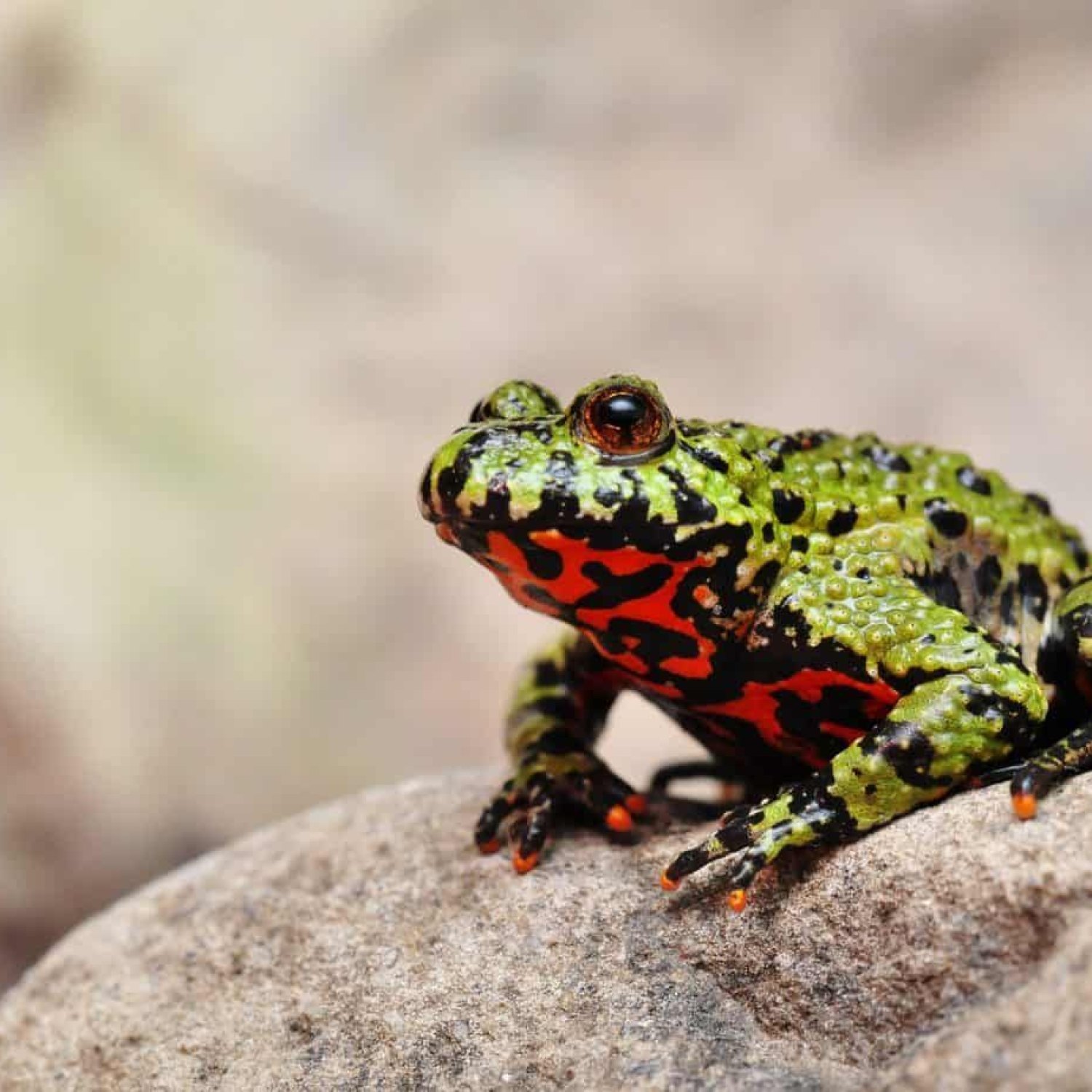
Fire Bellied Toad
5-10 centimeters
The Fire Bellied Toad is a small, plump-bodied amphibian found in Eastern China, Korea, and northeastern Russia. With a smooth skin and short legs, it can grow up to 5-10 centimeters in length. It belongs to the family Bombinatoridae and is known for its distinctive bright red or orange markings on its belly. These toads are popular pets for amphibian enthusiasts and can be easily cared for with a proper habitat and diet. #FireBelliedToad #amphibians #petcare
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Fire Bellied Toad
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Semi-aquatic habitats such as ponds, swamps, and marshes
The Fascinating Fire Bellied Toad: A Jewel of Eastern Asia
The Fire Bellied Toad, scientifically known as Bombina orientalis, is a true gem of Eastern Asia. This small, colorful amphibian with its vibrant orange and red underside is a sight to behold. It belongs to the family Bombinatoridae and is commonly found in countries like China, Korea, and northeastern Russia.But what makes this toad so special? Let's take a deep dive into its characteristics, habitat, and behavior to understand why it's such a fascinating creature Fire Bellied Toad.
Where Can You Find Fire Bellied Toads?
The Fire Bellied Toad is endemic to Eastern Asia, specifically in countries like China, Korea, and northeastern Russia. Within these countries, they can mostly be found in eastern China, Korea, and the Primorsky Krai region of Russia.They have a semi-aquatic habitat and can be found in a variety of wetland habitats, such as ponds, swamps, and marshes. These habitats provide the perfect combination of water and land that are essential for their survival.
The Physical Appearance of Fire Bellied Toads
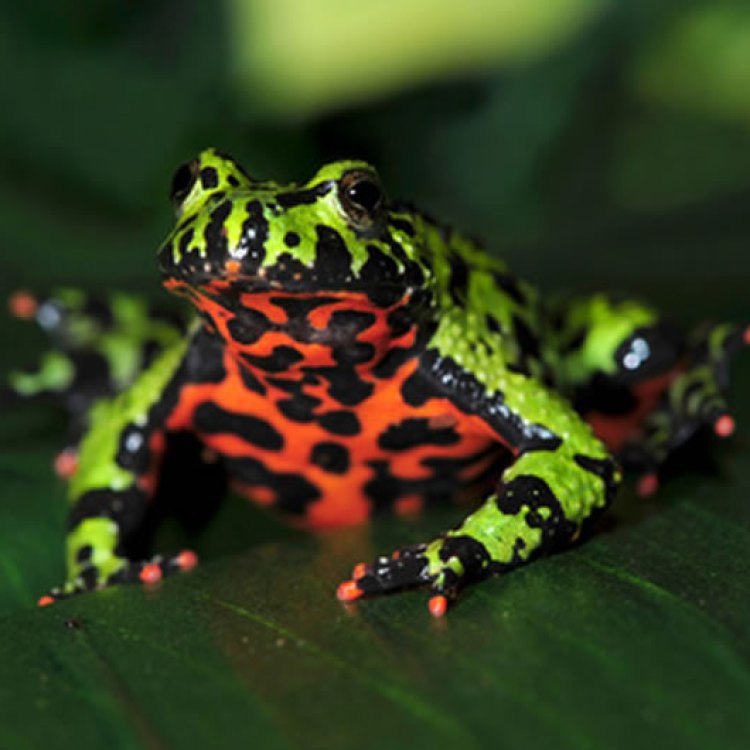
One look at a Fire Bellied Toad, and you'll be mesmerized by its vibrant colors. These toads have a bright green or brownish-black color on their dorsal side, with distinctive black markings. However, it's their ventral side that truly stands out. It is bright orange to red, with black spots and stripes, making them resemble a fiery belly.Their body shape is small and plump, with a short snout, short legs, and smooth skin Ferret. On average, they can grow up to 5-10 centimeters in length, making them one of the smaller species of toads.
The Diet of Fire Bellied Toads
The Fire Bellied Toad is a carnivorous animal, and its diet mainly consists of insects and other invertebrates. They have a keen sense of smell, allowing them to locate their prey easily. Once they spot their prey, they use their long sticky tongue to catch them.These toads are known to eat a variety of insects, including crickets, beetles, moths, and earthworms. They have also been observed snacking on smaller amphibians like tadpoles and even smaller Fire Bellied Toads. Being a dominant predator, they play a vital role in controlling the population of pest insects in their habitat.
Adaptations and Defense Mechanisms
Being a semi-aquatic species, Fire Bellied Toads have unique adaptations to help them survive in their habitat. One of the most notable adaptations is their brightly colored undersides. This is known as aposematic coloration and serves as a warning to potential predators.If threatened, these toads can also secrete a toxic substance through their skin, which acts as a defense mechanism. The toxins are not fatal to humans, but they can cause irritation, so it's best to admire these toads from a safe distance.
Their smooth skin also helps them to camouflage in the wetland environment, making them difficult to spot by predators or prey. They also have the ability to inflate their bodies, making it difficult for predators to swallow them.
The Lifecycle of Fire Bellied Toads
Like all amphibians, Fire Bellied Toads start their life as an egg. The males of this species will gather in shallow water to call out to females with their unique croaking sound. Once the females lay their eggs, the males will fertilize them externally.The tadpoles hatch from the eggs and spend the majority of their time in the water. As they grow, they develop front and back legs, and once fully developed, they will leave the water and become terrestrial adults.
One unique characteristic of Fire Bellied Toad tadpoles is that they have a transparent belly, allowing you to see their internal organs. This is known as "glassification" and helps them absorb sunlight and warmth in the water.
Conservation Status
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has classified the Fire Bellied Toad as a species of least concern. The toad has a wide distribution, and there have been no significant threats identified to its population.However, like many other amphibians, these toads are sensitive to habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. It is essential to protect their wetland habitats and ensure the quality of water in which they live to maintain their population.
The Role of Fire Bellied Toads in Human Culture
Fire Bellied Toads hold a special place in human culture, particularly in traditional Chinese medicine. It is believed that their secretions have medicinal properties and can be used to treat various ailments.In Korean culture, Fire Bellied Toads are seen as a symbol of good luck and are often depicted in paintings and ceramics. They are also a popular pet in the exotic pet trade, although this practice should be discouraged as it can negatively impact their wild populations.
The Growing Popularity of Fire Bellied Toads as Pets
Despite their toxic secretions, Fire Bellied Toads have become increasingly popular as pets in recent years. Their small size, low maintenance needs, and unique coloration make them an attractive choice for reptile enthusiasts.If you're considering getting a Fire Bellied Toad as a pet, it's essential to do your research and ensure you can provide them with a suitable habitat. They require a semi-aquatic setup with clean water, a variety of hiding spots, and a balanced diet.
The Future of Fire Bellied Toads
As we continue to explore and learn about our planet's incredible biodiversity, it's crucial to protect unique species like the Fire Bellied Toad. These little creatures play a crucial role in their ecosystem, and their vibrant colors and behaviors bring joy and fascination to all who encounter them.Despite their increasing popularity as pets, we must ensure that their wild populations remain healthy and thriving. By promoting responsible ownership and conservation efforts, we can help ensure that this jewel of Eastern Asia remains a treasured species for generations to come.
In conclusion, the Fire Bellied Toad, with its stunning coloration, unique adaptations, and role in human culture, is a truly fascinating animal. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the natural world, let's remember to appreciate and protect these incredible creatures.
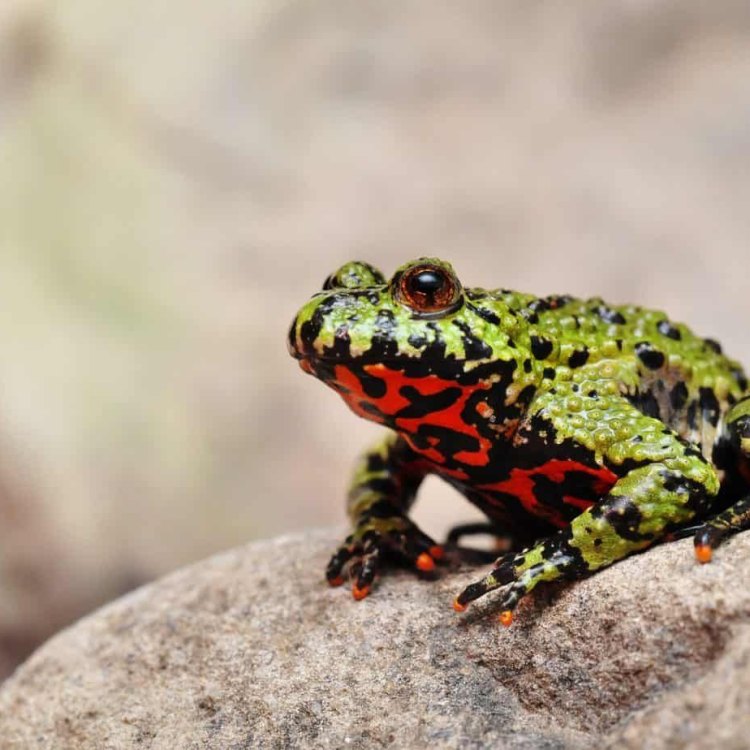

Fire Bellied Toad
Animal Details Fire Bellied Toad - Scientific Name: Bombina orientalis
- Category: Animals F
- Scientific Name: Bombina orientalis
- Common Name: Fire Bellied Toad
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Amphibia
- Order: Anura
- Family: Bombinatoridae
- Habitat: Semi-aquatic habitats such as ponds, swamps, and marshes
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Eastern Asia
- Country of Origin: China and Korea
- Location: Eastern China, Korea, and northeastern Russia
- Animal Coloration: Bright green or brownish-black on their dorsal side with bright orange to red coloration on their ventral side
- Body Shape: Small with a plump body, short legs, and smooth skin
- Length: 5-10 centimeters
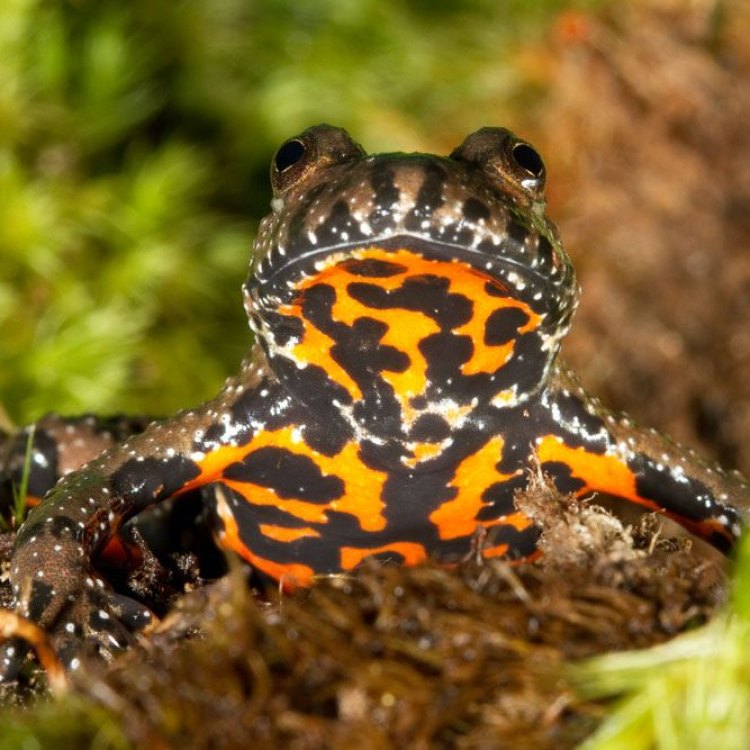

Fire Bellied Toad
- Adult Size: 6-10 centimeters
- Average Lifespan: 5-10 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males attract females by vocalizing and performing courtship displays in the water
- Sound or Call: Males make a soft, repetitive croaking sound during mating season
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal and primarily active at dusk and dawn
- Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, and invasive predators
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Impact on Ecosystem: Control population of insects and other invertebrates
- Human Use: Popular as pets due to their vibrant colors and ease of care
- Distinctive Features: Bright orange to red coloration on the ventral side and toxic skin secretions
- Interesting Facts: 1. Fire bellied toads have poison glands on their skin that secrete toxins to deter predators. 2. They are able to absorb oxygen through their skin, allowing them to partially breathe underwater. 3. When threatened, fire bellied toads will arch their bodies, exposing their brightly colored bellies as a warning signal. 4. They are agile swimmers and are often found hiding in the vegetation of their aquatic habitats.
- Predator: Predators include snakes, birds, and larger amphibians.

Bombina orientalis
The Colorful and Unique Fire Bellied Toad: A Fascinating Amphibian with Surprising Traits
In the world of amphibians, there is a creature that stands out with its vibrant colors, distinctive features, and surprising behavior. Meet the fire bellied toad, a small but fascinating species that has captured the hearts of many with its endearing appearance and unique traits.From its bright orange to red markings to its behavior of using vocalizations and courtship displays to attract a mate, the fire bellied toad is a species that has much to offer in terms of curiosity and wonder. In this article, we will take a closer look at this tiny but mighty amphibian and explore its intriguing features, behavior, and role in both the environment and human society PeaceOfAnimals.Com.
Size and Lifespan
The fire bellied toad, also known as the "bombina bombina," is a small amphibian that can grow up to 6-10 centimeters in length. Its small size makes it a favorite among amphibian enthusiasts as it is easy to care for and handle. However, don't let its size deceive you, as these toads have many unique capabilities that make them a strong and fascinating species.
On average, fire bellied toads can live for 5-10 years in captivity, but in the wild, their lifespan can vary depending on various factors such as habitat quality, food availability, and predators.
Reproduction and Sexual Behavior
Like most amphibians, fire bellied toads reproduce sexually, which means that a male fertilizes the eggs of a female. However, what makes their mating behavior unique is how males attract females. During mating season, male fire bellied toads will vocalize and perform courtship displays in the water, showcasing their strength and fitness to potential mates.
These vocalizations are also a way for males to establish dominance and claim territory, as they can be heard from quite a distance. According to researchers, the calls of male fire bellied toads are a series of soft, repetitive croaks that can help them find a mate in the noisy environment of their aquatic habitats Flour Beetle.
Migration and Social Behavior
Unlike other species of toads that may migrate to different habitats during certain times of the year, fire bellied toads are non-migratory. They are typically solitary creatures, only coming together during mating season. In their natural habitat, which consists of wetlands, ponds, and slow-moving streams, they are often found hiding in the vegetation or burrowing in the soft soil.
Behavior and Threats
Fire bellied toads are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night. However, they are also active during dawn and dusk, when they come out to hunt for food. As amphibians, they have the ability to absorb oxygen through their skin, which allows them to partially breathe underwater. This makes them excellent swimmers, and they can often be seen floating or navigating through the water with ease.
One of the biggest threats to fire bellied toads is habitat loss. As human development continues to expand, the natural wetlands and ponds they call home are being destroyed. Pollution is also a significant threat to their survival, as toxins can contaminate their aquatic habitats and harm their delicate skin. This not only affects fire bellied toads but also other species that rely on these habitats for survival.
Additionally, the introduction of invasive predators, such as fish and other amphibians, has also posed a threat to fire bellied toads. These predators can compete for resources and prey on their eggs and tadpoles, further endangering their population.
Conservation Status and Ecosystem Impact
Despite these threats, the fire bellied toad is currently listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. This is due to their relatively stable population, wide distribution, and adaptable nature. However, their habitat continues to face destruction and degradation, making conservation efforts crucial for their long-term survival.
Fire bellied toads play a vital role in their ecosystem as they help control the population of insects and other invertebrates, such as mosquitoes. This makes them an essential species for maintaining a balanced ecosystem and preventing the spread of disease.
Human Use and Distinctive Features
Aside from their role in the environment, fire bellied toads also hold a special place in human society. Their bright colors and ease of care have made them popular pets, especially among amphibian enthusiasts. However, it is essential to note that these toads should only be kept by experienced owners who understand their unique needs and provide them with a suitable environment.
One of the most distinctive features of the fire bellied toad is its bright orange to red coloration on the ventral side of its body. This bright and eye-catching marking is what gives the species its name. However, this vibrant color is not just for show. Underneath their skin, fire bellied toads have poison glands that secrete toxic substances as a defense mechanism against predators. These toxins can cause skin irritation, so it's essential to handle them with care and always wash your hands after handling them.
Interesting Facts
In addition to their distinctive markings and toxic skin secretions, fire bellied toads have more surprising facts that make them even more unique and fascinating. Here are some interesting facts about these tiny but mighty creatures:
1. Poisonous Defense Mechanism – Fire bellied toads have a unique adaptation where their skin secretes toxins to deter predators. However, their toxins are not lethal, and they primarily cause skin irritation.
2. Oxygen Absorption – These toads have a unique ability to absorb oxygen through their skin, which allows them to partially breathe underwater. This adaptation is vital for their survival in their aquatic habitats.
3. Warning Signal – When threatened, fire bellied toads will arch their bodies, exposing their brightly colored bellies as a warning signal to potential predators. This display is often enough to deter predators as it serves as a clear indication of their toxic nature.
4. Agile Swimmers – Despite their small size, fire bellied toads are agile swimmers and are often found hiding in the vegetation of their aquatic habitats. They use their powerful hind legs to navigate through the water and escape predators.
Predators
Predators of the fire bellied toad include snakes, birds, and larger amphibians such as bullfrogs. However, with their bright coloration and toxic skin secretions, they have adapted to deter predators and increase their chances of survival.
In conclusion, the fire bellied toad is a fascinating and unique species of amphibian that has captured the hearts of many with its stunning colors, distinctive features, and surprising behavior. However, as human activities continue to threaten their habitats, it is crucial to raise awareness and promote conservation efforts to ensure the survival of this species for future generations to come. While these toads continue to amaze us with their unique traits, we must also do our part in protecting and preserving their natural habitats.
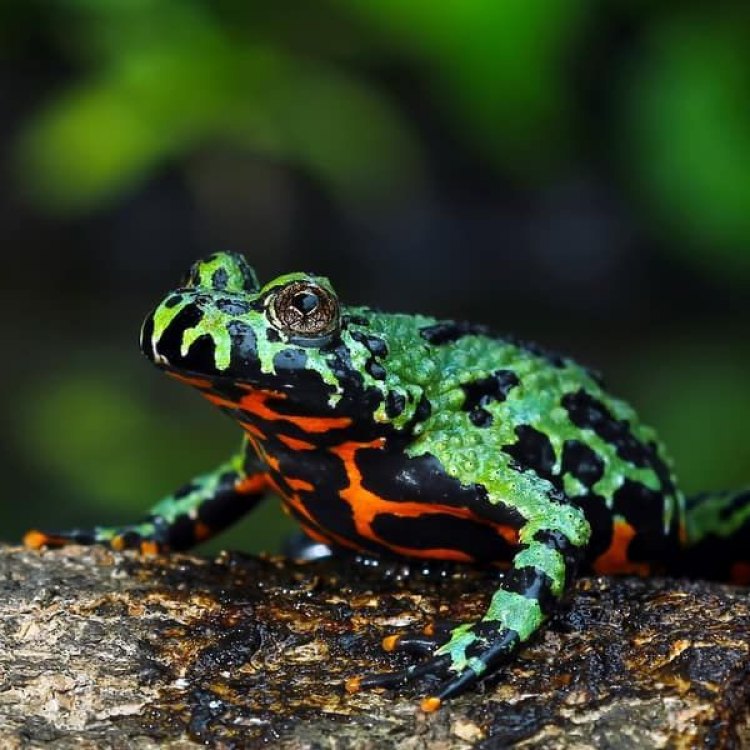

The Fascinating Fire Bellied Toad: A Jewel of Eastern Asia
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.