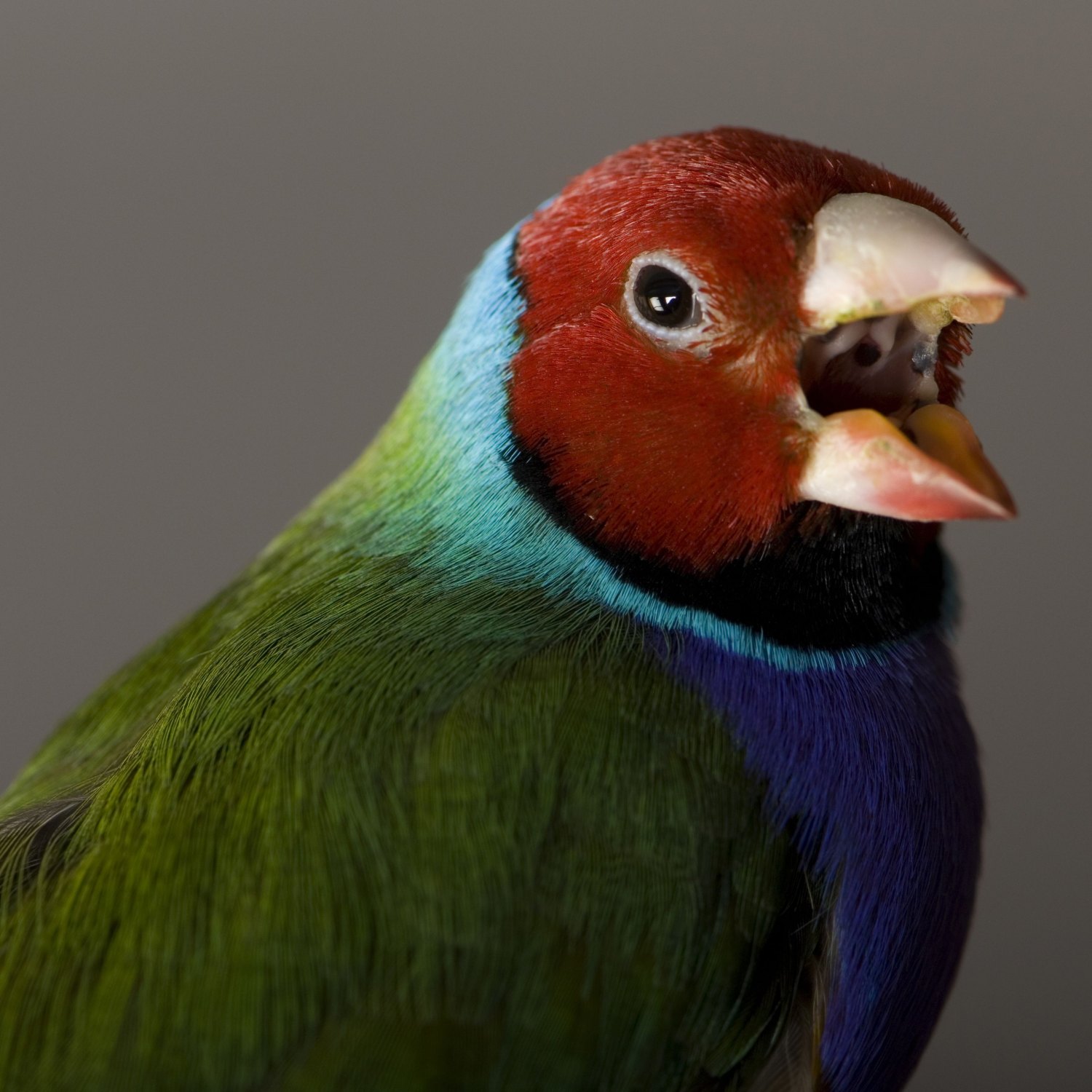
Finch
Varies depending on the species, ranging from 10 to 20 centimeters
. Finches are beloved birds found all over the world with a length ranging from 10 to 20 cm. Their small but strong bodies, short beaks, and sturdy legs make them well-adapted for survival in various locations worldwide. Belonging to the Passeridae family, these charming birds make for delightful pets and are a treat to watch in their natural habitats.
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Finch
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Various habitats including forests, grasslands, and deserts
The Secret Lives of Finches
Finches are a diverse group of birds that belong to the family Passeridae. They are found on all continents except for Antarctica and can be seen in various habitats including forests, grasslands, and deserts. These small, colorful birds have captured the fascination of bird enthusiasts and scientists alike due to their unique features and behaviors.In this article, we will delve into the world of finches and explore their fascinating characteristics, their diverse habitats, and their importance in the natural world Finch.
The Taxonomy of Finches
Before we dive into the intriguing world of finches, let's first understand their taxonomy. The scientific name for finches is Passeridae, and they belong to the kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, and class Aves. Within the order Passeriformes, finches are the largest family, comprising more than 140 species.The Many Faces of Finches
One of the most mesmerizing aspects of finches is their varied appearance. They come in a range of colors, shapes, and sizes, making them a delight for bird watchers to observe. Some species have striking colors, while others are more subtly colored, but each one is unique in its own way.Finches have a compact body with a round head, short neck, and thick, sturdy legs. Their beaks are short and strong, perfect for cracking open seeds, their primary source of food. The color of their plumage varies greatly, with some species displaying vibrant hues of blues, greens, and reds, while others have muted shades of brown and gray Flycatcher. This diversity of colors not only adds to their beauty but also serves as a form of camouflage, helping them blend into their natural surroundings.
Some of the most well-known species of finches are the zebra finch, yellow warbler, and the red-billed firefinch. Each one is distinct in appearance and can be found in different parts of the world.
A Habitat for Every Finch
Finches are highly adaptable birds, and they can be found in a variety of habitats. They are predominantly found in forests, grasslands, and deserts, but can also be seen in urban areas and cultivated lands. The wide range of habitats they occupy is a testament to their resilience and ability to thrive in different environments.One of the most interesting facts about finches is that they have evolved to fill different niches. Some species have short, strong beaks, perfect for cracking open hard seeds in dry environments, while others have longer, more delicate beaks suited for obtaining nectar from flowers. This adaptation allows them to survive in different habitats, each with its own unique set of challenges.
The Finicky Eaters
Finches are primarily seed eaters, and their beaks are specifically adapted for this type of diet. They have a unique mechanism that allows them to grind and crack open various types of seeds, making them well-equipped for consuming their preferred food.However, some species of finches are not limited to just seeds and have a diverse diet. For example, the red-billed firefinch also eats insects and fruits, while the yellow warbler feeds on insects and spiders. This variety in their diet makes them an essential link in the food chain, as they contribute to controlling insect populations and aid in pollination.
A World Tour of Finches
Finches can be found in various locations around the world, making them a truly global bird species. They are present in countries such as Australia, Peru, Japan, and the United States, among others. Their unique characteristics and their ability to survive in different environments have allowed them to thrive in diverse regions of the world.Whether you are in the mountains of Peru or the grasslands of Australia, chances are you will spot a finch darting through the sky or perched on a tree branch. These birds have adapted to their surroundings and have become an integral part of the ecosystems they inhabit.
Finches and Their Importance in the Natural World
Aside from their captivating appearances, finches also play a vital role in the natural world. As we mentioned earlier, they help control insect populations and contribute to the pollination of plants. But that's not all; their presence also serves as an indicator of the health of their habitats.Scientists and researchers often use finches as an indicator species to monitor the health of habitats and predict changes in the ecosystem. As finches are sensitive to environmental changes, their decline or disappearance can signal potential problems in their habitat, which can ultimately affect other species in the ecosystem.
A Fascination and Inspiration
Apart from their ecological importance, finches have piqued the interest of humans for centuries. Their unique behaviors and striking appearances have inspired many artists, writers, and poets throughout history.One of the most famous works inspired by finches is Charles Darwin's "On the Origin of Species." Darwin's study of the Galápagos finches, which played a crucial role in the development of his theory of evolution, highlights the impact and importance of these birds.
Today, finches continue to fascinate scientists and bird enthusiasts, providing insight into the wonders of the natural world and serving as a source of inspiration for many.
Rising Threats to Finches
Despite their resilience and adaptability, finches are facing increasing threats to their survival. Habitat loss, climate change, and the introduction of non-native species are some of the most significant challenges that finches are facing today.Human activities such as deforestation and development projects often disrupt their habitats, making it difficult for them to find food and shelter. Additionally, the introduction of non-native species can lead to competition for resources and the spread of diseases that can have a devastating effect on finch populations.
It is essential for us, as stewards of our planet, to recognize the value of finches and the role they play in the natural world. We must take measures to conserve their habitats and protect them from the ever-increasing threats they face.
The Wonders of Finches: A Never-Ending Story
In conclusion, finches are fascinating creatures that continue to capture our imagination and inspire us in many ways. From their diverse appearances to their critical role in the ecosystem, these birds are a testament to the incredible diversity of life on our planet.As we continue to learn more about finches, we must also work towards their conservation and protection. By doing so, we can ensure that these beautiful birds will continue to thrive and enchant us with their presence for years to come.
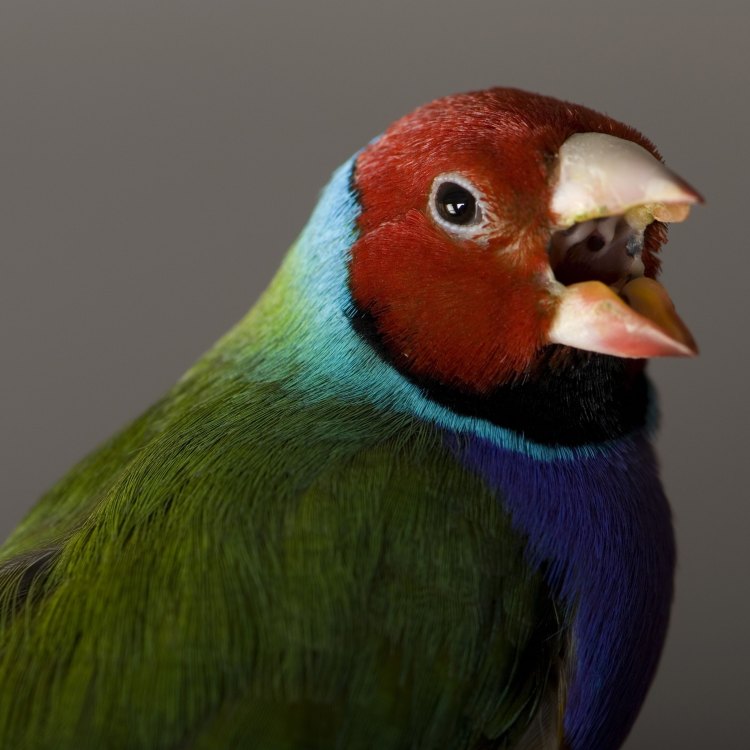

Finch
Animal Details Finch - Scientific Name: Passeridae
- Category: Animals F
- Scientific Name: Passeridae
- Common Name: Finch
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves
- Order: Passeriformes
- Family: Passeridae
- Habitat: Various habitats including forests, grasslands, and deserts
- Feeding Method: Primarily seed eaters, but some species also eat insects and fruits
- Geographical Distribution: Found on all continents except Antarctica
- Country of Origin: Various countries
- Location: Various locations worldwide
- Animal Coloration: Varies greatly depending on the species
- Body Shape: Small, compact bodies with short beaks and strong legs
- Length: Varies depending on the species, ranging from 10 to 20 centimeters
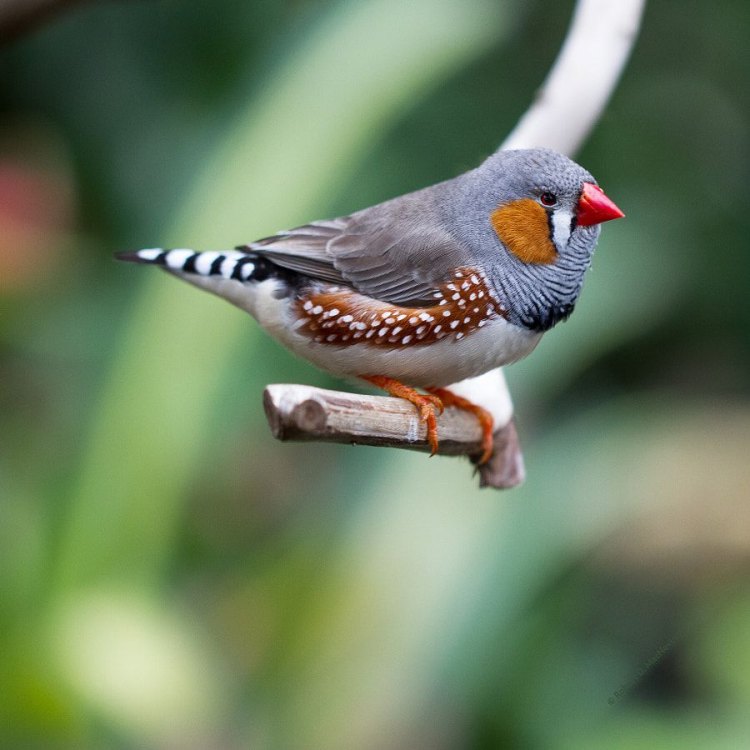

Finch
- Adult Size: Varies depending on the species, ranging from 10 to 20 centimeters
- Average Lifespan: Varies depending on the species, ranging from 5 to 10 years
- Reproduction: Sexual reproduction
- Reproductive Behavior: Monogamous, with pair bonding and both parents involved in raising the young
- Sound or Call: Varies depending on the species, but most finches are known for their melodious songs
- Migration Pattern: Some species are migratory, while others are resident
- Social Groups: Many species form large flocks
- Behavior: Active, social, and highly vocal
- Threats: Habitat loss, predation, and the illegal pet trade
- Conservation Status: Varies depending on the species, with some species being of least concern and others being endangered or threatened
- Impact on Ecosystem: Pollination of plants and seed dispersal
- Human Use: Kept as pets and used in aviculture
- Distinctive Features: Colorful plumage, especially in males, and unique beak shapes adapted for different types of feeding
- Interesting Facts: Finches played a significant role in the development of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution
- Predator: Various predators depending on the habitat, including birds of prey and snakes
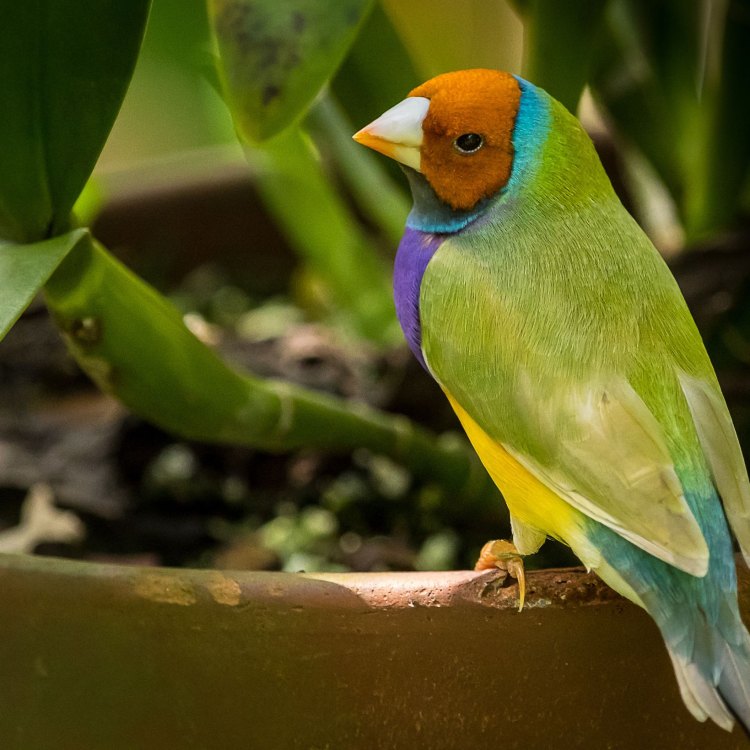

Passeridae
The Fascinating World of Finches: Their Behavior, Role in Ecosystems, and Impact on Human Culture
When we think of birds, big and majestic species like eagles or ostriches might come to mind. However, there is a small and incredibly diverse family of birds that often goes unnoticed – finches. These small and colorful birds have captured the attention of scientists, aviculturists, and bird lovers alike for centuries. From their beautiful songs to their important role in ecosystems, finches are truly fascinating creatures PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Adult Size and Lifespan
Finches belong to the family Fringillidae, which includes more than 200 species. They can be found in diverse habitats such as forests, woodlands, grasslands, and even urban areas. Their size varies depending on the species, with most finches ranging from 10 to 20 centimeters in length. They may not be as big as other birds, but their small size only adds to their charm.
The average lifespan of finches also varies depending on the species, with most living between 5 to 10 years. However, there have been reports of some species living up to 12-15 years in captivity. In the wild, finches face many threats that can reduce their lifespan, including habitat loss, predation, and the illegal pet trade.
Reproduction and Behavior
Like many other bird species, finches reproduce through sexual reproduction. However, what sets them apart is their unique reproductive behavior False Coral Snake. Most finches are monogamous, forming strong pair bonds that can last for multiple breeding seasons. Both parents take part in building the nest, incubating the eggs, and raising the young. This parental care is crucial for the survival of the offspring and is a behavior rarely seen in other bird families.
Aside from their reproductive behavior, finches are known for their active, social, and highly vocal nature. They are often seen in large flocks, communicating with each other through a variety of songs and calls. These melodious sounds are one of the most distinctive features of finches and are highly appreciated by bird enthusiasts.
Migration and Social Groups
The migration patterns of finches also vary depending on the species. Some are migratory, while others are resident, staying in the same area throughout the year. The migratory behavior of finches is influenced by factors such as food availability and weather conditions. Those that reside in colder regions may migrate to warmer areas during the winter, while those living in tropical habitats may stay in the same place year-round.
In terms of social groups, many species of finches form large flocks, often made up of their own kind or mixed with other bird species. This social behavior provides protection against predators and also allows for better foraging opportunities. It is not uncommon to see hundreds of finches gathered in one area, making for a spectacular sight.
Threats and Conservation Status
Unfortunately, like many other wildlife species, finches face numerous threats in their natural habitats. One of the main threats is habitat loss, as their preferred habitats are often destroyed for agricultural or urban development. This not only deprives finches of a place to breed and forage but also disrupts their food chain, making it difficult for them to survive.
Predation is another significant threat to finches. They are hunted by various predators, including birds of prey and snakes. Finches have also been captured for the pet trade, which is illegal in many countries. This trade poses a threat to the survival of certain species, especially those with small populations.
The conservation status of finches varies depending on the species. Some are of least concern, while others are endangered or threatened. It is crucial to implement conservation efforts to protect these beautiful birds and their habitats for future generations to enjoy.
Impact on Ecosystems and Human Culture
Aside from their beauty and unique behavior, finches play a crucial role in ecosystems. As seed-eating birds, they contribute to the pollination of plants and the dispersal of seeds. Their beaks are specially adapted for different types of feeding, making them important agents of ecosystem function and diversity.
Finches have also played a significant role in human culture. They are widely kept as pets and are considered ideal for aviculture due to their hardiness, adaptability, and beautiful songs. In fact, many species of finches have been domesticated and bred in captivity, leading to the development of different color mutations that are highly sought after by bird enthusiasts.
Moreover, finches have played a significant role in the development of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution. While traveling on the HMS Beagle, Darwin collected various bird species, including finches, from the Galapagos Islands. He noticed that the finches on different islands had distinct beak shapes, which he theorized had adapted to their specific diets. This observation led to his theory of natural selection, which revolutionized the field of biology.
Distinctive Features and Interesting Facts
When we think of finches, the first thing that comes to mind is their colorful plumage. Males are often more brightly colored than females, with vibrant feathers ranging from reds and yellows to blues and greens. This colorful display serves as a way for males to attract females during breeding season. In contrast, female finches have more subdued colors that help them blend in with their surroundings to protect their young.
Another unique feature of finches is their beak shapes, which are adapted for various types of feeding. For example, finches that mainly feed on seeds have thicker, stronger beaks, while those that feed on insects and nectar have thinner, more delicate beaks. This versatility in feeding allows finches to thrive in different environments and contribute to the overall balance of ecosystems.
In addition to their distinctive features, finches have some interesting facts that have captured the interest of scientists and bird enthusiasts. For instance, they are known to build intricate nests made of grass, twigs, and feathers. They also have a unique way of drinking water, known as "dip drinking," where they dip their beaks into the water rather than drinking directly from it. These little-known facts only add to the intrigue and charm of these small but magnificent birds.
In conclusion, finches may be small in size, but they have a significant impact on ecosystems and human culture. From their diverse reproductive behavior to their beautiful songs and distinctive features, finches continue to fascinate and inspire us. It is our responsibility to protect and preserve these wonderful birds for future generations to appreciate and enjoy. Next time you see a finch in your backyard or on a nature walk, take a moment to appreciate their beauty and remember the important role they play in our world.
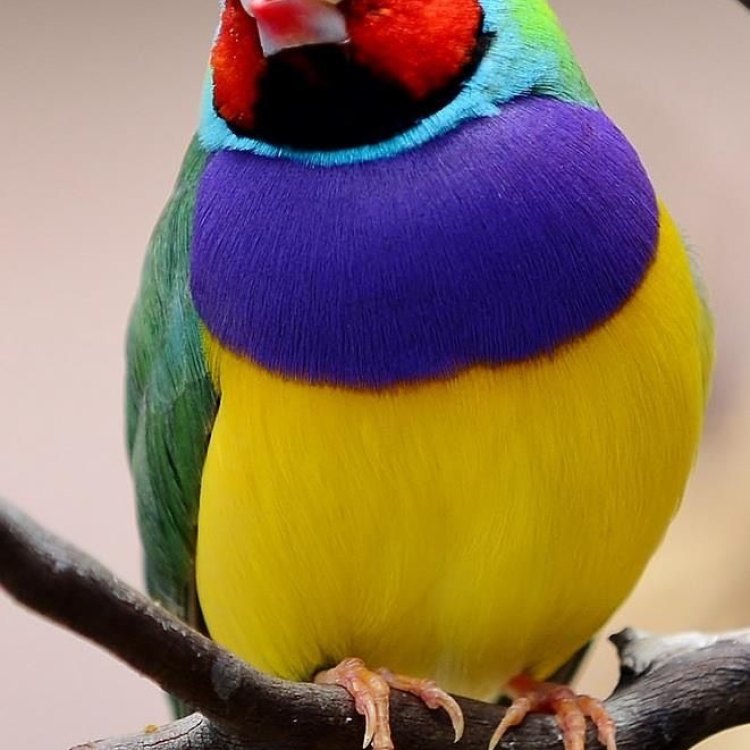

The Secret Lives of Finches
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.