
Dragonfish
Up to 15 centimeters (5.9 inches)
Dragonfish, also known as Stomiidae, are fascinating deep-sea creatures with a long and slender body. Growing up to 15cm, they are found in the darkest regions of the ocean. These powerful predators are a crucial part of the marine ecosystem, maintaining balance by feeding on smaller fish. Their striking bioluminescent features make them a must-see in the depths of the sea. #Dragonfish #DeepSeaCreatures #MarineLife
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Dragonfish
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Marine
Unveiling the Mysteries of the Mysterious Dragonfish
Deep in the dark, mysterious depths of the ocean, lies a creature so elusive and fascinating that it continues to captivate both scientists and nature enthusiasts alike - the Dragonfish, also known as Photoblepharon in the scientific community. This mystical creature, found in tropical and subtropical waters, has managed to remain a mystery to many, with its unique characteristics and abilities. Join us on a journey to uncover the secrets of this intriguing species.An Introduction to the Dragonfish
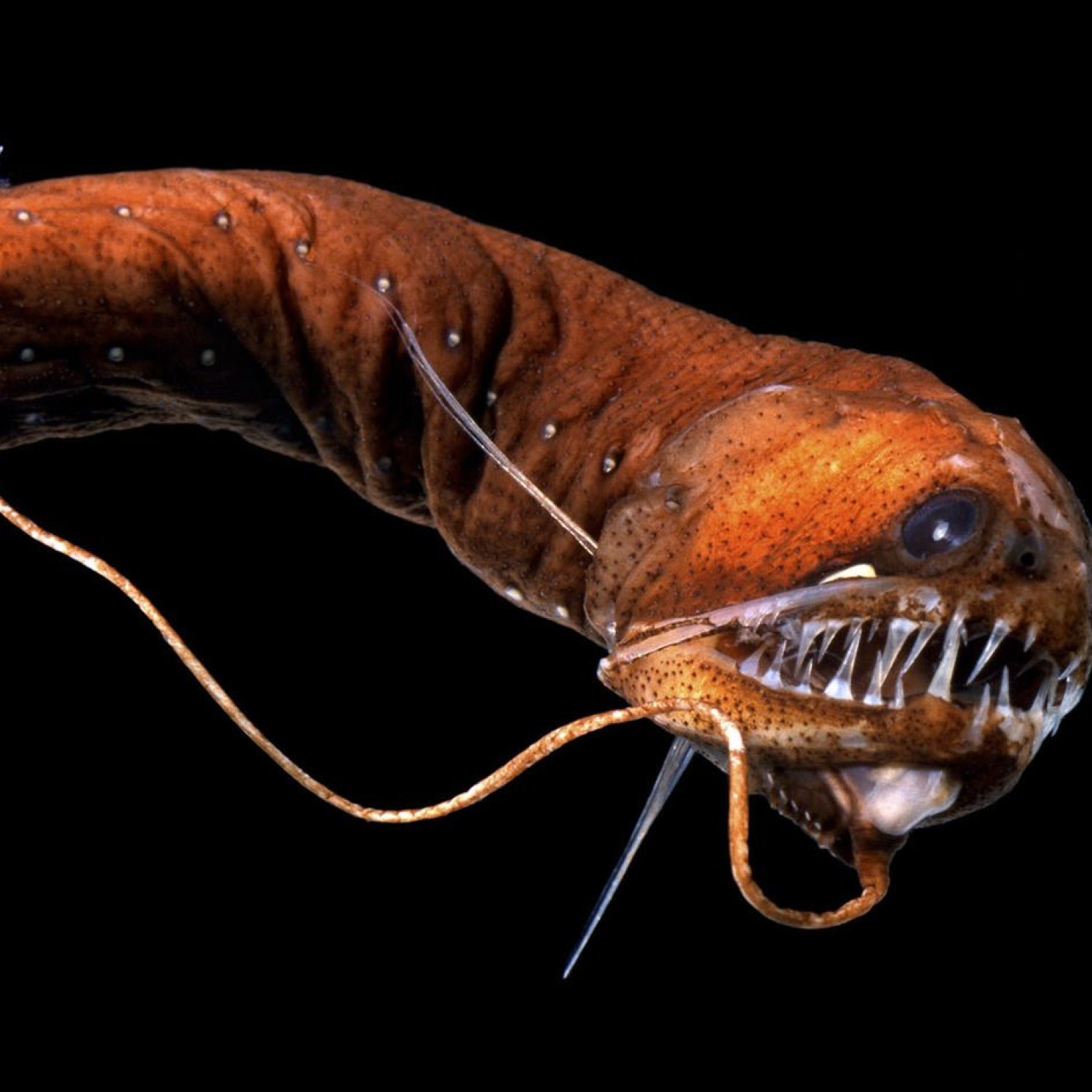
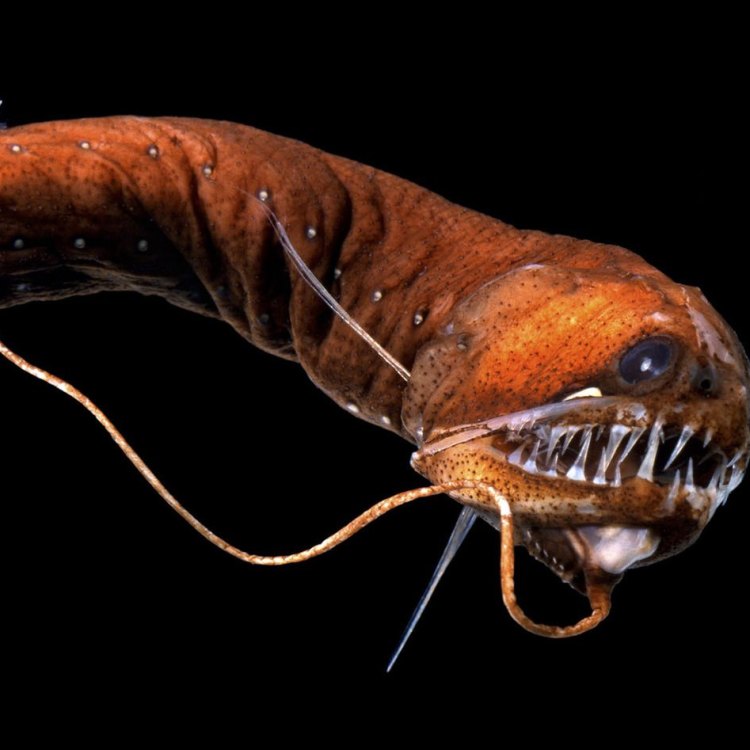
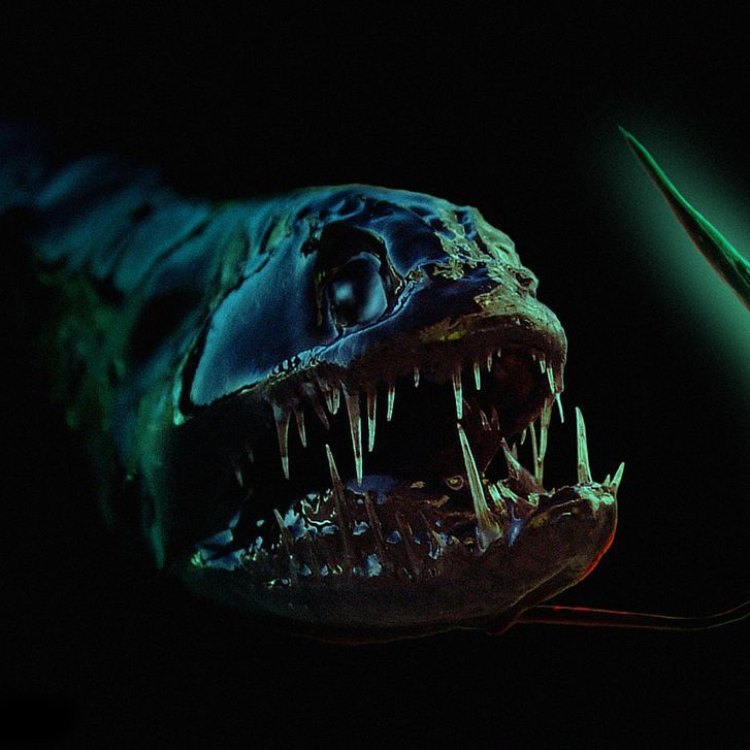
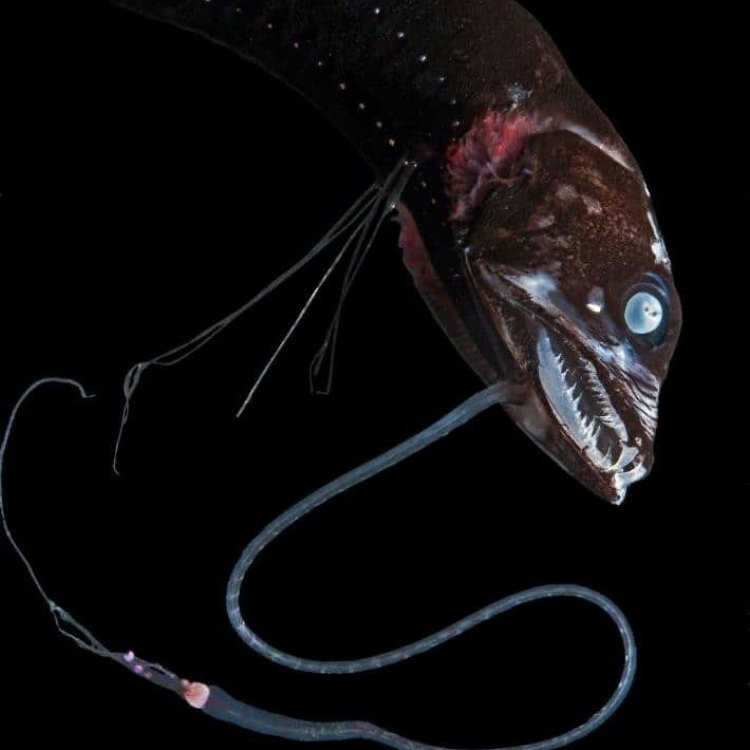
The Dragonfish belongs to the Animalia kingdom, Phylum Chordata, Class Actinopterygii, Order Stomiiformes, and Family Stomiidae Dragonfish. With its elongated, eel-like body and varying shades of black and red coloration, this species holds a truly remarkable appearance. It is commonly found in the Indo-Pacific region, in the deep-sea regions, making its presence known at depths of up to 5000 feet. Its name "dragonfish" is derived from its fierce-looking appearance similar to a dragon, with its sharp teeth, and glowing red photophores (light-producing organs) on its underside.The Dragonfish Habitat
Living in the deep-sea regions, the Dragonfish is known to inhabit a variety of marine habitats, ranging from the ocean floor to mid-water depths. They are often found near seamounts, at the edge of continental shelves, or in the vicinity of underwater volcanoes. Due to their elusive nature, it is challenging to study their behavior and habitat preferences. However, it is known that they require dark environments, as they have highly sensitive eyes that are adapted to low light levels.Eating Habits of the Dragonfish
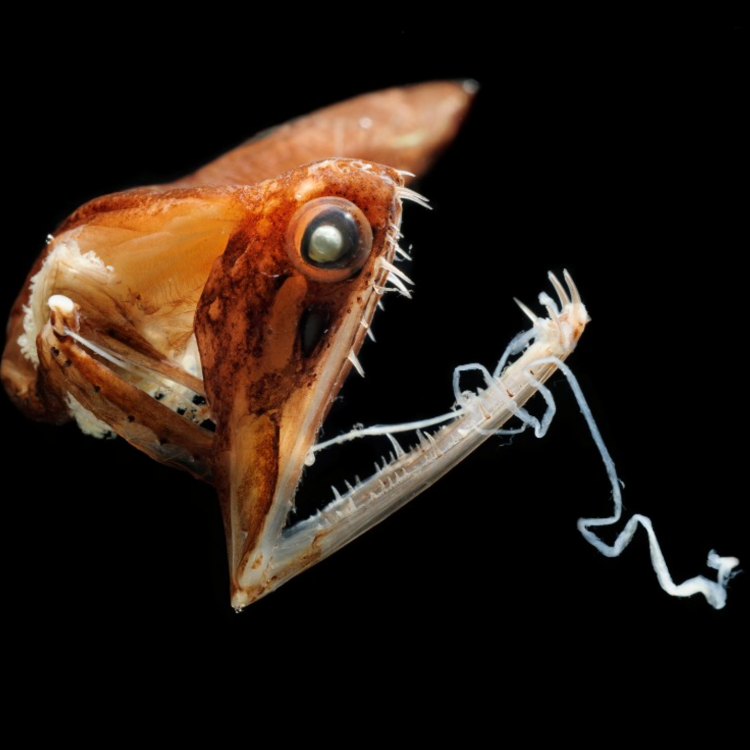
The Dragonfish is a carnivorous predator, with a uniquely modified lower jaw that can be protruded to catch its prey. As it lurks in the darkness of the ocean, it relies on its keen senses and specialized organs to hunt Dunnock. The photophores on its underside emit light, attracting unsuspecting prey towards its mouth. In addition, it also has a long, thin tongue-like appendage on its chin that is covered in sharp, needle-like teeth, used to scoop up small crustaceans, fish, and even other dragonfishes.The Geographical Distribution of the Dragonfish
The Dragonfish has a vast geographical distribution, found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world. With its main concentration in the Indo-Pacific region, sightings have also been reported in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. As they reside in the deep oceans, it is highly difficult to track their movements and distribution accurately. With the advancements in technology, scientists have been able to use remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to capture footage of these elusive creatures, giving us a glimpse into their world.The Dragonfish in Its Natural Habitat
As one of the most mysterious and unexplored habitats on our planet, the deep sea is home to a diverse range of marine life, including the Dragonfish. These creatures have evolved unique adaptations and abilities to survive in this challenging environment. With limited sunlight penetrating the depths of the ocean, the Dragonfish has developed its own light source through its photophores to attract prey and potential mates.One of the most fascinating features of the Dragonfish is its ability to produce light through bioluminescence - the production and emission of light by a living organism. This unique ability allows them to communicate and attract prey in the dark depths of the ocean. In addition, the Dragonfish also has a specialized organ, called the barbel, on its chin, which is used to detect and lure prey towards its mouth.
The Dragonfish and Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is a common phenomenon in marine animals, with over 90% of deep-sea species possessing the ability to produce light. However, the Dragonfish stands out with its distinctive use of bioluminescence. In the deep-sea environment, where light is scarce, bioluminescence serves as a crucial tool for survival, especially for hunting and finding mates.The glowing red photophores on the Dragonfish's underside are responsible for producing light. These photophores are filled with a light-producing chemical known as luciferin, which is activated by an enzyme called luciferase when the fish moves, causing a chemical reaction that produces light. This light can be either steady or flashing, depending on the species and its intent.
The Influence of AI in Studying the Dragonfish
With the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in research, scientists have been able to gain a better understanding of the Dragonfish's behavior, habitat, and evolution. AI has been instrumental in analyzing the vast amount of data collected by ROVs and other underwater vehicles, making it possible to study these elusive creatures in their natural habitat without disturbing or harming them.AI-powered algorithms have also been utilized to identify and classify different species of Dragonfish based on footage and images collected. This has been a groundbreaking discovery, as it has allowed researchers to get a more accurate estimate of the population of Dragonfish in the ocean.
The Threats Faced by the Dragonfish
As with many deep-sea creatures, the Dragonfish faces several threats due to human activities. The increase in deep-sea fishing, mining, and oil exploration has brought about significant concerns for the survival of this species. As they reside in the deep, dark regions of the ocean, they are often caught as bycatch in fishing nets and killed. The disruption of the deep-sea environment through oil spills and mining can also have a detrimental impact on the Dragonfish's habitat and food sources.In addition, with the rise in demand for rare and exotic marine species in the pet trade market, there are concerns that the Dragonfish might be illegally captured and sold. As with any wild animal, their captive survival rate is low, and their removal from their natural habitat can significantly affect their population.
The Conservation Efforts for the Dragonfish
The Dragonfish is not currently listed as an endangered species, but there is still much to learn about these creatures due to their deep-sea habitat. As a result, there are limited conservation efforts in place specifically for the Dragonfish. However, with the increase in ocean exploration and technological advancements, it is likely that more conservation programs will be put in place to protect this unique species in the future.Furthermore, it is essential for individuals to be aware of the impact of their actions on the deep-sea environment and its inhabitants. Simple actions, such as avoiding the purchase of exotic and rare marine species, can go a long way in preserving the natural balance of our oceans.
Conclusion
The Dragonfish is undoubtedly an enigma of the deep sea, with its unique adaptations, abilities, and elusive nature. Despite being a challenging species to study, the advancements in technology and AI have allowed us to gain a better understanding of this remarkable creature and its role in the ecosystem. However, it is crucial that we continue to protect and preserve their natural habitats to ensure the survival of this mysterious and captivating species. So, let us continue to unravel the mysteries of the deep sea, one creature at a time.

Dragonfish
Animal Details Dragonfish - Scientific Name: Photoblepharon
- Category: Animals D
- Scientific Name: Photoblepharon
- Common Name: Dragonfish
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Actinopterygii
- Order: Stomiiformes
- Family: Stomiidae
- Habitat: Marine
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Tropical and subtropical waters
- Country of Origin: Mainly found in the Indo-Pacific region
- Location: Deep-sea regions
- Animal Coloration: Varying shades of black and red
- Body Shape: Long and slender
- Length: Up to 15 centimeters (5.9 inches)

Dragonfish
- Adult Size: Up to 15 centimeters (5.9 inches)
- Average Lifespan: Unknown
- Reproduction: Sexual reproduction
- Reproductive Behavior: Males produce bioluminescent organs to attract females
- Sound or Call: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Unknown
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Predatory
- Threats: Unknown
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: As top predators, they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the marine food chain
- Human Use: Not commercially important
- Distinctive Features: Long, fang-like teeth and bioluminescent organs
- Interesting Facts: Dragonfish have long, sharp teeth that are capable of folding back into a groove in the roof of their mouth when not in use. They also have a specialized light-emitting organ called a photophore, which allows them to produce light for communication and attracting prey. Dragonfish are known for their ability to emit red light, which is invisible to most other deep-sea creatures and helps them remain hidden from predators.
- Predator: Unknown
Photoblepharon
The Enigmatic Dragonfish: Secrets of the Deep
In the vast depths of the ocean, there lives a creature so unique and mysterious that it has captured the curiosity of scientists and ocean enthusiasts alike. The dragonfish, also known as the viperfish, is a fascinating species that inhabits the dark and cold waters of the deep sea. With its distinctive features and intriguing behaviors, the dragonfish holds many secrets waiting to be uncovered.The dragonfish belongs to the family Stomiidae, which is a group of deep-sea fishes known for their elongated bodies and sharp teeth PeaceOfAnimals.Com. They typically range from 8 to 15 centimeters in length, making them relatively small compared to other deep-sea creatures. However, what they lack in size, they make up for in their unique adaptations and behaviors.
One of the most distinct features of the dragonfish is their long, fang-like teeth. These teeth are not only used for capturing prey but also for mating. Male dragonfish have specialized teeth called photophores that emit light to attract females during the reproductive season. This bioluminescent display is essential as male and female dragonfish do not have any contact with each other until mating.
Speaking of bioluminescence, this is one of the most intriguing aspects of the dragonfish. Like other deep-sea creatures, dragonfish use light to communicate, attract prey, and navigate the dark depths of the ocean. However, what makes them truly unique is their ability to produce red light, which is invisible to most other deep-sea creatures Dinocrocuta. This red light enables them to remain undetected by predators, making them masters of disguise.
But how do they produce this red light? The answer lies in their specialized light-emitting organ called a photophore. This organ contains bioluminescent bacteria, which produce the red light. As the bacteria feed on the nutrients provided by the dragonfish, they give off a subtle glow, making the dragonfish invisible to other deep-sea creatures that cannot see red light.
Another interesting fact about dragonfish is their ability to fold back their teeth into a groove in the roof of their mouth when not in use. This feature allows them to conserve energy and reduce the risk of damaging their teeth in the harsh deep-sea environment.
The reproductive behavior of dragonfish is also quite fascinating. As mentioned earlier, male dragonfish use their light-emitting organs to attract females. However, the females are much larger than the males and have a unique ability to store sperm for an extended period. This means that one successful mating can lead to multiple pregnancies, making the population of dragonfish relatively stable.
Despite being solitary creatures, dragonfish play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem. As top predators, they feed on a variety of fish, crustaceans, and squid, keeping their populations in check. Without dragonfish, these prey species could potentially overpopulate and disrupt the delicate balance of the marine food chain.
Dragonfish live in the depths of the ocean, making them challenging to study. As a result, there is limited information available about their average lifespan, migration patterns, or threats they may face in their natural habitat. However, due to their deep-sea habitat and elusive nature, they are not considered commercially important, nor have they been evaluated for conservation status.
One aspect that sets dragonfish apart from other deep-sea creatures is the mystery surrounding them. Despite ongoing efforts to study and understand these fascinating creatures, there are still so many unknowns about their behaviors, biology, and ecology. This just goes to show how little we know about the vast depths of the ocean and the creatures that live there.
In recent years, advances in technology and deep-sea exploration have shed some light on the world of dragonfish. Scientists have been able to capture images and videos of these elusive creatures in their natural habitat, providing valuable insights into their behavior and adaptations. However, there is still much to learn, and the dragonfish continues to intrigue and amaze researchers and the public alike.
In conclusion, the dragonfish is a truly remarkable creature, having adapted to thrive in one of the most hostile environments on Earth. From its long, fang-like teeth to its specialized light-emitting organs, the dragonfish has many unique features that make it stand out from other deep-sea creatures. Not only is it a top predator, but it also plays a vital role in the functioning of the marine ecosystem. As the unexplored depths of the ocean continue to reveal their secrets, we can only hope to unravel more mysteries surrounding this enigmatic species – the dragonfish.

Unveiling the Mysteries of the Mysterious Dragonfish
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












