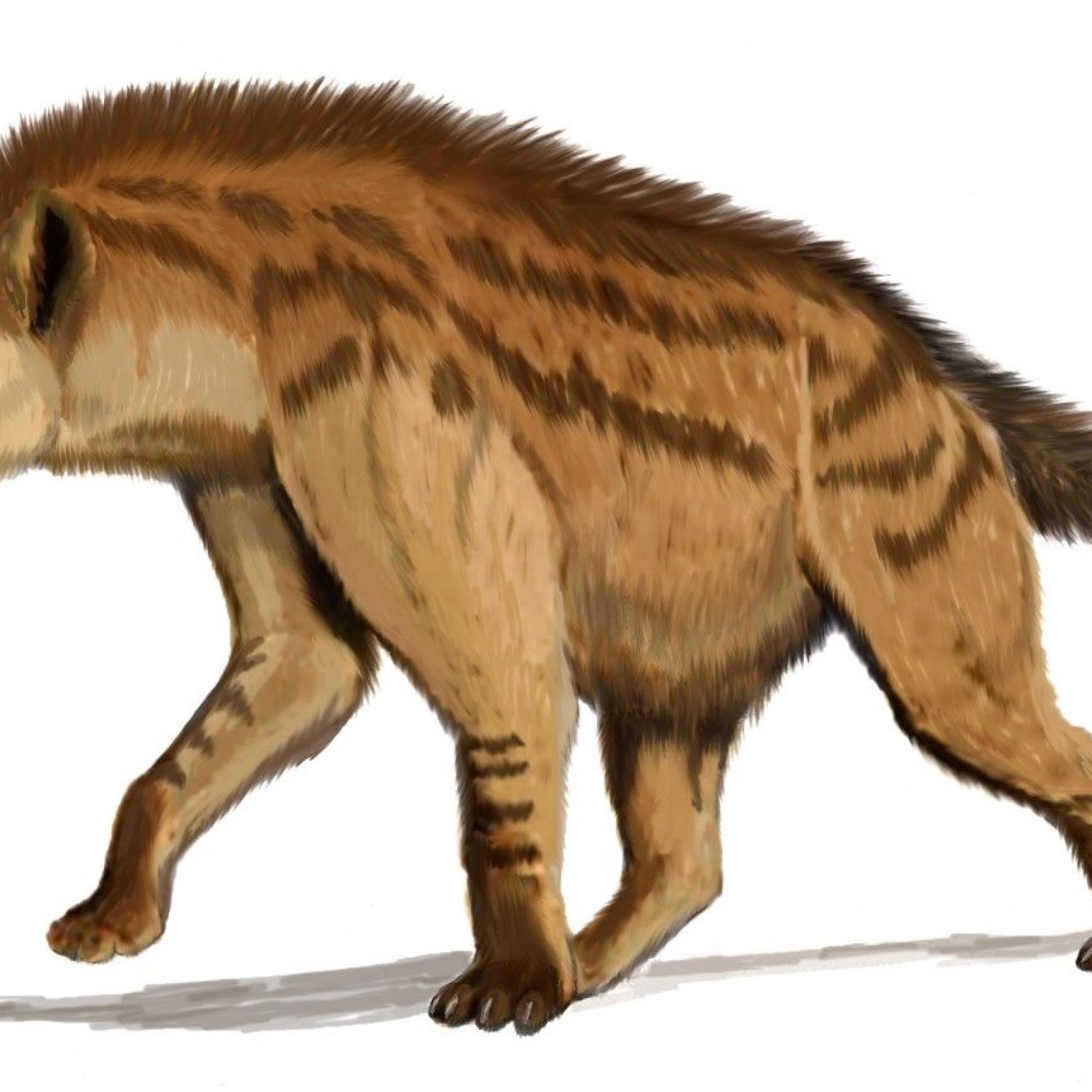
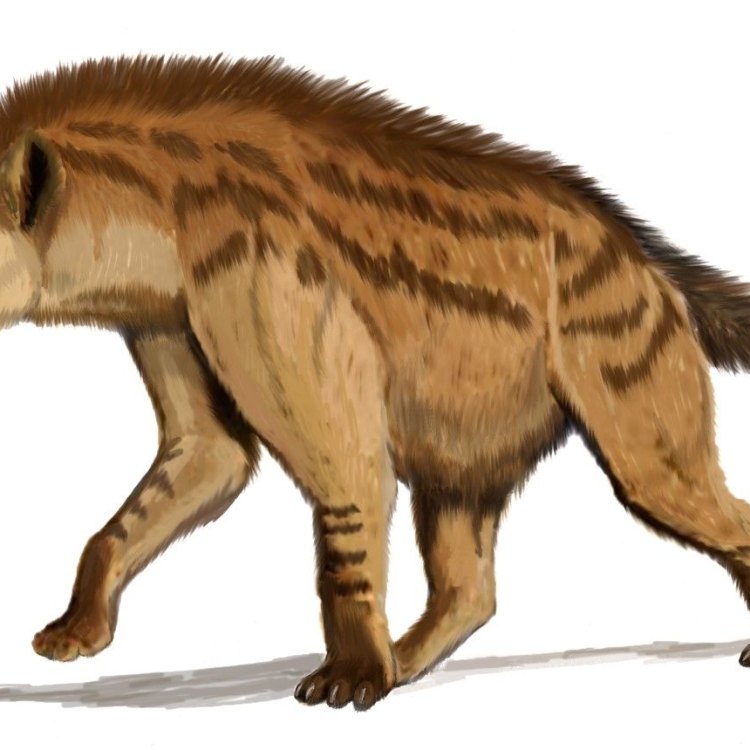
Dinocrocuta
Approximately 2.5 meters
Dinocrocuta, also known as the terrible hyena, was an ancient mammal that roamed Asia, Africa, and Europe during the Ice Age. With a length of about 2.5 meters and belonging to the Hyaenidae family, this large and robust predator was a formidable force. Its fossil remains have provided valuable insights into the evolution and behavior of hyenas. #Dinocrocuta #IceAge #FossilRemains #Predator
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Dinocrocuta
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Open grasslands and savannas
The Fascinating World of Dinocrocuta: A Giant Carnivorous Hyena
In the vast world of animals, there are some creatures that are known for their size, strength, and ferocity. One such animal is the Dinocrocuta, a giant hyena that roamed the earth millions of years ago. With its impressive size and carnivorous eating habits, Dinocrocuta gigantea is a formidable predator that has captured the interest and imagination of scientists and animal lovers alike.Dinocrocuta, also known as Giant Hyena, is a prehistoric animal that belongs to the Hyaenidae family Dinocrocuta. The name "Dinocrocuta" is derived from the Greek words "deinos," meaning terrible, and "krokóttas," meaning hyena. It is an apt name for this impressive creature, known for its intimidating appearance and predatory skills.
Ancient Origins
The fossil remains of Dinocrocuta have been found in various parts of the world, including Asia, Africa, and Europe. These remains are estimated to be around 5 million years old, placing Dinocrocuta in a time known as the Pliocene epoch. During this period, the earth experienced significant climate change, leading to the extinction of many large mammal species.Dinocrocuta has a diverse geographical distribution, with fossil remains found in Eurasia and Africa. These findings suggest that this giant hyena had a wide habitat range and adapted well to different environments. This adaptability is one of the reasons for its survival and dominance during the Pliocene epoch.
Anatomy and Physical Characteristics
Dinocrocuta gigantea was a massive animal, easily dwarfing its modern-day descendant, the spotted hyena Dragonfish. It had an elongated skull, with a wide jaw and powerful teeth that were able to crush bones and tear through tough meat. Its limbs were muscular and athletic, allowing it to move quickly and chase down prey.This prehistoric hyena had an estimated length of 2.5 meters and a height of 1.5 meters. Its body shape was large and robust, with a broad chest and powerful shoulders. Its weight is estimated to be around 500 kilograms, making it one of the largest carnivorous mammals of its time.
One of the most striking physical characteristics of Dinocrocuta is its massive head, which made up almost a third of its body length. This large head was an adaptation to its carnivorous diet, providing space for its powerful jaw muscles and sharp teeth.
Hunting and Feeding Habits
As a carnivorous animal, Dinocrocuta relied on hunting and killing its prey to survive. Its massive size and powerful jaws made it a formidable predator that would have been feared by other animals of the Pliocene epoch. It is believed that this giant hyena hunted in packs, using its keen sense of smell and excellent hearing to locate prey.One of the most intriguing aspects of Dinocrocuta's feeding habits is its ability to consume bones entirely. Unlike modern-day hyenas that regurgitate undigested bones and fur, Dinocrocuta had a unique digestive system that allowed it to extract all the nutrients from its prey, including bones.
Habitat and Distribution
Dinocrocuta is known to have inhabited open grasslands and savannas, similar to the habitats of modern-day lions and hyenas. Its wide geographical distribution suggests that it was well adapted to different environments and could survive in various climates.Its fossil remains have been found in Asia, Africa, and Europe, indicating that it may have migrated to different regions following its prey. This migration could have been influenced by changes in climate or the availability of food sources.
Threats and Extinction
Like many other large mammals of the Pliocene epoch, Dinocrocuta became extinct due to climate change and competition for resources. As the earth's climate became cooler and drier, the open grasslands and savannas that Dinocrocuta inhabited started to disappear.The decline of its prey, such as the giant giraffe-like creature, Sivatherium, also contributed to its extinction. As the food sources for Dinocrocuta diminished, it became increasingly difficult for the species to survive and reproduce, leading to its eventual extinction.
Influence on Modern-Day Ecosystems
Some remnants of Dinocrocuta's hunting techniques can be seen in modern-day species, such as the spotted hyena. Like its prehistoric ancestor, the spotted hyena is a formidable predator known for its scavenging and hunting abilities. It is also able to consume bones entirely, similar to Dinocrocuta.The extinction of Dinocrocuta has also had an impact on the modern-day ecosystem. As a top predator, its presence would have affected the population and behavior of other animals, such as herbivores. Its disappearance may have led to changes in the food chain and the evolution of other species.
Conclusion
In the world of prehistoric creatures, Dinocrocuta stands out as one of the most fascinating and intimidating animals. Its massive size, powerful jaws, and carnivorous diet make it an incredible predator that once ruled the earth. Its extinction is a reminder of the ever-changing nature of our planet and the delicate balance of the ecosystem.Through the discovery and study of fossil remains, scientists continue to uncover the mysteries of Dinocrocuta and its place in the natural world. With its unique characteristics and impressive adaptations, this giant hyena will continue to captivate and fascinate animal lovers for generations to come.

Dinocrocuta
Animal Details Dinocrocuta - Scientific Name: Dinocrocuta gigantea
- Category: Animals D
- Scientific Name: Dinocrocuta gigantea
- Common Name: Dinocrocuta
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Hyaenidae
- Habitat: Open grasslands and savannas
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Eurasia, Africa
- Country of Origin: Various
- Location: Fossil remains have been found in Asia, Africa, and Europe
- Animal Coloration: Unknown
- Body Shape: Large and robust
- Length: Approximately 2.5 meters
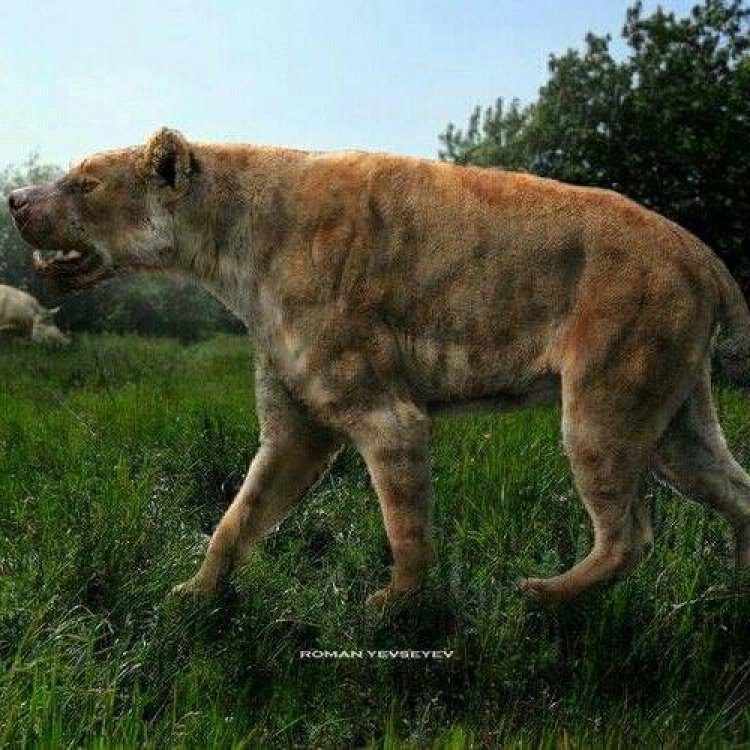

Dinocrocuta
- Adult Size: Unknown
- Average Lifespan: Unknown
- Reproduction: Unknown
- Reproductive Behavior: Unknown
- Sound or Call: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Unknown
- Social Groups: Unknown
- Behavior: Unknown
- Threats: Extinct
- Conservation Status: Extinct
- Impact on Ecosystem: Unknown
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Large size and hyena-like appearance
- Interesting Facts: Dinocrocuta is an extinct genus of hyena-like mammals that lived approximately 5 to 1.8 million years ago. It was significantly larger than modern hyenas and had a more robust build. Fossil evidence suggests that Dinocrocuta had a hypercarnivorous diet and may have been an apex predator in its environment.
- Predator: Unknown
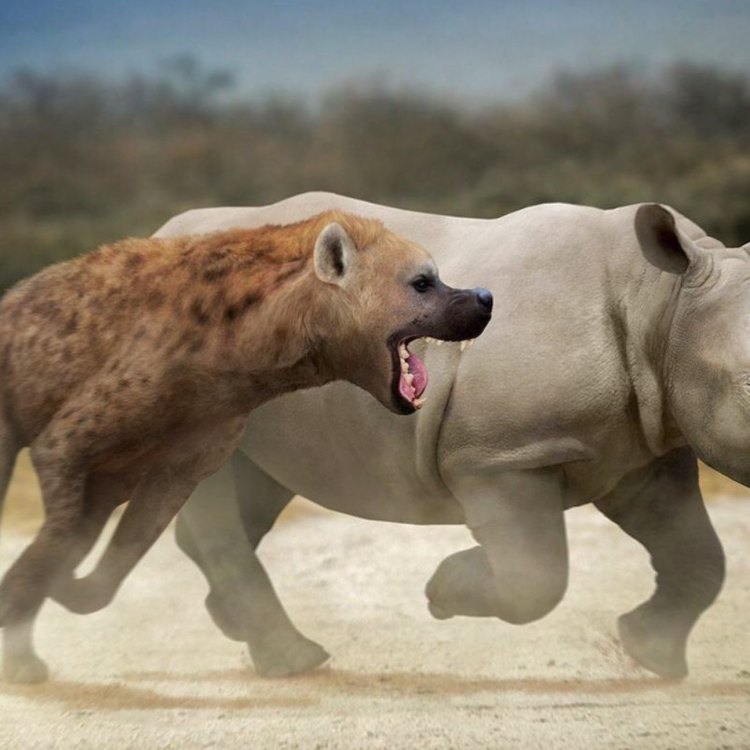

Dinocrocuta gigantea
The Enigmatic Dinocrocuta: Uncovering the Mysteries of the Extinct Hyena-Like Beast
In the history of our planet, numerous species have come and gone, leaving behind only traces of their existence in the form of fossils. Some of these species have become iconic and have captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike, like the dinosaurs or the wooly mammoths. However, there are still many lesser-known animals that have gone extinct, leaving behind little information about their lives and behavior. One such animal is the Dinocrocuta PeaceOfAnimals.Com.The Dinocrocuta, also known as the giant hyena, is an extinct genus of mammals that lived during the late Pliocene and early Pleistocene epochs, approximately 5 to 1.8 million years ago. The name Dinocrocuta comes from the Greek words "dino," meaning terrible, and "hyena," referring to its hyena-like appearance. While there is limited information about this enigmatic creature, it is believed to have been a fierce predator, dominating its environment as an apex predator.
Despite its intimidating name and reputation, many aspects of Dinocrocuta's life and behavior remain a mystery. In this article, we will delve deeper into the history and unique features of this extinct beast, seeking to unravel the secrets of the Dinocrocuta.
Appearance and Size
The exact size of Dinocrocuta is unknown, but it is estimated to have been significantly larger than modern hyenas. Based on fossil evidence, scientists believe that it could have weighed up to 500 kilograms (1100 pounds) and stood at a height of 1.2 meters (4 feet) at the shoulder Dunnock. This makes it one of the largest mammalian predators to have ever existed.One of the most distinctive features of Dinocrocuta is its hyena-like appearance. It had a large, powerful head with a long, robust jaw, similar to modern-day hyenas. Its teeth were massive, with oversized molars, making it a hypercarnivore, meaning it had a diet consisting mostly of meat. Its robust body was supported by strong limbs, allowing it to take down large prey.
Diet and Hunting Behavior
Fossil evidence suggests that Dinocrocuta was a fierce and efficient hunter. The structure of its jaws and teeth indicate that it had a powerful bite force, capable of crushing bones and tearing through tough animal hides. It is believed that it fed on large herbivores such as horses, antelopes, and elephants, as well as other carnivores like saber-toothed cats.Unlike modern hyenas, Dinocrocuta was not a scavenger. It had a well-developed sense of smell, allowing it to track and hunt down its prey. Its powerful jaws and massive teeth were also adapted for a crushing bite, which may have been used to immobilize its prey before delivering a fatal blow.
Behavior and Social Groups
Unfortunately, due to a lack of fossil evidence, little is known about Dinocrocuta's behavior and social structure. It is believed that they may have lived in groups, similar to modern-day hyenas, but this is still speculative. Scientists also suggest that the size and robustness of Dinocrocuta may have been an adaptation for hunting and scavenging large animals, indicating a potentially solitary lifestyle.Reproduction and Migration
As with many other aspects of the Dinocrocuta's life, its reproductive behavior and migration patterns remain a mystery. Without any living specimens to observe, scientists can only make educated guesses based on fossil evidence. It is believed that Dinocrocuta may have reproduced similarly to modern hyenas, giving birth to one or two cubs at a time, which were then raised and protected by their mother.Migration patterns are also difficult to determine, but there is some evidence that suggests that Dinocrocuta may have been nomadic, following the movements of their prey in search of food.
Threats and Extinction
Unfortunately, the Dinocrocuta's reign as an apex predator did not last long. It is believed that the main threat to Dinocrocuta's existence was competition with other large predators, such as saber-toothed cats. As the climate changed and other species evolved, the competition for food and resources became too intense, leading to the extinction of the Dinocrocuta.Extinction is a natural part of the evolutionary process, and while it may be concerning, it is a necessary occurrence for new species to emerge. However, the Dinocrocuta's extinction serves as a reminder of the fragility of life and the importance of preserving our planet's biodiversity.
Impact on the Ecosystem
The role of Dinocrocuta in its ecosystem is not fully understood, but it is believed that it played a crucial role as a top predator. As an apex predator, Dinocrocuta would have regulated the population of its prey, helping to maintain a balance within the ecosystem. After its extinction, the ecosystem may have undergone significant changes, with other species taking over its role as top predator.Human Use and Conservation Status
Unlike many extinct animals that have been hunted and exploited by humans, there is no evidence that Dinocrocuta was used by humans in any way. As it lived before the emergence of modern humans, it had no direct interaction with our species. Today, Dinocrocuta is classified as extinct, with no living specimens or known descendants.However, the study of this extinct creature is still essential in gaining a better understanding of our planet's history and evolution. By studying fossils and other remnants, scientists can piece together the puzzle of our planet's past and understand the role that different species played in shaping our world.
Fact or Fiction?
While much of what we know about Dinocrocuta is based on scientific research and evidence, there are some popular misconceptions about this creature. For example, it is often depicted as a fearsome giant with supernatural abilities in popular culture, but in reality, it was simply an apex predator living in a different time.Another common misconception is that Dinocrocuta was a direct ancestor of modern-day hyenas. However, there is no conclusive evidence to support this claim, and it is more likely that both the Dinocrocuta and modern hyenas evolved from a common ancestor.
The Mystery of the Dinocrocuta Continues
Despite being extinct for millions of years, the Dinocrocuta continues to capture our imagination and curiosity. Its unique features, such as its size and hyena-like appearance, make it an intriguing and fascinating animal to study. However, with limited fossil evidence available, much of this extinct creature's life remains a mystery, leaving us to imagine and speculate about its behavior and habits.The Dinocrocuta is a reminder that our planet's past is full of incredible and fascinating creatures, and it is our responsibility to learn from them and protect the fragile balance of our ecosystem. As we continue to uncover more information about this enigmatic beast, the mystery of the Dinocrocuta only grows, inspiring us to dig deeper and unravel the secrets of this extinct hyena-like predator.
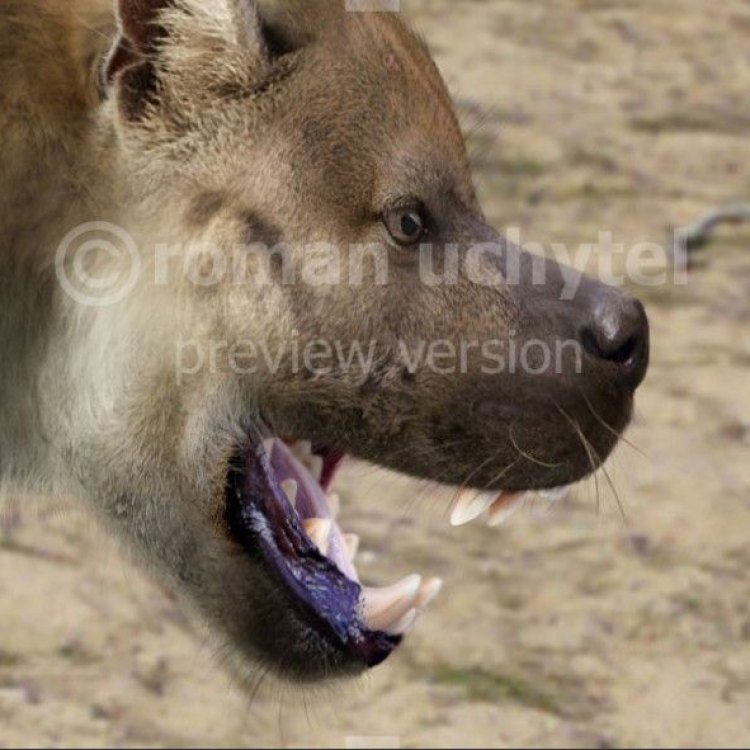

The Fascinating World of Dinocrocuta: A Giant Carnivorous Hyena
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












