact, they are one of the most intensely fished freshwater species in the world.
Unfortunately, this widespread human use has also led to some significant threats to the Common Carp population. Habitat loss, pollution, and overfishing have greatly impacted their numbers, especially in their native regions. In some countries, such as Australia and New Zealand, they have been classified as an invasive species, causing harm to the local ecosystem. This is due to their destructive bottom-feeding behavior, which stirs up sediment and disrupts native plant and animal species.
However, the Common Carp itself is under no threat of extinction. In fact, it is listed as “Least Concern” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. This status is due to the fact that they have a large and stable population, and their presence does not directly threaten any other species. However, their impact on ecosystems must not be overlooked, and measures must be taken to prevent further harm.
Despite their controversial presence in various environments, the Common Carp continues to fascinate scientists and fishermen alike. Their ability to grow to impressive sizes and their introduction to numerous countries worldwide have made them a global species. In some countries, such as Japan, they are even considered a delicacy, with a traditional dish called “Carp Sushi” being popular. However, their distinctive features, such as their large scales and two pairs of barbels, serve as a vital reminder of their unique and critical role in the aquatic world.
To better understand the Common Carp's impact on ecosystems, researchers have conducted various studies and experiments. One notable example is a study conducted by scientists at the University of Georgia, which found that Common Carp can significantly damage aquatic plant communities. As bottom-dwellers, they uproot and consume plants, causing a decline in water quality and a decrease in the diversity of other aquatic species.
Despite their negative impact, there are also some interesting facts about the Common Carp that may surprise you. Did you know that they can live up to several months out of the water? This is due to their ability to obtain oxygen through their gills even when they are not submerged. Additionally, they can survive in a variety of environments, from warm, shallow waters to cold, deep lakes. They have even been found living in highly polluted waters, further emphasizing their resilience and adaptability as a species.
In conclusion, the Common Carp is undoubtedly an extraordinary and fascinating species. From its impressive size to its unique reproductive behavior, this fish has captured the imagination of many. However, its presence in many environments and its human use have also sparked concerns about its impact on ecosystems. As a society, it is essential to strike a balance between appreciating the beauty of this species and understanding the potential harm it can cause. Only through proper conservation measures can we ensure the survival of the majestic Common Carp for future generations to admire and study.
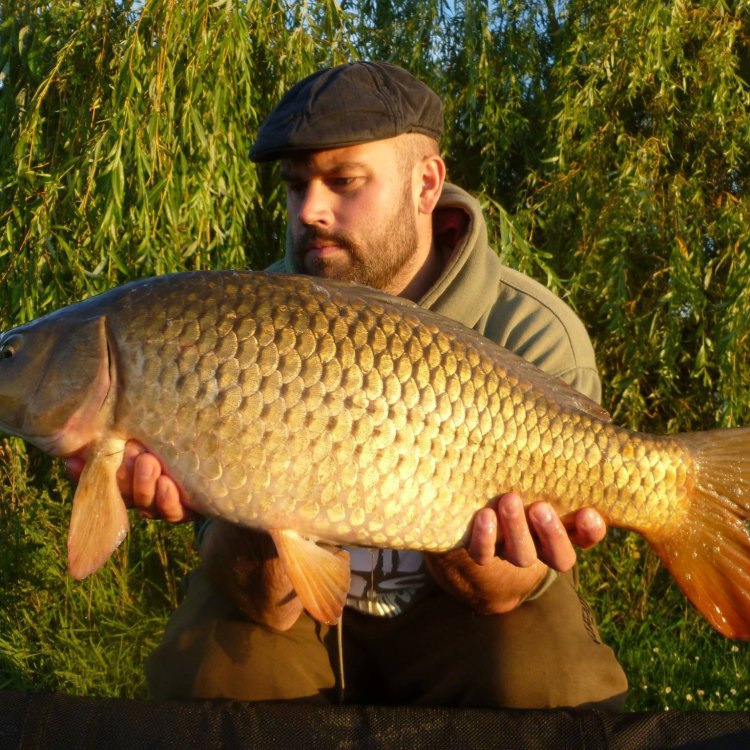

The Mighty Fish: Discovering the Wonders of the Common Carp
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.