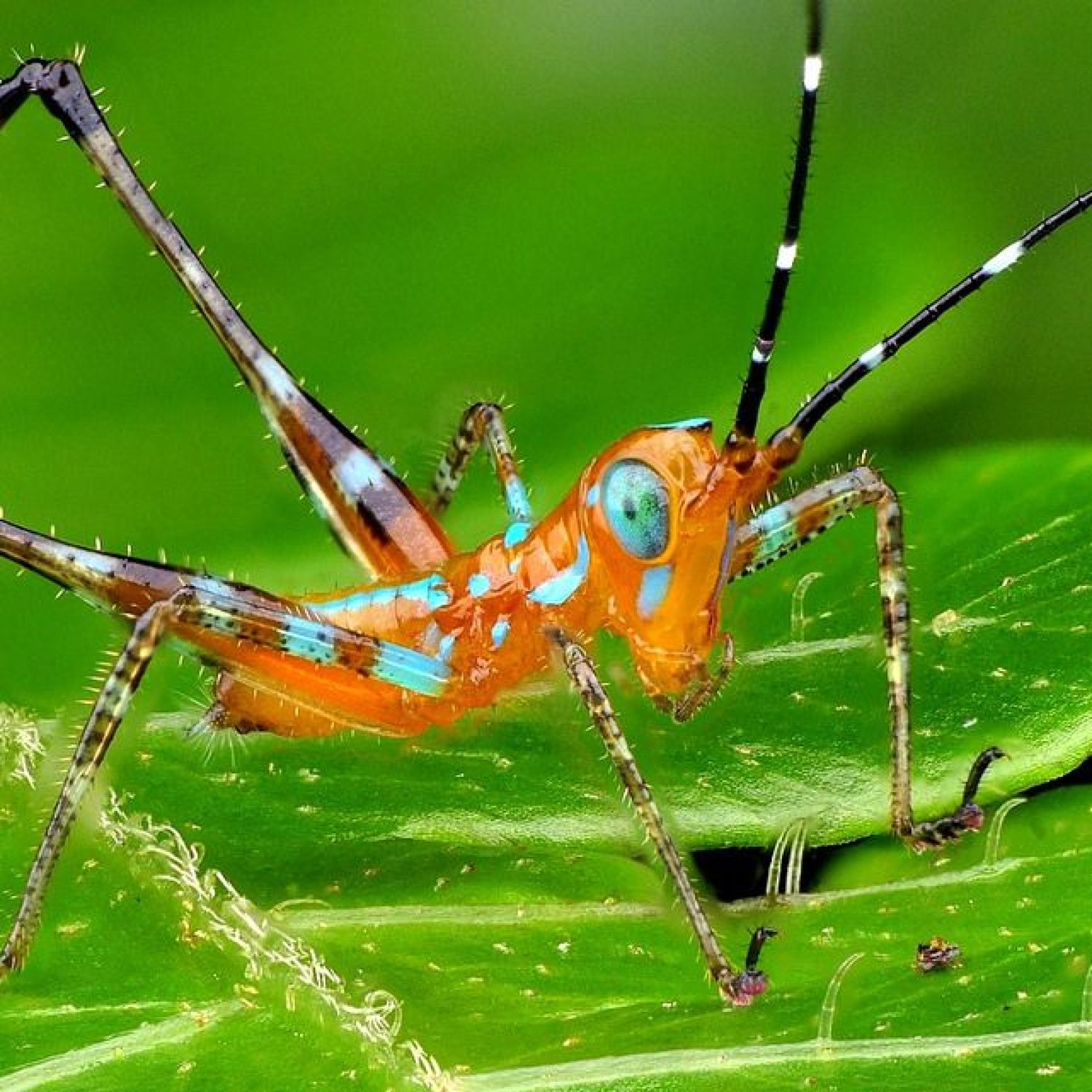
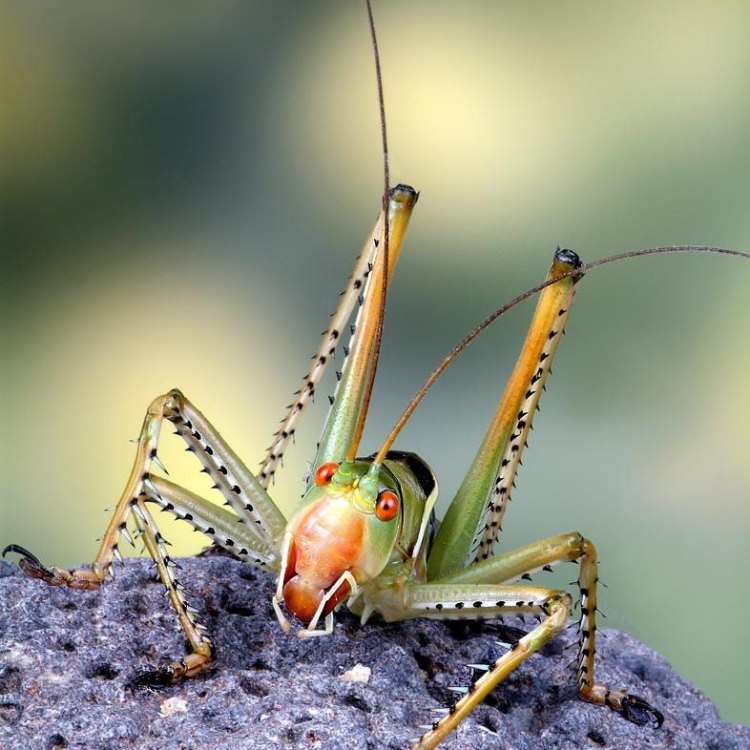
Katydid
2-4 inches (5-10 cm)
Katydid, also known as bush cricket, is a beautiful insect found in various locations worldwide. With a slim and elongated body shape, these fascinating creatures can grow up to 2-4 inches (5-10 cm). Belonging to the family Tettigoniidae, they are known for their loud and distinct mating calls. Keep an eye out for these amazing creatures on your next nature walk! #katydid #bushcricket #insects #naturewalk
Animal Details Summary:
Common Name: Katydid
Kingdom: Animalia
Habitat: Grasslands, forests, and gardens
The Fascinating World of Katydid: A Closer Look at These Unique Insects
When we think of insects, we often picture creepy crawlies that we would rather stay away from. However, there is one type of insect that is truly unique and captivating – the katydid. With its slim, elongated body and vibrant colors, the katydid has always intrigued and fascinated both researchers and animal enthusiasts alike. But there is so much more to these mysterious creatures than meets the eye Katydid.What is a Katydid?
Scientifically known as Tettigoniidae, katydids are a family of insects belonging to the order Orthoptera, which also includes grasshoppers and crickets. They are also commonly referred to as long-horned grasshoppers, bush crickets, or long-horned katydids. These insects are found all over the world, with over 6,400 species identified so far.Appearance and Physical Characteristics
The katydid's appearance can vary greatly depending on the species. However, they all share some common physical characteristics. They have a slim, elongated body with long legs and antennae, which can measure up to twice their body length. The body coloration of katydids also varies greatly, with different shades of green, brown, or even pink and red, making them well-camouflaged amongst plants and foliage.One of the most striking features of katydids is their large, leaf-shaped wings, which they use for flying and to produce a distinctive sound during mating rituals. The sound is produced by rubbing the wings together, and it can range from a low, buzzing noise to a loud, high-pitched sound, hence their name – katydid, which resembles the sound "ka-ty-did" to some people Kangaroo Rat.
Habitat and Distribution
Katydid's adaptable nature allows them to thrive in various habitats, including grasslands, forests, and gardens. They are distributed worldwide, with a presence in almost every continent, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and even the Pacific Islands. Interestingly, different katydid species have specific geographical distributions, and some can only be found in a particular country or region.Feeding Habits and Behavior
As herbivores, katydids primarily feed on leaves, but they have been known to also eat flowers and even other insects. They have strong mandibles that allow them to chew and consume a wide variety of plants. Some species are known to be selective in their food choices, while others show a more varied diet.However, what is truly fascinating about katydids is their behavior. They are primarily nocturnal insects, meaning they are most active at night. During the day, they often hide in foliage or other hiding places to avoid predators. While they do have wings and can fly, they prefer to walk or hop around.
Katydid's Classification and Evolution
Katydid's scientific classification is as follows:- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Orthoptera
- Family: Tettigoniidae
According to the fossil records, Tettigoniidae has been around for over 150 million years, making them one of the oldest insect families in existence. They are believed to have evolved from the same ancestor as crickets and grasshoppers, and their physical appearance and behavior reflect this ancestral heritage.
The Role of Katydids in the Ecosystem
Katydid's role in the ecosystem is crucial. They are important pollinators, by feeding on flowers and spreading pollen from plant to plant. They are also prey for many animals, including birds, spiders, and other insects, contributing to the food chain. In some cultures, katydids are considered a delicacy and are consumed by humans.Moreover, katydids play a significant role in seed dispersal. As they feed on plants, they may also ingest seeds, which can then be dispersed to new locations when they defecate. This dispersal process is crucial for maintaining plant diversity and ensuring the survival of many plant species.
Interesting Katydid Species Around the World
As mentioned earlier, there are over 6,400 katydid species identified so far, each with its unique characteristics and behaviors. Here are some of the most interesting katydid species from around the world.Angular-winged Katydid (Microcentrum rhombifolium)
The angular-winged katydid, also known as the Broad-winged Shieldback, is a common species found in the eastern United States. It has a distinctively shaped body, with broad, triangular wings, hence its name. It is also notable for its ability to camouflage itself by mimicking dead leaves, making it nearly invisible to predators.Goliath Shield-backed Katydid (Eurycorypha bigibba)
The Goliath shield-backed katydid is one of the largest katydid species, with some individuals reaching up to 7 inches in length. It is native to the rainforests of Central and South America and is recognizable by its bright green and spiky-looking body. Unlike most katydids, this species is diurnal, meaning they are active during the day.Eastern Lubber Grasshopper (Romalea microptera)
The Eastern Lubber Grasshopper, also known as the eastern lubber katydid, is a distinctive and colorful katydid that can be found in the southeastern United States. It is not a true katydid, but it is often confused with one due to its similar appearance and ability to create a buzzing sound by rubbing its wings together. It is also well-known for its slow and clumsy movements, which are quite different from other katydid species.The Challenges Faced by Katydids
Despite their importance in their respective habitats, katydids face many challenges, and their population is declining in many areas. Habitat loss is one of the main reasons for this decline, with urbanization and deforestation affecting their natural habitats. Pesticide use is also a significant threat to katydids, as it can directly kill them or reduce their food sources.Climate change is also affecting katydids, as they are sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity. Species that are adapted to cooler climates may struggle to survive as the temperature rises, and some species may even go extinct.
Conservation Efforts and Future Outlook
Fortunately, there are ongoing efforts to protect and conserve katydids and their habitats. Creating protected areas and implementing sustainable practices in agriculture can help preserve their natural habitats and reduce the use of pesticides. Raising awareness about the importance of katydids and their role in the ecosystem is also crucial for their protection.Furthermore, continued research and study of katydids can help us better understand their behavior and ecological roles, leading to more effective conservation measures. With these efforts, there is still hope for the survival of katydids and their diverse species.
Conclusion
In conclusion, katydids may seem like ordinary insects at first glance, but they are truly remarkable creatures with unique characteristics and behaviors. Their presence and diversity are vital for maintaining the balance of ecosystems, and it is our responsibility to protect and preserve them for future generations. As we continue to learn more about these fascinating insects, we are sure to discover even more incredible things about the mysterious world of katydids.
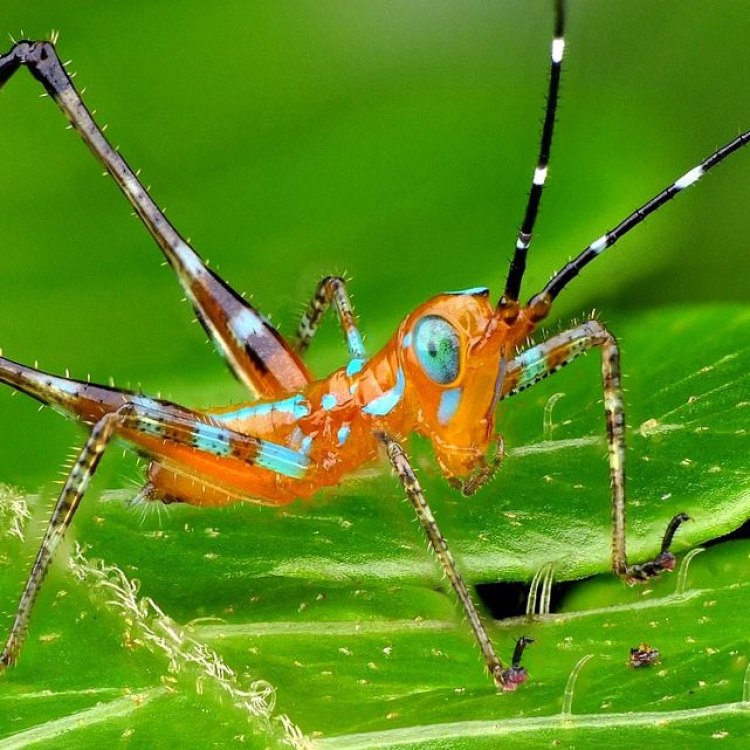

Katydid
Animal Details Katydid - Scientific Name: Tettigoniidae
- Category: Animals K
- Scientific Name: Tettigoniidae
- Common Name: Katydid
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Orthoptera
- Family: Tettigoniidae
- Habitat: Grasslands, forests, and gardens
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographical Distribution: Global
- Country of Origin: Varies by species
- Location: Various locations worldwide
- Animal Coloration: Varies by species
- Body Shape: Slim and elongated
- Length: 2-4 inches (5-10 cm)
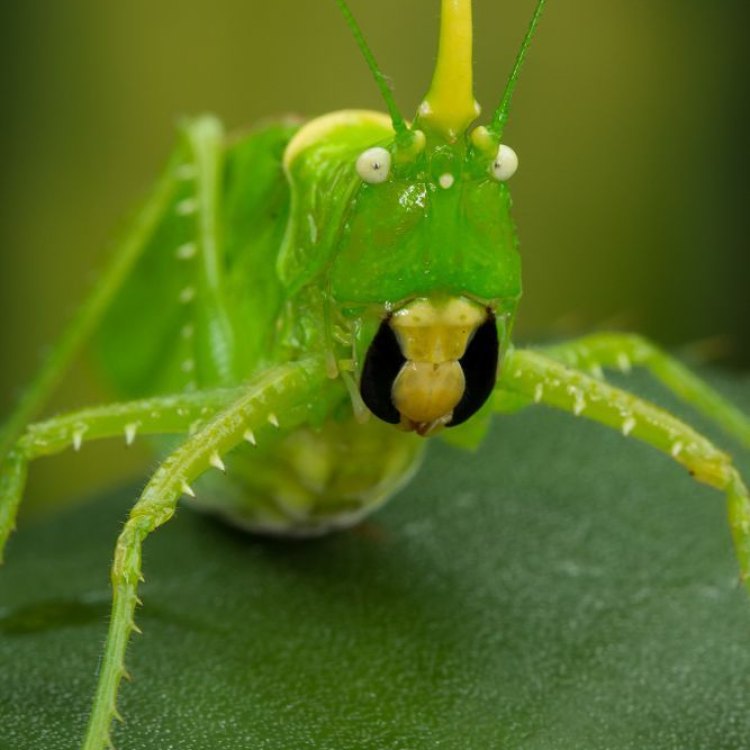

Katydid
- Adult Size: Medium-sized
- Average Lifespan: 1-2 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproductive Behavior: Males produce sounds to attract females
- Sound or Call: Loud and musical calls
- Migration Pattern: Some species migrate
- Social Groups: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Threats: Habitat loss, pesticides, predators
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Impact on Ecosystem: Important pollinators and prey for other animals
- Human Use: None
- Distinctive Features: Long, thread-like antennae and enlarged hind legs for jumping
- Interesting Facts: Katydid nymphs mimic leaves for camouflage
- Predator: Birds, bats, spiders, reptiles

Tettigoniidae
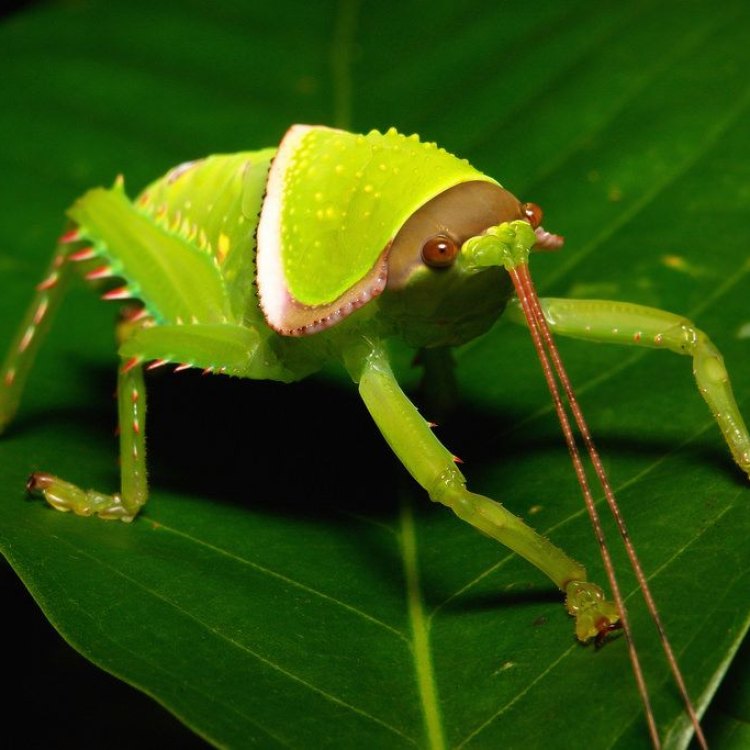
The Fascinating World of Katydid: Types, Behavior, and Role in Ecosystem
Nature has always been full of surprises, with diverse species inhabiting every corner of our planet. Some of these creatures possess extraordinary abilities and unique features that continue to amaze us. Insects, in particular, make up a significant portion of the animal kingdom, with over a million species known to humans. Among these insects, one group stands out for its extraordinary features and distinctive behavior: the katydids PeaceOfAnimals.Com.Named after the sound they produce, katydids belong to the family of Tettigoniidae and are known for their loud and musical calls. These medium-sized insects, with their fascinating features and behavior, have captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of katydids, exploring their physical characteristics, behavior, role in the ecosystem, and more.
The Basics: Size, Lifespan, and Reproduction
Katydids are medium-sized insects, with the average adult size ranging from 1-2 inches. They have elongated bodies, with long, thread-like antennae and enlarged hind legs, giving them a distinct appearance. These hind legs are used for jumping, making katydids excellent jumpers compared to other insects.In terms of lifespan, katydids have an average lifespan of 1-2 years, depending on the species and environmental conditions. However, their lifespan can vary, with some species living up to 3 years in captivity. Interestingly, katydids have asexual reproduction, meaning they require both a male and female to reproduce Kea. Males produce sounds to attract females for mating, which brings us to the unique behavior of katydids.
The Call of the Wild: Reproductive Behavior and Social Groups
One of the most fascinating aspects of katydids is their reproductive behavior. Males produce sounds by rubbing their wings together to attract females for mating. These sounds, commonly referred to as "calls," can be loud and musical, with each species producing a unique call. In fact, the intensity and complexity of their calls have led some scientists to label katydids as "musicians of the insect world."While males use their calls to attract females, they can also use them to warn off potential predators. Katydids are solitary creatures, meaning they do not live in social groups or colonies. The only time they come together is during the mating season, where males and females interact to reproduce. After mating, females lay eggs on leaves, and the young katydids, known as nymphs, will hatch and undergo several molting stages before reaching adulthood.
Nighttime Wonders: Nocturnal Behavior and Migration Patterns
One unique aspect of katydids is that they are nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active at night. This behavior is crucial for their survival as it helps them avoid predators and maximize their reproductive potential. Katydids usually spend their days resting on leaves or branches, camouflaging themselves to blend in with their surroundings.While most katydids are solitary creatures, some species have been observed to migrate in large groups. These migrations usually happen during the fall season, and the reason behind this behavior is still not fully understood. Some scientists speculate that it may be due to the search for better resources or to avoid harsh environmental conditions. Regardless of the reason, these migratory katydids can be spotted in large numbers, making for a remarkable natural phenomenon.
Survival in a Changing World: Threats and Conservation
Katydids play a crucial role in the ecosystem, acting as both pollinators and prey for other animals. As nocturnal creatures, they are important pollinators for night-blooming plants, such as cacti and some orchid species. They also serve as a vital food source for birds, bats, spiders, and reptiles, making them an essential part of the food chain.However, like many other insect species, katydids are facing threats to their survival. Habitat loss due to human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, is a significant threat to katydids. Pesticides, used extensively in agriculture, also pose a danger to their population. These chemicals not only directly harm katydids but also have an indirect effect by depleting their food sources, such as plants.
Despite these threats, katydids have not been evaluated for their conservation status yet. However, it is essential to raise awareness about their importance in the ecosystem and take steps to protect their habitats to ensure their survival and that of other animal species.
Behind the Scenes: Interesting Facts and Human Use
Apart from their distinctive features and behavior, there is more to katydids than meets the eye. Here are some interesting facts about these fascinating insects:- Katydids are masters of disguise. Nymphs, in particular, have a unique ability to mimic leaves for camouflage, making them almost invisible to predators.
- There are over 6,400 known species of katydids, with new species being discovered regularly.
- Some cultures consider katydids a symbol of good luck and fortune, while others view them as a sign of impending rain.
- While katydids are not commonly used by humans, some cultures utilize them for medicinal purposes, such as treating coughs and colds.
Nature's Balance: Predators and Prey
Like all other organisms, katydids have their share of predators in the wild. Birds, bats, spiders, and reptiles are among the most common predators of katydids. Birds, with their excellent eyesight, can spot katydids even at night and swoop in for a quick meal. Bats can also use echolocation to track down katydids, making it challenging for them to hide.Spiders, with their web-building abilities, can capture katydids with ease, while reptiles can quickly snatch them up with their quick reflexes. These predators play a crucial role in balancing the population of katydids and other insect species, preventing outbreaks and maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
The Enigmatic Katydid: A World of Wonders
In conclusion, katydids are truly remarkable creatures with their unique features, behavior, and role in the ecosystem. Their loud and musical calls, nocturnal nature, and incredible mimicry abilities continue to fascinate and captivate us. As we continue to explore and learn about the hidden wonders of the natural world, let us also strive to protect and conserve the delicate balance of life that sustains us all.

The Fascinating World of Katydid: A Closer Look at These Unique Insects
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.